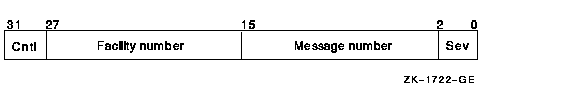|
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
If you do not specify facnam, $PUTMSG uses the default
facility prefix associated with the message.
actprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Parameter to be passed to the action routine. The
actprm argument is a longword value containing this
parameter. If you do not specify actprm, no parameter
is passed.
Description
In the operating system, a message is identified by a longword value,
which is called the message code. To construct a message code, you
specify values for its four fields, using the Message utility. The
following diagram depicts the longword message code:
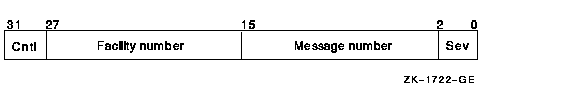
Thus, each message has a unique longword value associated with it: its
message code. You can give this longword value a symbolic name using
the Message utility. Such a symbolic name is called the message symbol.
The Message utility describes how to construct a message symbol
according to the conventions for operating system messages. Basically,
the message symbol has two parts: (1) a facility prefix, which is an
abbreviation of the name of the facility with which the message is
associated, and (2) a mnemonic name for the message text, which serves
to hint at the nature of the message. These two parts are separated by
an underscore character (_) in the case of a user-constructed message
and by a dollar sign/underscore ($_) in the case of system messages.
The message components written by $PUTMSG are derived both from the
message code and from the message symbol. For additional information
about both the message code and the message symbol, see the
HP OpenVMS Command Definition, Librarian, and Message Utilities Manual.
The $PUTMSG service writes the message components in the following
format:
%FACILITY-L-IDENT, message text
|
where:
|
%
|
Is the prefix used for the first message written. The hyphen (-) is the
prefix used for the remaining messages.
|
|
FACILITY
|
Is the facility prefix taken from the message symbol. This facility
prefix can be overridden by a facility prefix specified in the
facnam argument in the call to $PUTMSG.
|
|
L
|
Is the severity level indicator. The severity level indicator is taken
from the message code.
|
|
IDENT
|
Is a mnemonic name for the message text, taken from the message symbol.
|
|
message text
|
Is the message text specified in the message source file.
|
The $PUTMSG service does not check the length of the argument list and
therefore cannot return the SS$_INSFARG (insufficient arguments)
condition value. Be sure you specify the required number of arguments.
If an error occurs while $PUTMSG calls the Formatted ASCII Output
($FAO) service, $FAO parameters specified in the message vector do not
appear in the output.
You cannot call the $PUTMSG service from kernel mode.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
Example
|
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <rmsdef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
main()
{
int msgvec[] = {3, /* Arg count and message flags */
SS$_ABORT, /* Message code */
RMS$_FNF, /* RMS Message code */
0}; /* RMS Status value */
return (sys$putmsg(msgvec)); /* Generate message */
}
|
$QIO
Queues an I/O request to a channel associated with a device. This
service completes asynchronously; for synchronous completion, use the
Queue I/O Request and Wait ($QIOW) service.
For additional information about system service completion, see the
Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$QIO [efn] ,chan ,func ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[p1] ,[p2] ,[p3]
,[p4] ,[p5] ,[p6]
C Prototype
int sys$qio (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int
func, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64
astprm, void *p1, __int64 p2, __int64 p3, __int64 p4, __int64 p5,
__int64 p6);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event flag that $QIO is to set when the I/O operation completes. The
efn argument is a longword value containing the number
of the event flag; however, $QIO uses only the low-order byte.
If you do not specify efn, event flag 0 is used.
When $QIO begins execution, it clears the specified event flag or event
flag 0 if efn was not specified.
The specified event flag is set if the service terminates without
queuing an I/O request.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
I/O channel assigned to the device to which the request is directed.
The chan argument is a word value containing the
number of the I/O channel; however, $QIO uses only the low-order word.
Specifying an invalid value for the chan argument will
result in either SS$_IVCHAN or SS$_IVIDENT being returned.
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Device-specific function codes and function modifiers specifying the
operation to be performed. The func argument is a
longword containing the function code.
