Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 82final > 6297 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
HP COBOL
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
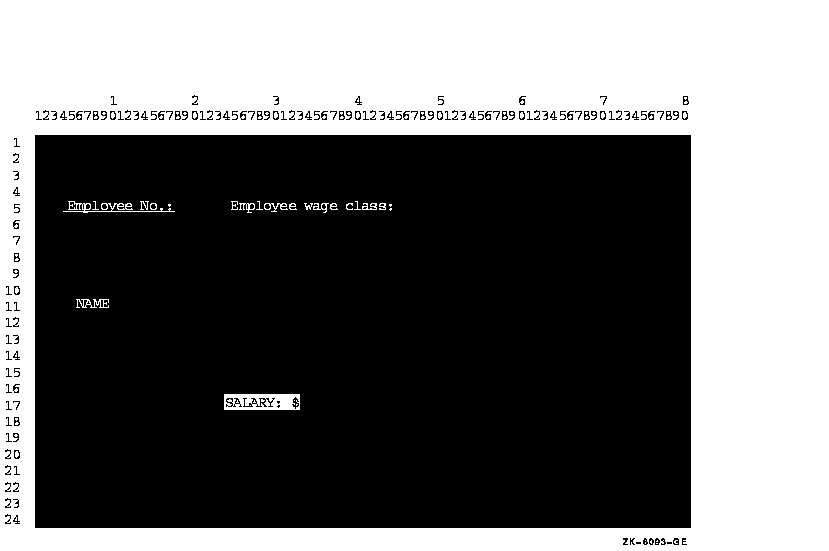
Depending on your terminal type, you can use one or more of the character attributes in Table 11-1 to highlight your screen data. Example 11-4 shows the use of these attributes in a program segment. Figure 11-5 shows the results of the program segment in Example 11-4.
| Character Attribute | VT500, VT400, VT300, VT200, and VT100 with Advanced Video Option | VT100 Without Advanced Video Option |
|---|---|---|
|
BELL
Sounds the terminal bell |
Available | Available |
|
UNDERLINED
Underlines the text |
Available | Not Available |
|
BOLD
Intensifies the text |
Available | Not Available |
|
BLINKING
Blinks the text |
Available | Not Available |
|
REVERSED
Changes the text's foreground & background colors |
Available | Not Available |
| Example 11-4 Using Character Attributes |
|---|
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. CHARATTR.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A00-BEGIN.
DISPLAY "Employee No:" UNDERLINED LINE 5 COLUMN 5 ERASE SCREEN.
DISPLAY "Employee wage class:" BOLD LINE 5 COLUMN 25.
DISPLAY "NAME" BLINKING LINE PLUS 6 COLUMN 6.
DISPLAY "SALARY: $" REVERSED LINE PLUS 6 COLUMN 24.
DISPLAY " " LINE 23 COLUMN 1.
|
Figure 11-5 Screen Display with Character Attributes
Use the CONVERSION phrase to convert the value of a numeric data item for display. It causes the value to appear on the screen as follows:
Thus, the values of non-DISPLAY data items can be converted to a readable form. The size of the displayed field is determined by the PICTURE clause of the displayed item. Example 11-5 and Figure 11-6 show how to display different types of data with the CONVERSION phrase.
| Example 11-5 Using the CONVERSION Phrase |
|---|
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. CONVERT.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 DATA1A PIC X(10).
01 DATA1B PIC X(10) JUST.
01 DATA2 PIC +++++9999.99.
01 DATA3 PIC S9(2)V9(2) COMP.
01 DATA4 PIC S9(3)V9(3) COMP.
01 DATA5 PIC S9(6)V9(6) COMP.
01 DATA6 PIC S9(4)V9(4) COMP-3.
01 DATA7 PIC S9(1)V9(7) SIGN LEADING SEPARATE.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
CONVERT-CHECK SECTION.
P1.
DISPLAY "to begin... press your carriage Return key"
LINE 1 COLUMN 1 ERASE SCREEN
BELL UNDERLINED REVERSED.
ACCEPT DATA1A.
DISPLAY "X(10) Test" LINE 8 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA1A WITH CONVERSION PROTECTED REVERSED
LINE 8 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA1A REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 8 COLUMN 65.
DISPLAY "X(10) JUSTIFIED Test" LINE 10 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA1B WITH CONVERSION PROTECTED REVERSED
LINE 10 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA1B REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 10 COLUMN 65.
P2.
DISPLAY "Num edited Test (+++++9999.99):" LINE 12 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA2 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 12 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA2 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 12 COLUMN 65.
P3.
DISPLAY "Num COMP Test S9(2)V9(2):" LINE 14 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA3 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 14 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA3 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION LINE 14 COLUMN 65.
P4.
DISPLAY "Num COMP Test S9(3)V9(3):" LINE 16 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA4 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 16 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA4 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 16 COLUMN 65.
P5.
DISPLAY "Num COMP Test S9(6)V9(6):" LINE 18 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA5 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 18 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA5 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 18 COLUMN 65.
P6.
DISPLAY "Num COMP-3 Test S9(4)V9(4):" LINE 20 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA6 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 20 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA6 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 20 COLUMN 65.
P7.
DISPLAY "Num DISPLAY Test S9(1)V9(7)Sign Lead Sep:"
LINE 22 ERASE LINE.
ACCEPT DATA7 PROTECTED REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 22 COLUMN 50.
DISPLAY DATA7 REVERSED WITH CONVERSION
LINE 22 COLUMN 65.
P8.
DISPLAY "To end...type END"
LINE PLUS COLUMN 1 ERASE LINE
BELL UNDERLINED REVERSED.
ACCEPT DATA1A.
IF DATA1A = "END" STOP RUN.
GO TO P1.
|
Figure 11-6 Sample Run of Program CONVERT
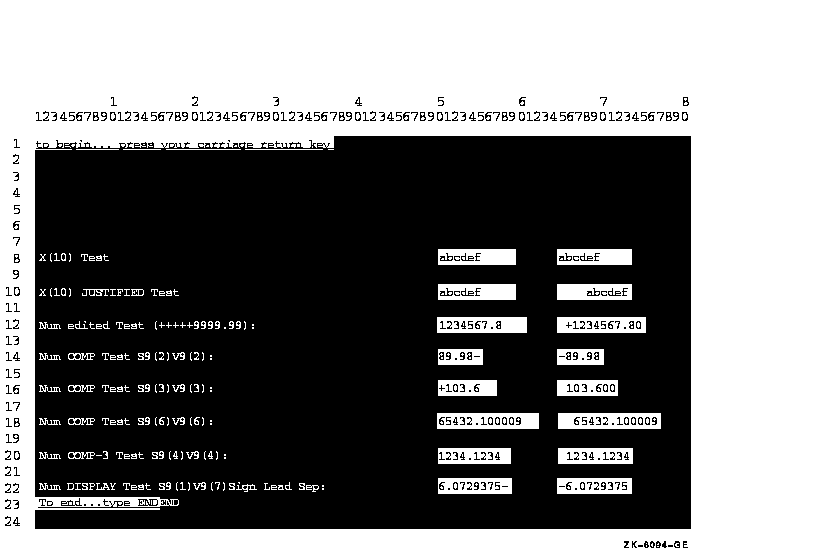
Note that, in addition to the items illustrated in Figure 11-6, you can also display the following:
The /DISPLAY_FORMATTED command-line qualifier is an alternative way to display numeric data without specifying the CONVERSION phrase. It accomplishes the same result, converting any nonprinting values for display. (The default is /NODISPLAY_FORMATTED.)
The ACCEPT options CONVERSION, ON EXCEPTION, PROTECTED, SIZE, NO ECHO, and DEFAULT are described in the following sections.
When you use the CONVERSION phrase with an ACCEPT numeric operand (other than floating point), HP COBOL converts the data entered on the form to a trailing-signed decimal field. Editing is performed when specified by destination. The data is then moved from the screen to your program using standard MOVE statement rules.
When you use the CONVERSION phrase with an ACCEPT numeric floating-point operand, HP COBOL converts input data to floating-point (COMP-1 or COMP-2 as appropriate). The converted result is then moved to the destination as if moving a numeric literal equivalent to the input data with the MOVE statement.
When an ACCEPT operand is not numeric, the CONVERSION phrase moves the input characters as an alphanumeric string, using standard MOVE statement rules. This lets you accept data into an alphanumeric-edited or JUSTIFIED field.
If you use the CONVERSION phrase while accepting numeric data, you can also use the ON EXCEPTION phrase to control data entry errors.
If you do not use the CONVERSION phrase, data is transferred to the destination item according to Format 1 ACCEPT statement rules.
If you enter illegal numeric data or exceed the PICTURE description (if not protected) of the ACCEPT data (with an overflow to either the left or right of the decimal point), the imperative statement associated with ON EXCEPTION executes, and the destination field does not change.
Example 11-6 (and Figure 11-7) show how the ON EXCEPTION phrase executes if you enter an alphanumeric or a numeric item out of the valid range. The statements following ON EXCEPTION prompt you to try again.
If you do not use ON EXCEPTION and a conversion error occurs:
| Example 11-6 Using the ON EXCEPTION Phrase |
|---|
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. ONEXC.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NUM-DATA PIC S9(3)V9(3) COMP-3.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A00-BEGIN.
DISPLAY "Enter any number in this range: -999.999 to +999.999"
LINE 10 COLUMN 1
ERASE SCREEN.
ACCEPT NUM-DATA WITH CONVERSION LINE 15 COLUMN 16
ON EXCEPTION
DISPLAY "Valid range is: -999.999 to +999.999"
LINE 20 REVERSED WITH BELL ERASE TO END OF SCREEN
DISPLAY
"PLEASE try again... press your carriage return key to continue"
LINE PLUS REVERSED
ACCEPT NUM-DATA
GO TO A00-BEGIN.
STOP RUN.
|
Figure 11-7 Accepting Data with the ON EXCEPTION Option

A DISPLAY statement within an ACCEPT [NOT] ON EXCEPTION statement must be terminated, with, for example, END-DISPLAY.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |