 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
Queue Protection
This section describes UIC-based protection checking that is performed
by the $SNDJBC service to control access to queues.
As an alternative to this form of protection checking, you can
associate ACLs with queues using the appropriate security services. See
the $GET_SECURITY and $SET_SECURITY system services for more
information.
There are two aspects to UIC-based queue protection:
- When you create a queue, you assign it a UIC by using the
SJC$_OWNER_UIC item code. If you do not specify this item code, the
queue is given the default UIC [1,4].
- You can assign a queue a protection mask by specifying the
SJC$_PROTECTION item code. This protection mask specifies read, submit,
manage, and delete access for the four categories of user: Owner,
Group, World, and System.
In addition, certain queue operations require the caller of $SNDJBC to
have certain privileges. The function codes that require privileges are
listed in the Privileges and Restrictions section.
When a job is submitted to a queue, it is assigned a UIC that is the
same as the UIC of the process submitting the job, unless the SJC$_UIC
item code is specified to supply a different UIC.
For each requested operation, the $SNDJBC service checks the UIC and
privileges of the requesting process against the UIC of the queue,
protection specified for the queue, and the privileges, if any,
required for the operation. This checking is performed in a way similar
to the way that the file system checks access to a file by comparing
the owner UIC and protection of the file with the UIC and privileges of
the requester.
Operations that apply to jobs are checked against read and delete
protection specified for the queue in which the job is entered and the
owner UIC of the job. In general, read access to a job allows you to
determine that the job exists; delete access to a job allows you to
affect the job.
Operations that apply to queues are checked against the submit and
manage protection specified for the queue and the owner UIC of the
queue. In general, submit access to a queue allows you to submit jobs
to the queue; manage access to a queue allows you to act as an operator
for the queue, including the ability to affect jobs in the queue, to
affect accounting, and to alter queues. OPER privilege grants manage
access to all queues.
Privileges and Restrictions
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have both OPER
and SYSNAM privilege:
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege:
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_DELETE_FORM
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING
SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING
To specify the following function code, the caller can have OPER
privilege or manage access:
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
To specify the following function code, the caller must have OPER
privilege, execute access to the queue containing the specified job, or
read access to the specified job:
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege, manage access to the specified queue, or submit access to
the specified queue:
SJC$_ADD_FILE
SJC$_CLOSE_DELETE
SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege or manage access to the specified queue or queues:
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART
SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE
SJC$_PAUSE_QUEUE
SJC$_RESET_QUEUE
SJC$_START_QUEUE
SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege, manage access to the queue containing the specified job, or
delete access to the specified job:
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_DELETE_JOB
To specify the following function codes, no privilege is required:
SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT
SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING
To specify a scheduling priority (using the SJC$_PRIORITY item code)
higher than the value of the system parameter MAXQUEPRI, the caller
needs OPER or ALTPRI privilege.
To specify the following item codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege:
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
SJC$_PROTECTION
To specify the following item codes, the caller must have CMKRNL
privilege:
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
SJC$_UIC
SJC$_USERNAME
Required Quota
To specify the astadr argument, the process must have
sufficient ASTLM quota.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the
return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written
by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The function code is invalid; the item descriptor contains an invalid
buffer length value; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the
reserved parameter has a nonzero value.
|
|
SS$_DEVOFFLINE
|
The job controller process is not running.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
You specified the
astadr argument, and the process has exceeded its
ASTLM quota.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The
efn argument specifies an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient space exists for completing the request.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
Queue form or characteristic name is not a valid logical name.
|
|
SS$_MBFULL
|
The job controller mailbox is full.
|
|
SS$_MBTOOSML
|
The mailbox message is too large for the job controller mailbox.
|
|
SS$_SHELVED
|
The job controller attempted to access a shelved file. The service does
not automatically unshelve files.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The
efn argument specifies an unassociated event flag
cluster.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
|
JBC$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
JBC$_AUTONOTSTART
|
The queue is autostart active, but not started. You have tried to start
an autostart queue when none of its available nodes has autostart
enabled.
|
|
JBC$_BUFTOOSMALL
|
The request could not be completely satisfied due to limited buffer
size. The amount of information retrieved in response to the query
exceeds the amount of data the queue manager can return in response to
a single request.
|
|
JBC$_DELACCESS
|
The file protection of the specified file, which was entered with the
delete option, does not allow delete access to the caller.
|
|
JBC$_DUPCHARNAME
|
The command specified a duplicate characteristic name. Each
characteristic must have a unique name.
|
|
JBC$_DUPCHARNUM
|
The command specified a duplicate characteristic number. Each
characteristic must have a unique number.
