 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
7.26 MIDRANGE
Description
The MIDRANGE (middle range) function returns a numeric value that is
the arithmetic mean (average) of the values of the minimum argument and
the maximum argument.

num
is a numeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The returned value is the arithmetic mean of the greatest argument
value and the least argument value. The comparisons used to determine
the greatest and least values are made according to the rules for
simple conditions. (See Chapter 6.)
- The values of the arguments that are neither the greatest nor the
least in value do not affect the value returned.
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION MIDRANGE (1, 2, 50, 4, 3).
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is 25.5,
which is the arithmetic mean of the greatest and least arguments; that
is, the sum of 50 and 1 divided by 2.
7.27 MIN
Description
The MIN function returns the content of the argument that contains the
minimum value.

argument
is an alphabetic, alphanumeric, integer, or numeric argument.
Rules
- The arguments must be all alphabetic, all alphanumeric, all
integer, or all numeric, except that integer and numeric arguments can
be mixed and alphabetic and alphanumeric arguments can be mixed.
- The type of the function depends on the arguments, as follows:
| Arguments |
Function Type |
|
Alphabetic and/or alphanumeric
|
Alphanumeric
|
|
Integer (all arguments)
|
Integer
|
|
Numeric (some arguments might be integer)
|
Numeric
|
- The returned value consists of the contents of the argument having
the least value, as determined by comparisons made according to the
rules for simple conditions. (See Chapter 6.)
- If more than one argument has the same value, and that value is
the minimum, the returned value consists of the contents of the
leftmost of these arguments.
- If there is only one argument, the returned value consists of the
contents of that argument.
- If the type of the function is alphanumeric, the size of the
returned value is the same as the size of the argument selected as the
minimum.
Example
COMPUTE ITEMC = (ITEMA + FUNCTION MIN (ITEMB, 10)).
|
If ITEMA and ITEMB both contain the value 1, this statement results in
ITEMC having the value 2.
7.28 MOD
Description
The MOD function returns the value of argument-1 modulo argument-2.
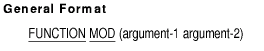
argument-1
is an integer argument.
argument-2
is an integer argument whose value cannot be 0.
Rules
- The type of this function is integer.
- The returned value is an integer value and is defined as the
following:
argument-1 -- (argument-2 * FUNCTION INTEGER (argument-1 / argument-2))
|
(The INTEGER function returns the greatest integer value that is less
than or equal to the argument. See Section 7.15 for more information.)
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION MOD (ARGUMENT-1, ARGUMENT-2).
|
ARGUMENT-1 and ARGUMENT-2 are numeric integer data items. Following are
the expected results for some values of ARGUMENT-1 and ARGUMENT-2:
| ARGUMENT-1 |
ARGUMENT-2 |
RETURN |
|
11
|
5
|
1
|
|
-11
|
5
|
4
|
|
11
|
-5
|
-4
|
|
-11
|
-5
|
-1
|
7.29 NUMVAL
Description
The NUMVAL function returns the numeric value represented by the
character string specified by the argument. Leading and trailing spaces
are ignored.

arg
is an alphanumeric argument whose content has one of the following two
formats:
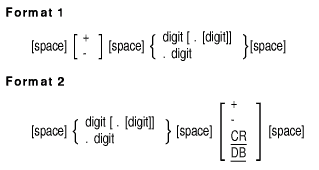 where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, and digit is a string of 1
to 18 digits.
where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, and digit is a string of 1
to 18 digits.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The total number of digits in the argument must not exceed 18.
- If the DECIMAL-POINT IS COMMA clause is specified in the
SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph, a comma must be used in the argument rather
than a decimal point.
- The returned value is the numeric value represented by the argument.
- The number of digits returned is 18.
Examples
-
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION NUMVAL ("4540").
|
The value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is 4540.
-
MOVE "-123.49" TO OLD-ID.
COMPUTE NEW-ID = 2 + FUNCTION NUMVAL (OLD-ID).
|
OLD-ID is an alphanumeric data item, and NEW-ID is a numeric data item.
The value returned by the function is the numeric value -123.49, which
is added to 2, giving the sum -121.49, which is stored in NEW-ID.
7.30 NUMVAL-C
Description
The NUMVAL-C function returns the numeric value represented by the
character string specified by the first argument. Any currency sign
found in the character string and any commas preceding the decimal
point are ignored in determining the result.

arg-1
is an alphanumeric argument whose content has one of the following two
formats:
 where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, cs is a
string of 1 or more characters specified by arg-2, and
digit is a string of 1 or more digits.
where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, cs is a
string of 1 or more characters specified by arg-2, and
digit is a string of 1 or more digits.
arg-2
is an alphanumeric argument.
Rules
- The type of this function is numeric.
- The total number of digits in the first argument must not exceed 18.
- If the DECIMAL-POINT IS COMMA clause is specified in the
SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph, the functions of the comma and decimal point
in the first argument are reversed.
- If the optional second argument is not specified, the character
used for cs is the currency symbol specified for the program.
- The returned value is the numeric value represented by the first
argument.
- The number of digits returned is 18.
Example
COMPUTE RSULT = FUNCTION NUMVAL-C ("#1,000.00", "#").
|
The numeric value returned and stored in RSULT (a numeric data item) is
1000.
|


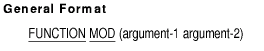

 where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, and digit is a string of 1
to 18 digits.
where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, and digit is a string of 1
to 18 digits.

 where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, cs is a
string of 1 or more characters specified by arg-2, and
digit is a string of 1 or more digits.
where space is a string of 0 or more spaces, cs is a
string of 1 or more characters specified by arg-2, and
digit is a string of 1 or more digits.