 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
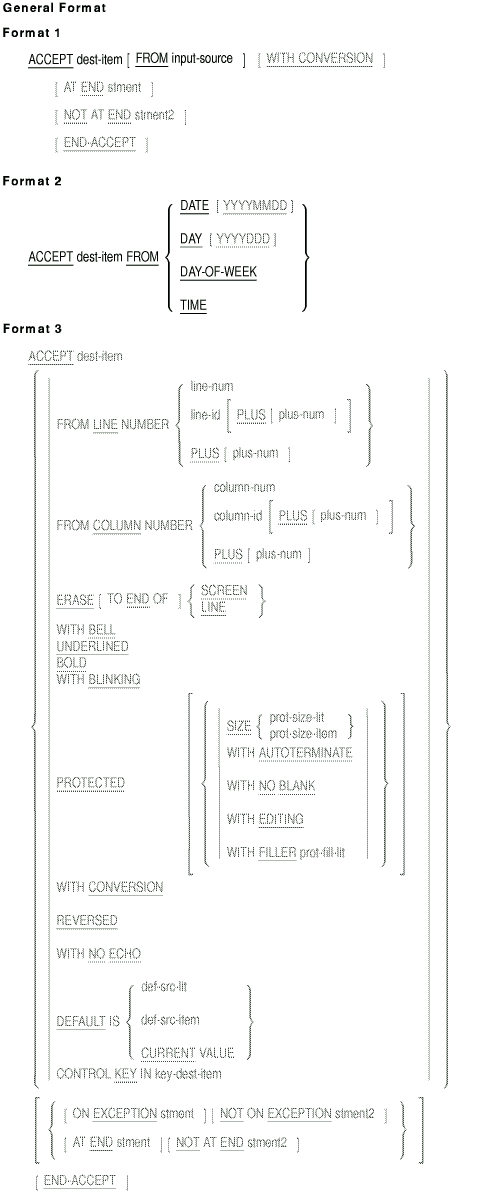
6.8.1 ACCEPT
Function
The ACCEPT statement makes low-volume data available to the program.
The Hewlett-Packard extensions to the ACCEPT statement (Formats 3, 4,
and 5) are COBOL language additions that facilitate video forms
design and data handling. The WITH CONVERSION phrase and some other
options in Format 1 are also Hewlett-Packard extensions.
Format 6 retrieves the number of arguments on the program run command
line, Format 7 reads those command line arguments into designated
program variables, and Format 8 reads environment variables and
logicals into designated program variables.
dest-item
is the identifier of a data item into which data is accepted.
input-source
is a mnemonic-name defined in the SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph of the
Environment Division.
stment
is an imperative statement executed when the relevant condition (at end
or on exception) occurs.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed when the relevant condition (not at
end or not on exception) occurs.
stment3
is an imperative statement executed when an attempt is made to read
beyond the last argument on the command line, or if the command line
argument does not exist.
stment4
is an imperative statement executed if the name of a referenced
environment variable or logical has not been set, or if the referenced
environment variable or logical does not exist.
stment5
is an imperative statement executed if the exception condition does not
exist.
line-num
is a numeric literal that specifies a line position on the terminal
screen. line-num must be a positive integer; it cannot be zero.
line-id
is the identifier of a data item that provides a line position on the
terminal screen. It must be a positive integer; it cannot be zero.
plus-num
is a numeric literal that increments the current value for line or
column position, or that increments the value of line-id or
column-id. plus-num can be zero or a positive integer.
column-num
is a numeric literal that specifies a column position on the terminal
screen. column-num must be a positive integer; it cannot be
zero.
column-id
is the identifier of a data item that provides a column position on the
terminal screen. It must be a positive integer; it cannot be zero.
prot-size-lit
is a numeric literal that specifies the maximum length of the video
screen field into which data can be typed. prot-size-lit must
be a positive integer; it cannot be zero.
prot-size-item
is the identifier of a numeric integer data item that specifies the
maximum length of the video screen field into which data can be typed.
prot-size-item must be a positive integer; it cannot be zero.
prot-fill-lit
is a single character alphanumeric literal that is used to initialize
each character position of a protected video screen field into which
data can be typed.
def-src-lit
is a nonnumeric literal or a figurative constant. However, it cannot be
the figurative constant ALL literal.
def-src-item
is the identifier of an alphanumeric data item.
key-dest-item
is the identifier of a data item that defines a control key.
key-dest-item must specify an alphanumeric data item at least
four characters in length.
screen-name
is the name of a screen item defined in the SCREEN SECTION of the
program.
arg-count
is a mnemonic name associated with ARGUMENT-NUMBER in the SPECIAL-NAMES
paragraph in the Environment Division. It represents the number of
arguments present on the run command line.
arg-value
is a mnemonic name associated with ARGUMENT-VALUE in the SPECIAL-NAMES
paragraph in the Environment Division. It contains the value of the
argument on the run command line specivied by the current argument
position indicator.
envlog-value
is a mnemonic name associated with ENVIRONMENT-VALUE in the
SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph in the Environment Division. It contains the
value of a selected environment variable or system logical.
Syntax Rules
Format 3
- You cannot specify a phrase more than once for any
dest-item.
- When you use the DEFAULT phrase and the PROTECTED phrase without
the SIZE option, the size of def-src-item or
def-src-lit must be less than or equal to the size of
dest-item.
- When you use the DEFAULT phrase and the PROTECTED phrase with the
SIZE option, the size of def-src-item and def-src-lit
must be less than or equal to prot-size-lit. If
prot-size-item is specified and the specified size at run time
is less than the length of def-src-item or
def-src-lit, reprompting occurs.
- The FILLER phrase cannot be used with the EDITING phrase. If both
are present, the FILLER phrase is ignored.
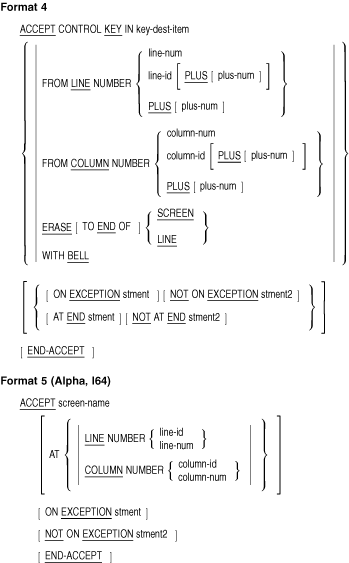
Format 4
- You cannot specify a phrase more than once for any
key-dest-item.
Format 6 (Alpha, I64)
- dest-item must reference a data item described as an
unsigned integer.
Formats 7 and 8 (Alpha, I64)
- dest-item must reference an alphanumeric data item.
<>
General Rules
Format 1
- The ACCEPT statement transfers data from input-source. The
transferred data replaces the contents of dest-item.
- The ACCEPT statement transfers a stream of characters with no
editing or conversion, unless the WITH CONVERSION phrase is specified.
Data transfer begins with the leftmost character position of
dest-item and continues to the right.
- If the data does not completely fill dest-item, remaining
character positions are filled with spaces. If the data is too long for
dest-item, it is truncated on the right.
- The ACCEPT statement treats dest-item as alphanumeric,
regardless of its class, unless the WITH CONVERSION phrase is specified.
- If there is no FROM phrase, the ACCEPT statement transfers data
from the default system input device.
Format 2
- The ACCEPT statement transfers data to dest-item according
to the MOVE statement rules.
- DATE, DAY, DAY-OF-WEEK, and TIME are not actual data items.
Therefore, the source program must not describe them.
