 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$FIND_HOLDER
Returns the holder of a specified identifier.
Format
SYS$FIND_HOLDER id ,[holder] ,[attrib] ,[contxt]
C Prototype
int sys$find_holder (unsigned int id, struct _generic_64 *holder,
unsigned int *attrib, unsigned int *contxt);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary identifier value whose holders are found by $FIND_HOLDER. The
id argument is a longword containing the binary
identifier value.
holder
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_holder |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Holder identifier returned when $FIND_HOLDER completes execution. The
holder argument is the address of a quadword
containing the holder identifier. The first longword contains the UIC
of the holder with the high-order word containing the group number and
the low-order word containing the member number. The second longword
contains the value 0.
attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Mask of attributes associated with the holder record specified by
holder. The attrib argument is the
address of a longword containing the attribute mask.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The symbols are defined in the system
macro library ($KGBDEF). The following are the symbols for each bit
position:
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. For more
information on SET RIGHTS_LIST, refer to the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is
intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows the holder of an identifier to charge disk space to the
identifier. It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of an identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Context value used while searching for all the holders of the specified
identifier when executing $FIND_HOLDER. The contxt
argument is the address of a longword containing the context value.
When calling $FIND_HOLDER repeatedly, contxt must be
set initially to 0 and the resulting context of each call to
$FIND_HOLDER must be presented to each subsequent call. After the
argument is passed to $FIND_HOLDER, you must not modify its value.
Description
The Find Holder of Identifier service returns the holder of the
specified identifier. To determine all the holders of the specified
identifier, you call SYS$FIND_HOLDER repeatedly until it returns the
status code SS$_NOSUCHID, which indicates that $FIND_HOLDER has
returned all identifiers, cleared the context longword, and deallocated
the record stream. If you complete your calls to $FIND_HOLDER before
SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, you use the $FINISH_RDB service to clear the
context value and deallocate the record stream.
Note that when you use wildcards with this service, the records are
returned in the order in which they were originally written. (This
action results from the fact that the first record is located on the
basis of the identifier. Thus, all the target records have the same
identifier or, in other words, they have duplicate keys, which leads to
retrieval in the order in which they were written.)
Required Access or Privileges
Read access to the rights database is required to obtain information
about identifiers marked HOLDER_HIDDEN.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD,
$FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER,
$REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
id argument cannot be read by the caller, or the
holder,
attrib, or
contxt argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
The contents of the
contxt longword are not valid.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier or holder identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
SS$_NOIOCHAN
|
No more rights database context streams are available.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database, or no
further holders exist for the specified identifier.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have read access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$FINISH_RDB
Deallocates the record stream and clears the context value used with
$FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, or $IDTOASC.
On Alpha and I64 systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$FINISH_RDB contxt
C Prototype
int sys$finish_rdb (unsigned int *contxt);
Argument
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Context value to be cleared when $FINISH_RDB completes execution. The
contxt argument is a longword containing the address
of the context value.
Description
The Terminate Rights Database Context service clears the context
longword and deallocates the record stream associated with a sequence
of rights database lookups performed by the $IDTOASC, $FIND_HOLDER, and
$FIND_HELD services.
If you repeatedly call $IDTOASC, $FIND_HOLDER, or $FIND_HELD until
SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, you do not need to call $FINISH_RDB because
the record stream has already been deallocated and the context longword
has already been cleared.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB,
$ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT,
$GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER,
$MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
contxt argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
The contents of the
contxt longword are not valid.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$FLUSH
The Flush service writes out all modified I/O buffers and file
attributes associated with the file. This ensures that all record
activity up to the point at which the Flush service executes is
actually reflected in the file.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$FORCEX
Causes an Exit ($EXIT) service call to be issued on behalf of a
specified process.
Format
SYS$FORCEX [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[code]
C Prototype
int sys$forcex (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, unsigned int code);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be forced to exit. The
pidadr argument is the address of a longword
containing the PID.
The pidadr argument can refer to a process running on
the local node or a process running on another node in the OpenVMS
Cluster system.
The pidadr argument is optional but must be specified
if the process that is to be forced to exit is not in the same UIC
group as the calling process.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process that is to be forced to exit. The
prcnam argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process running on
the local node can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. To
identify a process on a particular node in a cluster, specify the full
process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name.
The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
The prcnam argument can be used only on behalf of
processes in the same UIC group as the calling process. To force
processes in other groups to exit, you must specify the
pidadr argument. This restriction exists because the
operating system interprets the UIC group number of the calling process
as part of the specified process name; the names of processes are
unique to UIC groups.
code
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Completion code value to be used as the exit parameter. The
code argument is a longword containing this value. If
you do not specify the code argument, the value 0 is
passed as the completion code.
Description
The Force Exit service causes an Exit service call to be issued on
behalf of a specified process.
