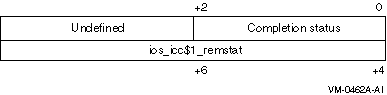|
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$ICC_CONNECT
Establishes a connection to a remote application over an open
association.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECT ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,assoc_handle ,conn_handle
,remote_assoc ,[remote_node] ,[user_context] ,[conn_buf]
,[conn_buf_len] ,[return_buf] ,[return_buf_len] ,[retlen_addr] ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_connect (struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle,
unsigned int *conn_handle, void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node,
unsigned int user_context, char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len,
char *return_buf, unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int
*retlen_addr, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
I/O status block:
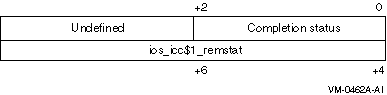
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_BUFFEROVF, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_IVBUFLEN,
SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON, SS$_NOLOGNAM, SS$_NOSUCHOBJ,
SS$_NOSUCHNODE, SS$_PATHLOST, SS$_REJECT, SS$_SSFAIL, SS$_UNREACHABLE,
SS$_WRONGSTATE
The second longword is undefined unless the completion code is
SS$_REJECT. In this case, the application-defined rejection reason code
is supplied by the server when $ICC_REJECT is called.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
assoc_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
association_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the association on which the connection is to be opened.
The constant ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE, if used, indicates that the
default association is to be used (and opened if necessary).
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of
a longword into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the connection handle of the
created connection on a successful call.
remote_assoc
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
An ASCII character string (31 characters maximum) specifying the name
of the target application to connect to. Association names are case
sensitive.
remote_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The name of the node where the target association resides. A null or
blank string can be used to indicate the local node. If omitted (by
passing zero by value), the simple clusterwide association registry is
to be used. Each node name is a one-to-six character SCS node name. A
comma-delimited list of nodes may be specified, indicating that one is
to be chosen at random.
user_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A user-specified value to be subsequently returned on any disconnect or
data events on this connection.
conn_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of connection data to be sent to the
target of the connection during the connection process.
conn_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes in conn_buf to be sent.
return_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes in length to receive any incoming
connection accept or reject data returned.
return_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length of the supplied return_buf.
retlen_addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems) of
a longword into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the actual length (in bytes)
of any user accept or reject data returned in the buffer
return_buf.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
ICC$M_SYNCH_MODE can be specified to indicate that the data
transmission and reception routines $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_RECEIVE, and
$ICC_REPLY are allowed to return the status SS$_SYNCH in the case of
synchronous completion, indicating that the AST will not be called.
Description
This service establishes a connection to a remote application over an
open association. Connections must be opened in the same mode as their
association. If the user provides the default association constant
ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE as its association handle, the default
association will be used; it will be opened if it is not already open.
Multiple connections are possible over a single association. When
completion is signaled by the AST routine, the application must check
the completion status field of the IOS_ICC to determine if the server
has accepted or rejected the connection request. The number of
connections is subject to process BYTLM quota.
At image exit, as a result of closing any open user mode associations,
all user mode connections are disconnected. Inner mode connections are
the responsibility of the inner mode code, but are disconnected at
process termination when inner mode associations are closed.
Connections are only visible to the mode in which they were opened.
A client opens connections with the $ICC_CONNECT service; a server
opens connections with the $ICC_ACCEPT service.
Required Access or Privileges
SYSNAM, or access via ICC Security Object. For more information, see
the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
Required Quota
$ICC_CONNECT changes the process BYTLM quota for the length of the
conn_buf parameter, as well as a fixed value for each
potential Receive buffer on the connection. The number of potential
Receive buffers is specified by the MAXFLOWBUFCNT parameter in the
$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
If $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC is not called before $ICC_CONNECT, the default value
of MAXFLOWBUFCNT is used (currently 5).
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
Overflow on inbound accept or reject data.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
Not enough AST quota (asynchronous request) or insufficient
BYTLM/BYTCNT.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments were supplied, or required arguments not supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
|
|
SS$_INSFP1POOL
|
Not enough process P1 space available.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The length of the context data or the accept or reject data buffer is
more than 1000 bytes.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Invalid association handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to open a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the requested association.
|
|
SS$_LINKABORT
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_NOLINKS
|
Too many connections open.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGNAM
|
The underlying layers failed to start properly during system
initialization.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
No privilege to connect to the specified association. Connection access
is granted either through an ICC security object or through the SYSNAM
privilege. If no security object exists and the caller lacks the SYSNAM
privilege, SS$_NOPRIV is returned rather than SS$_NOSUCHOBJ.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
The remote association name and/or node was not found.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The target node is not known.
|
|
SS$_PATHLOST
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
Insufficient resources at remote node.
|
|
SS$_REJECT
|
The remote association or node rejected the connection request.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
Target node currently unreachable.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_CONNECTW
Establishes a link between two ICC associations.
The $ICC_CONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns
to the caller after the server has either accepted or rejected the
connection request.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_CONNECT service; $ICC_CONNECT
returns to the caller as soon as the connection request has been sent
to the server, without waiting for a response from the server.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECTW ios_icc, [astadr], [astprm], assoc_handle,
conn_handle, remote_assoc, [remote_node], [user_context], [conn_buf],
[conn_buf_len], [return_buf], [return_buf_len], [retlen_addr], [flags]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_connectw (struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle,
unsigned int *conn_handle, void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node,
unsigned int user_context, char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len,
char *return_buf, unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int
*retlen_addr, unsigned int flags);
$ICC_DISCONNECT
Terminates the specified connection.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECT conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf]
,[disc_buf_len]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnect (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The ID of the connection to be disconnected.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
I/O status block:
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_LINKDISCON, $ICC_REJECT
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
disc_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of disconnect data to be sent to the
partner in the connection when notifying it that disconnection is being
initiated. Delivery of this data is not guaranteed.
disc_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes in disc_buf to be sent.
Description
This service must be called in the mode in which the association was
opened.
This service terminates the specified connection. After this service is
called, no further communication is possible over this connection. All
outstanding data transmission and reception functions are terminated
with an error before completion is signaled by calling the AST (if
supplied).
A connection may be disconnected by either party. Proper programming
procedure for network communications strongly recommends that the party
that last received a message initiate the disconnection. If the party
that last sent a message initiates the disconnection, there is no
guarantee that the message was delivered.
Similarly, although this interface provides the ability to send
disconnect data, only noncritical information should be transmitted
with the disconnect data mechanism, because there is no guarantee that
the data will have been received or acted upon by the other party to
the connection.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM (disc_buf)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal successful completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough nonpaged pool.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The length of the disconnect data buffer is more than 1000 bytes.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to disconnect a connection from a more privileged access mode
than the requested connection.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The remote association closed the connection before it was accepted or
rejected.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
$ICC_DISCONNECTW
Terminates a link between two ICC associations.
The $ICC_DISCONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it
returns to the caller after the connection has completely finished the
disconnection request.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_DISCONNECT service;
$ICC_DISCONNECT returns to the caller as soon as the disconnection
request has been sent to the transport layer, without waiting for
notification that the disconnection has completed.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECTW conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf]
,[disc_buf_len]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnectw (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);
$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC
Declares an application association with ICC.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC assoc_handle ,[assoc_name] ,[logical_name]
,[logical_table] ,[conn_event_rtn] ,[disc_event_rtn] ,[recv_rtn]
,[maxflowbufcnt] ,[prot]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_open_assoc (unsigned int *assoc_handle, void *assoc_name,
void *logical_name, void *logical_table, void
(*conn_event_rtn)(__unknown_params), void
(*disc_event_rtn)(__unknown_params), void
(*recv_rtn)(__unknown_params), unsigned int maxflowbufcnt, unsigned int
prot);
Arguments
assoc_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
association_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha and Integrity server systems)
into which $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC writes the handle assigned to the opened
association.
assoc_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
An ASCII character string of up to 31 characters in length specifying
the name of the application opening the association. Null (0 length),
and empty or blank association names are not allowed. If this argument
is omitted (that is, a zero is passed in by value), it signifies that
the user wants to open the default association. This argument is case
sensitive.
logical_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
A logical name in a clusterwide logical name table used to maintain the
simple association registry. The logical name represents the name of
the service provided by the application. Logical names are case
sensitive.
logical_table
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical name table |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The table containing the logical name logical_name.
Logical name tables are converted to uppercase. Unless your application
requires an application-specific logical name table, this argument
should be either the default ICC Registry search list (ICC$REGISTRY),
or the default registry table (ICC$REGISTRY_TABLE).
conn_event_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming connect
events. This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No
mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different mode).
You must have a conn_event_rtn to operate as a server.
disc_event_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming disconnect
events. This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No
mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different
mode). The arguments, conn_event_rtn, and
disc_event_rtn, may reference the same routine.
recv_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming new data
events.
If the user provides this routine, it indicates that the user will
supply a buffer of the size required (specified in an argument to the
recv_rtn at each call) each time one is requested. If
the user supplies this routine, receive calls should only be issued
after receive events arrive and sufficient buffer space has been
allocated to handle the incoming data.
|