Software > OpenVMS Systems > Documentation > 84final > 4538 HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
OpenVMS Debugger Manual
10.10.4.1 Defining the Key Sequence to Display the Breakpoint Dialog BoxBy default, the key sequence for displaying the dialog box for conditional and action breakpoints is Ctrl/MB1 (see Section 10.4.6 and Section 10.4.7). To define another key sequence, edit the current definition of the following resource in the resource file. For example:
10.10.4.2 Defining the Key Sequence for Language-Sensitive Text SelectionBy default, the key sequence for language-sensitive text selection in the main window and instruction view is Ctrl/MB1 (see Section 10.5.1). To define another key sequence, edit the current definition of the following resource in the resource file. For example:
To avoid conflict with standard HP DECwindows Motif for OpenVMS word selection, do not use a double-click combination, such as Ctrl<Btn1Down>(2). 10.10.4.3 Defining the Font for Displayed TextTo define another font for the text displayed in various debugger windows and views, edit the current definition of the following resources in the resource file. For example:
10.10.4.4 Defining the Key Bindings on the KeypadTo bind a different command to a key that is already associated with a command, edit the current definition of the following resources in the resource file. For example:
To bind a command to a key that is not currently associated with a command, refer to the Keysym Encoding chapter of the X and Motif Quick Reference Guide for key designations. 10.11 Debugging Detached ProcessesYou cannot use the HP DECwindows Motif for OpenVMS user interface to the debugger to debug detached processes, such as print symbionts, which run without a command line interpreter (CLI). To debug a detached process that runs without a CLI, use the character-cell (screen mode) interface to the debugger (see Section 1.11).
Part IV
|
The OpenVMS Version 7.3 debugger does not support previous versions of the PC client. You must install the Version 1.1 PC client that is found in the kit on the OpenVMS Version 7.3 distribution media, as identified in Section 11.2. Version 1.1 PC client is compatible with OpenVMS Version 7.3 and prior debugger servers. |
The debug server runs on OpenVMS systems. The client is the user interface to the debugger, from which you enter debugger commands that are sent to the server. The server executes the commands and sends the results to the client for display. The client runs on Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, and Windows XP.
[DEBUG_CLIENTS011.KIT]DEBUGX86011.EXE
There is no special installation procedure for the components that run on OpenVMS. The system administrator must move the OpenVMS debug client kit listed in the previous section from the OpenVMS distribution media to a place accessible to PC users, such as a PATHWORKS share or an FTP server. The client kit is a self-extracting .EXE file.
Once the appropriate executable file has been transferred to the PC, you can run the file to install the debug client on the PC. The InstallShield installation procedure guides you through the installation.
By default, the debug client is installed in the \Program Files\OpenVMS Debugger folder. You can also click Browse to select an alternate location.
The installation creates an OpenVMS Debugger program folder that contains shortcuts to the following items:
The primary client is the first client to connect to the server. A secondary client is an additional client that has connected to the same server. The primary client controls whether or not any secondary clients can connect to the server.
See Section 11.5 for details about specifying the number of secondary clients allowed to connect to a debugging session.
The PC client workspace is analogous to the workspace of the Motif client (see Chapter 8). The client workspace contains views to display dynamic information and toolbars to contain shortcuts to debugger commands. You can configure the views and toolbars to suit your personal requirements, create your own shortcuts, and save your personal configurations.
These topics are discussed at length in the PC client Help file. You can access the PC client Help directly from the OpenVMS Debugger folder that you created during PC client installation (see Section 11.2), or from the Help menu within the client. See the following topics:
You can start the debug server after logging in directly to the OpenVMS system, or you may find it more convenient to log in remotely with a product such as eXcursion, or a terminal emulator such as Telnet.
You must hold the DBG$ENABLE_SERVER identifier in the rights database to be able to run the debug server. Exercise care when using the debug server. Once a debug server is running, anyone on the network has the ability to connect to the debug server. |
Before granting the DBG$ENABLE_SERVER identifier, the system manager must create it by entering the command DEBUG/SERVER from an account with write access to the rights database. The system manager needs to do this only once. The system manager can then run the Authorize utility to grant the DBG$ENABLE_SERVER identifier to the user.
To start the debug server, enter the following command:
$ DEBUG/SERVER |
The server displays its network binding strings. The server port number is enclosed in square brackets ([]). For example:
$ DEBUG/SERVER %DEBUG-I-SPEAK: TCP/IP: YES, DECnet: YES, UDP: YES %DEBUG-I-WATCH: Network Binding: ncacn_ip_tcp:16.32.16.138[1034] %DEBUG-I-WATCH: Network Binding: ncacn_dnet_nsp:19.10[RPC224002690001] %DEBUG-I-WATCH: Network Binding: ncadg_ip_udp:16.32.16.138[1045] %DEBUG-I-AWAIT: Ready for client connection... |
Use one of the network binding strings to identify this server when you connect from the client (see Section 9.9.4).
You can usually identify the server using only the node name and the port number. For example, nodnam[1034] . |
To establish a connection from the PC client, invoke the Connection dialog, either from the File pull-down menu, or by selecting the C/S button on the Main toolbar. The dialog displays the servers already known to this client, and the sessions currently active by this client.
You can specify a server for a new connection, or select a particular session for use.
From the buttons at the bottom of the dialog, you can
In addition, the Advanced button allows you to select the network protocol to be used (see Section 11.5.1), and to select the number of secondary clients (0-30) allowed for the client/server connection to be established (see Section 11.5.2).
From the Connection dialog, you can enable up to 30 secondary clients to connect to the server. You must be the primary client (the first client to connect to this server), and perform the following steps:
The debugger dismisses the Connection dialog, makes the connection, and indicates success (or failure) in the Command view. You can now begin your debugging procedures.
You can stop a server by entering Ctrl-Y on the node on which the server is running. If you do so, then enter the DCL STOP command.
To stop the server from the client, perform the following steps:
An alternative way to stop the server is to perform the following steps:
To stop both the server and the client, perform the following steps:
To stop only the client, perform the following steps:
To stop only the server, perform the following steps:
The Heap Analyzer, available on OpenVMS Integrity servers and Alpha systems, is a feature of the debugger that provides a graphical representation of memory use in real time. By studying this representation, you can identify areas in your application where memory usage and performance can be improved. For example, you might notice allocations that are made too often, memory blocks that are too large, evidence of fragmentation, or memory leaks.
After you locate an area of interest, you can request an enlarged, more detailed, or altered view. You can also request additional information on the size, contents, or address of the allocations shown.
After you narrow your interest to an individual allocation, you can request traceback information. The analyzer allows you to correlate the traceback entry for an allocation with source code in your application program. By scrolling through the source code display, you can then identify problematic code and decide how to correct it.
This chapter describes the following:
The following sections describe how to invoke the Heap Analyzer and run your application.
You can invoke the Heap Analyzer during a debugging session in one of the following ways:
$ DEFINE/USER/NAME=CONFINE LIBRTL SYS$LIBRARY:LIBRTL_INSTRUMENTED |
$ DEFINE/EXEC/NAME=CONFINE LIBRTL SYS$LIBRARY:LIBRTL_INSTRUMENTED |
$ INSTALL ADD imagename/PROTECTED |
The Heap Analyzer startup and the Heap Analyzer START command on the Integrity servers kept debugger (START HEAP_ANALYZER) hangs for threaded applications with upcalls enabled. In such instances, for threaded or AST-involved applications, HP strongly recommends that you either start the Heap Analyzer before setting up any debug events or after disabling or canceling the debug events. (You can enable/reset events after the Heap Analyzer startup and START returns you to debugger control.) |
After you successfully invoke the Heap Analyzer, the Heap Analyzer startup screen appears.
On OpenVMS Alpha systems, the Heap Analyzer does not work on programs linked with the /NODEBUG qualifier. On OpenVMS Integrity server systems, the Heap Analyzer does work on programs linked with the /NODEBUG qualifier, although the traceback information displayed is minimal. |
The Heap Analyzer contains a main window, six subsidiary windows, and a control panel (see Figure 12-1.)
The Memory Map, the most important window, displays a representation of your application's dynamic memory use. At startup, the Memory Map shows the images that comprise your application. As your application executes, you can see the relative location and size of individual memory blocks, images, program regions, memory zones, and dynamic strings as they are allocated and deallocated in memory space.
