Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 83final > 6677 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 Release Notes
5.9.25 No New Entries for DECC$*.OLB Object LibrariesV8.3 As of OpenVMS Alpha and I64 Version 8.2, no new entry points are being added to the DECC$*.OLB object libraries. This means new C RTL entry points do not get mapped through these libraries to prefixed entries. For example, the new OpenVMS Version 8.3 entry point crypt , compiled with /PREFIX=NONE, does not get mapped from crypt to decc$crypt . 5.10 Calling Standard and Rotating Registers (I64 Only)V8.3 This note supplements information in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard. The Calling Standard invocation context block (ICB) (see Table 4-16 in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard) and mechanism vector (see Figure 8-7 and Table 8-6 in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard) always record general, floating-point, and predicate registers as if the register rename base (CFM.rrb) and rotating size (CFM.sor) were both zero. That is, when rotating registers are in use, the effects of the rotation are ignored. This is also true of the register masks used by the LIB$I64_PUT_INVO_REGISTERS routine (see Section 4.8.3.13 in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard), because these masks are defined in terms of fields in the ICB structure. Previously, the supplemental access routines LIB$I64_GET_FR, LIB$I64_SET_FR, LIB$I64_GET_GR and LIB$I64_SET_GR (see Section 4.8.4 in the HP OpenVMS Calling Standard) improperly interpreted their register number parameters without applying an adjustment for the effects of the register rename base and rotating size registers. This error is corrected. 5.11 Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) ConsiderationsThe following notes pertain to CDSA. 5.11.1 Secure DeliveryV8.3 Downloading of files over the Internet is becoming a requirement of OpenVMS customers who want to use this easy and convenient method to acquire software updates, but are wary of the security vulnerabilities. Secure Delivery makes use of public key and digital signature technology to implement a system that provides OpenVMS users with the ability to authenticate and validate the files they download from OpenVMS and third-party OpenVMS vendors. Secure Delivery is fully functional with OpenVMS Version 8.3. For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 New Features and Documentation Overview. 5.11.2 Installation and Initialization ConsiderationsV7.3-2 Installation of CDSA is done automatically when you install the operating system.
5.12 Debugging Modes: Avoiding CPUSPINWAIT BugchecksPermanent Condition The OpenVMS operating system has a number of special modes of operation designed to help you debug complex hardware and software problems. In general terms, these special modes enable an extra level of tracing, data recording, and consistency checking that is useful in identifying a failing hardware or software component. These modes of operation are controlled by several system parameters: MULTIPROCESSING, POOLCHECK, BUGCHECKFATAL, and SYSTEM_CHECK. If you are using one of these special modes (for example, to debug a device driver or other complex application), under certain conditions, generally related to high I/O loads, it is possible to incur a CPUSPINWAIT bugcheck. Specifically, any privileged code that runs for extended periods of time while holding a spinlock can cause a CPU spinwait bugcheck. Spinlocks are used to delineate the entry and exit points for critical sections, and should not be held continuously, as can occur in this situation. To prevent a CPUSPINWAIT bugcheck, either use the system default settings for these system parameters, or reduce the loading of the system. If you have reason to change the default settings, you can reduce the likelihood of encountering a problem by setting the SMP_LNGSPINWAIT system parameter to a value of 9000000. 5.13 Delta/XDelta DebuggersThe following release notes pertain to the OpenVMS Delta and XDelta debuggers running on OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems. OpenVMS Debugger release notes are in Section 5.29. 5.13.1 XDELTA Register Display Consideration (I64 Only)V8.2 XDELTA on OpenVMS I64 displays general, floating-point, and predicate registers as if the register rename base (CFM.rrb) and the rotating size (CFM.sor) are both zero. In other words, when rotating registers are in use, the effects of the rotation are ignored. This condition will be corrected in a future release. See Section 5.10 for additional details. 5.14 File Applications: Corrections to Guide to OpenVMS File ApplicationsPermanent Correction The following corrections will be made to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications if this manual is revised in the future.
