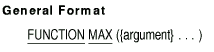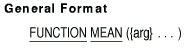|
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
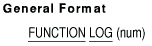
7.20 LOG
Description
The LOG function returns a numeric value that approximates the
logarithm to the base e (natural log) of the argument.
num
is a positive numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is an approximation of the logarithm to the base
e of the argument.
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION LOG (NUM).
|
NUM and RSULT are numeric data items; the value of NUM must be greater
than 0. The value returned and stored in RSULT is an approximation of
the logarithm to the base e of NUM.
7.21 LOG10
Description
The LOG10 function returns a numeric value that approximates the
logarithm to the base 10 of the argument.

num
is a positive numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is an approximation of the logarithm to the base
10 of the argument.
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION LOG10 (NUM).
|
NUM and RSULT are numeric data items; the value of NUM must be greater
than 0. The value returned and stored in RSULT is an approximation of
the logarithm to the base 10 of NUM.
7.22 LOWER-CASE
Description
The LOWER-CASE function returns a character string that is the same
length as the argument with each uppercase letter in the argument
replaced by the corresponding lowercase letter.

string
is an alphabetic or alphanumeric argument at least one character in
length.
Rules
- The type of this function is alphanumeric.
- The returned value is the same character string as the argument,
except that each uppercase letter in the argument is replaced by the
corresponding lowercase letter.
Example
MOVE FUNCTION LOWER-CASE (STR) TO LC-STR.
|
If STR (an alphanumeric data item six characters in length) contains
the value "Autumn" the value returned and stored in LC-STR (also an
alphanumeric data item six characters in length) is "autumn"; if STR
contains "fall98" the value returned is unchanged ("fall98").
7.23 MAX
Description
The MAX function returns the contents of the argument that contains the
maximum value.
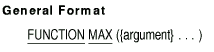
argument
is an alphabetic, alphanumeric, integer, or numeric argument.
Rules
- The arguments must be all alphabetic, all alphanumeric, all
integer, or all numeric, except that integer and numeric arguments can
be mixed and alphabetic and alphanumeric arguments can be mixed.
- The type of the function depends on the arguments, as follows:
| Arguments |
Function Type |
|
Alphabetic and/or alphanumeric
|
Alphanumeric
|
|
Integer (all arguments)
|
Integer
|
|
Numeric (some arguments might be integer)
|
Numeric
|
- The returned value consists of the contents of the argument having
the greatest value, as determined by comparisons made according to the
rules for simple conditions. (See Chapter 6.)
- If more than one argument has the same value, and that value is
the maximum, the returned value consists of the contents of the
leftmost of these arguments.
- If there is only one argument, the returned value consists of the
contents of that argument.
- If the type of the function is alphanumeric, the size of the
returned value is the same as the size of the argument selected as the
maximum.
Examples
-
MOVE FUNCTION MAX ("A", "B", "C") TO MAX-LETTER-OUT.
MOVE FUNCTION MAX (1, 2, 3) TO MAX-NUMBER-OUT.
|
MAX-LETTER-OUT is alphabetic or alphanumeric, and receives the value
"C"; MAX-NUMBER-OUT is integer and receives the value 3.
-
COMPUTE ITEMC = (ITEMA + FUNCTION MAX (ITEMB, 10)).
|
If ITEM A and ITEMB both contain the value 1, this statement results in
ITEMC having the value 11.
IF FUNCTION MAX (A, B, C) > 100 ...
|
This is equivalent to the following more complex code:
IF A >= B
IF A >= C
MOVE A TO TMP
ELSE
MOVE C TO TMP
ELSE
IF B >= C
MOVE B TO TMP
ELSE
MOVE C TO TMP.
IF TMP > 100 ...
|
- The following example shows generic subscripting with reference
modification:
05 TABLE1 PIC X(7) OCCURS 3 TIMES.
.
.
.
MOVE "XAAAAAQ" TO TABLE1(1).
MOVE "XBBBBBQ" TO TABLE1(2).
MOVE "XCCCCCQ" TO TABLE1(3).
MOVE FUNCTION MAX(TABLE1(ALL)(2:5)) TO RSULT.
|
The value "CCCCC" is returned and stored in RSULT, an alphanumeric
data item. The reference modifier, (2:5), applies to each element
implicitly specified by the ALL subscript. Thus,
FUNCTION MAX(TABLE1(ALL)(2:5))
|
is equivalent to
FUNCTION MAX(TABLE1(1)(2:5),
TABLE1(2)(2:5),
TABLE1(3)(2:5))
|
7.24 MEAN
Description
The MEAN function returns a numeric value that is the arithmetic mean
(average) of its arguments.
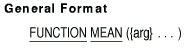
arg
is a numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The return value is the arithmetic mean of the arguments in the
argument list; that is, it is the sum of the arguments divided by the
number of arguments.
Examples
-
COMPUTE AVERAGE-VALUE = FUNCTION MEAN (9, 2, 6, 7, 1).
|
The value returned and stored in AVERAGE-VALUE (a numeric data item) is
5 (the sum of the arguments divided by the number of arguments).
-
COMPUTE MEAN-ANSWER = FUNCTION MEAN(A, B, C).
|
MEAN-ANSWER, A, B, and C are numeric data items. This code is
equivalent to
COMPUTE MEAN-ANSWER = (A + B + C ) / 3.
|
7.25 MEDIAN
Description
The MEDIAN function returns the median value of a list of numbers,
represented by the arguments. This value is such that at least half of
the values are greater than or equal to the returned value, and at
least half are less than or equal.

num
is a numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- If the number of arguments is odd, the returned value is the middle
occurrence in the sorted list.
- If the number of arguments is even, the returned value is the
arithmetic mean of the values referenced by the two middle occurrences
in the sorted list.
- The comparisons used to arrange the argument values in sorted order
are made according to the rules for simple conditions. (See
Chapter 6.)
Examples
-
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION MEDIAN (1, 1, 9, 2, 1).
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is 1.
-
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION MEDIAN (1, 1, 9, 2).
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT is 1.5.
|