|
|
JBC$_DUPFORM
|
The specified form number is invalid because it is already defined;
each form must have a unique form number.
|
|
JBC$_DUPFORMNAME
|
The command specified a duplicate form name. Each form must have a
unique name.
|
|
JBC$_EMPTYJOB
|
The open job cannot be closed because it contains no files.
|
|
JBC$_EXECUTING
|
The parameters of the specified job cannot be modified because the job
is currently executing.
|
|
JBC$_INCDSTQUE
|
The type of the specified destination queue is inconsistent with the
requested operation.
|
|
JBC$_INCFORMPAR
|
The specified length, width, and margin parameters are inconsistent;
the value of the difference between the top and bottom margin
parameters must be less than the form length, and the difference
between the left and right margin parameters must be less than the line
width.
|
|
JBC$_INCOMPLETE
|
The requested queue management operation cannot be executed because a
previously requested queue management operation has not yet completed.
|
|
JBC$_INCQUETYP
|
The type of the specified queue is inconsistent with the requested
operation.
|
|
JBC$_INTERNALERROR
|
An internal error caused loss of process status. A system error
prevented the queue manager from obtaining the completion status of a
process.
|
|
JBC$_INVCHANAM
|
A specified characteristic name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVDSTQUE
|
The destination queue name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVFORNAM
|
The form name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVFUNCOD
|
The specified function code is invalid.
|
|
JBC$_INVITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVPARLEN
|
The length of a specified string is outside the valid range for that
item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVPARVAL
|
A parameter value specified for an item code is outside the valid range
for that item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVQUENAM
|
The queue name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_ITMREMOVED
|
The meaningless items were removed from the request. One or more item
codes not meaningful to this command were specified. The command is
processed and the meaningless items are ignored.
|
|
JBC$_JOBNOTEXEC
|
The specified job is not executing.
|
|
JBC$_JOBQUEDIS
|
The request cannot be executed because the system job queue manager has
not been started.
|
|
JBC$_JOBQUEENA
|
The system job queue manager cannot be started because it is already
running.
|
|
JBC$_MISREQPAR
|
An item code that is required for the specified function code has not
been specified.
|
|
JBC$_NOAUTOSTART
|
The node does not have the autostart feature enabled.
|
|
JBC$_NODSTQUE
|
The specified destination queue does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOOPENJOB
|
The requesting process did not open a job with the SJC$_CREATE_JOB
function.
|
|
JBC$_NOPRIV
|
The queue protection denies access to the queue for the specified
operation.
|
|
JBC$_NOQUESPACE
|
The system job queue file was full and could not be extended.
|
|
JBC$_NORESTART
|
The specified job cannot be requeued because it was not defined as
restartable.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHCHAR
|
The specified characteristic does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHENT
|
There is no job with the specified entry number.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHFORM
|
The specified form does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHJOB
|
The specified job does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHMGR
|
The specified queue manager does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The specified node does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHQUE
|
The specified queue does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOTALLREQUE
|
Not all jobs in the source queue could be requeued to the target queue.
Some of the jobs specified were not suitable for execution on the
specified target queue.
|
|
JBC$_NOTASSIGN
|
The specified queue cannot be deassigned because it is not assigned.
|
|
JBC$_NOTMEANINGFUL
|
The specified item code is no longer meaningful.
|
|
JBC$_NOTSUPPORTED
|
The specified item code or function code is not supported.
|
|
JBC$_PRIOSMALL
|
The scheduling priority has a smaller value than requested. A user
without ALTPRI or OPER privilege specified a value for a job's priority
that exceeded the queue's maximum priority for nonprivileged jobs. The
job is entered in the queue, but its scheduling priority is lower than
the value requested by the user.
|
|
JBC$_QMANNOTSTARTED
|
The queue manager could not be started.
|
|
JBC$_QUEDISABLED
|
The disabled queue cannot be modified, nor can jobs be submitted to it.
|
|
JBC$_QUENOTMOD
|
The modifications were not made because the queue was not stopped.
|
|
JBC$_QUENOTSTOP
|
The specified queue cannot be deleted because it is not in a stopped
state.
|
|
JBC$_REFERENCED
|
The specified queue cannot be deleted because of existing references by
other queues or jobs.
|
|
JBC$_STARTED
|
The specified queue cannot be started because it is already running.
|
|
JBC$_STKNOTCHANGE
|
The stock associated with a form cannot be changed.
|
|
JBC$_TOOMUCHINFO
|
The size of the data in request exceeds system constraints. The amount
of data specified for a record within the queue manager's database is
too large.
|
When you use the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code, the return value
is the exit status of the specified job.
