Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 82final > 6296 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
HP COBOL
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
The Environment Division describes the program's physical environment. It also specifies input-output control and describes special control techniques and hardware characteristics.
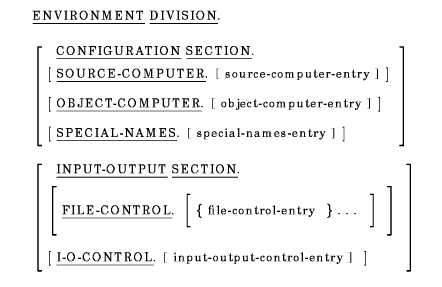
The Environment Division can contain two sections:
Explicit or implicit Configuration Section entries in a program containing other programs apply to each contained program.
The Configuration Section must not be stated in a program that is contained within another program. If Configuration Section entries are stated in a program that contains other programs, they apply to each contained program.
The SOURCE-COMPUTER paragraph specifies the computer on which the source program is to be compiled.
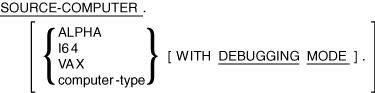
computer-type
is a user-defined word that names the computer.
ALPHA, I64, and VAX are system-names. They are not reserved words, and are for documentation only.
The OBJECT-COMPUTER paragraph describes the computer on which the program is to execute.
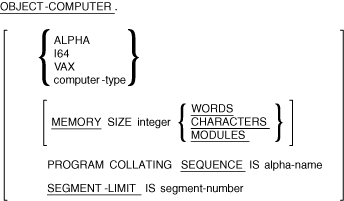
computer-type
is a user-defined word that names the computer.integer
is a numeric literal that has no digits to the right of the assumed decimal point.alpha-name
is the name of a collating sequence defined in the ALPHABET clause of the SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph.segment-number
is an integer from 1 to 49.
ALPHA, I64, and VAX are system-names. They are not reserved words, and are for documentation only.
Additionally, refer to the information on SORT and MERGE statements in the HP COBOL User Manual.
OBJECT-COMPUTER. Alpha. |
OBJECT-COMPUTER. |
OBJECT-COMPUTER. Alpha
PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE IS ALPH-A.
|
OBJECT-COMPUTER. Alpha
SEQUENCE IS EBCDIC.
|
ALPHABET EBCDIC IS EBCDIC |
The SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph: (1) associates compiler features and logical names (on OpenVMS systems) or environment variables (on Tru64 UNIX systems) with user-defined mnemonic-names, (2) provides a way to reference command-line arguments and (on Tru64 UNIX) environment variables or (on OpenVMS) logical names with user-defined mnemonic names, (3) defines symbolic-characters, (4) specifies the currency sign, (5) selects the decimal point, (6) relates alphabet-names to character sets or collating sequences, (7) relates class-names to character sets, (8) provides for cursor positioning for an ACCEPT (Format 5) statement, and (9) provides information on the cause of termination of an ACCEPT (Format 5) statement.
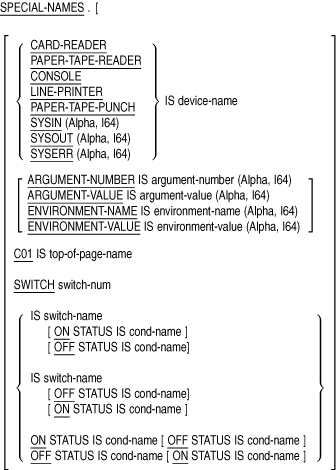
device-name
is a user-defined word for a device. Only the ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements can refer to it.argument-number
is a user-defined word that contains the current argument position indicator number when used with DISPLAY, or the count of command line arguments when used with ACCEPT. Only the ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements can refer to it.argument-value
is a user-defined word that contains the value of the current command line argument as indicated by the current ARGUMENT-NUMBER. Only the ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements can refer to it.environment-name
is a user-defined word that contains the name of an environment variable or system logical. Only the ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements can refer to it.environment-value
is a user-defined word that contains the value of the environment variable or logical named by the current ENVIRONMENT-NAME. Only the ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements can refer to it.top-of-page-name
is a user-defined word for the top of a page. Only the WRITE statement can refer to it.switch-num
is the number of a program switch. Its value can range from 1 to 16.switch-name
is a mnemonic-name for the program switch.cond-name
is a condition-name for the on or off status of the switch. It always possesses the global attribute. Its truth value is true when the STATUS phrase matches the status of the switch, false when it does not.alpha-name
is the user-defined word for a character set, collating sequence, or both. It always possesses the global attribute.first-literal
is a literal. It specifies either: (1) the value of one or more alphabet characters, or (2) the first in a range of values.last-literal
is a literal. It specifies the last in a range of values.lit
is a literal. It specifies an alphabet character value.symbol-char
is a user-defined word that names the symbolic-character. It always possesses the global attribute. The same symbol-char cannot appear more than once in the SYMBOLIC CHARACTERS clause.char-val
is an integer that indicates the ordinal position of a character in the native character set.class-name
is the user-defined word for a class. It always possesses a global attribute.char
is a one-character nonnumeric literal that specifies the currency symbol. It cannot be a symbolic-character or figurative constant.literal-7 (Alpha, I64)
is an alphanumeric literal. It cannot be a figurative constant.literal-8 (Alpha, I64)
is an alphanumeric literal consisting of a single character. It cannot be a figurative constant. No two occurrences of literal-8 can have the same value.cursor-position (Alpha, I64)
is a data item declared in the Working-Storage Section of the program. It is either an elementary unsigned numeric integer either four or six characters in length, described as USAGE IS DISPLAY, or a group item either four or six characters in length, consisting of two elementary unsigned data items.crt-status-code (Alpha, I64)
is a group data item three characters in length, declared in the Working-Storage Section of the program. <>
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |