Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 83final > 5763 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
HP C
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
The ISO/ANSI C standard defines a library of functions, as well as related types and macros, to be provided with any implementation of ANSI C. The HP C Language Reference Manual describes the ANSI-conformant library features common to all HP C platforms. The HP C Run-Time Library Reference Manual for OpenVMS Systems provides a more detailed description of these routines and their use in the OpenVMS environment. It also documents additional header files, functions, types, and macros that are available on the OpenVMS system.
All library functions are declared in a header file. To make the contents of a header file available to your program, include the header file with an #include preprocessor directive. For example:
#include <stdlib.h> |
Each header file contains function prototypes for a set of related functions, and defines any types and macros needed for their use.
To list the header files on OpenVMS Alpha or I64 systems, use the following commands:
$ LIBRARY/LIST SYS$LIBRARY:SYS$STARLET_C.TLB $ LIBRARY/LIST SYS$LIBRARY:DECC$RTLDEF.TLB $ DIR SYS$COMMON:[DECC$LIB.REFERENCE.DECC$RTLDEF]*.H; $ DIR SYS$LIBRARY:*.H; |
The first command lists the text module form of the header files for the OpenVMS system interfaces. The second lists the text module form of the header files for the HP C language interface. The third lists *.H header files for the HP C language interfaces. The fourth lists *.H header files for layered products and other applications.
The SYS$COMMON:[DECC$LIB.REFERENCE.DECC$RTLDEF] directory is only a reference area for your viewing. The compiler still looks in the *.TLB files for #include file searches. |
To list the header files on OpenVMS VAX systems, use the following commands:
$ DIR 'F$TRNLMN("DECC$LIBRARY_INCLUDE")'*.H;
$ DIR DECC$LIBRARY_INCLUDE:*.H;
|
On OpenVMS VAX systems, the following command might also find additional or duplicate header files:
$ DIR SYS$LIBRARY:*.H; |
However, duplicate files (such as <stdio.h> ) found in SYS$LIBRARY probably support the VAX C Version 3.2 environment and should not be used with HP C.
Function definitions themselves are not included in the header files, but are contained in the HP C Run-Time Library (RTL) shipped with the OpenVMS operating system. Before using the HP C RTL, you must be familiar with the following topics:
A knowledge of all these topics is necessary to effectively use the HP C RTL. This chapter shows the connections between these topics and the HP C RTL. Read this chapter before any of the other chapters in this manual.
The primary purpose of the HP C RTL is to provide a means for C programs to perform I/O operations; the C language itself has no facilities for reading and writing information. In addition to I/O support, the HP C RTL also provides a means to perform many other tasks.
Chapters 2 through 11 describe the various tasks supported by the HP C RTL. The Reference Section alphabetically lists and describes all the functions and macros available to perform these tasks.
When working with the HP C RTL, you must be aware of some implementation specifics.
First, if you plan to use HP C RTL functions in your C programs, make sure that a function named main or a function that uses the main_program option exists in your program. For more information, see the HP C Language Reference Manual or the HP C User's Guide for OpenVMS Systems.
Second, the HP C RTL functions are executed at run time, but references to these functions are resolved at link time. When you link your program, the OpenVMS linker resolves all references to HP C RTL functions by searching any shareable code libraries or object code libraries specified on the LINK command line.
You can use the HP C RTL as a shareable image or you can use the HP C RTL object libraries.
When you use the HP C RTL as a shareable image, the code for the RTL resides in an image file in SYS$SHARE and is shared by all HP C programs. After execution, control returns to your program. This process has a number of advantages:
When linking to the HP C RTL, you do not need to define any LNK$LIBRARY logicals. In fact, you should deassign LNK$LIBRARY because linking with the shareable image is more convenient than linking with the HP C RTL object libraries.
See your OpenVMS, HP C, or HP C++ release notes for any supplemental information about linking with the HP C RTL.
The following sections describe several ways of linking HP C and HP C++ programs with the HP C RTL on OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems.
Most linking needs should be satisfied by using the HP C RTL shareable image DECC$SHR.EXE in the ALPHA$LIBRARY (ALPHA ONLY) or IA64$LIBRARY (I64 ONLY) directory.
The shareable images VAXCRTL.EXE and VAXCRTLG.EXE do not exist on OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems. The only C RTL shareable image is ALPHA$LIBRARY:DECC$SHR.EXE (ALPHA ONLY) or IA64$LIBRARY:DECC$SHR.EXE (I64 ONLY) , which the linker automatically finds through IMAGELIB.OLB.
The fact that VAXCRTL*.EXE does not exist on Alpha and I64 systems has the following ramifications:
To link against the shareable image, use the LINK command. For example:
$ LINK PROG1 |
The linker automatically searches IMAGELIB.OLB to find DECC$SHR.EXE, and resolves all C RTL references.
The HP C RTL object libraries on OpenVMS Alpha systems are used solely for linking programs compiled without /PREFIX=ALL. Please note that these object libraries do not exist on OpenVMS I64 systems.
On OpenVMS Alpha systems, the HP C RTL provides the following object libraries in the ALPHA$LIBRARY directory:
The object library VAXCCURSE.OLB, which provides access to the Curses functions, contains unprefixed entry points that vector to the appropriate prefixed entry points.
The object libraries VAXCRTL.OLB, VAXCRTLD.OLB, VAXCRTLT.OLB, VAXCRTLX.OLB, VAXCRTLDX.OLB, and VAXCRTLTX.OLB also contain unprefixed entry points that vector to the appropriate prefixed entry points, depending on the floating-point type specified by the object library used:
/L_DOUBLE_SIZE=128 is the default.
On the LINK command, specify only one of the VAXCRTL*.OLB libraries and, if needed, the VAXCCURSE.OLB library.
In the default mode of the compiler (/STANDARD=RELAXED_ANSI89) and also in strict ANSI C mode, all calls to ANSI C standard library routines are automatically prefixed with DECC$. With the /[NO]PREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES qualifier, you can change this to prefix all HP C RTL names with DECC$, or to not prefix any HP C RTL names. Other options are also available for this qualifer. See the /[NO]PREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES qualifier in this chapter for more information.
When linking with /NOSYSSHR, if calls to the HP C RTL routines are prefixed with DECC$, then the modules in STARLET.OLB are the only ones you need to link against. Since STARLET.OLB is automatically searched by the linker (unless the link qualifier /NOSYSLIB is used), all prefixed RTL external names are automatically resolved.
If any calls to the HP C RTL routines are not prefixed, then you need to explicitly link against VAXCRTL.OLB, VAXCRTLD.OLB, VAXCRTLT.OLB (or VAXCRTLX.OLB, VAXCRTLDX.OLB, or VAXCRTLDX.OLB), or VAXCCURSE.OLB, depending on which floating-point types you need, or if you want Curses functions. If you are linking with /NOSYSSHR, prefixed HP C RTL entry points are resolved in STARLET.OLB. If you are linking with /SYSSHR (the default), prefixed HP C RTL entry points are resolved in DECC$SHR.EXE.
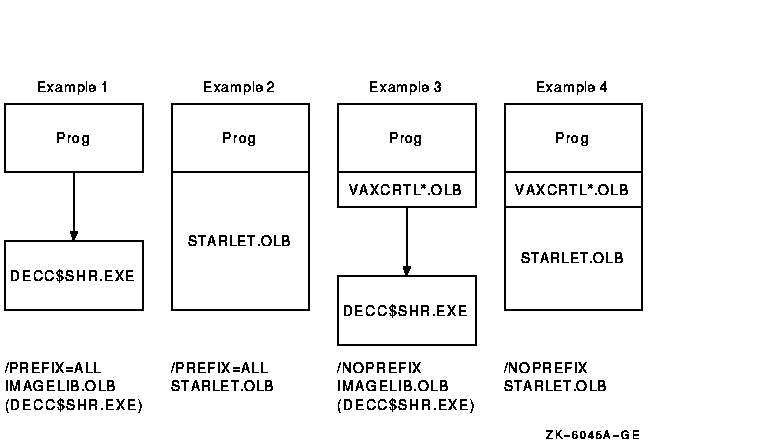
The following examples show several different ways you might want to link with the HP C RTL. See Figure 1-1 for a graphical summary of these examples.
$ CC/PREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES=ALL_ENTRIES PROG1 $ LINK PROG1 |
$ CC/PREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES=ALL_ENTRIES PROG1 $ LINK/NOSYSSHR PROG1 |
|
$ CC/NOPREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES PROG1 $ LINK PROG1, MYLIB/LIBRARY, ALPHA$LIBRARY:VAXCRTLX.OLB/LIBRARY |
$ CC/NOPREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES/FLOAT=IEEE_FLOAT PROG1 $ LINK PROG1, MYLIB/LIBRARY, ALPHA$LIBRARY:VAXCRTLTX.OLB/LIBRARY |
$ CC/NOPREFIX_LIBRARY_ENTRIES PROG1 $ LINK/NOSYSSHR PROG1, MYLIB/LIBRARY, ALPHA$LIBRARY:VAXCRTLX.OLB/LIBRARY |
Figure 1-1 Linking with the HP C RTL on OpenVMS Alpha and I64 Systems
Both the VAX C RTL and the HP C RTL can coexist on your OpenVMS VAX system. The VAX C RTL supports existing VAX C applications. The HP C RTL supports ANSI-compliant HP C and HP C++, as well as other components of the OpenVMS environment. The HP C RTL also provides a mechanism for thread safety and performance improvements.
Applications developed with VAX C will continue to use the VAX C RTL. However, you can relink VAX C applications to use the HP C RTL instead. This lets you take advantage of the new features of the HP C RTL and solve potential interoperability problems in complex applications that incorporate both the VAX C RTL and the HP C RTL. Existing applications that are relinked to use the HP C RTL should be carefully tested for possible problems resulting from the differences in behavior between the VAX C RTL and the HP C RTL. See the applicable HP C release notes and OpenVMS release notes for more information.
The following sections describe several ways of linking HP C programs with the HP C RTL and VAX C RTL on OpenVMS VAX systems.
The HP C RTL provides a new set of files with different names from the VAX C RTL files. If you want to link with the HP C RTL, you need to change your link procedures to use the new file names. The following sections describe linking with the HP C RTL files.
Most linking needs should be satisfied by using the HP C RTL shareable image DECC$SHR.EXE in the SYS$LIBRARY directory. Use this linking method for programs that are written entirely in HP C or HP C++ code; that is, with no VAX C object modules.
Because DECC$SHR.EXE exports only prefixed universal symbols (ones that begin with DECC$), to successfully link against it make sure you cause prefixing to occur for all HP C RTL entry points.
If you use only the HP C RTL functions defined in the ANSI C Standard, all entry points will be prefixed.
If you use HP C RTL functions not defined in the ANSI C Standard, you must compile in one of two ways to ensure prefixing:
Then link against the shareable image using the LINK command. For example:
$ LINK PROG1 |
If you are using the VAX C compiler and you want to link with DECC$SHR.EXE, you must link to one of the following files:
VAXC2DECC.EXE
VAXCG2DECC.EXE
You link with them as follows:
$ LINK PROG1,TT:/OPTIONS SYS$LIBRARY:VAXC2DECC/SHARE [Ctrl/Z] |
Use the G-floating version, VAXCG2DECC.EXE, if you compiled with the /G_FLOAT or /FLOAT=G_FLOAT qualifier.
Most linking needs for an application using a shareable image are handled by a straightforward link command, regardless of whether the shared image uses HP C, VAX C, or some other programming language.
For example, assume that SHARE1.EXE is a shareable image linked with VAXCRTL.EXE. Also assume that your program, PROG1, is compiled with HP C and, therefore, references prefixed names for C RTL functions. You can then use the following commands:
$ LINK PROG1, SYS$INPUT:/OPTIONS MYDISK:[TEXT]SHARE1.EXE/SHARE |
If PROG1 does not use prefixed names, the link could result in link conflicts. If this occurs, see Section 1.3.2.
The HP C RTL object libraries are used primarily for linking with the /NOSYSSHR qualifier.
On OpenVMS VAX systems, the HP C RTL provides the following object libraries in the SYS$LIBRARY directory:
As with VAX C, if you specify more than one object library on the LINK command, you must do so in the order listed.
You use these object libraries in the same way that you would use the VAX C RTL object libraries VAXCRTL.OLB, VAXCRTLG.OLB, and VAXCCURSE.OLB. For example:
$ ! Link a D-float program $ LINK PROG1, SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTL.OLB/LIBRARY $ ! $ ! Link a G-float program $ LINK PROG2, SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTLG.OLB/LIBRARY, - _$ SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTL.OLB/LIBRARY $ ! $ ! Link a D-float, Curses program $ LINK PROG1, SYS$LIBRARY:DECCCURSE.OLB/LIBRARY, - _$ SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTL.OLB/LIBRARY |
If you want to link your program with the HP C RTL object libraries using the /NOSYSSHR qualifier, you must specify /INCLUDE=CMA$TIS for the object library. For OpenVMS VAX Version 7.3 and higher, you must specify /INCLUDE=(CMA$TIS,CMA$TIS_VEC). Otherwise, several symbols will be undefined and the resulting image will not execute.
In order to add this qualifier, you cannot use the LNK$LIBRARY logicals to link with the HP C RTL. You must use a linker options file or list the HP C RTL object library on the command line. For example:
$ LINK/NOSYSSHR PROG1, SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTL.OLB/LIBRARY/INCLUDE=CMA$TIS $ LINK/NOSYSSHR PROG1, SYS$LIBRARY:DECCRTL.OLB - _$ /LIBRARY/INCLUDE=(CMA$TIS,CMA$TIS_VEC) (OPENVMS V7.3 AND HIGHER) |
|
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |