 HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 1:...
HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 1:... |
 Managing the Queue Manager and Queue Database
Managing the Queue Manager and Queue Database |
|
|
|
| |
Understanding the Queue Manager
Before you can perform any queue operation, you must start the queue manager and create the queue database. Starting the Queue Manager and Creating a Queue Database contains instructions for doing this.
OpenVMS Batch and Print Queuing System illustrates how the queue manager works to manage queue activity in an OpenVMS Cluster environment.
|
Figure 1 OpenVMS Batch and Print Queuing System |
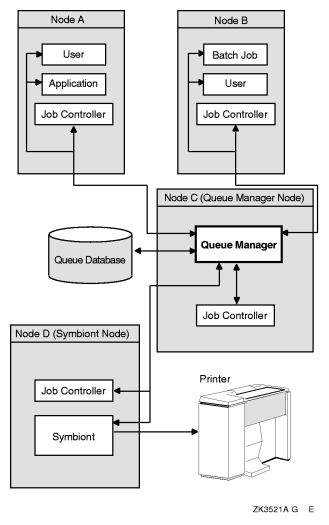 |
When a user submits a batch or print job to a queue, the queue manager performs the following tasks:
One or more queue manager processes control queuing for all processes on a node or in an OpenVMS Cluster environment. Jobs can be submitted from one node and executed on a queue running on another cluster node. User processes, symbionts, and job controllers on each node communicate directly with queue managers.
In addition, the job controller works with the queue manager to perform the following queue management tasks:
By default, in an OpenVMS Cluster environment, the queue manager tries to fail over to another node if the node on which the queue manager is running leaves the cluster.
You can specify the order in which OpenVMS Cluster nodes claim the queue manager process; you can also limit the nodes that can run the queue manager. For more information, see Customizing Queue Manager Failover.
To work around CPU, disk space, or memory limitations, you can use multiple queue managers to distribute the batch and print work load among nodes as well as to distribute the database files among disks.
For example, you might create separate queue managers for batch queues and print queues. Run the batch queue manager on one node and the print queue manager on a different node. You can also maintain queue and journal files on separate disks.
For information about creating additional queue managers, including reasons and restrictions for using multiple queue managers, see Using Multiple Queue Managers.
|
|
|