No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will
transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
bit in the flags argument requires that the final
thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise,
interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread
is already in one.
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call
SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES to modify its own user capability mask. To
modify another process' user capability mask, the caller must have:
To call SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES simply to retrieve the specific
process or global mask, the caller need only have the following
privileges:
The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor
that passes the selection criterion as a value:
The following diagram depicts the format of a 32-bit item descriptor
that passes the selection criterion by reference:
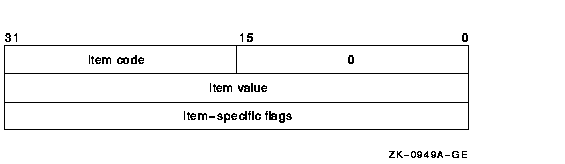
The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor
that passes the selection criterion by reference:
PSCAN$_ACCOUNT
When you specify PSCAN$_ACCOUNT, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the account field.
If the string supplied in the item descriptor is shorter than the
account field, the string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the
item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the buffer is placed in the first
word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in
the second longword.
Although the current length of the account field is 8 bytes, the
PSCAN$_ACCOUNT buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer
length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
PSCAN$_AUTHPRI
When you specify PSCAN$_AUTHPRI, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the authorized base priority field.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_CURPRIV
When you specify PSCAN$_CURPRIV, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the current privilege field. Privilege bits are
defined by the $PRVDEF macro.
Because the bit mask information is too long to be passed by value, the
information is passed by reference. The privilege buffer must be
exactly 8 bytes, otherwise the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE
When you specify PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE, you determine the size of a
buffer to be used by $GETJPI to process multiple requests in a single
message. Using this item code can greatly improve the performance of
scans on remote nodes, because fewer messages are needed. This item
code is ignored during scans on the local node.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0. The buffer is allocated by $PROCESS_SCAN; you do not
have to allocate a buffer.
If you use PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE with $PROCESS_SCAN, all calls to
$GETJPI using the context established by $PROCESS_SCAN must request the
same item code information. Because $GETJPI locates information for
more than one process at a time, it is not possible to change the item
codes or the length of the buffers used in the $GETJPI item list.
$GETJPI checks each call and returns the error SS$_BADPARAM if an
attempt is made to change the item list during a buffered process scan;
however, the buffer addresses can be changed between $GETJPI calls.
Because the locating and buffering of information by $GETJPI is
transparent to a calling program, you are not required to change the
way $GETJPI is called when you use this item code.
The $GETJPI buffer uses the process quota BYTLM. If the buffer is too
large for the process quota, $GETJPI (not $PROCESS_SCAN) returns the
error SS$_EXBYTLM. If the buffer specified is not large enough to
contain the data for at least one process, $GETJPI returns the error
SS$_BADPARAM.
No item-specific flags are used with PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE.
PSCAN$_GRP
When you specify PSCAN$_GRP, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the UIC group number.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. Because the value of the group
number is a word, the high-order word of the value is ignored. The
buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_HW_MODEL
When you specify PSCAN$_HW_MODEL, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified CPU hardware model number.
The hardware model number is an integer, such as VAX$K_V8840. The VAX$
symbols are defined by the $VAXDEF macro.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_HW_NAME
When you specify PSCAN$_HW_NAME, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified CPU hardware name, such as
VAX-11/780, VAX 8800, or VAXstation II/GPX.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the
first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is
placed in the second longword.
The PSCAN$_HW_NAME buffer can be up to 128 bytes in length. If the
buffer length is 0 or greater than 128, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is
returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT
When you specify PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the subprocess count for the job (the count of all
subprocesses in the job tree).