When you start a symbiont queue with the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code
or the SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code with the SJC$_CREATE_START item
code, any error encountered by the symbiont process will be returned in
the IOSB.
Examples
| #1 |
$ vfyold = f$verify(1)
$ create sys$scratch:accounting.c
#include <efndef.h>
#include <lib$routines.h>
#include <sjcdef.h>
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stsdef.h>
struct ItemList3
{
short int ItemLength;
short int ItemCode;
void *ItemBuffer;
void *ItemRetLen;
};
#define MAXITMLST 3
main()
{
int i;
struct ItemList3 JbcIL[MAXITMLST];
unsigned short int IOSB[4];
int RetStat, JbcMask, JbcFunc;
/* To start accounting: */
JbcFunc = SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING;
/* Specify image and interactive */
JbcMask = SJC$M_ACCT_IMAGE | SJC$M_ACCT_INTERACTIVE;
i = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemLength = sizeof( JbcMask );
JbcIL[i].ItemCode = SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES;
JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = (void *) &JbcMask;
JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL;
JbcIL[i].ItemLength = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemCode = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = NULL;
JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL;
RetStat = sys$sndjbcw(EFN$C_ENF,JbcFunc,0, JbcIL,IOSB,0,0);
if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( RetStat ))
lib$signal( RetStat );
if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( IOSB[0] ))
lib$signal( IOSB[0] );
return SS$_NORMAL;
}
$ cc/decc/prefix=all sys$scratch:accounting.c/object=sys$scratch:
$ link/executable=sys$scratch:accounting.exe sys$scratch:accounting
$ show accounting
$ prvold = f$setprv("OPER")
$ run sys$scratch:accounting
$ show accounting
$ priv = f$setprv(prvold)
$ vfyold = f$verify(vfyold)
$ exit
|
This C program demonstrates an $SNDJBCW call.
| #2 |
! Declare system service related symbols
INTEGER*4 SYS$SNDJBCW,
2 STATUS
INCLUDE '($SJCDEF)'
! Define item list structure
STRUCTURE /ITMLST/
UNION
MAP
INTEGER*2 BUFLEN, ITMCOD
INTEGER*4 BUFADR, RETADR
END MAP
MAP
INTEGER*4 END_LIST
END MAP
END UNION
END STRUCTURE
! Define I/O status block structure
STRUCTURE /IOSBLK/
INTEGER*4 STS, ZEROED
END STRUCTURE
! Declare $SNDJBCW item list and I/O status block
RECORD /ITMLST/ SUBMIT_LIST(6)
RECORD /IOSBLK/ IOSB
! Declare variables used in $SNDJBCW item list
CHARACTER*9 QUEUE /'SYS$BATCH'/
CHARACTER*23 FILE_SPECIFICATION /'$DISK1:[COMMON]TEST.COM'/
CHARACTER*12 USERNAME /'PROJ3036 '/
INTEGER*4 ENTRY_NUMBER
! Initialize item list for the enter file operation
SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFLEN = 9
SUBMIT_LIST(1).ITMCOD = SJC$_QUEUE
SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(QUEUE)
SUBMIT_LIST(1).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 23
SUBMIT_LIST(2).ITMCOD = SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(FILE_SPECIFICATION)
SUBMIT_LIST(2).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 12
SUBMIT_LIST(3).ITMCOD = SJC$_USERNAME
SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(USERNAME)
SUBMIT_LIST(3).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFLEN = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).ITMCOD = SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFLEN = 4
SUBMIT_LIST(5).ITMCOD = SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFADR = %LOC(ENTRY_NUMBER)
SUBMIT_LIST(5).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(6).END_LIST = 0
! Call $SNDJBCW service to submit the batch job
STATUS = SYS$SNDJBCW (,
2 %VAL(SJC$_ENTER_FILE),,
2 SUBMIT_LIST,
2 IOSB,,)
IF (STATUS) STATUS = IOSB.STS
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS))
END
|
This Fortran program demonstrates the use of the $SNDJBCW service to
submit a batch job that is to execute on behalf of another user. No log
file is produced for the batch job. This program saves the job's entry
number. You need CMKRNL privilege to run this program.
$SNDJBCW
The Send to Job Controller and Wait and $GETQUI services together
provide the user interface to the Job Controller (JBC) facility. The
$SNDJBCW service allows you to create, stop, and manage queues and the
jobs in those queues. Queues can be generic, batch, execution, or
output queues. Jobs can be batch or print jobs.