5.15 HP BLISS Compiler Warnings with RMS Structures (I64 Only)Permanent Condition Quadword alignment has been added to the BLISS macros ($xxx_DECL) that can be used to allocate RMS user structures (for example, FAB, RAB). Alignment faults are costly to performance---especially as processors get faster. By implementing the alignment directly in the macros, a number of OpenVMS utilities and user applications written in BLISS that use these macros show improved performance. The specific names of the macros are: $FAB_DECL, $NAM_DECL, $NAML_DECL, $RAB_DECL, $RAB64_DECL, $XABALL_DECL, $XABDAT_DECL, $XABFHC_DECL, $XABITM_DECL, $XABJNL_DECL, $XABKEY_DECL, $XABPRO_DECL, $XABRDT_DECL, $XABRU_DECL, $XABTRM_DECL, and $XABSUM_DECL. The alignment added in the RMS macros might result in compiler warnings of conflicting alignment. Programs with compiler warnings should link and execute correctly. However, the minor source changes to eliminate the warnings are recommended. If you use any of these macros in a BLISS application and the declaration includes the ALIGN attribute, the BLISS compiler issues a "conflicting or multiply specified attribute" warning. For example, the warning is issued for the following declaration: FAB: $FAB_DECL ALIGN(2). The compiler also issues this warning even if quadword alignment (ALIGN(3)) is specified. You should remove any explicit ALIGN attributes associated with these macros. In addition, if any of these allocations is included in a PSECT that contains an explicit alignment that is in conflict with ALIGN(3) (that is, is lower than ALIGN(3)), the BLISS compiler issues an "align request negative or exceeds that of psect" warning. For example, the warning would be issued for the following declaration:
If warnings on PSECT alignment are seen when recompiling a BLISS application, the correction is to increase the alignment of the PSECT to ALIGN(3) (or higher). In rare cases, applications may have assumptions on adjacency of data between PSECTs. Those assumptions could be broken in making this change. Therefore, check the code for such assumptions and make any necessary corrections. While a number of OpenVMS utilities are written in BLISS, only a few warnings were generated in a full OpenVMS build. Changes in OpenVMS to eliminate warnings did not require other changes to correct assumptions. Based on this, few user applications likely will require modification. 5.16 Potential Must-Be-Zero RMS Error: Making Room for New File Options in the FABThere is very little remaining unassigned space in the RMS user file access block (FAB). To allow for future growth in file-processing options implemented through the FAB, the last unassigned bit in the file-processing options field in the FAB (FAB$L_FOP) has been defined as the FAB$V_EXTEND_FOP option. This option will be used in the future to request and validate assignments to two new FAB fields that span previously unused bytes in the FAB:
In a future release, when one or more new file-processing options are implemented, the FAB$V_EXTEND_FOP bit will have to be set in the FAB$L_FOP field to take advantage of any new option in the FOPEXT field. However, when it is set, it will also indicate that any undefined bits in the FOPEXT field are clear and FAB$W_RESERVED_MBZ contains a zero. If these conditions are not met when this bit is set, a fatal error (RMS-F-FOPEXTMBZ) will be returned to the user for any RMS file-level service. The addition of the EXTEND_FOP option is fully upwardly compatible except if a user sets this last bit in the FAB$L_FOP field by accident and either of these two new FAB fields happens to be nonzero. Previously, RMS ignored this last bit in the FAB$L_FOP field if it was set by accident. If the RMS-F-FOPEXTMBZ error is returned, you must clear either the EXTEND_FOP option in the FAB$L_FOP field or the two new fields (FAB$W_FOPEXT) and FAB$W_RESERVED_MBZ . 5.17 HP COBOL Run-Time Library (RTL)V8.3 For OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS I64 Version 8.3, the HP COBOL RTL (DEC$COBRTL) has been updated to V2.8-781. 5.18 HP Fortran for I64V8.3 The HP Fortran for OpenVMS Integrity servers compiler is a port of HP Fortran 90 for OpenVMS Alpha. It runs on OpenVMS I64 systems and produces objects for OpenVMS I64 systems. The objects are linked using the standard linker on OpenVMS I64. This compiler requires OpenVMS I64 Version 8.2 or greater. HP Fortran for OpenVMS Integrity servers features the same command-line options and language features as HP Fortran 90 for OpenVMS Alpha systems with the following exceptions:
