 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64
Returns the address of a 64-bit signal array. A 32-bit signal array and
a mechanism array are passed to a condition handler when it is called.
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit signal array, which
might be required for programs that use 64-bit address space.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 mcharg, sigarg_64
C Prototype
int sys$signal_array_64 (unsigned __int64 mcharg, unsigned __int64
sigarg_64);
Arguments
mcharg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mechanism array |
| type: |
vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The mechanism array. The mcharg argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of this array, which was passed to the condition
handler. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 uses this structure to determine the 64-bit
signal array address.
sigarg_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
64-bit signal array |
| type: |
vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The 32- or 64-bit address of the 64-bit signal array is returned in
this argument.
Description
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit version of the
signal array for condition handlers that need it. It is normally needed
only by applications that use 64-bit address space and want to handle
errors involving addresses in that region.
For example, if an access violation occurs on a 64-bit address, the
32-bit signal array passed to the handler will contain only the low 32
bits of the effective address, because each entry is a longword. The
64-bit signal array, which can be obtained using this service, contains
quadword entries, so the 64-bit address can be fully expressed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PUTMSG, which accepts either a 32-bit or 64-bit signal array as an
argument.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed succesfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
sigarg_64 argument cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
mcharg argument is not a mechanism array in the
expected format.
|
$SNDERR
Writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding
it with the date and time.
Format
SYS$SNDERR msgbuf
C Prototype
int sys$snderr (void *msgbuf);
Argument
msgbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Message to be written to the error log file. The
msgbuf argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the message text.
Description
The Send Message to Error Logger service writes a user-specified
message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and
time. The $SNDERR service requires system dynamic memory.
Required Access or Privileges
To send a message to the error log file, the calling process must have
BUGCHK privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the required BUGCHK privilege.
|
$SNDJBC
Creates, stops, and manages queues and the batch and print jobs in
those queues. The $SNDJBC service completes asynchronously; to
synchronize the completion of most operations, use the Send to Job
Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service.
Format
SYS$SNDJBC [efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$sndjbc (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int
nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $SNDJBC completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $SNDJBC uses only the low-order byte.
When you queue the request, $SNDJBC clears the specified event flag (or
event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the
operation completes, $SNDJBC sets the specified event flag (or event
flag 0).
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function code specifying the function that $SNDJBC is to perform. The
func argument is a word containing this function code.
The $SJCDEF macro defines the names of each function code.
You can specify only one function code in a single call to $SNDJBC.
Most function codes require or allow for additional information to be
passed in the call. You pass this information by using the
itmlst argument, which specifies a list of one or more
item descriptors. Each item descriptor in turn specifies an item code,
which modifies, restricts, or otherwise affects the action designated
by the function code.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list supplying information to be used in performing the function
specified by the func argument. The
itmlst argument is the address of the item list. The
item list consists of one or more item descriptors, each of which
specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by an item code of
0 or by a longword of 0. The following diagram depicts the structure of
a single item descriptor:
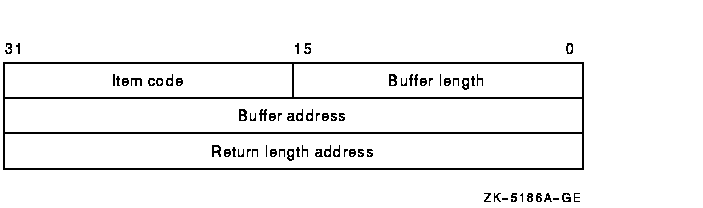
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length of the buffer; the buffer either supplies
information to be used by $SNDJBC or receives information from $SNDJBC.
The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code
specified, and is given in the description of each item code.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing an item code, which identifies the nature of the
information supplied for use by $SNDJBC or received from $SNDJBC. Each
item code has a symbolic name. The $SJCDEF macro defines these symbol
names.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies or
receives the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word to receive the length (in
bytes) of information returned by $SNDJBC. If you specify this address
as 0, no length is returned.
|
The item codes' symbolic names have the following format:
There are three types of item code:
- Boolean item code. Boolean item codes specify a true or false
value: the form SJC$_code specifies a true value; SJC$_NO_code
specifies a false value. The default value for the Boolean item codes
is false. For all Boolean item codes, the buffer length, buffer
address, and return length fields of the item descriptor must be 0.
- Input value item code. Input value item codes specify an input
value to be used by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer address
fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field
must be 0. Specific buffer length requirements are given in the
description of each item code.
- Output value item code. Output value item codes specify a buffer
for information returned by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer
address fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return
length field can be 0 or nonzero. Specific buffer length requirements
are given in the description of each item code.
Several item codes specify a queue name, form name, or characteristic
name. For these item codes, the buffer must specify a string containing
from 1 to 31 characters, exclusive of spaces, tabs, and null
characters, which are ignored. Allowable characters in the string are
uppercase alphabetic characters, lowercase alphabetic characters (which
are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, the dollar sign ($),
and the underscore (_).
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block into which $SNDJBC writes the completion status after
the requested operation has completed. The iosb
argument is the address of the I/O status block.
At request initiation, $SNDJBC sets the value of the quadword I/O
status block to 0. When the requested operation completes, $SNDJBC
writes a condition value in the first longword of the I/O status block.
It writes the value 0 into the second longword; this longword is unused
and reserved for future use.
The condition values returned by $SNDJBC in the I/O status block are
usually condition values from the JBC facility. These condition values
are defined by the $JBCMSGDEF macro. In some cases, the condition value
returned by $SNDJBC can be an error return from a system service or an
OpenVMS RMS service that is used in executing the request. For the
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB request, the condition value returned is the
completion status of the requested job.
The condition values returned from the JBC facility are listed in the
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block section.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $SNDJBC service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$SNDJBC, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $SNDJBC completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If specified, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the
caller of $SNDJBC.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is this longword parameter.
Function Codes This section describes the various function codes that
are applicable to the $SNDJBC system service.
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
Aborts the execution of the current job from an output execution queue
or the job you specified from a batch queue. By default, the job is
deleted. However, for a restartable job, you can requeue it to the same
queue or to another queue.
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
SJC$_QUEUE
You must specify the following input value item code for batch jobs:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
You can specify the following optional input value or Boolean item
codes:
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_REQUEUE
|
---
|
SJC$_ADD_FILE
Adds a file to the open job owned by the requesting process. You use
this operation as part of a sequence of calls to the $SNDJBC service to
create a job with one or more files. The first call in the sequence
specifies the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation to create an open job. Each
subsequent SJC$_ADD_FILE request associates an additional file with the
job. Finally, you make an SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request to complete the batch
or print job specification.
To create a job that contains only one file, you can make a single call
to $SNDJBC that specifies the SJC$_ENTER_FILE function code.
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_DELETE_FILE
|
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
|
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PASSALL
|
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
|
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
Alters the parameters of an existing job that is not currently
executing.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME
|
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
---
|
SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA
|
|
SJC$_CLI
|
SJC$_NO_CLI
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
---
|
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
|
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
|
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE
|
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
|
|
SJC$_NOTE
|
SJC$_NO_NOTE
|
|
SJC$_NOTIFY
|
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
|
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8
|
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
|
|
SJC$_PASSALL
|
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RESTART
|
SJC$_NO_RESTART
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies
that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before
modifying the job.
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
Alters the parameters of a queue. The execution of current jobs is
unaffected.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
|
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PROTECTION
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
|
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SWAP
|
SJC$_NO_SWAP
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
Assigns a logical queue to an execution queue. The SJC$_QUEUE item code
specifies the logical queue; the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code
specifies the execution queue.
|
