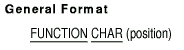|
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
Description
The ACOS function returns a numeric value in radians that approximates
the arccosine of the argument.
General Format
arg
is a numeric argument with a value greater than or equal to -1 and less
than or equal to +1.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is the approximation of the arccosine of arg and
is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to Pi sign
(approximately 3.14159).
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION ACOS (.85).
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is a
number that approximates the arccosine of .85.
7.3 ANNUITY
Description
The ANNUITY function (annuity immediate) returns a numeric value that
approximates the ratio of an annuity paid at the end of each period for
the number of periods specified (by the second argument) to an initial
investment of one. Interest is earned at the rate specified (by the
first argument), and is applied at the end of the period, before the
payment.

interest-rate
is a numeric argument with a value greater than or equal to 0,
representing the interest rate applied at the end of the period before
the payment.
num-periods
is a positive integer argument representing the number of periods.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- When the value of interest-rate is 0, the value of the function is
the approximation of 1 / num-periods.
- When the value of interest-rate is not 0, the value of the function
is the approximation of
interest-rate / (1 --(1 + interest-rate) ** (-- num-periods)).
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION ANNUITY (INTEREST-RATE, NUM-PERIODS).
|
INTEREST-RATE is a numeric data item, and NUM-PERIODS is a numeric
integer data item. If the value of INTEREST-RATE is 0 and the value of
NUM-PERIODS is 6, RSULT has a value approximating 1/6. If the value of
INTEREST-RATE is .11 and the value of NUM-PERIODS is 6, RSULT (a
numeric data item) has a value of approximately 0.2364.
7.4 ARGCOUNT (OpenVMS Only)
Description
The ARGCOUNT function returns a numeric integer equal to the number of
arguments passed to the HP COBOL program.

Rules
- The type of this function is integer.
- The returned value represents the actual number of arguments passed
to the HP COBOL program that contains the function.
Example
IF FUNCTION ARGCOUNT = 3
PERFORM PROCESS-OPTIONAL-3RD-ARGUMENT.
|
If there are three arguments passed to the HP COBOL program
containing the ARGCOUNT function, a third argument supplied with the
COBOL program calling command will be parsed and processed.
Additional Reference
Refer to the Argument Information Register in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard.
<>
Description
The ASIN function returns a numeric value in radians that approximates
the arcsine of the argument.

arg
is a numeric argument with a value greater than or equal to -1 and less
than or equal to +1.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is the approximation of the arcsine of arg and
is greater than or equal to - Pi sign /2 and less than or equal to + Pi
sign /2. ( Pi sign is approximately 3.14159.)
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION ASIN (.675).
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is a
number that approximates the arcsine of .675.
7.6 ATAN
Description
The ATAN function returns a numeric value in radians that approximates
the arctangent of the argument.

arg
is a numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is the approximation of the arctangent of arg
and is greater than - Pi sign /2 and less than + Pi sign /2. ( Pi sign
is approximately 3.14159.)
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION ATAN (MEASUREMENT-IN-RADIANS).
|
MEASUREMENT-IN-RADIANS and RSULT are numeric data items. The value
returned and stored in RSULT is a number that approximates the
arctangent of the value of MEASUREMENT-IN-RADIANS.
7.7 CHAR
Description
The CHAR function returns a one-character alphanumeric value that is a
character in the program collating sequence having the ordinal position
equal to the value of the argument.
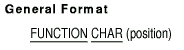
position
is a positive integer argument representing the ordinal position of the
desired character in the program collating sequence, and having a value
less than or equal to the number of positions in the collating sequence.
Rules
- The type of this function is alphanumeric.
- The character returned as the function value is the character in
the program collating sequence. (See the information on the ALPHABET
clause in Chapter 4.)
- If more than one character has the same position in the program
collating sequence, the character returned as the function value is
that of the first literal specified for that character position in the
ALPHABET clause.
Example
MOVE FUNCTION CHAR (13) TO FORM-FEED-CH.
|
The character occupying the 13th position in the program collating
sequence (that is, a form feed in the default collating sequence) is
returned and stored in FORM-FEED-CH, which is an alphanumeric data item
one character in length. (The numeric representation of a character is
not the same as its ordinal position. Numeric representation starts at
0, whereas ordinals start at 1. Always add 1 to the numeric value of
the desired character.)
7.8 COS
Description
The COS function returns a numeric value that approximates the cosine
of an angle or arc, expressed in radians, that is specified by the
argument.
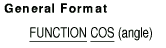
angle
is a numeric argument having the value of the measurement in radians of
an angle or arc.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is the approximation of the cosine of angle, and
is greater than or equal to -1 and less than or equal to +1.
Example
COMPUTE COSIN-RSLT = FUNCTION COS (X).
|
X and COSIN-RSULT are numeric data items. If the value of X is 3, the
approximate cosine of an angle of 3 radians is moved to COSIN-RSLT.
|