 |
HP OpenVMS Utility Routines Manual
TPU$FILE_SEARCH
The TPU$FILE_SEARCH routine provides a simplified interface to the
$SEARCH system service. DECTPU call this routine when TPU code executes
the FILE_SEARCH built-in procedure.
Format
TPU$FILE_SEARCH result-string ,flags ,filespec ,default-spec
,related-spec
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword condition value. Most utility routines return a condition
value in R0. See Condition Values Returned.
Arguments
result-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Includes the components of the file specification passed by the
flags argument. The memory for the return string is
allocated via the Run-Time Library routine LIB$SGET1_DD. To deallocate
memory for the string, use the Run-Time Library routine LIB$SFREE1_DD.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Determines what file specification components should be returned. The
following table lists the valid flag values:
| Flag1 |
Function |
|
TPU$M_NODE
|
Returns the node component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_DEV
|
Returns the device component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_DIR
|
Returns the directory component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_NAME
|
Returns the name component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_TYPE
|
Returns the type component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_VER
|
Returns the version component of the file specification.
|
|
TPU$M_REPARSE
|
Reparses the file specification before processing. This is intended to
be used to reset the file search.
|
|
TPU$M_HEAD
|
Returns NODE, DEVICE, and DIRECTORY components of the file
specification. If the TPU$M_NODE, TPU$M_DEV or TPU$M_DIR bits are set
while TPU$M_HEAD is set, the routine will signal the error
TPU$_INCKWDCOM and return.
|
|
TPU$M_TAIL
|
Returns NAME, TYPE and VERSION components of the file specification. If
the TPU$M_NAME, TPU$M_TYPE or TPU$M_VER bits are set while TPU$M_TAIL
is set, the routine will signal the error TPU$_INCKWDCOM and return.
|
1TPU$M... indicates a mask. There is a corresponding value
for each mask in the form TPU$V....
filespec
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Object file specification.
default-spec
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
The default file specification. The default file specification fields
are used to fill in the result-string when fields are
omitted in the filespec argument. Use the
related-spec argument to specify other substitutions.
Use the value 0 when no default-spec is to be applied
to the file specification.
related-spec
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Contains the related file specification. The fields in the related file
specification are used in the result-string for fields
omitted in the filespec and
default-spec arguments.
Use the value 0 when no default-spec is to be applied
to the file specification.
Description
This routine allows an application to verify the existence of, and
return components of, a file specification. Wildcard operations are
permitted. The routine uses the $PARSE and $SEARCH system services to
seek the file specification.
If no wildcards are included in the file specification string and the
result-string returns a zero (0) length string, no
file was found. If wildcard characters were present in the file
specification and the result-string returns a zero (0)
length string, there are no more files that match the wildcards.
To find all the files that match a wildcard specification, repeatedly
call this routine, passing the same arguments, until the routine
returns a zero-length result string.
The TPU$FILE_SEARCH routine is called by DECTPU when the TPU built-in
procedure FILE_SEARCH is executed from TPU code. The return value of
the built-in procedure is the string returned in the
result-string argument.
Condition Values Returned
|
TPU$_SUCCESS
|
Normal successful completion. If the return string contains a null
string, the final match operation was detected.
|
|
TPU$_INCKWDCOM
|
The
flags argument had an illegal combination of values.
|
|
TPU$_PARSEFAIL
|
The requested repeat parse failed.
|
|
TPU$_SEARCHFAIL
|
An error occurred during the search operation.
|
TPU$HANDLER
The TPU$HANDLER routine is the DECTPU condition handler.
The DECTPU condition handler invokes the $PUTMSG system service,
passing it the address of TPU$MESSAGE.
Format
TPU$HANDLER signal_vector ,mechanism_vector
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword condition value. Most utility routines return a condition
value in R0. See Condition Values Returned.
Arguments
signal_vector
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Signal vector. See the HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual for information about the signal
vector passed to a condition handler.
mechanism_vector
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Mechanism vector. See the HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual for information about the
mechanism vector passed to a condition handler.
Description
The TPU$MESSAGE routine performs the actual output of the message. The
$PUTMSG system service only formats the message. It gets the settings
for the message flags and facility name from the variables described in
Section 8.1.2. Those values can be modified only by the DECTPU built-in
procedure SET.
If the condition value received by the handler has a FATAL status or
does not have the DECTPU facility code, the condition is resignaled.
If the condition is TPU$_QUITTING, TPU$_EXITING, or TPU$_RECOVERFAIL, a
request to UNWIND is made to the establisher of the condition handler.
After handling the message, the condition handler returns with a
continue status. DECTPU error message requests are made by signaling a
condition to indicate which message should be written out. The
arguments in the signal array are a correctly formatted message
argument vector. This vector sometimes contains multiple conditions and
formatted ASCII output (FAO) arguments for the associated messages. For
example, if the editor attempts to open a file that does not exist, the
DECTPU message TPU$_NOFILEACCESS is signaled. The FAO argument to this
message is a string for the name of the file. This condition has an
error status, followed by the OpenVMS RMS status field (STS) and status
value field (STV). Because this condition does not have a fatal
severity, the editor continues after handling the error.
The editor does not automatically return from TPU$CONTROL. If you call
the TPU$CONTROL routine, you must explicitly establish a way to regain
control (for example, using the built-in procedure CALL_USER). If you
establish your own condition handler but call the DECTPU handler for
certain conditions, the default condition handler must be
established at the point in your program where you want to return
control.
You can also interrupt TPU$CONTROL by having your program specify and
then trigger an asynchronous routine via the TPU$SPECIFY_ASNYC_ACTION
and TPU$TRIGGER_ASYNC_ACTION routines.
See the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard for details on writing a condition handler.
TPU$INITIALIZE
The TPU$INITIALIZE routine initializes DECTPU for text processing. This
routine allocates global data structures, initializes global variables,
and calls the appropriate setup routines for each of the major
components of the editor, including the Screen Manager and the I/O
subsystem.
Format
TPU$INITIALIZE callback [,user_arg]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword condition value. Most utility routines return a condition
value in R0. Condition values that this routine can return are listed
under Condition Values Returned.
Argument
callback
| OpenVMS usage: |
vector_longword_unsigned |
| type: |
bound procedure value |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Callback routine. The callback argument is the address
of a user-written routine that returns the address of an item list
containing initialization parameters or a routine for handling file I/O
operations. This callback routine must call a command line parsing
routine, which can be TPU$CLIPARSE or a user-written parsing routine.
Callable DECTPU defines item codes that you can use to specify
initialization parameters. The following rules must be followed when
building the item list:
- If you use the TPU$_OTHER_FILENAMES item code, it must follow the
TPU$_FILENAME item code.
- If you use either the TPU$_CHAIN item code or the TPU$_ENDLIST
code, it must be the last item code in the list.
The following figure shows the general format of an item descriptor.
For information about how to build an item list, refer to the
programmer's manual associated with the language you are using. Any
reference to command line qualifiers refer to those command line
qualifiers that you use with the EDIT/TPU command.
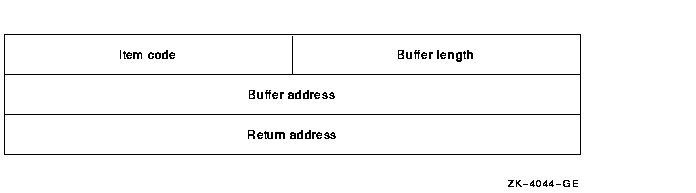
The return address in an item descriptor is usually 0.
The following item codes are available:
| Item Code |
Description |
|
TPU$_OPTIONS
|
Enables the command qualifiers. The bits in the bit mask specified by
the buffer address field correspond to the various DECTPU command
qualifiers.
|
|
TPU$_JOURNALFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /JOURNAL qualifier. The buffer
length field is the length of the string, and the buffer address field
is the address of the string. This string is available with GET_INFO
(COMMAND_LINE,"JOURNAL_FILE"). This string can be a null
string.
|
|
TPU$_SECTIONFILE
|
Passes the string that is the name of the binary initialization file
(section file) to be mapped in. The buffer length field is the length
of the string, and the buffer address field is the address of the
string. If the TPU$V_SECTION bit is set, this item code must be
specified.
|
|
TPU$_OUTPUTFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /OUTPUT qualifier. The buffer
length field is the length of the string, and the buffer address field
specifies the address of the string. This string is returned by the
built-in procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE, "OUTPUT_FILE").
The string can be a null string.
|
|
TPU$_DISPLAYFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /DISPLAY qualifier. The buffer
length field defines the length of the string, and the buffer address
field defines the string address. The interface between the TPUSHR
image and the display file image is not documented. Applications should
only use this option with documented display files such as TPU$CCTSHR
or TPU$MOTIFSHR.
|
|
TPU$_COMMANDFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /COMMAND qualifier. The buffer
length field is the length of the string, and the buffer address field
is the address of the string. This string is returned by the built-in
procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE, "COMMAND_FILE"). The string
can be a null string.
|
|
TPU$_FILENAME
|
Passes the string that is the name of the first input file specified on
the command line. The buffer length field specifies the length of this
string, and the buffer address field specifies its address. This string
is returned by the built-in procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,
"FIRST_FILE_NAME"). This file name can be a null string.
|
|
TPU$_OTHER_FILENAMES
|
Passes a string that contains the name of an input file that follows
the first input file on the command line. The buffer length field
specifies the length of this string, and the buffer address field
specifies its address. Each additional file specified on the command
line requires its own TPU$_OTHER_FILENAMES item entry. These strings
are returned by the GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,"NEXT_FILE_NAME")
built-in procedure in the order they appear in the item list. This item
code must appear after the TPU$_FILENAME item in the item list.
|
|
TPU$_FILEIO
|
Passes the bound procedure value of a routine to be used for handling
file operations. You can provide your own file I/O routine, or you can
call TPU$FILEIO, the utility routine provided by DECTPU for handling
file operations. The buffer address field specifies the address of a
two-longword vector. The first longword of the vector contains the
address of the routine. The second longword specifies the environment
value that DECTPU loads into R1 before calling the routine.
|
|
TPU$_CALLUSER
|
Passes the bound procedure value of the user-written routine that the
built-in procedure CALL_USER is to call. The buffer address field
specifies the address of a two-longword vector. The first longword of
the vector contains the address of the routine. The second longword
specifies the environment value that DECTPU loads into R1 before
calling the routine.
|
|
TPU$_INIT_FILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /INITIALIZATION qualifier. The
buffer length field is the length of the string, and the buffer address
field is the address of the string. This string is returned by the
built-in procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,"INIT_FILE").
|
|
TPU$_START_LINE
|
Passes the starting line number for the edit. The buffer address field
contains the first of the two integer values you specified as part of
the /START_POSITION command qualifier. The value is available using the
built-in procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,"LINE"). Usually an
initialization procedure uses this information to set the starting
position in the main editing buffer. The first line in the buffer is
line 1.
|
|
TPU$_START_CHAR
|
Passes the starting column position for the edit. The buffer address
field contains the second of the two integer values you specified as
part of the /START_POSITION command qualifier. The value is available
using the built-in procedure GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,
"CHARACTER"). Usually an initialization procedure uses this
information to set the starting position in the main editing buffer.
The first column on a line to character 1.
|
|
TPU$_CHARACTERSET
|
Passes the string specified with the /CHARACTER_SET qualifier. The
buffer length field specifies the string length and the buffer address
field specifies the string address. Valid strings are
"DEC_MCS" (the default value), "ISO_LATIN1", and
"GENERAL". If the application tries to pass any other string,
the routine signals an error and passes the default string (DEC_MCS).
|
|
TPU$_WORKFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /WORK qualifier. The buffer length
field specifies the string length and the buffer address specifies the
string address. This string is available with GET_INFO (COMMAND_LINE,
"WORK_FILE").
|
|
TPU$_CHAIN
|
Passes the address of the next item list to the process specified by
the buffer address field.
|
|
TPU$_ENDLIST
|
Signals the end of the item list.
|
|
TPU$_PARENT_WIDGET
|
Passes the appropriate parent widget when invoking the DECwindows
version of the editor. This routine is not specified by the
application; DECTPU invokes its own application shell. The widget
address is passed in the buffer address field. This item code is only
valid when using the DECwindows interface.
|
|
TPU$_APPLICATION_CONTEXT
|
Passes the application context to use with the TPU$_PARENT_WIDGET.
DECTPU defaults to its own application context. The buffer address
field specifies the application context address. This item code is only
valid when using the DECwindows interface.
|
|
TPU$_DEFAULTSFILE
|
Specifies which file DECTPU uses to initialize the X defaults database.
The buffer length field specifies the string length and the buffer
address field specifies the string address. This item code is only
valid when using the DECwindows interface.
|
|
TPU$_CTRL_C_ROUTINE
|
Passes the bound procedure value of a routine to be used for handling
Ctrl/C asynchronous system traps (ASTs). DECTPU calls the routine when
a Ctrl/C AST occurs. If the routine returns a FALSE value, DECTPU
assumes that the Ctrl/C has been handled. If the routine returns a TRUE
value, DECTPU aborts any currently executing DECTPU procedure. The
buffer address field specifies the address of a two-longword vector.
The first longword of the vector contains the address of the routine.
The second longword specifies the environment value that DECTPU loads
into R1 before calling the routine.
|
|
TPU$_DEBUGFILE
|
Passes the string specified with the /DEBUG command qualifier. The
buffer length field is the length of the string, and the buffer address
field is the address of the string.
|
|
TPU$_FILE_SEARCH
|
Passes the bound procedure value of a routine to be used to replace the
TPU$FILE_SEARCH routine which is called when the built-in procedure
FILE_SEARCH is called from TPU code. See the description of the
TPU$FILE_SEARCH and the user routine FILE_SEARCH for more information.
|
|
TPU$_FILE_PARSE
|
Passes the bound procedure value of a routine to be used to replace the
TPU$FILE_PARSE routine which is called when the built-in procedure
FILE_PARSE is called from TPU code. See the description of the
TPU$FILE_PARSE and the user routine FILE_PARSE for more information.
|
Table 8-1 lists the bits and corresponding masks enabled by the
item code TPU$K_OPTIONS and shows how each bit affects TPU$INITIALIZE
operation. Several bits in the TPU$_OPTIONS mask require additional
item code entries in the item list. An example of this is TPU$M_COMMAND
which requires a TPU$_COMMANDFILE entry in the item list.
Table 8-1 Valid Masks for the TPU$K_OPTIONS Item Code
| Mask1 |
GET_INFO
Request String2 |
Description |
|
TPU$M_COMMAND
|
COMMAND
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_COMMANDFILE item, it tries to
read, compile and execute the unbound TPU code.
|
|
TPU$M_COMMAND_DFLTED
|
Not applicable
|
Specifies that DECTPU should use the default command file name of
TPU$COMMAND.TPU when reading in the command file. No error is reported
if the default command file is not found. TPU$INITIALIZE fails when the
TPU$M_COMMAND_DFLTED bit is set to 0 and no file is specified in the
item list.
|
|
TPU$M_CREATE
|
CREATE
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_DEBUG
|
Not applicable
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_DEBUGFILE item, it tries to
read the file, and then proceeds to compile and execute its contents as
TPU statements.
|
|
TPU$M_DEFAULTS
|
Not applicable
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_DEFAULTSFILE item, it uses
the specified DECwindows X resource file to initialize the DECwindows X
resource database.
|
|
TPU$M_DISPLAY
|
DISPLAY
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_DISPLAYFILE item, it tries to
image activate the specified image as its screen manager. When the bit
is 0, DECTPU uses SYS$OUTPUT for display and only the READ_LINE
built-in procedure may be used for input.
|
|
TPU$M_INIT
|
INITIALIZATION
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_INIT_FILE item, it returns
the specified string through the built-in procedure GET_INFO
(COMMAND_LINE, "INITIALIZATION_FILE"). Processing of the
initialization file is left to the application.
|
|
TPU$M_JOURNAL
|
JOURNAL
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_JOURNALFILE item, it outputs
the keystrokes entered during the editing session to the specified file.
Note: HP recommends the use of buffer change
journaling in new applications.
|
|
TPU$M_MODIFY
|
MODIFY
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_NODEFAULTS
|
Not applicable
|
DECTPU initializes the DECwindows X resource database only with
resource files that the DECwindows toolkit routine
XtApplInitialize loads into the database.
|
|
TPU$M_NOMODIFY
|
NOMODIFY
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_OUTPUT
|
OUTPUT
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_READ
|
READ_ONLY
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_RECOVER
|
RECOVER
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
|
TPU$M_SECTION
|
SECTION
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_SECTIONFILE item, it tries to
read the specified file as a binary initialization file. TPU$INITIALIZE
fails if this bit is set to 1 and the TPU$_SECTIONFILE item is not
present in the item list.
|
|
TPU$M_SEC_LNM_MODE
|
Not applicable
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$M_SEC_LNM_MODE item, it looks
only at executive mode logical names when attempting to read in a
section file.
|
|
TPU$M_WORK
|
WORK
|
If DECTPU senses the presence of the TPU$_WORKFILE item, it uses the
specifed file for memory management. If no item list entry is present,
and this bit is set to 1, a file is created in SYS$LOGIN:.TPU$WORK.
|
|
TPU$M_WRITE
|
WRITE
|
The behavior of DECTPU is not affected by this bit. Its interpretation
is left to the application layered on DECTPU.
|
1The prefix can be TPU$M_ or TPU$V_. TPU$M_ denotes a mask
corresponding to the specific field in which the bit is set. TPU$V_ is
a bit number.
2Most bits in the mask have a corresponding GET_INFO
(COMMAND_LINE) request string.
|