For more information about this release, including installation instructions, read the Fortran V8.0 or V8.1 product release notes. To extract the release notes, set your default to the directory that contains the Fortran PCSI kit and enter one of the following commands:
5.19 HP MACRO for OpenVMSThe OpenVMS MACRO compiler compiles Macro-32 source code written for OpenVMS VAX systems (the VAX MACRO assembler) into machine code that runs on OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS I64 systems. The following notes pertain to the MACRO compiler. 5.19.1 HP MACRO for OpenVMS I64V8.3 The following notes pertain to the HP MACRO for OpenVMS I64 compiler:
5.19.2 HP MACRO for OpenVMS Alpha SystemsV8.3 The compiler might optimize away apparently unused memory loads. The compiler's new optimizer can recognize whether or not the result of a memory load is used. If the result appears to be unused, the optimizer removes the memory load as well. However, some code may be using the memory load to fault a page into memory before raising IPL for example. In these cases, the removed instruction prevents the page from being faulted into memory, and the subsequent code at high IPL experiences a fatal page fault at high IPL exception. The only workaround is either to use /NOOPTIMIZE or revert to the prior Macro-32 compiler, which does not contain the optimization. The new Macro-32 compiler is named SYS$SYSTEM:MACRO.EXE and is the default image activated by the DCL MACRO command. The older compiler can be found at SYS$SYSTEM:ALPHA_MACRO.EXE . For the DCL command MACRO to use the older compiler, define a MACRO logical name as follows:
5.19.3 /TIE Qualifier Defaults Differ on Alpha and I64V8.2 The default for the /TIE qualifier is different on Alpha and I64 systems. On Alpha, the default is /TIE. On I64, the default is /NOTIE. 5.19.4 /OPTIMIZE=VAXREGS Qualifier Not Supported on I64V8.2 The /OPTIMIZE=VAXREGS qualifier, which is supported on Alpha, is not supported on I64. Unfortunately, all of the related code was not removed from the command line processing. If you specify /OPTIMIZE=ALL on I64, you will accidentally turn on the unsupported VAXREGS optimization. A future release will correct the command line process to avoid turning on the VAXREGS optimization. 5.19.5 Floating Divide-by-Zero Error Not Raised (I64 Only)V8.2 The Macro-32 floating-point support routines do not detect floating division by zero. The support routines convert the VAX floating values to IEEE floating values and perform the division. Without the check, the division produces an IEEE NaN value. The support routines then attempt to convert the NaN value back into a VAX floating value. That operation raises a floating invalid error. A future release will fix the support routines to properly raise the floating divide-by-zero error. 5.20 Hypersort UtilityThe following notes pertain to Hypersort V08-006 for OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS I64 Version 8.2. As always, continue to use SORT32 as a workaround for any unresolved problems with Hypersort or any functionality not implemented in Hypersort. Release notes for SORT32 are in Section 5.35. 5.20.1 Reporting a Problem to HPPermanent Condition If you find a problem with SORT or MERGE, execute the following commands before you submit a problem report:
Include the output in your problem report along with the input files that demonstrate the problem. 5.20.2 Large Files RestrictionV8.2 Hypersort V08-010 includes an improved memory allocation algorithm, but Hypersort still sometimes hangs or ACCVIOs with large input files. To reduce the chances of a hang or an ACCVIO, make sure to set page file quota and working set extent as noted in Section 5.20.8. If you encounter a hang or an ACCVIO with Hypersort, use SORT32 instead. 5.20.3 Hypersort and VFC Files RestrictionV7.3-2 Use of VFC files with Hypersort requires /FORMAT=RECORD_SIZE:n. 5.20.4 /FORMAT=RECORD_SIZE RestrictionPermanent Restriction Hypersort supports /FORMAT=RECORD_SIZE:n for use with both SORT and MERGE, with the following two restrictions:
5.20.5 Using Hypersort with Search Lists and Other Uses of Logical NamesPermanent Restriction Hypersort does not fully support search lists and logical names used for input files and work files. If you encounter this problem, use SORT32. 5.20.6 Lack of Free Space for Work FilesPermanent Restriction Hypersort does not properly terminate if free space is exhausted in all available sort work files. To avoid this problem, do one of the following:
