 |
HP OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual
SHOW LOCKS
Displays information about all lock management locks in the system, or
about a specified lock.
Format
SHOW LOCKS [ lock-id
| /ADDRESS=n
| /ALL (d)
|
/BRIEF
| /BLOCKING
| /CACHED
| /CONVERT
| /GRANTED
| /NAME=name
| /STATUS=(keyword[,...])
| /WAITING ] or
SHOW LOCKS {/POOL | /SUMMARY}
Parameter
lock-id
Name of a specific lock.
Qualifiers
/ADDRESS=n
Displays a specific lock, given the address of the lock block.
/ALL
Lists all locks that exist in the system. This is the default behavior
of the SHOW LOCKS command.
/BLOCKING
Displays only the locks that have a blocking AST specified or attached.
/BRIEF
Displays a single line of information for each lock.
/CACHED
Displays locks that are no longer valid. The memory for these locks is
saved so that later requests for locks can use them. Cached locks are
not displayed in the other SHOW LOCKS commands.
/CONVERT
Displays only the locks that are on the conversion queue.
/GRANTED
Displays only the locks that are on the granted queue.
/NAME=name
Displays all locks on the specified resource. Name can be the
actual name of the resource, if it only contains uppercase letters,
numerals, the underscore (_), dollar sign, colon (:), and some other
printable characters, as for example, /NAME=MY_LOCK. If it contains
other printable characters (including lowercase letters), you may need
to enclose the name in quotation marks (""), as for example,
/NAME="My_Lock/47". If it contains nonprintable characters, you can
specify the name as a comma-separated list comprised of strings and
hexadecimal numbers. For example, /NAME=("My_Lock",0C00,"/47") would
specify the name "My_Lock<NUL><FF>/47". The hexadecimal
number can be no more than 8 digits (4 bytes) in length. Nonprintable
sequences of more than 4 bytes must be split into multiple hexadecimal
numbers. The maximum length of a resource name is 32 characters.
/POOL
Displays the lock manager's poolzone information, which contains the
lock blocks (LKB) and resource blocks (RSB).
/STATUS=(keyword[,...])
Displays only the locks that have the specified status bits set in the
LKB$L_STATUS field. If you specify only one keyword, you can omit the
parentheses. Status keywords are as follows:
| Keyword |
Meaning |
|
2PC_IP
|
Indicates a two-phase operation in progress
|
|
2PC_PEND
|
Indicates a two-phase operation pending
|
|
ASYNC
|
Completes request asynchronously
|
|
BLKASTFLG
|
Specifies a blocking AST
|
|
BLKASTQED
|
Indicates a blocking AST is queued
|
|
BRL
|
Indicates a byte range lock
|
|
CACHED
|
Indicates a lock block in cache
|
|
CVTSUBRNG
|
Indicates a sub-range convert request
|
|
CVTTOSYS
|
Converts back to system-owned lock
|
|
DBLKAST
|
Delivers a blocking AST
|
|
DCPLAST
|
Delivers a completion AST
|
|
DPC
|
Indicates a delete pending cache lock
|
|
FLOCK
|
Indicates a fork lock
|
|
GRSUBRNG
|
Grants sub-range lock
|
|
IP
|
Indicates operation in process
|
|
MSTCPY
|
Indicates a lock block is a master copy
|
|
NEWSUBRNG
|
Indicates a new sub-range request
|
|
NOQUOTA
|
Does not charge quota
|
|
PCACHED
|
Indicates lock block needs to be cached
|
|
PROTECT
|
Indicates a protected lock
|
|
RESEND
|
Resends during failover
|
|
RM_RBRQD
|
Requires remaster rebuild
|
|
RNGBLK
|
Specifies a range block
|
|
RNGCHG
|
Indicates a changing range
|
|
TIMOUTQ
|
Indicates lock block is on timeout queue
|
|
VALBLKRD
|
Indicates read access to lock value block
|
|
VALBLKWRT
|
Indicates write access to lock value block
|
|
WASSYSOWN
|
Indicates was system-owned lock
|
/SUMMARY
Displays summary data and performance counters.
/WAITING
Displays only the waiting locks.
Description
The SHOW LOCKS command displays the information described in
Table 4-7 for each lock management lock in the system, or for the
lock indicated by lock-id, an address or name. (Use
the SHOW SPINLOCKS command to display information about spinlocks.) You
can obtain a similar display for the locks owned by a specific process
by issuing the appropriate SHOW PROCESS/LOCKS command. See the
HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual for additional information.
You can display information about the resource to which a lock is
queued by issuing the SHOW RESOURCES command specifying the resource's
lock-id.
Table 4-7 Contents of the SHOW LOCKS and SHOW PROCESS/LOCKS Displays
| Display Element |
Description |
|
Process Index
1
|
Index in the PCB array to a pointer to the process control block (PCB)
of the process that owns the lock.
|
|
Name
1
|
Name of the process that owns the lock.
|
|
Extended PID
1
|
Clusterwide identification of the process that owns the lock.
|
|
Lock ID
|
Identification of the lock.
|
|
PID
|
Systemwide identification of the lock.
|
|
Flags
|
Information specified in the request for the lock.
|
|
Par. ID
|
Identification of the lock's parent lock.
|
|
Sublocks
|
Count of the locks that the lock owns.
|
|
LKB
|
Address of the lock block (LKB). If a blocking AST has been enabled for
this lock, the notation "BLKAST" appears next to the LKB
address.
|
|
Priority
|
The lock priority.
|
|
Granted at
|
Lock mode at which the lock was granted.
|
|
RSB
|
Address of the resource block.
|
|
Resource
|
Dump of the resource name. The two leftmost columns of the dump show
its contents as hexadecimal values, the least significant byte being
represented by the rightmost two digits. The rightmost column
represents its contents as ASCII text, the least significant byte being
represented by the leftmost character.
|
|
Status
|
Status of the lock, information used internally by the lock manager.
|
|
Length
|
Length of the resource name.
|
|
Mode
|
Processor access mode of the namespace in which the resource block
(RSB) associated with the lock resides.
|
|
Owner
|
Owner of the resource. Certain resources owned by the operating system
list "System" as the owner. Resources owned by a group have
the number (in octal) of the owning group in this field.
|
|
Copy
|
Indication of whether the lock is mastered on the local system or is a
process copy.
|
1This display element is produced only by the SHOW
PROCESS/LOCKS command.
Examples
| #1 |
SDA> SHOW LOCKS
Lock Database
-------------
Lock id: 3E000002 PID: 00000000 Flags: CONVERT NOQUEUE SYNCSTS
Par. id: 00000000 SUBLCKs: 0 NOQUOTA CVTSYS
LKB: FFFFFFFF.7DF48150 BLKAST: 81107278
Priority: 0000
Granted at CR 00000000-FFFFFFFF
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7DF68D50
Resource: 494D6224 42313146 F11B$bMI Status: NOQUOTA VALBLKR VALBLKW
Length 18 4D55445F 5944414C LADY_DUM
Kernel mode 00000000 00005350 PS......
System 00000000 00000000 ........
Local copy
Lock Database
-------------
Lock id: 3F000003 PID: 00000000 Flags: VALBLK CONVERT SYNCSTS
Par. id: 0100007A SUBLCKs: 0 CVTSYS
LKB: FFFFFFFF.7DF48250 BLKAST: 00000000
Priority: 0000
Granted at NL 00000000-FFFFFFFF
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7DF51D50
Resource: 01F77324 42313146 F11B$s÷. Status: NOQUOTA VALBLKR VALBLKW
Length 10 00000000 00000000 ........
Kernel mode 00000000 00000000 ........
System 00000000 00000000 ........
Local copy
Lock Database
-------------
Lock id: 0A000004 PID: 0001000F Flags: VALBLK CONVERT SYNCSTS
Par. id: 00000000 SUBLCKs: 0 SYSTEM NODLCKW NODLCKB
LKB: FFFFFFFF.7DF48350 BLKAST: 81190420 QUECVT
Priority: 0000
Granted at EX 00000000-FFFFFFFF
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7DF50850
Resource: 004F0FDF 24534D52 RMS$ß.O. Status: VALBLKR VALBLKW
Length 26 5F313039 58020000 ...X901_
Exec. mode 00202020 204C354B K5L .
System 00000000 00000000 ........
Local copy
.
.
.
|
| #2 |
SDA> SHOW RESOURCES/LOCKID=0A000004
Resource Database
-----------------
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7DF50850 GGMODE: EX Status: DIRENTR VALID
Parent RSB: 00000000.00000000 CGMODE: EX
Sub-RSB count: 0 FGMODE: EX
Lock Count: 1 RQSEQNM: 0000
BLKAST count: 1 CSID: 00000000 (MILADY)
Resource: 004F0FDF 24534D52 RMS$ß.O. Valblk: 00000000 00000000
Length 26 5F313039 58020000 ...X901_ 00000000 00000000
Exec. mode 00202020 204C354B K5L .
System 00000000 00000000 ........ Seqnum: 00000000
Granted queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range):
0A000004 EX 00000000-FFFFFFFF
Conversion queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range -> Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Waiting queue (Lock ID / Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
|
This SDA session shows the output of the SHOW LOCKS command for several
locks. The SHOW RESOURCES command, executed for the last displayed
lock, verifies that the lock is in the resource's granted queue. (See
Table 4-26 for a full explanation of the contents of the display of
the SHOW RESOURCES command.)
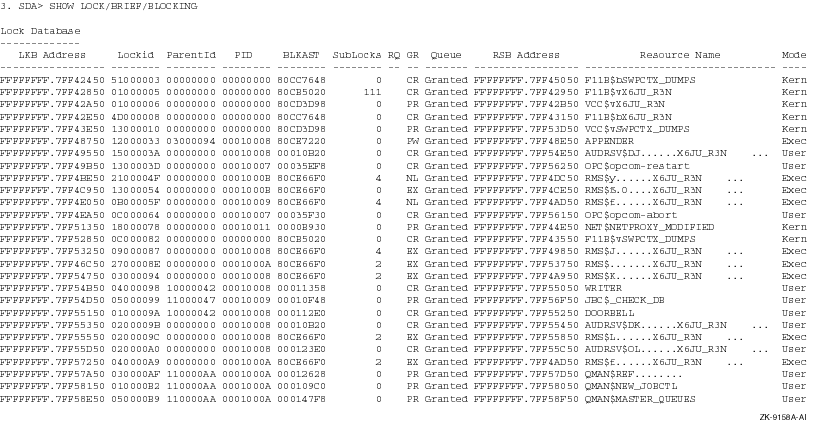
This example shows the brief display for all locks with a blocking AST.
|
