 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
6.8 General Formats and Rules for Statements
Function
The Procedure Division contains the routines that process the files and
data described in the Environment and Data Divisions.
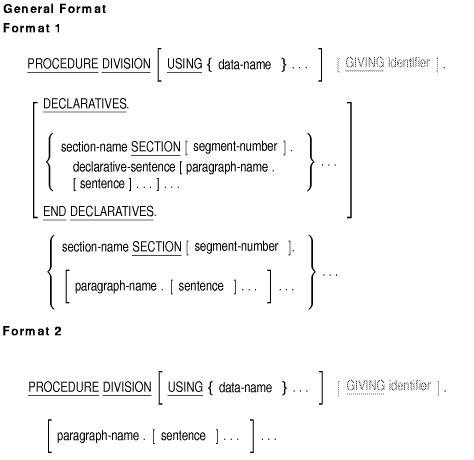
Syntax Rules
- The Procedure Division follows the Data Division.
- The Procedure Division must begin with the Procedure Division
header.
- The end of the Procedure Division is indicated by one of the
following:
- The Identification Division header of another source program
- The END PROGRAM header
- The physical position in the Procedure Division after which no
further processing occurs
- A procedure consists of either:
- One or more successive sections
- One or more successive paragraphs
- If one paragraph is in a section, all paragraphs must be in
sections.
- A procedure-name refers to a paragraph or section in the source
program. It is either paragraph-name (which can be qualified)
or section-name.
- A section consists of a section header followed by zero or more
successive paragraphs. A section ends immediately before the next
section or at the end of the Procedure Division. In the declaratives
part of the Procedure Division, a section can also end at the key words
END DECLARATIVES. See Section 2.3 for more information on
declaratives.
- A paragraph consists of a paragraph-name followed by a
separator period, and by zero or more successive sentences. A paragraph
ends immediately before the next paragraph-name or
section-name or at the end of the Procedure Division. In the
declaratives part of the Procedure Division, a paragraph can also end
at the key words END DECLARATIVE. See Section 2.3 for more
information on declaratives.
- sentence contains one or more statements terminated by a
separator period.
- A statement is a syntactically valid combination of words and
symbols that begins with a COBOL verb.
- identifier is the word or words necessary to refer
uniquely to a data item.
Procedure Division Header
- The Procedure Division header identifies and begins the Procedure
Division. It consists of the reserved words PROCEDURE DIVISION and
optional USING and GIVING phrases followed by a separator period.
- The USING phrase is required only if the program is invoked by a
CALL statement with a USING phrase.
- The Procedure Division header USING phrase identifies the names
used in the program to refer to arguments from the calling program. In
the calling program, the USING phrase of the CALL statement identifies
the arguments. The data items in the two USING phrase lists correspond
positionally.
- Each data-name in the USING phrase must be defined in the
Linkage Section with a level-01 or level-77 entry.
- Each data-name cannot appear more than once in the USING
phrase.
- In the USING phrase, data-name cannot have the external
attribute.
- In the USING phrase, the data description for data-name
cannot contain a REDEFINES clause. However, the data description can be
the object of a REDEFINES clause.
- The Procedure Division header GIVING phrase specifies a function
result of the program. The identifier must refer to an
elementary integer numeric data item with COMP, COMP-1, or COMP-2 usage
and no scaling positions. The identifier cannot be
subscripted, but it can be qualified.
Procedure Division Body
- The Procedure Division body consists of all Procedure Division text
following the Procedure Division header.
General Rules
- References to USING phrase data-names operate according to
data descriptions in the called program's Linkage Section, regardless
of the descriptions in the calling program.
- The called program can refer, in its Procedure Division, to a
Linkage Section data item only if the data item satisfies one of these
conditions:
- It is in the Procedure Division header USING phrase.
- It is subordinate to data-name that is in the Procedure
Division header USING phrase.
- Its definition includes a REDEFINES or RENAMES clause, the object
of which is in the Procedure Division header USING phrase.