5.20.7 Input Asterisk (*) RestrictionPermanent Restriction Hypersort does not support asterisk (*) as an input file specification. 5.20.8 Optimal Working Set Extent and Page File Quota SettingsPermanent Restriction SORT32 and Hypersort use different sorting and work file algorithms. The relative speed of these utilities depends on the input file and the memory/disk/CPU configuration. Make sure that the working set extent is no more than one third of the page file quota. Both SORT32 and Hypersort perform best with a working set extent appropriate to a specific input file. 5.21 Intel® Assembler (I64 Only)Permanent Restriction All modules written in Intel assembly language must contain appropriate unwind directives, either by automatic generation using the -Xunwind flag or by explicitly placing unwind directives into the source module. Without accurate unwind information, the operating system's condition handling and exception dispatching does not work, and your program fails in unexpected ways. Programs without accurate unwind information are not supported by OpenVMS. This is a permanent requirement. 5.22 Librarian UtilityThe following release notes pertain to the Librarian Utility and Library Service routines. 5.22.1 Linking Against Data-Reduced ELF Object Libraries Not Recommended (I64 Only)V8.2 DCX data-reduced ELF object libraries are not stored in contiguous space in the library. As a result, the module cannot be directly mapped into process P2 space because data expansion must first occur. The LBR$MAP_MODULE library service expands and copies the module into process P2 space. This action causes the resulting pages in P2 space to be counted against process quota. The LBR$UNMAP_MODULE library service recovers those pages, but the pages remain in a heap storage free list and continue to be counted against process quota. For this reason, HP strongly recommends that DCX data-reduced ELF object libraries first be expanded before performing Linker operations. 5.22.2 Failure to Insert or Replace .STB files in an I64 Library (I64 Only)V8.2 On OpenVMS VAX and Alpha, .STB files can be stored in object libraries. On OpenVMS I64, the Librarian does not do this. For example:
Because .STB files are neither objects nor images, the Librarian does not currently put them into an .OLB file on I64 systems. On Alpha and VAX, however, STB files are formatted as object files. On VAX, .STB files can be used as input to the Linker. On Alpha, .STB file formats are identical to .OBJ file format (that is, nothing distinguishes them except for the .STB file extension). As such, the Alpha Librarian accepts the file, but it cannot be used as input to the Linker. On I64, the file type (ET_VMS_LINK_STB) is embedded in the .STB file, allowing the Librarian and Linker to determine that the .STB file cannot be processed. This is a permanent condition. 5.22.3 Librarian Fails to Report Errors When Process Quota Too LowPermanent Restriction The OpenVMS Alpha and I64 Librarian sometimes does not inform you of errors during compression, data reduction, or data expansion operations. This problem occurs if the account or process in which the Librarian is running has a low PGFLQUOTA process quota. Operation failure is not readily apparent because the $PUTMSG system service always returns a status of SS$_NORMAL, even when the system service fails. However, when a failure occurs, the Librarian returns a status other than Success. To work around this problem, increase your PGFLQUOTA before running compression, data reduction, or data expansion operations. In addition, ensure that your command procedures check the return status from the LIBRARY command. 5.23 Analyze Utility for OpenVMS (I64 Only)The following release notes pertain to the Analyze utility on OpenVMS I64. 5.23.1 Releasing Process Resources Fixed in I64 Analyze Image /SELECTV8.3 For I64 image files, ANALYZE/SELECT did not release process resources; a wild card operation could fail with SECTBLFUL (or other exceeded quota messages). This problem is fixed in Version 8.3. 5.23.2 Selective Output for Debug Line Information FixedV8.3 For I64 image files, ANALYZE/IMAGE/SELECT=DEBUG=LINE did not format the corresponding debug line information. The line selection only worked with /TRACE. This problem is fixed in Version 8.3. 