Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 83final > 4527 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
If $GETSYI returns the number 0 for SYI$_DAY_OVERRIDE, the number returned for SYI$_DAY_SECONDARY is meaningless. 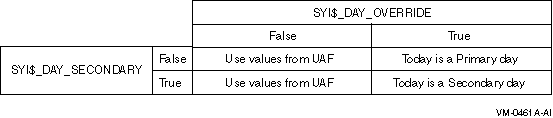
SYI$_DECIMAL_EMULATEDReturns the number 1 if the decimal string instructions are emulated on the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte). SYI$_DECNET_FULLNAMEReturns, as a character string, the DECnet for OpenVMS full name of the node.Because the DECnet for OpenVMS full name of a node can contain up to 255 characters, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 255 (bytes). SYI$_D_FLOAT_EMULATEDReturns the number 1 if the D_floating instructions are emulated on the CPU and 0 if they are not.Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte). SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MAXOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the maximum priority for the default scheduling policy.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MINOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the minimum priority for the default scheduling policy.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_ERLBUFFERPAGESReturns the number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64 systems) in an error log buffer.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_ERRORLOGBUFFERSReturns the number of system pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64 systems) in use as buffers for the error logger.Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes). SYI$_F_FLOAT_EMULATEDReturns the number 1 if the F_floating instructions are emulated on the CPU and 0 if they are not.Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte). SYI$_FREE_GBLPAGESReturns the current number of free global pages. The system parameter GBLPAGES sets the number of global pages that can exist systemwide.Because the current number is a longword, the buffer length in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_FREE_GBLSECTSReturns the current number of free global section table entries. The system parameter GBLSECTIONS sets the maximum number of global sections that can exist systemwide.Because the current number is a longword, the buffer length in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_G_FLOAT_EMULATEDReturns the number 1 if the G_floating instructions are emulated on the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte). SYI$_GALAXY_IDOn Alpha systems, returns the 128-bit Galaxy ID. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GALAXY_MEMBEROn Alpha systems, returns 1 if you are member of a Galaxy sharing community, 0 if you are not a member. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GALAXY_PLATFORMOn Alpha systems, returns 1 if you are running on a Galaxy platform, 0 if you are not running on a Galaxy platform. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GALAXY_SHMEMSIZEOn Alpha systems, returns the number of shared memory pages. If the current instance is not a member of a Galaxy, no shared memory is reported. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GH_RSRVPGCNTOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the number of pages covered by granularity hints to reserve for use by the Install utility after system startup has completed.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_GLX_FORMATIONOn Alpha systems, returns the a time-stamp string when the Galaxy configuration, of which this instance is a member, was created. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GLX_MAX_MEMBERSOn Alpha systems, returns the maximum count of instances that may join the current Galaxy configuration. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GLX_MBR_MEMBEROn Alpha systems, returns the 64-byte integer. Each 8 bytes represents a Galaxy member number, listed from 7 to 0. The value is 1 if the instance is currently a member, 0 if not a member. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GLX_MBR_NAMEOn Alpha systems, returns a string indicating the names that are known in the Galaxy membership. Returned names are separated by two spaces, with an additional two spaces following the last name in the list. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_GLX_TERMINATIONOn Alpha systems, returns a time-stamp string when the Galaxy configuration, of which this instance last was a member, was terminated. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.SYI$_H_FLOAT_EMULATEDReturns the number 1 if the H_floating instructions are emulated on the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte). SYI$_HP_ACTIVE_CPU_CNTReturns the number of active CPUs in this hard partition that are not currently in firmware console mode. For OpenVMS, this implies that the CPU is in, or in the process of joining, the active set in one of the instances in the hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.SYI$_HP_ACTIVE_SP_CNTReturns the count of active operating system instances currently executing within the hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.SYI$_HP_CONFIG_SBB_CNTReturns a count of the existing system building blocks within the current hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.SYI$_HP_CONFIG_SP_CNTReturns the maximum count of soft partitions within the current hard partition. This count does not imply that an operating system instance is currently running within any given soft partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.SYI$_HW_MODELReturns a small integer that can be used to identify the model type of the node.An integer greater than 1023 indicates an Alpha and I64 node. An integer less than or equal to 1023 indicates a VAX node. The $ALPHADEF and $VAXDEF macros in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET define the model type integers. See the tables under the SYI$_HW_NAME item code for the VAX processor names and the corresponding model types. Because SYI$_HW_MODEL is a word, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes). SYI$_HW_NAMEReturns the model name string of the node. The model name is a character string that describes the model of the node (such as VAX 8800, MicroVAX II). The model name usually corresponds to the nameplate that appears on the outside of the CPU cabinet.Because SYI$_HW_NAME can include up to 60 characters plus one for the byte count, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 61 (bytes). An example of an I64 processor follows:
The following table lists the Alpha model processor names and the corresponding model types:
The following table lists the VAX model processor names and the corresponding model types:
SYI$_IO_PRCPU_BITMAPThe return argument is a bitmap with a bit indicating a preferred CPU -- one available for Fast Path operations.The size of the returned bitmap is determined by the number of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and divide the result by 8. SYI$_IO_PREFER_CPUNote that this item code is becoming obsolete; HP recommends that you not use it because it represents only up to 64 CPUs. The service continues to return the correct data for systems with up to 64 CPUs but fails for systems with more than 64 CPUs. For greater flexibility, use item code SYI$_IO_PRCPU_BITMAP instead.On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the bit mask of CPUs available to be Fast Path preferred CPUs. The service continues to return the correct data for systems with up to 64 CPUs but fails for systems with more than 64 CPUs. SYI$_ITB_ENTRIESOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the number of instruction stream translation buffer entries that support granularity hints to be allocated for resident code.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_MAX_CPUSOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the maximum number of CPUs that could be recognized by this instance.SYI$_MAX_PFNReturns the highest numbered PFN in use by the operating system. The highest numbered PFN used by OpenVMS is influenced by the PHYSICAL_MEMORY system parameter.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_MEMSIZEReturns the total number of pages of physical memory in the system configuration.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_AREAReturns the DECnet area of the node.Because the DECnet area is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_CSIDReturns the OpenVMS Cluster system ID (CSID) of the node. The CSID is a longword hexadecimal number assigned to the node by the cluster management software.Because the CSID is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_EVOTESReturns the number of votes the node expects to find in the OpenVMS Cluster system. This number is determined by the system parameter EXPECTED_VOTES.Because the number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_HWVERSReturns the platform-specific hardware version information associated with the node. The high word of the buffer contains the CPU type. The $VAXDEF and $ALPHADEF macros define the CPU model types for VAX and Alpha systems, respectively. (HP recommends acquiring the model type using the SYI$_HW_MODEL item code.)Because the hardware version is a 12-byte hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 12 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_NUMBERReturns the DECnet for OpenVMS number of the node.Because the DECnet for OpenVMS number is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_QUORUMReturns the value (in decimal) of the quorum held by the node. This number is derived from the node's system parameter EXPECTED_VOTES.Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_SWINCARNReturns the software incarnation of the node.Because the software incarnation of the node is an 8-byte hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_SWTYPEReturns the software type of the node. The software type indicates whether the node is a VAX system, an Alpha or I64 system, or an HSC storage controller.Because the software type is a 4-byte ASCII string, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_SWVERSReturns the software version of the node.Because the software version is a 4-byte ASCII string, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_SYSTEMIDReturns the system identification of the node.The OpenVMS Cluster management software assigns this system identification to the node. You can obtain this information by using the DCL command SHOW CLUSTER. Because the system identification is a 6-byte hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 6 (bytes). SYI$_NODE_VOTESReturns the number (in decimal) of votes held by the node. This number is determined by the node's system parameter VOTES.Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes). SYI$_NODENAMEReturns, as a character string, the name of the node in the buffer specified in the item list.Because this name can include up to 15 characters, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 15 (bytes). SYI$_PAGEFILE_FREEReturns the number of free pages in the currently installed page files.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_PAGEFILE_PAGEReturns the number of pages in the currently installed page files.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_PAGE_SIZEReturns the number of CPU-specific bytes per page in the system.On VAX systems, $GETSYI always returns 512. On Alpha and I64 systems, CPU page size varies from system to system. On Alpha, and I64, and VAX systems, because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_PARTITION_IDOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the soft partition ID. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP---Alpha OnlyReturns a map describing the system's use of physical memory. Figure SYS-1 shows an example of a physical memory map.Figure SYS-1 SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP---Alpha Only 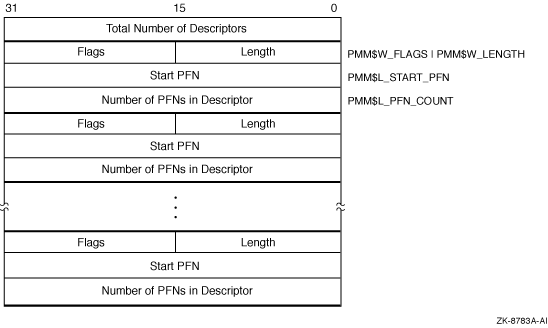
The first longword of the physical memory contains a count of descriptors. This number is equal to the value returned when the SYI$_PMD_COUNT item code is specified. Each descriptor contains at least 3 longwords: a word containing the length of the descriptor (always use PMM$C_LENGTH when determining descriptor size); a flags word (whose bits are defined in the following table); and the starting PFN for that physical memory cluster and the number of PFNs in that cluster.
The structure definition for the physical memory descriptor resides in PMMDEF.H. Because the size of the physical memory map returned by $GETSYI can vary from system to system, HP recommends using the following steps when using this item code:
SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP_64---on Alpha and I64Returns a map describing the system's use of physical memory on Alpha and I64 only. Figure SYS-2 shows an example of a physical memory map.Figure SYS-2 SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP---Alpha and I64 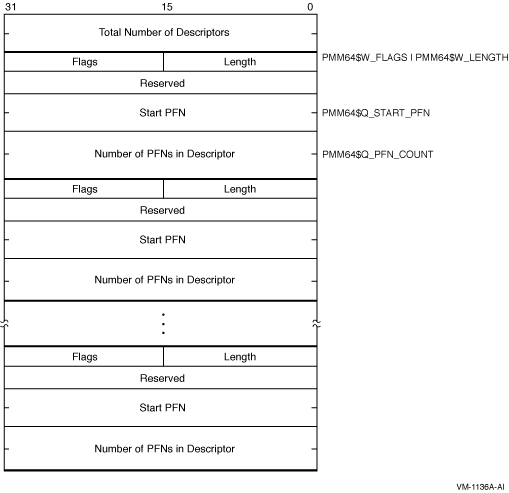
The first longword of the physical memory contains a count of descriptors. This number is equal to the value returned when the SYI$_PMD_COUNT item code is specified. Each descriptor contains at least 3 longwords: a word containing the length of the descriptor (always use PMM64$C_LENGTH when determining descriptor size); a flags word (whose bits are defined in the following table); and the starting PFN for that physical memory cluster and the number of PFNs in that cluster.
The structure definition for the physical memory descriptor resides in PMMDEF.H. Because the size of the physical memory map returned by $GETSYI can vary from system to system, HP recommends using the following steps when using this item code:
SYI$_PHYSICALPAGESReturns the total number of PFNs that exist between the first PFN (typically PFN 0) and the highest numbered PFN.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_PMD_COUNTReturns the total number of physical memory descriptors defined by the system. The return value of this parameter can be used to determine the buffer size to use when specifying the SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP item code.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes). SYI$_POTENTIAL_CPU_BITMAPThe return argument is a bitmap with a bit indicating a member of the instance's potential set. A CPU in the potential set implies that it could actively join the OpenVMS active set for this instance if it is ever owned by it. To meet this rule the CPU's characteristics must match hardware and software compatibility rules defined particularly for that instance.The size of the returned bitmap is determined by the number of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and divide the result by 8. SYI$_POTENTIAL_CPU_MASKNote that this item code is becoming obsolete; HP recommends that you not use it because it represents only up to 64 CPUs. The service continues to return the correct data for systems with up to 64 CPUs but fails for systems with more than 64 CPUs. For greater flexibility, use item code SYI$_POTENTIAL_CPU_BITMAP instead.On Alpha and I64 systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed bit vector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's potential set. A CPU in the potential set implies that it could actively join the OpenVMS active set for this instance if it is ever owned by it. To meet this rule, the CPU's characteristics must match hardware and software compatibility rules defined particularly for that instance. SYI$_POTENTIALCPU_CNTOn Alpha and I64 systems, returns the count of CPUs in the hard partition that are members of the potential set for this instance. A CPU in the potential set implies that it could actively join the OpenVMS active set for this instance if it is ever owned by it. To meet this rule the CPU's characteristics must match hardware and software compatibility rules defined particularly for that instance.SYI$_POWERED_CPU_BITMAPThe return argument is a bitmap with a bit indicating a member of the instance's powered set---those CPUs physically existing within the hard partition and powered up for operation.
|