 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$IO_CLEANUP (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns all resources allocated by $IO_SETUP.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_CLEANUP fandle
C Prototype
int sys$io_cleanup (unsigned __int64 fandl);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle, passed by value, returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
Description
The Clean Up Fast I/O system service returns various internal resources
allocated by the $IO_SETUP system service. Buffer objects passed to
$IO_SETUP cannot be deleted until every $IO_SETUP call has had a
corresponding $IO_CLEANUP call.
Image rundown executes any required $IO_CLEANUP operations on behalf of
the process.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_PERFORM(W), $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADFANDLE
|
Argument was not a valid
fandle.
|
|
SS$_BUSY
|
The fandle cannot be cleaned up because an I/O is in progress. Reissue
the call to $IO_CLEANUP after the I/O has finished.
|
$IO_FASTPATH (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, provides the ability to control the set of
Fast Path devices and their assignment to CPUs enabled for Fast Path
use.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATH efn ,cpu_mask ,function_code
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpath (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, unsigned int
function_code);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the IO_FASTPATH(W) operation
completes. The efn argument is a longword containing
the number of the event flag.
cpu_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The cpu_mask argument specifies a set of CPUs to be
operated upon.
function_code
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The function_code specifies the operation to be
performed. Note that there is currently only one function code:
FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS - Distribute Fast Path ports across CPUs.
Description
The $IO_FASTPATH system service performs operations on the set of Fast
Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use. The $IO_FASTPATHW
system service completes synchronously. That is, it returns after the
operation is complete.
The FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS function code specifies that the system service
is to distribute the set of system assignable Fast Path ports across
the intersection of a caller-supplied set of candidate CPUs
(cpu_mask) and the current set of usable CPUs. Usable
CPUs are the intersection of the set of CPUs both enabled for Fast Path
use by IO$_PREFERRED_CPUS and whose current state is RUN.
The service does this by:
- Eliminating all CPUs not in the set of usable CPUs from the set of
candidate CPUs.
- Restoring any user assigned ports that are not currently on the
user's preferred CPU to the user's preferred CPU, if that CPU is in the
set of usable CPUs.
- Spreading the system assignable Fast Path ports, and any Fast Path
ports whose user preferred CPU is unavailable, evenly across the set of
usable candidate CPUs.
If the primary CPU is in the set of usable
candidate CPUs, the distribution will be biased against the primary CPU
in that a port will only be assigned to the primary after ports have
been assigned to each of the other usable candidate CPUs.
Required Access or Privileges
PHYS_IO
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$GETDVI, $QIO
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Unsupported value for cpu_mask.
|
|
SS$_ILLIOFUNC
|
Illegal function code.
|
$IO_FASTPATHW (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, performs operations on the set of Fast Path
devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use.
The $IO_FASTPATHW system service is functionally equivalent to the
$IO_FASTPATH service except that it completes synchronously. That is,
it returns after the operation is complete.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATHW efn ,cpu_mask ,function_code
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpathw (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, unsigned
int function_code);
$IO_PERFORM (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, starts the Fast I/O operation. The
$IO_PERFORM service completes asynchronously. For synchronous
completion, use the Perform Fast I/O and Wait ($IO_PERFORMW) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORM fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdata
C Prototype
int sys$io_perform (unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan,
struct _iosa *iosadr, void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned
__int64 devdata);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Software I/O channel number.
iosadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Address of the I/O Status Area (IOSA). This value cannot be 0; that is,
an IOSA is required. The iosadr must be aligned to a
quadword boundary.
bufadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The process buffer address. Must be aligned on a 512-byte boundary.
buflen
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
64-bit integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The byte count for the I/O. The buflen argument must
be a multiple of 512 bytes. Drivers have further limitations on the
maximum size of an I/O request.
devdata
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
pointer or integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A hardware integer passed unchanged to the driver. For disk devices,
this is the media address for the transfer; that is, the virtual block
number (VBN) for virtual I/O functions or the logical block number
(LBN) for logical I/O functions. This argument is ignored for tape
devices.
For drivers with complex parameters, devdata would be
the address of a descriptor or buffer specific to the device and
function and would be documented with the driver.
Description
The Perform Fast I/O system service initiates an I/O operation on the
channel number specified by the chan argument. The
bytes specified by the buflen argument are transferred
between the location (devdata) on the device driver
and the user's buffer starting at the process buffer address
(bufadr). The byte count is read or written according
to the function code previously specified in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with the fandle argument.
Upon completion, the I/O status is written to the IOSA starting at the
location specified by iosadr, and an AST is delivered
to the astadr address supplied in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with fandle. The IOSA address is passed to
the AST as the AST parameter.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_SETUP, $IO_PERFORMW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFADR
|
The data buffer does not reside within the bounds of the data buffer
object for the fandle.
|
|
SS$_BADIOSADR
|
The IOSA does not reside within the bounds of the IOSA buffer object
for this fandle.
|
|
SS$_FANDLEBUSY
|
The operation using this fandle is already in progress.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_UNALIGNED
|
The buffer specified by
bufadr or
iosadr is not properly aligned.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The request is invalid because the
fandle was created from a more privileged access mode,
or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
The HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these device-specific condition values for each
device.
$IO_PERFORMW (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, starts a Fast I/O operation. The $IO_PERFORMW
service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller
after performing the Fast I/O operation.