- DATE has three elements. From left to right, they are as follows:
- Year of century
(four digits if you specify YYYYMMDD, two digits if you do not)
- Month of year (two digits)
- Day of month (two digits)
The ACCEPT statement operates as if DATE were described in the
program as an eight-digit or six-digit, unsigned, elementary, numeric
integer data item (PIC 9(8) or PIC 9(6)).
For example, June 3, 1997
is expressed as 19970603 or 970603.5
- DAY has two elements. From left to right, they are as follows:
- Year of century (four digits if you specify YYYYDDD, two digits if
you do not)
- Day of year (three digits)
The ACCEPT statement operates as if DAY were described in the
program as a seven-digit or five-digit, unsigned, elementary, numeric
integer data item (PIC 9(7) or (PIC 9(5)).
For example, the
fifteenth day of 1998 is expressed as 1998015 or 98015.+
The
YYYYMMDD and YYYYDDD options are Hewlett-Packard extensions.
- DAY-OF-WEEK is a one-digit item that represents the day of the
week.
The ACCEPT statement operates as if DAY-OF-WEEK were
described in the program as a one-digit, unsigned, elementary numeric
integer data item.
The values of DAY-OF-WEEK range from 1 (for
Monday) to 7 (for Sunday).
- TIME represents elapsed time after midnight, as shown on a 24-hour
clock. It has four, two-digit elements. From left to right, they are as
follows:
- Hours
- Minutes
- Seconds
- Hundredths of a second <>
The ACCEPT statement operates as if TIME were described in the
program as an eight-digit, unsigned elementary numeric integer data
item (PIC 9(8)).
The time 6:13 PM is expressed as 18130000. The
minimum and maximum values of TIME are 00000000 and 23595999.
Formats 3 and 4
- The ACCEPT statement transfers data from a video terminal. The data
replaces the contents of dest-item (Format 3), or
key-dest-item (Format 4). Format 3 can also update
key-dest-item.
- The presence of either the LINE NUMBER phrase or the COLUMN NUMBER
phrase implies NO ADVANCING. The cursor remains on the character
position immediately following the position of the last input character
or in the position immediately following the rightmost position in the
protected area. (For example, ACCEPT... PROTECTED SIZE 10 LINE 1 COLUMN
1, leaves the cursor at line 1, column 11, no matter what is typed in.)
This is the default starting position of the next data item the program
will input from or display upon the terminal.
- If you do not use either the LINE NUMBER phrase or the COLUMN
NUMBER phrase, data is accepted according to positioning rules for the
Format 1 ACCEPT statement.
Formats 3, 4, and 5
- The execution of certain extended ACCEPTs when the input source is
assigned to a file (for example, in batch mode on OpenVMS systems), is
a restriction. Syntax and actions that result in outputs from the
ACCEPT operation (positioning, erasing, setting character attributes,
reprompting, and protecting) to a nonvideo terminal are not supported
and are ignored.
LINE NUMBER Phrase (Formats 3 and 4)
- The LINE NUMBER phrase positions the cursor on a specific line of
the video screen for data input.
- If the LINE NUMBER phrase does not appear, but the COLUMN NUMBER
phrase does, then data is accepted from the current line
position and specified column position.
- If line-num or the value of line-id is greater
than the bottommost line position of the current screen, program
results are undefined. (See Technical Notes.) Scrolling results if
relative positioning is attempted past the bottom of the screen.
- If you use line-id without its PLUS option, the line
position is the value of line-id.
- If you use line-id with its PLUS option, the line position
is the sum of plus-num and the value of line-id.
- If you use the PLUS option without line-id, the line
position is the sum of plus-num and the value of the current
line position.
- If you use the PLUS option, but you do not specify
plus-num, then PLUS 1 is implied.
- Data input results are undefined if your program generates a value
for line-id that is one of the following:
- Zero
- Negative
- Greater than the bottommost line position of the current screen
Note
5 HP COBOL also supports four-digit
years using the CURRENT-DATE intrinsic function (see Chapter 7.)
Hewlett-Packard recommends the use of four-digit years.
|
|