Each device has its own function codes and function modifiers. For
complete information about the function codes and function modifiers
that apply to the particular device to which the I/O operation is to be
directed, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status of the I/O
operation. The iosb argument is the address of the
quadword I/O status block. The following diagram depicts the structure
of the I/O status block.

The following table defines the I/O status block fields.
| Status Block Field |
Definition |
|
Condition value
|
Word-length condition value that $QIO returns when the I/O operation
actually completes.
|
|
Transfer count
|
Number of bytes of data transferred in the I/O operation. For
information about how specific devices handle this field of the I/O
status block, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
|
|
Device-specific information
|
Contents of this field vary depending on the specific device and on the
specified function code. For information on how specific devices handle
this field of the I/O status block, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
|
When $QIO begins execution, it clears the quadword I/O status block if
the iosb argument is specified.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $QIO service. The condition value returned in R0 gives
you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$QIO, you must first check the condition value returned in R0. If R0
contains a successful value, then you must check the condition value in
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
AST service routine to be executed when the I/O completes. The
astadr argument is the address of the AST routine.
The AST routine executes at the access mode of the caller of $QIO.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword unsigned (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine. On Alpha and
Integrity server systems, the astprm argument is a
quadword value containing the AST parameter.
p1 to p6
| OpenVMS usage: |
varying_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference or by 64-bit value, depending on
the I/O function (Alpha and Integrity servers) |
Optional device-specific and function-specific I/O request parameters.
For example, the p1 parameter usually specifies a
buffer by reference. Other parameters, such as the buffer size, disk
block number, or carriage control are often passed by value.
For more information about these parameters, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
Description
The Queue I/O Request service operates only on assigned I/O channels
and only from access modes that are equal to or more privileged than
the access mode from which the original channel assignment was made.
The $QIO service uses system dynamic memory to construct a database to
queue the I/O request and might require additional memory depending on
the queued device.
For $QIO, you can synchronize completion (1) by specifying the
astadr argument to have an AST routine execute when
the I/O completes or (2) by calling the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service to
await completion of the I/O operation. The $QIOW service completes
synchronously, and it is the best choice when synchronous completion is
required.
For information about how to use the $QIO service for network
operations, see the DECnet for OpenVMS Networking Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
LOG_IO or PHY_IO is required, depending upon the device type and the
requested operation. DIAGNOSE is required to issue a $QIO with an
associated diagnostic buffer. In addition, read or write access is
generally required for the device. For more information, see the
HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Required Quota
The $QIO service uses the following quotas:
- The process's quota for buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) or direct I/O
limit (DIOLM)
- The process's buffered I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota
- The process's AST limit (ASTLM) quota, if an AST service routine is
specified
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $IO_CLEANUP, $IO_PERFORM, $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The I/O request was successfully
queued.
|
|
SS$_ABORT
|
A network logical link was broken.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Either the I/O status block cannot be written by the caller, or the
parameters for device-dependent function codes are specified
incorrectly.
|
|
SS$_CONNECFAIL
|
The connection to a network object timed out or failed.
|
|
SS$_DEVOFFLINE
|
The specified device is off line and not currently available for use.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has (1) exceeded its AST limit (ASTLM) quota, (2) exceeded
its buffered I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota, (3) exceeded its buffered
I/O limit (BIOLM) quota, (4) exceeded its direct I/O limit (DIOLM)
quota, or (5) requested a buffered I/O transfer smaller than the
buffered byte count quota limit (BYTLM), but when added to other
current buffer requests, the buffered I/O byte count quota was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_FILALRACC
|
A logical link is already accessed on the channel (that is, a previous
connect on the channel).
|
|
SS$_FILEFULL
|
File full; allocation failure. An attempt to extend a file will exceed
the maximum supported size of the file. For ODS-2 and ODS-5 disks, this
is 2 TB (4,294,967,295 blocks). Reduce the size of the extend request.
