HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
In either case, a handle to the resulting persona will be returned as
specified by item code ACME$_PERSONA_HANDLE_OUT.
When a new persona is created, the ISS$_PRIMARY_EXTENSION designator
indicates which persona extension representing the domain of
interpretation was responsible for authenticating the user.
On a subsequent call $ACM will use that designator to guide processing
of the ACME$M_DEFAULT_PRINCIPAL function modifier, for instance when
there is an ACME$_FC_CHANGE_PASSWORD request.
ACME$_FC_CHANGE_PASSWORD
The ACME$_FC_CHANGE_PASSWORD function performs a password change
operation. All aspects of the ACME$FC_CHANGE_PASSWORD function can also
be performed as part of the ACME$_FC_AUTHENTICATE_PRINCIPAL function.
Some degree of the ACME$_FC_AUTHENTICATE_PRINCIPAL function is also
performed as part of ACME$_FC_CHANGE_PASSWORD to ensure the identity of
the user changing the password. The primary and secondary passwords can
be changed independently.
This function requires the ACME$_NEW_PASSWORD_FLAGS item code.
ACME$_FC_EVENT
The ACME$_FC_EVENT function provides a simple logging feature that can
be used to generate certain events related to the policy of a domain of
interpretation. To log an event, supply the desired "event type" item
code followed by the appropriate "data" item codes pertaining to the
"target" domain of interpretation.
To determine what event processing might be available, see the
documentation provided by the vendors of the supporting ACME agents.
ACME$_FC_FREE_CONTEXT
The ACME$_FC_FREE_CONTEXT function is used to terminate iterative
processing of a request. The address of the ACM communications buffer
associated with the request must be specified using the
context argument.
ACME$_FC_QUERY
The ACME$_FC_QUERY function provides a simple key-based query feature
that can be used to obtain certain information related to the policy of
a domain of interpretation. To look up an item of information, supply
the desired "key" item code followed by the appropriate "data" item
code.
To determine what query processing might be available, see the
documentation provided by the vendors of the supporting ACME agents.
ACME$_FC_RELEASE_CREDENTIALS
The ACME$_FC_RELEASE_CREDENTIALS function removes credentials for a
particular domain of interpretation from the specified persona. When
the domain of interpretation is specified as "VMS", all non-native
credentials are released and the persona is deleted. The "VMS"
credentials cannot be removed from either the currently active or the
process' natural persona. Thus, you cannot use the $ACM service to
delete these personae.
Function Modifiers This section describes the various function
modifiers for the function codes supported by the $ACM service.
Table SYS-11 indicates which Function Modifiers are applicable to the
various Function Codes:
Table SYS-11 Function Codes and Function Modifiers
| |
Function Codes |
| Function Modifiers |
Authenticate Principal |
Change Password |
Event |
Free Context |
Query |
Release Credentials |
|
ACME$M_ACQUIRE_CREDENTIALS
|
IP
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_COPY_PERSONA
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_DEFAULT_PRINCIPAL
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_FOREIGN_POLICY_HINTS
|
SR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_MERGE_PERSONA
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_NOAUDIT
|
SR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_NOAUTHORIZATION
|
SR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_OVERRIDE_MAPPING
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_TIMEOUT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$M_UCS2_4
|
<>
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
<>
|
<>
|
+Required
++Either ID or Name Required
Key to Codes
<>
---Permitted
IP---IMPERSONATE Privilege Required for the MAPPED
_VMS
_USERNAME
to differ from the one current when the initial call to
$ACM is made
IR---IMPERSONATE Privilege Required to override default values
SR---SECURITY Privilege Required
ACME$M_ACQUIRE_CREDENTIALS
The ACME$M_ACQUIRE_CREDENTIALS function modifier requests credentials
be acquired during a successful authentication.
ACME$M_COPY_PERSONA
The ACME$M_COPY_PERSONA function modifier requests acquired credentials
be attached to a copy of the persona specified with item code
ACME$_PERSONA_HANDLE_IN.
ACME$M_DEFAULT_PRINCIPAL
The ACME$M_DEFAULT_PRINCIPAL specifies that the principal name and
target domain of interpretation should be taken from the input persona,
such as for changing the password of the logged-in user or
reauthenticating the logged-in user.
ACME$M_FOREIGN_POLICY_HINTS
The ACME$M_FOREIGN_POLICY_HINTS function modifier indicates ACME agents
should honor the ACME$M_NOAUDIT and ACME$M_NOAUTHORIZATION function
modifiers for non-VMS domains of interpretation.
ACME$M_MERGE_PERSONA
The ACME$M_MERGE_PERSONA function modifier requests acquired
credentials be attached to the persona specified with item code
ACME$_PERSONA_HANDLE_IN.
ACME$M_NOAUDIT
The ACME$M_NOAUDIT function modifier indicates that auditing actions
should not be performed. Unless the ACME$M_FOREIGN_POLICY_HINTS
function modifier is also specified, this modifier applies only to the
VMS domain of interpretation.
ACME$M_NOAUTHORIZATION
The ACME$M_NOAUTHORIZATION function modifier indicates authorization
restrictions, such as the enforcement of modal constraints, should not
apply. This provides a mechanism for performing pure authentication
operations. Unless the ACME$M_FOREIGN_POLICY_HINTS function modifier is
also specified, this modifier applies only to the VMS domain of
interpretation.
ACME$M_OVERRIDE_MAPPING
The ACME$M_OVERRIDE_MAPPING function modifier allows for the
acquisition of non-VMS credentials during a persona merge or copy
operation. This occurs when an externally authorized principal name
maps to an OpenVMS user name that differs from the user name associated
with the native (VMS) credentials. By default, mixing credentials is
prohibited.
ACME$M_TIMEOUT
The ACME$M_TIMEOUT modifier indicates that the caller requests timeout
processing. The timeout interval is specified by the
ACME$_TIMEOUT_INTERVAL item code.
Timeout processing is always enforced for non-privileged callers.
Privileged callers (those running in exec mode or kernel mode or
possessing SECURITY privilege) must explicitly specify ACME$M_TIMEOUT
for timeout processing to be enforced.
ACME$M_UCS2_4
The ACME$M_UCS2_4 function modifier indicates item codes that specify
string values use a 4-byte UCS-2 (Unicode) representation rather than
8-bit ASCII.
Item Code Encoding
Item codes are 16-bit unsigned values and are encoded as follows:
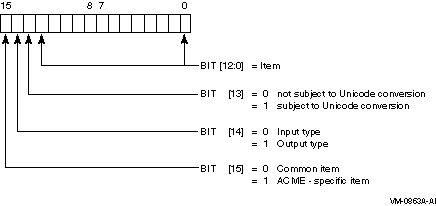
The item codes can be categorized in three different ways and are
described as follows:
- Common and ACME-specific Item Codes
- Common item codes
These item codes are defined for the $ACM
system service itself and are available to all ACME agents.
- ACME-specific item codes
These item codes are defined
separately for each ACME agent.
- Input and Output Item Codes
- Input item code
Input item codes specify a buffer that contains
information provided to $ACM. The buffer length and buffer address
fields in the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field
is ignored.
- Output item code
Output item codes specify a buffer in which
$ACM is to return information. The buffer length and buffer address
fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field
can be zero or nonzero.
- Subject and Not Subject to Unicode Conversion
- Subject to Unicode Conversion
Text strings can be specified as
Latin1 or 4-byte UCS-2 characters, depending on the setting of the
ACME$M_UCS2_4 function modifier. An item code that is subject to
Unicode conversion indicates it is a text item.
- Not subject to Unicode Conversion
Item codes that are not
subject to Unicode conversion have a data format implied by the item
code, and the nature of the data format must be explicitly understood
by the programmer who calls $ACM.
See the Item Codes section for a description of the common item codes
and their data formats.
Documentation of ACME-specific codes in general comes in the
documentation from the vendor of each ACME agent.
For documentation of ACME-specific codes for the VMS ACME, see the VMS
ACME-specific Item Codes section of this description. Common Item Codes
This section describes the common item codes for the function codes
supported by the $ACM service.
The item code space is partitioned into common items and ACME-specific
items. ACME-specific items are used to request information that is
unique to a particular domain of interpretation. The item codes
described in this section fall into the common item code space.
Table SYS-12 indicates which Common Item Codes are applicable to the
various Function Codes:
Table SYS-12 Function Codes and Common Item Codes
| |
Function Codes |
| Item Codes |
Authenticate Principal |
Change Password |
Event |
Free Context |
Query |
Release Credentials |
|
ACME$_ACCESS_MODE
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_ACCESS_PORT
(U)
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_AUTH_MECHANISM
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_ID
(O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_NAME
(U,O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_CHAIN
|
<>
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
ACME$_CHALLENGE_DATA
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_CONTEXT_ACME_ID
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_CONTEXT_ACME_NAME
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_CREDENTIALS_NAME
(U)
|
|
|
|
|
|
<>++
|
|
ACME$_CREDENTIALS_TYPE
|
|
|
|
|
|
<>++
|
|
ACME$_DIALOGUE_SUPPORT
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_EVENT_DATA_IN
|
|
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_EVENT_DATA_OUT
(O)
|
|
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_EVENT_TYPE
|
|
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_LOCALE
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_LOGON_INFORMATION
(O)
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_LOGON_TYPE
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_MAPPED_VMS_USERNAME
(U,O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_MAPPING_ACME_ID
(O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_MAPPING_ACME_NAME
(U,O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_NEW_PASSWORD_1
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_NEW_PASSWORD_2
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_NEW_PASSWORD_FLAGS
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_NEW_PASSWORD_SYSTEM
(U)
|
SR
|
SR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_NULL
|
<>
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
ACME$_PASSWORD_1
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PASSWORD_2
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PASSWORD_SYSTEM
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PERSONA_HANDLE_IN
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PERSONA_HANDLE_OUT
(O)
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PHASE_TRANSITION
(O)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PRINCIPAL_NAME_IN
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_PRINCIPAL_NAME_OUT
(U,O)
|
<>
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_QUERY_DATA
(O)
|
|
|
|
|
<>+
|
|
|
ACME$_QUERY_KEY_TYPE
|
|
|
|
|
<>+
|
|
|
ACME$_QUERY_KEY_VALUE
|
|
|
|
|
<>+
|
|
|
ACME$_QUERY_TYPE
|
|
|
|
|
<>+
|
|
|
ACME$_REMOTE_HOST_ADDRESS
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_REMOTE_HOST_ADDRESS_TYPE
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_REMOTE_HOST_FULLNAME
(U)
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_REMOTE_HOST_NAME
(U)
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_REMOTE_USERNAME
(U)
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_RESPONSE_DATA
|
<>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACME$_SERVER_NAME_IN
(U)
|
|
|
|
<>
|
|
|
|
ACME$_SERVER_NAME_OUT
(U,O)
|
|
|
|
<>
|
|
|
|
ACME$_SERVICE_NAME
(U)
|
IR
|
IR
|
IR
|
IR
|
IR
|
IR
|
|
ACME$_TARGET_DOI_ID
|
<>
|
<>
|
<>++
|
|
<>++
|
|
|
ACME$_TARGET_DOI_NAME
(U)
|
<>
|
<>
|
<>++
|
|
<>++
|
|
|
ACME$_TIMEOUT_INTERVAL
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+Required
++Either ID or Name Required
Key to Codes
<>
---Permitted
IR---IMPERSONATE Privilege Required to override default values
SR---SECURITY Privilege Required
O---Output item code
U---Subject to Unicode Conversion
ACME$_ACCESS_MODE
The ACME$_ACCESS_MODE item code is an input item code. It specifies the
access mode at which a new persona, resulting from credential
acquisition processing, is to be created. The buffer must contain a
longword value specifying the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
PSL$C_KERNEL
PSL$C_EXEC
PSL$C_SUPER
PSL$C_USER
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The specified access mode and the access mode of the caller are
compared. The less privileged of the two access modes becomes the
access mode at which the persona is created.
ACME$_ACCESS_PORT
The ACME$_ACCESS_PORT item code is an input item code. It specifies the
name of local device (for example, a terminal) applicable to an
authentication request. The buffer must contain a case-insensitive name
string.
If not specified, $ACM passes the name string contained in the
PCB$T_TERMINAL field of the process control block for the process, or,
if that is empty, for the nearest ancestor process (if any) where the
PCB$T_TERMINAL field is not empty.
ACME$_AUTH_MECHANISM
The ACME$_AUTH_MECHANISM item code is an input item code. It specifies
the authentication mechanism applicable to an authentication request.
The buffer must contain a longword value specifying the desired
mechanism code. If not specified, the authenticating domain of
interpretation applies its default mechanism.
The $ACMEDEF macro defines the following symbols for the standard
mechanism types:
ACMEMECH$K_CHALLENGE_RESPONSE
ACMEMECH$K_PASSWORD
Individual ACME agents may define their own authentication mechanisms
specific to their domain of interpretation.
ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_ID
The ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_ID item code is an output item code. It
specifies the buffer to receive the agent ID of the domain of
interpretation that successfully authenticated the principal.
ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_NAME
The ACME$_AUTHENTICATING_DOI_NAME item code is an output item code. It
specifies the buffer to receive the name of the domain of
interpretation that successfully authenticated the principal.
The maximum data returned for this item code is the number of
characters represented by the symbol, ACME$K_MAXCHAR_DOI_NAME, so a
caller's buffer should be at least that long, with the number of bytes
allocated dependent on whether the ACME$M_UCS2_4 function code modifier
was specified on the call to $ACM[W].
ACME$_CHAIN
The ACME$_CHAIN item code is an input item code. It specifies the
address of the next item list segment to process immediately after
processing the current list segment.
The buffer address field in the item descriptor specifies the address
of the next item list segment to be processed. The ACME$_CHAIN item
code must be last in the item list segment; $ACM treats this as the
logical end of the current item list segment. Any item list entries
following the ACME$_CHAIN item code are ignored.
On Alpha and I64 platforms, both 32- and 64-bit item lists can be
chained together.
ACME$_CHALLENGE_DATA
The ACME$_CHALLENGE_DATA item code is an input item code. It specifies
the challenge data that was used as the basis for generating the
response data specified by the ACME$_RESPONSE_DATA item code. The
meaning of this data is specific to the domain of interpretation for
which it is used.
|