- It is subordinate to an item that satisfies the previous conditions.
- It is a condition-name or index-name associated with a data item
that satisfies any of the previous conditions.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, when a called program returns control to
the calling program, the return value is made available to the calling
program in the data item specified in its CALL statement GIVING phrase.
The value is moved to that data item according to the rules for the
MOVE statement. If the calling program does not specify a GIVING
phrase, then the return value is made available in the calling
program's RETURN-CODE special register. Note that the value in the
called program's RETURN-CODE is not returned to the caller.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, if no GIVING phrase is specified in the
called program, the value in the RETURN-CODE special register is made
available to the calling program in the data item specified in the
calling program's CALL statement GIVING phrase. The value is moved
according to the rules for the MOVE statement. If the calling program
does not specify a CALL GIVING phrase, the value in the called
program's RETURN-CODE special register is made available to the calling
program in the calling program's RETURN-CODE special register.
Table 6-7 shows the relationship between the GIVING phrase and
RETURN-CODE.
Table 6-7 Relation of GIVING Phrase to RETURN-CODE Special Register (Alpha, I64)
| Calling program has CALL GIVING X |
Called program has PROCEDURE DIVISION GIVING Y |
Called program puts result in |
Calling program gets result in |
|
YES
|
YES
|
Y (also RETURN-CODE)
|
X (moved from Y)
|
|
YES
|
NO
|
RETURN-CODE
|
X (moved from called program's RETURN-CODE)
|
|
NO
|
YES
|
Y (also RETURN-CODE)
|
RETURN-CODE (moved from Y)
|
|
NO
|
NO
|
RETURN-CODE
|
RETURN-CODE (moved from called program's RETURN-CODE)
|
Technical Notes
- On Alpha and I64 systems, because the reserved word RETURN-CODE is
one of the X/Open reserved words, you cannot use the compilation flag
-rsv noxopen
(for Tru64 UNIX systems) or the corresponding qualifier
/RESERVED_WORDS = NOXOPEN (for OpenVMS systems) if your program uses
the RETURN-CODE special register.
-
On Alpha and I64 systems, HP COBOL supports passing status to the
operating system for RETURN-CODE and PROCEDURE DIVISION GIVING when
EXIT PROGRAM or STOP RUN is executed. <>
Four of the data
types supported by PROCEDURE DIVISION GIVING can be used to communicate
status to the operating system. Following is a summary of what is
supported for both RETURN CODE and PROCEDURE DIVISION GIVING:
RETURN-CODE (Alpha and I-64 only*)
EXIT PROGRAM /STA=V3 yes
EXIT PROGRAM /STA=85 yes
STOP RUN yes
PROCEDURE DIVISION GIVING
EXIT PROGRAM /STA=V3 yes
EXIT PROGRAM /STA=85 yes
STOP RUN yes*
Data Types
COMP-1,COMP-2 no
PIC 9(04) COMP no
PIC S9(04) COMP no
PIC 9(09) COMP yes
PIC S9(09) COMP yes
PIC 9(18) COMP yes
PIC S9(18) COMP yes
PIC 9(31) COMP no
PIC S9(31) COMP no
*Refer to the appendix on compatibility in the
HP COBOL User Manual for differences on VAX.
|
This support is subject to the limitations on status handling
imposed by the operating system. If PIC S9(18) COMP or PIC 9(18) COMP
is used, the high-order 32 bits are truncated before the status is
passed on to the operating system.
To display the operating system
status information, do the following:
[UNIX] echo $status
[OpenVMS] show symbol $status
|
Additional References
Example
The following is an example of a Procedure Division header:
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 RETURN-RESULT PIC 9(8) COMP.
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 ARG1.
03 ARG2 PIC X(6).
03 ARG3 PIC S9(6) COMP.
01 ARG4 PIC X(4).
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING ARG1 ARG4 GIVING RETURN-RESULT.
.
.
.
MOVE 17 TO RETURN-RESULT.
EXIT PROGRAM.
|
|