5.24 Command Definition Utility (I64 Only)The following release notes pertain to the Command Definition utility on OpenVMS I64. 5.24.1 Record Attributes Fixed for I64 ImagesV8.3 For I64 images (command tables), the Command Definition Utility (CDU) set record attributes, which caused warnings when copying or appending image files. Despite these warning messages, the copied or appended files contained correct content. In Version 8.3, CDU sets compatible attributes that allow these file operations to complete without a warning message. 5.25 Linker Utility for OpenVMS AlphaThe following release notes pertain to the Alpha Linker Utility on all OpenVMS platforms. For I64 Linker release notes, see Section 5.26. 5.25.1 Linker Appears to Hang When Many Files Are SpecifiedV8.3 When the RMS_RELATED_CONTEXT linker option is on (the default is RMS_RELATED_CONTEXT=YES) and a nonexistent file is specified in a list of files for the LINK command, the linker's call to LIB$FIND_FILE may take a long time to complete and the linker may appear to hang. Depending on the number of files being linked and the use of logical names in their specification, the linker may take hours to finish because LIB$FIND_FILE locates every combination of the missing file's prefix before displaying a "file not found" message. Note that you cannot terminate the linker process by pressing Ctrl/Y after the linker has called LIB$FIND_FILE. To determine which file is missing, follow the steps described with the RMS_RELATED_CONTEXT= option in the Linker Manual, Part IV, LINK Command Reference. 5.25.2 Change in Linker Default Behavior with Library CheckV7.3-1 Previously, the linker's check between the library and the shareable image was too sensitive. It compared against the exact date and time, signaling LINK-I-DATMISMCH, if no match was found. Now, however, it makes only the same check that the image activator does: that is, it uses the GSMATCH criteria to verify compatibility. The old behavior (check for date and time) can be obtained by setting the logical name LINK$SHR_DATE_CHECK. For more information, see the /LIBRARY qualifier in the Linker Manual Part IV, LINK Command Reference. Shareable image libraries do not contain a copy of an image. They contain the image's name, the image's identification information, and a table including the image's universal symbols. The identification information is provided by the GSMATCH= option when the shareable image is linked. For more information, see the GSMATCH= option in the Linker Manual Part IV, LINK Command Reference. It may happen that a shareable image is relinked but that a library is not updated. To handle such a case, the linker checks for compatibility. The linker makes the same check that the image activator does: that is, it uses the GSMATCH criteria to verify compatibility. For VAX, the linker also compares against the date and time, signaling LINK-I-DATMISMCH , if they are different. For Alpha, the initial behavior of linker was the same as the VAX linker. The check was seen as too sensitive and the default behavior was changed to use only the GSMATCH criteria. The old VAX behavior can be obtained by setting the logical name LINK$SHR_DATE_CHECK . 5.25.3 Limit of 25 Elements on StackPermanent Restriction Developers who are creating object files should be aware that the linker's internal stack is guaranteed for only 25 elements. Any calculations must be done within this constraint. 5.26 Linker Utility for OpenVMS I64V8.3 The following release notes pertain to the I64 Linker utility. For Alpha Linker release notes, see Section 5.25. 5.26.1 Linker Writes Incorrect Interimage Debug Fixups into Debug Symbol FileV8.3 In some situations, the linker creates interimage fixups for the OpenVMS debugger. The interimage debug fixup is a result of compiler-generated debug relocations, which the linker cannot resolve. That is, the debugger requires these fixups to determine a value from a shareable image at run-time. Compilers might differ on how often they require the linker to create inter-image fixups for the debugger. The C compiler rarely uses inter-image debug fixups, but the C++ compiler often uses them. When linking such images with /DEBUG, the linker writes the debug information followed by the interimage debug fixups. With /NODSF (the default) the information is written correctly into the image file, but with /DSF the information is sometimes written incorrectly into the DSF file. For example, the DEBUG informationals and the DEBUG error in the following sample occur because the linker has written the DSF file incorrectly:
