HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
The first longword specifies, in its low-order two bits, the matching
criteria. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be
specified, and their meanings are as follows:
| Value/Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0 SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1 SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2 SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored.
If you do not specify the ident argument or specify it
as 0 (the default), the version number and match control fields default
to 0.
relpag
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Relative page number within the global section of the first page in the
section to be mapped. The relpag argument is a
longword containing this page number.
On Alpha and I64 systems, the relpag argument is
interpreted as an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for
a file-backed section or in CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section.
On Alpha or I64 and VAX systems, you use this argument only for global
sections. If you do not specify the relpag argument or
specify it as 0 (the default), the global section is mapped beginning
with the first virtual block in the file.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. The
chan argument is a word containing this number.
The file must have been accessed with the OpenVMS RMS macro $OPEN; the
file options parameter (FOP) in the FAB must indicate a user file open
(UFO keyword). The access mode at which the channel was opened must be
equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
pagcnt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64 systems)
in the section. The pagcnt argument is a longword
containing this number.
On Alpha and I64 systems, the smallest allocation is an Alpha or I64
page, which is 8192 bytes. When requesting pagelets, the size requested
is a multiple of 512 bytes, but the actual allocation is rounded to
8192. For example, when requesting 17 pagelets, the allocation is for
two Alpha or I64 pages, 16384 bytes.
On Alpha and I64 systems, if the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag bit is set, the
pagcnt argument is interpreted as CPU-specific pages,
not as pagelets.
On Alpha or I64 and VAX systems, the specified page count is compared
with the number of blocks in the section file; if they are different,
the lower value is used. If you do not specify the page count or
specify it as 0 (the default), the size of the section file is used.
However, for physical page frame sections, this argument must not be 0.
vbn
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Virtual block number in the file that marks the beginning of the
section. The vbn argument is a longword containing
this number. If you do not specify the vbn argument or
specify it as 0 (the default), the section is created beginning with
the first virtual block in the file.
If you specified page frame number mapping (by setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP
flag), the vbn argument specifies the CPU-specific
page frame number where the section begins in memory.
Table SYS-21 shows which arguments are required and which are optional
for three different uses of the $CRMPSC service.
Table SYS-21 Required and Optional Arguments for the$CRMPSC Service
| Argument |
Create/Map
Global Section |
Map Global1
Section |
Create/Map
Private Section |
|
inadr
|
Optional
2
|
Required
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
retadr
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
acmode
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
flags
|
|
|
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Required
|
Ignored
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_CRF
3
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
3
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Optional
2
|
Not used
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gsdnam
|
Required
|
Required
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ident
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
relpag
3
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
chan
3
|
Required
|
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pagcnt
|
Required
|
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vbn
3
|
Optional
|
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
prot
|
Optional
|
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pfc
3
|
Optional
|
|
Optional
|
1The Map Global Section ($MGBLSC) service maps an existing
global section.
2See the description of inadr for the rules
governing the omission of the argument.
3For physical page frame sections: vbn
specifies the starting page frame number; chan must be
0; pfc is not used; and the SEC$M_CRF and SEC$M_DZRO
flag bit settings are invalid. For page file sections,
chan must be 0 and pfc not used.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file and PFN sections. For
file-backed sections, the protection is taken from the backing file and
the prot argument is ignored.
The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left
in each field.
The following diagram depicts the mask:
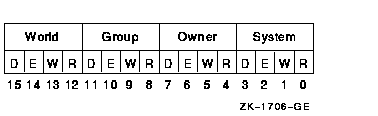
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user.
Only read, write, and execute access are meaningful for section
protection. Delete access bits are ignored. Read access also grants
execute access for those situations where execute access applies.
Protection is taken from the system or group global section template
for page file or PFN global sections if the prot
argument is not specified.
pfc
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Page fault cluster size indicating how many pages (on VAX systems) or
pagelets (on Alpha and I64 systems) are to be brought into memory when
a page fault occurs for a single page.
On Alpha and I64 systems, this argument is not used for page file
sections or physical page frame sections. The pfc
argument is rounded up to CPU-specific pages. That is, at least 16
pagelets (on an Alpha or I64 system with an 8KB page size) will be
mapped for each physical page. The system cannot map less than one
physical page.
On VAX systems, this argument is not used for page file sections or
physical page frame sections.
Description
The Create and Map Section service allows a process to associate (map)
a section of its address space with (1) a specified section of a file
(a disk file section) or (2) specified physical addresses represented
by page frame numbers (a page frame section). This service also allows
the process to create either type of section and to specify that the
section be available only to the creating process (private section) or
to all processes that map to it (global section).
Creating a disk file section involves defining all or part of a disk
file as a section. Mapping a disk file section involves making a
correspondence between virtual blocks in the file and pages (on VAX
systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64 systems) in the caller's virtual
address space. If the $CRMPSC service specifies a global section that
already exists, the service maps it.
Any section created is created as entire pages. Refer to the memory
management section in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Depending on the actual operation requested, certain arguments are
required or optional. Table SYS-21 summarizes how the $CRMPSC service
interprets the arguments passed to it and under what circumstances it
requires or ignores arguments.
The $CRMPSC service returns the virtual addresses of the virtual
address space created in the retadr argument, if
specified. The section is mapped from a low address to a high address,
whether the section is mapped in the program or control region.
If an error occurs during the mapping of a global section, the
retadr argument, if specified, indicates the pages
that were successfully mapped when the error occurred. If no pages were
mapped, the value of the longwords is indeterminate. In this case,
either both longwords of the retadr argument will
contain the value --1, or the value of the longwords will be unaltered.
The SEC$M_PFNMAP flag setting identifies the memory for the section as
starting at the page frame number specified in the vbn
argument and extending for the number of CPU-specific pages specified
in the pagcnt argument. Setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag
places restrictions on the following arguments:
| Argument |
Restriction |
|
chan
|
Must be 0
|
|
pagcnt
|
Must be specified; cannot be 0
|
|
vbn
|
Specifies first page frame to be mapped
|
|
pfc
|
Does not apply
|
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Must be 1 if the flags SEC$M_GBL or SEC$M_SYSGBL are set
|
Setting the SEC$M_PAGFIL flag places the following restrictions on the
following flags:
| Flag |
Restriction |
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Assumed to be 0
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Must be 1
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Assumed to be 0
|
The flags argument bits 4 through 13 and 18 through 31
must be 0.
If the global section is mapped to a file (neither SEC$M_PAGFIL nor
SEC$M_PFNMAP is set), the security profile of the file is used to
determine access to the global section.
On VAX systems, by default, the initial security profile created for a
page file or PFN global section is taken from the group global section
template. If the SEC$M_SYSGBL flag is set, the profile is taken from
the system global section template. The owner is then set to the
process UIC. If the prot argument is nonzero, it
replaces the protection mask from the template.
On Alpha or I64 and VAX systems, the flag bit SEC$M_WRT applies only to
the way in which the newly created section is mapped. For a file to be
made writable, the channel used to open the file must allow write
access to the file.
If the flag bit SEC$M_SYSGBL is set, the flag bit SEC$M_GBL must be set
also.
Required Access or Privileges
If $CRMPSC specifies a global section and the SS$_NOPRIV condition
value is returned, the process does not have the required privilege to
create that section. To create global sections, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
- SHMEM privilege to create a global section in memory shared by
multiple processors (VAX only)
Note that you do not need PFNMAP privilege to map an existing page
frame section.
Required Quota
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). The systemwide number of
global page file pages is limited by the system parameter GBLPAGFIL.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,
$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
inadr argument,
gsdnam argument, or name descriptor cannot be read by
the caller; the
inadr argument was omitted; or the
retadr argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The starting virtual block number specified is beyond the logical
end-of-file, or the value in the
relpag argument is greater than or equal to the actual
size of the global section.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to
map the requested file.
|
|
SS$_EXGBLPAGFIL
|
The process has exceeded the systemwide limit on global page file
pages; no part of the section was mapped.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota while creating
copy-on-reference or page file backing store pages.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_ILLPAGCNT
|
The page count value is negative or is 0 for a physical page frame
section.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough pages are available in the specified shared memory to create
the section.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased size of the address space.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified, that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
The channel number specified is currently active.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLVEC
|
The specified section was not installed using the /PROTECT qualifier.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, a flag requiring a privilege you
lack, or an invalid combination of flags was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privileges to create a system global
section (SYSGBL) or a permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
The process does not have the privilege to create a section
starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP).
The process does not have the privilege to create a global section
in memory shared by multiple processors (SHMEM).
A page in the input address range is in the system address space.
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device.
|
|
SS$_NOWRT
|
The section cannot be written to because the flag bit SEC$M_WRT is set,
the file is read only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table or in
the process section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gsdnam argument exceeded the allowed depth.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped, and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The process's virtual address space is full; no space is available in
the page tables for the pages created to contain the mapped global
section.
|
|