The $SNDJBCW service queues a request to the job controller. For most
operations, $SNDJBCW completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller after the operation completes; however, if the requested
operation is a pause queue, stop queue, or abort job operation,
$SNDJBCW returns to the caller after queuing the request. There is no
way to synchronize completion of these operations. Also, $SNDJBCW does
not wait for a job to complete before it returns to the caller. To
synchronize completion of a job, the caller must specify the
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code.
The $SNDJBCW service is identical to the Send to Job Controller
($SNDJBC) service except that $SNDJBC completes asynchronously; the
$SNDJBC service returns to the caller immediately after queuing the
request, without waiting for the operation to complete.
For additional information about $SNDJBCW, see the documentation of
$SNDJBC.
The $SNDJBC and $SNDJBCW services supersede the Send Message to
Symbiont Manager ($SNDSMB) and Send Message to Accounting Manager
($SNDACC) services. You should write new programs using $SNDJBC or
$SNDJBCW, instead of $SNDSMB or $SNDACC. You should convert old
programs using $SNDSMB or $SNDACC to use $SNDJBC or $SNDJBCW, as
convenient.
Format
SYS$SNDJBCW [efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$sndjbcw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned
int nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$SNDOPR
Performs the following functions:
- Sends a user request to operator terminals
- Sends a user cancellation request to operator terminals
- Sends an operator reply to a user terminal
- Enables an operator terminal
- Displays the status of an operator terminal
- Initializes the operator log file
Format
SYS$SNDOPR msgbuf ,[chan]
C Prototype
int sys$sndopr (void *msgbuf, unsigned short int chan);
Arguments
msgbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
User buffer specifying the operation to be performed and the
information needed to perform that operation. The
msgbuf argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the buffer.
The format and contents of the buffer vary with the requested
operation; however, the first byte in any buffer is the request code,
which specifies the operation to be performed. The $OPCMSG macro
defines the symbolic names for these request codes.
The following table shows each operation that $SNDOPR performs and the
request code that specifies that operation:
| Request Code |
Corresponding Operation |
|
OPC$_RQ_CANCEL
|
Sends a user cancellation request to specified operator terminals. You
use this request code to notify one or more operators that a previous
request is to be canceled. To specify OPC$_RQ_CANCEL, you must also
specify the
chan argument.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_LOGI
|
Initializes the operator log file.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_REPLY
|
Sends an operator reply to a user who has made a request. Operators use
this request code to report the status of a user request. The format of
the message buffer for this request is the format of the reply found in
the user's mailbox after the call to $SNDOPR completes. All functions
of $SNDOPR that deliver a reply to a mailbox do so in the format
described for this request code.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_RQST
|
Sends a user request to operator terminals. This request code is used
to make an operator request. If you specify a reply to the request (by
using the
chan argument), the operator request is kept active
until the operator responds.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_STATUS
|
Reports the status of an operator terminal. Operators use this request
to display the operator classes for which the specified terminal is
enabled and a list of outstanding requests.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_TERME
|
Enables an operator terminal. You use this request to enable a
specified terminal to receive operator messages.
|
The following diagrams depict the message buffer for each of these
request codes. Each field within a diagram has a symbolic name, which
serves to identify the field; in other words, these names specify
offsets into the message buffer. The list following each diagram shows
each field name and what its contents can or should be. The $OPCDEF
macro defines the field names, as well as any other symbolic name that
can be specified as the contents of a field.
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_RQST
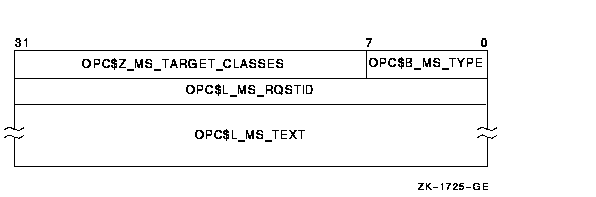
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_RQST.
|
|
OPC$Z_MS_TARGET_CLASSES
|
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which
operator terminal types are to receive the request. The $OPCDEF macro
defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct
the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR
operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal
type:
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS
|
Card device operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL
|
Central operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER
|
OpenVMS Cluster operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE
|
Device status information
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS
|
Disk operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK
|
Network operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES
|
Tape operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT
|
Printer operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY
|
Security operator
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1
through
OPC$M_NM_OPER12
|
System-manager-defined operator functions
|
|
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID
|
This longword field contains a user-supplied longword message code.
|
|
OPC$L_MS_TEXT
|
This variable-length field contains an ASCII string specifying text to
be sent to the specified operator terminals. $SNDOPR uses the buffer
size of the device to which the message is being sent.
|
|