If the difference between the maximum file size and the current file is
less than the cluster size, the file cannot be extended.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_INVLOGIN
|
The access control information was invalid at the remote node.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of
0, or you failed to specify a channel number.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
You specified a channel number greater than the number of channels
assigned for the process.
|
|
SS$_IVDEVNAM
|
The NCB has an invalid format or content.
|
|
SS$_LINKABORT
|
The network partner task aborted the logical link.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The network partner task disconnected the logical link.
|
|
SS$_LINKEXIT
|
The network partner task was started, but exited before confirming the
logical link (that is, $ASSIGN to SYS$NET).
|
|
SS$_NOLINKS
|
No logical links are available. The maximum number of logical links as
set for the executor MAXIMUM LINKS parameter was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel does not exist or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode, or the process does not have the necessary
privileges to perform the specified functions on the device associated
with the specified channel.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The specified node is unknown.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
The network object number is unknown at the remote node; or for a TASK=
connect, the named DCL command procedure file cannot be found at the
remote node.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHUSER
|
The remote node could not recognize the login information supplied with
the connection request.
|
|
SS$_NOT64DEVFUNC
|
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this fatal condition value is
returned under the following circumstances: (1) The caller has
specified a 64-bit virtual address in the P1 device dependent parameter
but the device driver does not support 64-bit addresses with the
requested I/O function. (2) The caller has specified a 64-bit address
for a diagnostic buffer but the device driver does not support 64-bit
addresses for diagnostic buffers. (3) Some device drivers might also
return this condition value when 64-bit buffer addresses are passed
using the P2 through P6 parameters and the driver does not support a
64-bit address with the requested I/O function.
|
|
SS$_PATHLOST
|
The path to the network partner task node was lost.
|
|
SS$_PROTOCOL
|
A network protocol error occurred. This error is most likely due to a
network software error.
|
|
SS$_REJECT
|
The network object rejected the connection.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The link could not be established because system resources at the
remote node were insufficient.
|
|
SS$_SHUT
|
The local or remote node is no longer accepting connections.
|
|
SS$_THIRDPARTY
|
The logical link was terminated by a third party (for example, the
system manager).
|
|
SS$_TOOMUCHDATA
|
The task specified too much optional or interrupt data.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is currently unreachable.
|
|
SS$_UNSUPPORTED
|
Unsupported operation or function. An attempt has been made to create a
contiguous file with a size greater than the supported maximum. For
ODS-2 and ODS-5 disks, this value is 1,073,741,824 blocks. Reduce the
size of the request when creating such a file.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
Device-specific condition values; the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these
condition values for each device.
$QIOW
The Queue I/O Request and Wait service queues an I/O request to a
channel associated with a device.
The $QIOW service completes synchronously; however, Digital recommends
that you use an IOSB with this service to avoid premature completion.
For asynchronous completion, use the Queue I/O Request ($QIO) service.
In all other respects, $QIOW is identical to $QIO. For more information
about $QIOW, refer to the description of $QIO.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$QIOW [efn] ,chan ,func ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[p1] ,[p2]
,[p3] ,[p4] ,[p5] ,[p6]
C Prototype
int sys$qiow (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int
func, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64
astprm, void *p1, __int64 p2, __int64 p3, __int64 p4, __int64 p5,
__int64 p6);
$READ
The Read service retrieves a specified number of bytes from a file
(beginning on a block boundary) and transfers them to memory. A Read
service using block I/O can be performed on any file organization.
For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$READEF
Returns the current status of all 32 event flags in a local or common
event flag cluster and indicates whether the specified event flag is
set or clear.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$READEF efn ,state
C Prototype
int sys$readef (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *state);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of any event flag in the cluster whose status is to be returned.
The efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $READEF uses only the low-order byte. Specifying an event flag
within a cluster requests that $READEF return the status of all event
flags in that cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters, which are local to the
process: cluster 0 and cluster 1. Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers
0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3.
Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains
event flag numbers 96 to 127.
state
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and Integrity
servers) |
State of all event flags in the specified cluster. The
state argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
and Integrity server systems) of a longword into which $READEF writes
the state (set or clear) of the 32 event flags in the cluster.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag is clear.
Note that this is also the same value as SS$_NORMAL.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag is set.
Note that while the message id is the same as SS$_ACCVIO, the severity
bits are different.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The longword that is to receive the current state of all event flags in
the cluster cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
|