In all other respects, $IO_PERFORMW is identical to $IO_PERFORM. For
all other information about the IO_PERFORMW service, refer to the
description of $IO_PERFORM in this manual.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORMW fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdata
C Prototype
int sys$io_performw (unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan,
struct _iosa *iosadr, void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned
__int64 devdata);
$IO_SETUP (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, allocates resources for Fast I/O.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_SETUP func ,bufobj ,iosobj ,astadr ,flags ,return_fandle
C Prototype
int sys$io_setup (unsigned int func, struct _generic_64 *bufobj, struct
_generic_64 *iosobj, void (*astadr)(struct _iosa *), unsigned int
flags, unsigned __int64 *return_fandle);
Arguments
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
I/O function code. Must be one of the following:
- IO$_READVBLK
- IO$_WRITEVBLK
- IO$_READLBLK
- IO$_WRITELBLK
Various function modifiers are supported, depending on the device and
driver. Disk drivers support IO$M_NOVCACHE and IO$M_DATACHECK. Some
tape devices support IO$M_REVERSE. Illegal modifiers are detected by
the $IO_PERFORM(W) service.
bufobj
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer object |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Handle describing the buffer object that contains the user's buffer.
This identifier cannot be 0.
iosobj
| OpenVMS usage: |
object handle |
| type: |
vector longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Buffer object handle describing the buffer object that contains the I/O
Status Area (IOSA). This might or might not be the same identifier as
the bufobj argument. This identifier cannot be 0.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Completion AST routine address (0, if none). There is no AST
parameter argument. When the AST routine is called, the AST
parameter will be the address of the IOSA for the operation.
Applications can store data in the IOSA at offset IOSA$IH_CONTEXT.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask. The flags argument is a bit vector in which
each bit corresponds to a flag. Flags are defined in the module IOSADEF.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$IO_SETUP service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
FIO$M_EXPEDITE
|
This is a
high priority I/O; that is, it is to be given preferential
treatment by the I/O subsystem. Use of this bit requires ALTPRI or
PHY_IO privilege.
|
|
FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT
|
The AST procedure does not use, or call any procedure that uses, any
floating-point registers. This is a performance option. If set, AST
delivery will neither save nor restore floating-point registers.
Caution: Use of floating-point registers when FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT has
been specified can cause unpredictable, difficult to detect, error
conditions.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0.
return_fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Address of an aligned quadword to receive the fandle for this I/O
operation.
Description
The Set Up Fast I/O system service allocates and initializes a number
of internal objects based on the parameters supplied. Because these
objects are then ready for use when a subsequent $IO_PERFORM or
$IO_PERFORMW is issued, the I/O operation will require less CPU time
and fewer multiprocessor steps.
Required Privileges
If you use the flags argument FIO$M_EXPEDITE, a
process must have ALTPRI or PHY_IO privilege.
Required Quota
Byte count
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_PERFORM(W)
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The fandle does not have 8 bytes of writability, or the two buffer
objects do not have 8 bytes of readability each.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid flags options specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBUFOBJLM
|
Buffer object cannot be created because it would bring the total number
of buffer object pages above the systemwide limit MAXBOBMEM.
|
|
SS$_ILLBUFOBJ
|
The buffer object is not valid.
|
|
SS$_ILLIOFUNC
|
The function code is not valid.
|
|
SS$_ILLMODIFIER
|
The I/O function modifier is not permitted.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There is no pool available from which to create a fandle vector, or the
fandle vector is already full and an attempted expansion failed.
|
|
SS$_INSFSPTS
|
Insufficient system page table entries.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
The specified status flag is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOBUFOBJID
|
The process attempted to create a buffer object from user mode but was
not holding required rights identifier VMS$BUFFER_OBJECT_USER.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Valid flag options were specified but from user mode.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTWRITE
|
A page within the address range is not writable.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
Page owner violation. The pages could not be put into the buffer object
because the access mode associated with the call to $IO_SETUP was less
privileged than the access mode associated with the pages. See
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 for additional information.
|
|
SS$_UNALIGNED
|
The I/O Status Area (IOSA) or data buffer is not aligned on a quadword
boundary.
|
$JOIN_RM
Adds a new Resource Manager (RM) participant to a transaction.
Format
SYS$JOIN_RM [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id [,[tid]
,[part_name] ,[rm_context] ,[timout] ,[bid]]
C Prototype
int sys$join_rm (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
rm_id,...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags described in Table SYS-48. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-48 $JOIN_RM Option Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_COORDINATOR
|
Set this flag to specify that the new RM participant is to be a
coordinator of the transaction on this node.
|
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
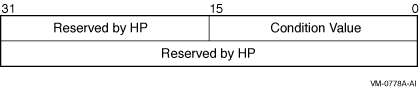
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if
SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The astadr argument is
the address of the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed
in the same access mode as that of the caller of the $JOIN_RM service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The identifier of the RMI with which the new RM participant is
associated. This identifies:
- Types of event that are to be reported to the new RM participant.
- Event handler to which these event reports are to be delivered, and
the access mode in which its ASTs are to be fired.
- Minimum access mode that the new RM participant must be in to
acknowledge one of these event reports by calling $ACK_EVENT.
- Whether or not the DECdtm transaction manager may log information
about the new RM participant.
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the transaction to which the new RM participant
is to be added.
If this argument is omitted (the default) or its value is zero,
$JOIN_RM adds an RM participant to the default transaction of the
calling process.
part_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the new RM participant.
Used by recoverable resource managers to specify the RM participant to
use in a subsequent call to $GETDTI or $SETDTI during recovery.
This argument has no effect if the RMI is volatile. If this argument is
omitted (the default) or its value is zero, the name of the new RM
participant is the same as that of the RMI with which it is associated.
The string passed in this argument can be no longer than 32 characters.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
rm_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
userarg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The context associated with the new RM participant. This is passed in
the event reports subsequently delivered to the new RM participant.
|
