 HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 2:...
HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 2:... |
 Managing System Parameters
Managing System Parameters |
|
|
| |
Managing System Parameters with SYSMAN
| HP recommends that you use AUTOGEN to modify system parameters. For more information, see Modifying System Parameters with AUTOGEN. To view system parameters for a group of nodes or change parameters temporarily, use the System Management utility (SYSMAN). |
You can use SYSMAN to manage system parameters as follows:
| Task | For More Information |
|---|---|
|
Show parameter
values
|
Showing Parameter Values with SYSMAN
|
|
Modify current
values in the parameter file
|
Modifying a Parameter File with SYSMAN
|
|
Modify active values on
a running system1
|
Modifying Active Values with SYSMAN
|
SYSMAN provides the commands and functions shown in SYSMAN PARAMETERS Commands.
For more information about the temporary work area, see the next section.
Understanding Parameter Values and SYSMAN ![]()
It helps to understand the different system parameter values
explained in
Default, Current, and Active Values.
Briefly, current values are stored in the
default parameter file on disk. Active values are
stored in memory and are used while the system is running. In addition
to these values, SYSMAN writes a temporary copy into its own work
area on disk.
SYSMAN Temporary, Active, and Current Parameter Values illustrates
these different sets of values and how SYSMAN commands affect them.
In this figure:
|
Figure 2 SYSMAN Temporary, Active, and Current Parameter
Values |
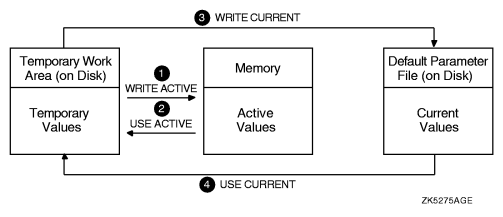 |
During a typical session, you can display and change values in the following sequence:
For a list of all the system parameters, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Showing Parameter Values with SYSMAN ![]()
Use the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS SHOW to display parameter
values for all the nodes in a cluster.
$RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMANSYSMAN>PARAMETERS SHOW/LGIParameters in use: Active Parameter Name Current Default Min. Max. Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TERM 0 1 0 1 Boolean D LGI_BRK_DISUSER 0 0 0 1 Boolean D LGI_PWD_TMO 30 30 0 255 Seconds D LGI_RETRY_LIM 3 3 0 255 Tries D LGI_RETRY_TMO 20 20 0 255 Seconds D LGI_BRK_LIM 5 5 0 255 Failures D LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds DLGI_HID_TIM 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D
$RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMANSYSMAN>SET ENVIRONMENT/CLUSTER%SYSMAN-I-ENV, Current command environment: Clusterwide on local cluster Username MORIN will be used on nonlocal nodesSYSMAN>PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMONode NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D
Modifying a Parameter File with SYSMAN ![]()
Use the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS WRITE to write system parameter
values and the name of the site-independent startup command procedure
to your choice of parameter file or the current system parameter
file on disk.
The PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command sends a message to OPCOM to record the event, unless you have changed the system message format with the DCL command SET MESSAGE.
| The PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command writes all of the active or current parameter values--not just the one you may be working on--to disk. |
SYSMAN>PARAMETERS WRITE SYS$SYSTEM:NEWPARAM
SYSMAN>PARAMETERS SET LGI_BRK_TMO 300SYSMAN>PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT
Modifying Active Values with SYSMAN ![]()
Using the SYSMAN commands PARAMETERS SET, PARAMETERS WRITE,
and PARAMETERS USE enables you to modify active parameter values.
Modifying active values immediately affects dynamic parameters by changing their values in memory. Appendix C of the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual identifies dynamic parameters, as does the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS SHOW/DYNAMIC. Values for nondynamic parameters cannot be changed while the system is running.
Modifying active values does not affect current values in the system parameter file on disk, because the next time you boot the system, the values on disk are established as the active values.
If you set new active parameter values and you want to use the new values for subsequent boot operations, write the new values to the current parameter file with the PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command, as shown in the Examples section.
| Parameter values modified with SYSMAN will be overridden by the AUTOGEN command procedure. To keep parameter modifications made with SYSMAN, edit the file SYS$SYSTEM:MODPARAMS.DAT as explained in Controlling AUTOGEN's Parameter Settings with MODPARAMS.DAT to specify the new parameter values. |
SYSMAN>PARAMETERS SET LGI_BRK_TMO 300SYSMAN>PARAMETERS WRITE ACTIVESYSMAN>PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMONode NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D
SYSMAN>PARAMETERS USE CURRENTSYSMAN>PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMONode NODE21: Parameters in use: CURRENT Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: CURRENT Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D
SYSMAN>PARAMETERS WRITE ACTIVESYSMAN>PARAMETERS USE ACTIVESYSMAN>PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMONode NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D
1 Applies only to dynamic system parameters.
( Number takes you back )
|
|