The image file is not affected; it can be executed with the RUN command without any problem:
This error will be corrected in the next release of the I64 Linker: 5.26.2 OpenVMS I64 Object Module and Image File Information Currently UnavailableV8.3 Information about the OpenVMS I64 extension to ELF (Executable and Linkable Format; the object module and image file format on I64) is not available at this time. It will be provided in a future release. For information about the Alpha or VAX object language format, see the respective appendixes in the OpenVMS Alpha/VAX Version 7.3 OpenVMS Linker Utility Manual, available from the documentation bookshelf at the following URL:
5.26.3 /SELECTIVE_SEARCH Might Incorrectly Ignore Transfer AddressV8.3 If you have an I64 object module containing a transfer address and you include the module in the link operation with the /SELECTIVE_SEARCH qualifier, the linker will not find its transfer address. In the following example, the object module (MAIN.OBJ) contains a transfer address but /SELECTIVE_SEARCH ignores it:
This condition happens only when I64 object modules, meant to provide the program's transfer address, are included in the link operation with the SELECTIVE_SEARCH attribute. The SELECTIVE_SEARCH attribute is given to an object module when you specify /SELECTIVE_SEARCH qualifier to the object module in the LINK command. For example,
A LIBRARY command,
when that module from the library is used to resolve references in a link operation, either implicitly,
or explicitly:
This problem manifests itself in one of two ways:
5.26.4 Differences Between the I64 Linker and the Alpha LinkerV8.3 Be sure to read the HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 New Features and Documentation Overview for a complete description of the differences between the OpenVMS I64 Linker and the OpenVMS Alpha Linker. The HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 New Features and Documentation Overview also contains a description of features that are new with the OpenVMS I64 Linker. 5.26.5 LINK_ORDER Section Header Flag Not SupportedV8.2 The Linker does not support the LINK_ORDER ELF section header flag. However, unwind sections, which have this flag set, are placed in the correct order. This flag indicates that the section, if combined with other sections in the image file, be combined in the same order as the order of the sections to which they refer are combined. Unwind sections are handled as special cases and appear in the correct order. The following figure illustrates this concept. 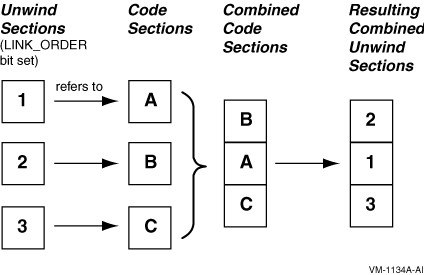
5.26.6 Linking Against Data-Reduced ELF Object Libraries Not RecommendedV8.2 DCX data-reduced ELF object libraries are not stored in contiguous space in the library. As a result, the module cannot be directly mapped into process P2 space because data expansion must first occur. The LBR$MAP_MODULE library service expands and copies the module into process P2 space. This action causes the resulting pages in P2 space to be counted against process quota. The LBR$UNMAP_MODULE library service recovers those pages but the pages remain in a heap storage free list and continue to be counted against process quota. For this reason, HP strongly recommends that DCX data-reduced ELF object libraries first be expanded before performing Linker operations. This is a permanent condition. 5.26.7 Error in Handling Initialized Overlaid Program Sections FixedV8.3 In previous versions of the I64 linker, initialized overlaid program sections with zeros are incorrectly seen as compatible initializations. In OpenVMS Version 8.2 and Version 8.21, the I64 Linker accepts sections initialized with zeros to be compatible with sections containing nonzero initial values. Under this condition, the order of modules in a link operation can result in different initial values in the image. This problem is fixed in Version 8.3. 5.26.8 Removal of Linker Qualifiers /EXPORT_SYMBOL_VECTOR and /PUBLISH_GLOBAL_SYMBOLSV8.3 Creating a shareable image by simply exporting all global symbols does not work. Previous I64 Linker versions provide the /EXPORT_SYMBOL_VECTOR and /PUBLISH_ GLOBAL_ SYMBOLS qualifiers to assist in creating symbol vector options for all global symbols on a per-module basis. However, using these qualifiers exports the same universal symbol from different images. Because you cannot exclude exporting the same C++ template from different images, this creates problems. Both qualifiers are removed from the Version 8.3. This problem will be fixed for the I64 Linker in a future release of OpenVMS for I64. 