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_JOBTYPE
When you specify PSCAN$_JOBTYPE, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the job type. The job type values include the
following:
| Value |
Description |
|
JPI$K_LOCAL
|
Local interactive process
|
|
JPI$K_DIALUP
|
Interactive process accessed by a modem line
|
|
JPI$K_REMOTE
|
Interactive process accessed by using SET HOST
|
|
JPI$K_BATCH
|
Batch process
|
|
JPI$K_NETWORK
|
Noninteractive network process
|
|
JPI$K_DETACHED
|
Detached process
|
These values are defined by the $JPIDEF macro. Note that values checked
by PSCAN$_JOBTYPE are similar to PSCAN$_MODE values.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_KT_COUNT
When you specify PSCAN$_KT_COUNT, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the current count
of kernel threads for the process as a selection criteria.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_MASTER_PID
When you specify PSCAN$_MASTER_PID, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that are descendants of the specified parent process. The
master process is the first process created in the job tree. The
PSCAN$_OWNER item is similar, but the owner process is the process that
created the target process (the owner process might itself be a
subprocess). Although all jobs in a job tree must have the same master,
they can have different owners.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_MEM
When you specify PSCAN$_MEM, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the UIC member number.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. Because the value of the member
number is a word, the high-order word of the value is ignored. The
buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_MODE
When you specify PSCAN$_MODE, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified mode. Mode values include the
following:
| Value |
Description |
|
JPI$K_INTERACTIVE
|
Interactive process
|
|
JPI$K_BATCH
|
Batch job
|
|
JPI$K_NETWORK
|
Noninteractive network job
|
|
JPI$K_OTHER
|
Detached and other process
|
These values are defined by the $JPIDEF macro. Note that values checked
by PSCAN$_MODE are similar to PSCAN$_JOBTYPE values.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_MULTITHREAD
When you specify PSCAN$_MULTITHREAD, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the maximum
count of kernel threads for the process as a selection criteria.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_NODE_CSID
When you specify PSCAN$_NODE_CSID, $GETJPI returns information about
processes on the specified nodes. To scan all nodes in an OpenVMS
Cluster system, you specify a CSID of 0 and the item-specific flag
PSCAN$M_NEQ.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_NODENAME
When you specify PSCAN$_NODENAME, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified node names.
To scan all of the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system, specify the node
name using an asterisk wildcard (*) and the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD
item-specific flag.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the
first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is
placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the node name is 6 bytes, the
PSCAN$_NODENAME buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer
length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_OWNER
When you specify PSCAN$_OWNER, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that are immediate descendants of the specified process. The
PSCAN$_MASTER_PID item is similar, but the owner process is the process
that created the target process (the owner process might itself be a
subprocess). Although all jobs in a job tree must have the same master,
they can have different owners.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_PRCCNT
When you specify PSCAN$_PRCCNT, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the subprocess count (the count of all immediate
descendants of a given process). The PSCAN$_JOBPRCCNT item code is
similar, except that JOBPRCCNT is the count of all subprocesses in a
job.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_PRCNAM
When you specify PSCAN$_PRCNAM, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified process names.
The process name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the
item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the
first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is
placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the process name field is 15 bytes, the
PSCAN$_PRCNAM buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer
length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_PRI
When you specify PSCAN$_PRI, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match current priority. Note that the current priority
of a process can be temporarily increased as a result of system events
such as the completion of I/O.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_PRIB
When you specify PSCAN$_PRIB, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match base priority.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_STATE
When you specify PSCAN$_STATE, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified process state. State values, for
example SCH$C_COM and SCH$C_PFW, are defined by the $STATEDEF macro.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_STS
When you specify PSCAN$_STS, $GETJPI returns information that matches
the current status mask. Without any item-specific flags, the match is
for a process mask that is equal to the pattern. Status bits, for
example PCB$V_ASTPEN or PCB$V_PSWAPM, are defined by the $PCBDEF macro.
This bit mask item code uses an immediate value descriptor; the
selection value is placed in the second longword of the item
descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_TERMINAL
When you specify PSCAN$_TERMINAL, $GETJPI returns information that
matches the specified terminal names. The terminal name string is
blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag
PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the
first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is
placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the terminal name field is 8 bytes, the
PSCAN$_TERMINAL buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer
length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_UIC
When you specify PSCAN$_UIC, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the UIC identifier. To convert an alphanumeric
identifier name to the internal identifier, use the $ASCTOID system
service before calling $PROCESS_SCAN.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the
second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be
specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
PSCAN$_USERNAME
When you specify PSCAN$_USERNAME, $GETJPI returns information about
processes that match the specified user name.
The user name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the
item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is
passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the
first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is
placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the user name field is 12 bytes, the
PSCAN$_USERNAME buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer
length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in
Table SYS-48.
Item-Specific Flags