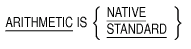|
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
2.3 Declaratives
Declaratives specify USE procedures to be executed
only when certain conditions occur. You must write USE procedures at
the beginning of the Procedure Division in consecutive sections. The
key word DECLARATIVES begins the DECLARATIVES part of the Procedure
Division; the pair of key words END DECLARATIVES ends it. Each of these
reserved word phrases must be on a line by itself, starting in Area A;
and be followed by a separator period. For example:
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
DECLARATIVES.
IOERROR SECTION.
USE AFTER ... .
PAR-1.
.
.
.
END DECLARATIVES.
|
When you specify USE procedures, you must divide the remainder of the
Procedure Division into sections.
Chapter 3
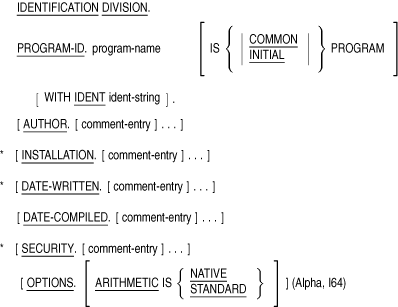
Identification Division
3.1 Function
The Identification Division marks the beginning of a COBOL program. It
also identifies a program and its source listing.
* These paragraphs are not described in individual entries; they follow
the same format as the AUTHOR paragraph and are for documentation only.
Syntax Rules
- The Identification Division must be the first entry in a COBOL
program.
- The Identification Division must begin with the IDENTIFICATION
DIVISION header. The header consists of the reserved words
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION followed by a separator period.
- The PROGRAM-ID paragraph must immediately follow the IDENTIFICATION
DIVISION header.
3.1.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
Function
The PROGRAM-ID paragraph identifies a program and assigns selected
program attributes.
General Format
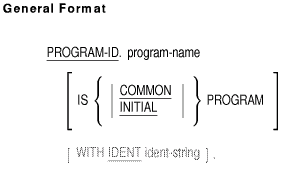
program-name
is a user-defined word that names the program.
Syntax Rules
- The PROGRAM-ID paragraph must be present in every program.
- program-name must contain 1 to 31 characters and follow
the rules for user-defined words.
- Programs contained within a separately compiled program must have a
unique program-name.
- The optional COMMON clause may be used only if the program is
contained within another program.
- ident-string must be a nonnumeric literal 1 to 31
characters in length.
- The optional IDENT clause cannot be used in a contained program.
General Rules
- program-name is a user-defined word that identifies a
COBOL program and its source listing. It appears as the first word in
the first line of every page in the compiler source listing.
- program-name represents the object program entry point.
- If an executable image includes more than one separately compiled
program, each separately compiled program must have a unique
program-name.
- The COMMON clause specifies a common program. A common program is
contained within another program but may be called from programs other
than that directly containing it.
- Files associated with a called program's internal file connectors
are not in the open mode:
- The first time the program is called
- The first time the program is called after execution of a CANCEL
statement referring to the program
- Every time the program is called, if it has the INITIAL attribute
On all other entries, the status and positioning of files in a
called program are the same as when the program last exited.
- The INITIAL clause specifies an initial program. Whenever the
program is called, it and any programs contained within it are placed
in their initial state, and the internal data in each program is
initialized.
-
On OpenVMS, the IDENT clause specifies a literal string that is used
for identification purposes. This string is written to the object file
as the "module version."
When the /ANALYSIS_DATA qualifier is
included on the COBOL command, the string is written to the analysis
data file as the module ident. <>
- On Tru64 UNIX systems, program-name is case-sensitive. By
default, program-name is converted to lowercase for all
separately compiled program units. Any calls from other programs
(HP COBOL as well as other languages) must specify the routine to
be called in lowercase.
However, if the
names
option is set to
uppercase
on the command line, calls from other programs must specify the routine
to be called in uppercase. If the
names
option is set to
as_is
, the effect on program-name is as if
uppercase
were specified. (The
as_is
setting is used for calling non-COBOL programs with mixed case.)
<>
Additional Reference
See Section 6.2.6, Scope of Names.
Examples
PROGRAM-ID. PROGA.
PROGRAM-ID. SUBR1 INITIAL.
PROGRAM-ID. COMPUTE-PAY WITH IDENT "JOB6a-V1.1". (OpenVMS)
PROGRAM-ID.
WRITEMASTERREPORT.
PROGRAM-ID. PAYROLL IS COMMON.
|
3.1.2 AUTHOR
Function
The AUTHOR paragraph is for documentation only.

comment-entry
is a user-supplied comment about the program's author.
Syntax Rules
- comment-entry can consist of any combination of characters
from the computer character set.
- comment-entry can span several lines in Area B. However,
they cannot be continued by using a hyphen in the indicator area.
- The end of comment-entry is the line before the next entry
in Area A.
Examples
AUTHOR. JOHN SMITH.
AUTHOR. This program was written by John Smith
1226 Main St.
Merrimack, NH 03054
AUTHOR.
|
3.1.3 DATE-COMPILED
Function
The DATE-COMPILED paragraph provides the compilation date in the source
program listing file.

comment-entry
is user-supplied information about the date compiled.
Syntax Rules
- comment-entry can consist of any combination of characters
from the computer character set.
- comment-entry can span several lines in Area B. However,
it cannot be continued by using a hyphen in the indicator area.
- The end of comment-entry is the line before the next entry
in Area A.
General Rule
The paragraph-name DATE-COMPILED causes the current date to be inserted
in your source program listing during compilation. Therefore, if a
DATE-COMPILED paragraph is present in your source program, it will be
replaced with a paragraph of the following form:
DATE-COMPILED. dd-mmm-yyyy.
Function
The OPTIONS paragraph specifies information for use by the compiler in
generating executable code for a source unit.

arithmetic-clause
specifies the method used in developing the intermediate results. The
format is:
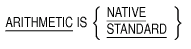
Syntax Rule
The period appearing in the general format after the arithmetic-clause
may be omitted if the arithmetic-clause is not specified.
General Rules
- The ARITHMETIC clause in the OPTIONS paragraph applies to the
source element in which it is specified and to all source elements
contained in that source element unless overridden by an ARITHMETIC
clause in an OPTIONS paragraph in a contained source element.
- If the NATIVE phrase is specified, the techniques used in handling
arithmetic expressions and arithmetic statements shall be those
specified for native arithmetic in the appendix on compatibility in the
HP COBOL User Manual.
- If the STANDARD phrase is specified, the techniques used in
handling arithmetic expressions and arithmetic statements shall be
those specified for standard arithmetic in the ANSI Standard for COBOL.
(Refer to the appendix on compatibility in the HP COBOL User Manual.)
- If the ARITHMETIC clause is not specified in this source element
or a containing source element, it is as if the ARITHMETIC clause were
specified with the NATIVE phrase. <>
|