5.26.9 Support for Longer Symbol Names in OptionsV8.3 For options, the linker internal line buffer is increased to hold 2048 characters. This allows specifying options with symbol names of the maximum supported length of 1024 characters. 5.26.10 Better Use of Memory for Linker-Created Code StubsV8.3 The I64 linker generates code stubs, which are visible when stepping through the code with the OpenVMS Debugger. Code can be inserted for calls and can have different sizes. However, the earlier linker added the code as fixed-size code sections using the maximum necessary code size. The Version 8.3 linker writes the code stubs using the actual size. This eliminates unused space between the stubs and might also release unused memory. 5.26.11 Compiler Support for Demangled Symbol NamesV8.3 To make symbol names unique, name mangling is used for some programming languages. Starting with Version 8.3, the linker tries to display the demangled names, also known as source code names. These names are used in linker messages and, on request, in a translation table for mangled global symbols that appears in the linker map (see HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 New Features and Documentation Overview). This feature depends on compiler support for name demangling. 5.26.12 Maximum Number of SectionsV8.3 For more than 65280 sections, the ELF format uses an extended numbering scheme, which is currently not implemented in the I64 linker. That limits the number of sections a single input object module or shareable image can have. Because the linker usually creates the shareable images with sections, this limit applies for creating shareable images as well. Here, ELF sections are used for exporting C++ templates or shared sections. That is the maximum number of such interfaces in a shareable image must be fewer than 65280. 5.26.13 Incorrect Creation Date of Shareable Images in the Map FileV8.2 On OpenVMS I64 platforms, shareable images might show an incorrect creation date in the linker map. The incorrect date is shown is usually 3686. This condition occurs when the linker processes the shareable image as an input file and then extracts the date field, which is shown in the map. The image itself has the correct date that you can see from ANALYZE/IMAGE output. This problem will be fixed in a future release of the I64 Linker. 5.27 LTDRIVER: CANCEL SELECTIVE RestrictionIn releases prior to OpenVMS Version 6.1, LTDRIVER did not set the "extended DDT" bit; therefore, the POSIX function CANCEL SELECTIVE did not work with LTDRIVER. This problem has been corrected, but a restriction remains. Although this fix allows $QIO reads and writes to be selectively canceled, any $QIO done to the port driver (that is, with the IO$_TTY_PORT function modifier --- such as a LAT connect $QIO) cannot be canceled with CANCEL SELECTIVE. 5.28 Mail Utility: Threads Restriction for Callable MailV7.1 OpenVMS callable mail routines are not thread-safe. Refer to the Guide to the POSIX Threads Library for more information about calling non-thread-safe routines within a threaded application. Because callable mail context information is maintained on a per-process (rather than a per-thread) basis, multiple threads performing context-based processing must be synchronized so that only one mail context of a given type is active at once. Otherwise, one thread could corrupt another thread's mail operations. On OpenVMS Alpha systems, there is an additional restriction when kernel threads is enabled in a multithreaded environment. In this environment, callable mail should be used only in the initial thread. 5.29 OpenVMS DebuggerThe following release notes describe conditions specific to the OpenVMS Debugger on OpenVMS I64 and Alpha systems. For release notes about the DELTA and XDELTA debuggers, see Section 5.13. 5.29.1 STEP/SEMANTIC_EVENT Information Missing in Debugger Command-Line HelpV8.3 Information for the /SEMANTIC_EVENT qualifier does not display properly in Debugger command-line help under the STEP command. Information for this qualifier can be found in the command reference section of the HP OpenVMS Debugger Manual, under STEP command. 5.29.2 Problems and Conditions Corrected in this Release (I64 Only)V8.3 The following list describes conditions that are corrected in this release: General Condition: Arrays whose elements are on unaligned boundaries formerly did not displayed properly. This occurred when a programming language construct was used to force unnatural data alignment (for example, #pragma nomember_align in C or the PACKED keyword in Pascal). This condition is fixed. 5.29.3 General Conditions and Workarounds (I64 Only)The following general conditions have been identified, along with user workarounds: Condition: Arrays whose elements are on unaligned boundaries are not displayed properly. This occurs when a programming language construct is used to force unnatural data alignment (for example, #pragma nomember_align in C or the PACKED keyword in Pascal). Workaround: None. Condition: When examining an array with scalar (integer) subscripts, the debugger prints the array index values in the currently defined radix, rather than in the decimal radix. Workaround: Issue the SET RADIX DECIMAL command. Condition: OpenVMS Debugger on I64 systems displays general, floating-point and predicate registers as if the register rename base (CFM.rrb) and rotating size (CFM.sor) are both zero. In other words, when rotating registers are in use, the effects of the rotation are ignored. This will be corrected in a future release. See Section 5.10 for additional details.
Workaround: Examine the CFM register and manually adjust the EXAMINE command to account for the nonzero CFM.rrb and CFM.sor fields. 5.29.4 BASIC Language Issues (I64 Only)Condition: When examining a range of a multi-dimensional array, the debugger does not correctly symbolize the element's location. That is, the array row and column values are incorrect. 5.29.5 C++ Language Issues (I64 Only)Condition: The SHOW CALLS command sometimes displays C++ mangled names, rather than unmangled names. 5.29.6 COBOL Language Issues (I64 Only)Condition: Data declared with EDIT picture clauses are only partially supported. Examining the item (using the EXAMINE command) displays the raw data without scaling or other adjustments. Changing the item by depositing an integer or decimal constant (using the DEPOSIT command) may result in an error. Workaround: Manually adjust the displayed value by the appropriate scale factor. If you need to change the value, execute the DEPOSIT command using another variable or a quoted string as the source. 5.29.7 Fortran Language Issues (I64 Only)Condition: A deposit of a value into a data item declared as REAL*16 always results in a zero being stored rather than the actual value. 5.29.8 Pascal Language Issues (I64 Only)Condition: Arrays declared with dynamic bounds (for example, "array [1..n]") are not always handled correctly. When examining the array, the debugger will sometimes display INVARRDSC or IVALOUTBNDS errors, and SHOW SYMBOL/TYPE may incorrectly display the array bounds. 5.29.9 SET SCOPE Command: Behavior ChangeV8.2 The behavior of the SET SCOPE command has changed in this release. SET SCOPE now changes the debugger's language setting to the language of the specified scope. Previously, SET SCOPE did not affect the language setting. You can disable this capability by issuing the SET LANGUAGE NODYNAMIC command. 5.29.10 SHOW IMAGE Command ChangeV8.2 The SHOW IMAGE command now displays a summary of the address space occupied by the images in your process. To see the full image section information, use SHOW IMAGE/FULL, or specify an image name (for example, SHOW IMAGE FOO). 5.29.11 Client/Server Interface: Previous Versions Not Supported (Alpha Only)V7.3 The Debugger for OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 and later does not support previous versions of the client/server interface. You must install the client/server interface found in the kit on the distribution media, as identified in the following table.
These client kits are self-extracting .EXE files. Once the appropriate executable file has been transferred to the PC, you can run the file to install the debug client on the PC. The InstallShield installation procedure guides you through the installation. 5.30 OpenVMS System Dump Analyzer (SDA)The following notes pertain to the System Dump Analyzer (SDA). 5.30.1 CLUE Commands Not Ported to OpenVMS I64V8.2 The following CLUE commands have not yet been ported to OpenVMS I64 and will return a message to that effect: CLUE CALL
|