If you specify neither the pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, the caller is forced to exit and
control is not returned.
If the longword at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the
target process is returned.
The Force Exit system service requires system dynamic memory.
The image executing in the target process follows normal exit
procedures. For example, if any exit handlers have been specified, they
gain control before the actual exit occurs. Use the Delete Process
($DELPRC) service if you do not want a normal exit.
When a forced exit is requested for a process, a user-mode asynchronous
system trap (AST) is queued for the target process. The AST routine
causes the $EXIT service call to be issued by the target process.
Because the AST mechanism is used, user mode ASTs must be enabled for
the target process, or no exit occurs until ASTs are reenabled. Thus,
for example, a suspended process cannot be stopped by $FORCEX. The
process that calls $FORCEX receives no notification that the exit is
not being performed.
If an exit handler resumes normal processing, the process will not
exit. In particular, if the program is written in Ada and there is a
task within the program that will not terminate, the program will not
exit.
The $FORCEX service completes successfully if a force exit request is
already in effect for the target process but the exit is not yet
completed.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need a certain
privilege to use $FORCEX:
- You need GROUP privilege to force an exit for a process in the same
group that does not have the same UIC as the calling process.
- You need WORLD privilege to force an exit for any process in the
system.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,
$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,
$WAKE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for the operation.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length equal to 0 or greater than 15.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to force an exit for the
specified process.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
$FORGET_RM
Deletes a Resource Manager instance (RMI) from the calling process.
Format
SYS$FORGET_RM [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
C Prototype
int sys$forget_rm (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
rm_id);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for the option
flag listed in Table SYS-38. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-38 $FORGET_RM Option Flag
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
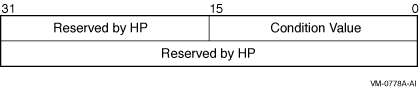
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of
the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same
access mode as that of the caller of the $FORGET_RM service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The identifier of the RMI to be deleted from the calling process.
Description
The $FORGET_RM system service:
- Deletes the specified Resource Manager instance (RMI) from the
calling process.
- Tries to abort all transactions that have not already committed and
that have Resource Manager (RM) participants associated with that RMI.
- Removes all RM participants associated with the RMI from their
transactions.
- Implicitly acknowledges all unacknowledged event reports delivered
to that RMI or to its RM participants. The reply given in the implicit
acknowledgment depends on the type of the event as follows:
Table SYS-39 $FORGET_RM's Implicit Acknowledgments
| Type of Event |
Reply |
|
Abort
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
|
Commit
|
SS$_REMEMBER
|
|
Prepare
|
SS$_VETO (with the DDTM$_SEG_FAIL reason code)
|
|
One-phase commit
|
SS$_VETO
|
|
Default transaction started
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
|
Nondefault transaction started
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Preconditions for the successful completion of $FORGET_RM are:
- The calling process must contain the specified RMI.
- The access mode of the caller must be the same as or more
privileged than that of the specified RMI.
Postconditions on successful completion of $FORGET_RM are described in
Table SYS-40:
Table SYS-40 Postconditions When$FORGET_RM Completes Successfully
| Postcondition |
Meaning |
|
The specified RMI is deleted from the calling process.
|
The result is that:
- Its identifier is invalid. Any subsequent calls to $JOIN_RM or
$FORGET_RM that pass its identifier will fail.
- The DECdtm transaction manager will deliver no more event reports
to that RMI.
|
|
There are no RM participants associated with the RMI.
|
Removes all RM participants associated with the specified RMI from
their transactions. Thus the DECdtm transaction manager will deliver no
more event reports to those RM participants.
For an RM participant that had an unacknowledged event report, the
postconditions are the same as those of the appropriate implicit
acknowledgment (see Table SYS-39) except that the RM participant is
always removed from the transaction.
|
|
There are no unacknowledged event reports delivered to the RMI or its
RM participants.
|
All unacknowledged event reports are implicitly acknowledged by this
call to $FORGET_RM (see Table SYS-39). Thus a subsequent call to
$ACK_EVENT that acknowledges one of these event reports will fail.
|
|
Quotas are returned.
|
Returns the following quotas:
- The BYTLM quota consumed by the call to $DECLARE_RM that created
the RMI.
- The ASTLM quotas consumed by all calls to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT
that added RM participants associated with the RMI.
|
Note that when a process terminates (normally or abnormally), a
$FORGET_RM is automatically performed for each RMI in that process. And
when an image terminates (normally or abnormally), a $FORGET_RM is
automatically performed for each user mode RMI in that process.
There is also a wait form of the service, $FORGET_RMW.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,
$START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An option flag was invalid.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The access mode of the caller was less privileged than that of the RMI.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHRM
|
The calling process did not contain the specified RMI.
|
|