The Message window displays information on your Heap Analyzer session. At startup, the Message window contains the message "Heap Analyzer initialization complete. Press Start button to begin program." As your application executes, informational and error messages appear in this window.
The Push Button Control Panel contains buttons that allow you to control the speed of the Memory Map display. At startup, you click on the Start button to begin executing your application. As your application executes, you can click on other buttons in the panel to pause, slow, or otherwise affect the continuous display.
The Information window displays information on Memory Map segments. As your application executes, you can pause execution at any time to request specific information.
The Source window displays the application source code associated with a segment in the Memory Map.
The Do-not-use Type List allows you to adjust the Memory Map display by redetermining a segment's type, or group name.
The Views-and-Types Display allows you to adjust the Memory Map display by selectively viewing certain segment types.
The Type Histogram displays summary and statistical information on segment types.
As you use the Heap Analyzer, you may need to increase or decrease the size of the window in which you are working. To do this, pull the window pane sashes between windows or resize the screen as a whole.
Figure 12-1 Heap Analyzer Windows
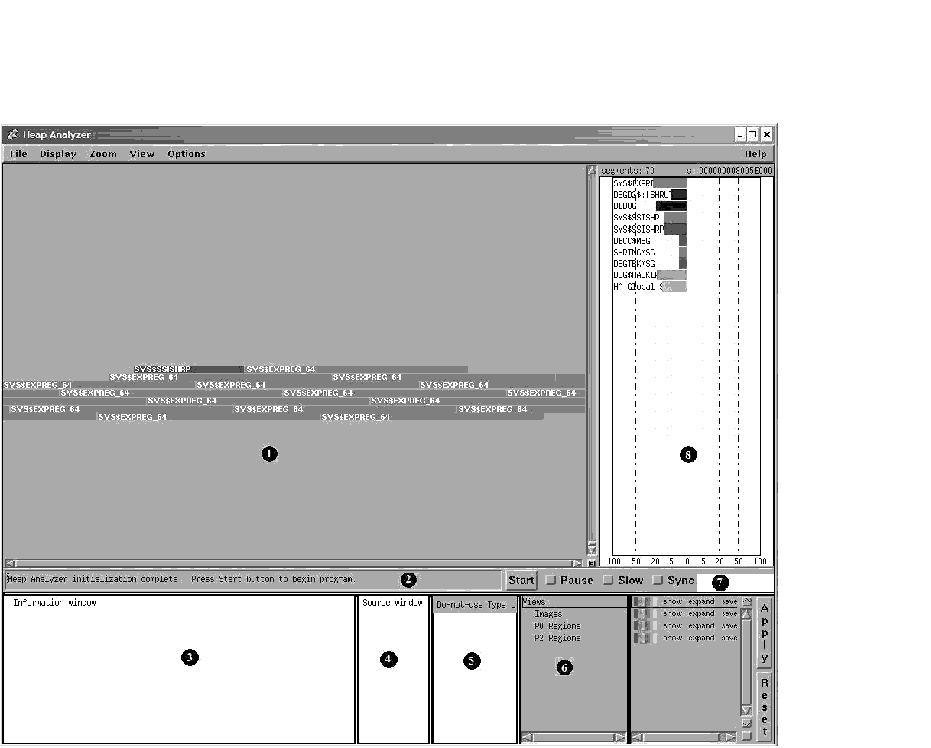
| 1. Memory Map | Shows the graphical representation of memory, that is, the part of P0-space that is in use. Each allocation appears as a colored strip, or segment. |
| 2. Message Window | Displays Heap Analyzer informational and error messages and one-line segment descriptions. |
| 3. Information Window | Shows additional information on segments and segment types that appear in the Memory Map. |
| 4. Source Window | Shows application source code. |
| 5. Do-not-use Type List | Lists routines not used as segment types, the name that characterizes segments. |
| 6. Views-and-Types Display | Lists all segment types known to the Heap Analyzer and allows you to alter the segment display. |
| 7. Push Button Control Panel | Provides Start/Step, Pause, Slow, and Sync buttons that allow you to control the speed of Memory Map display. |
| 8. Type Histogram | Shows statistics on segment size and use. |
Figure 12-2 Heap Analyzer Pull-Down Menus
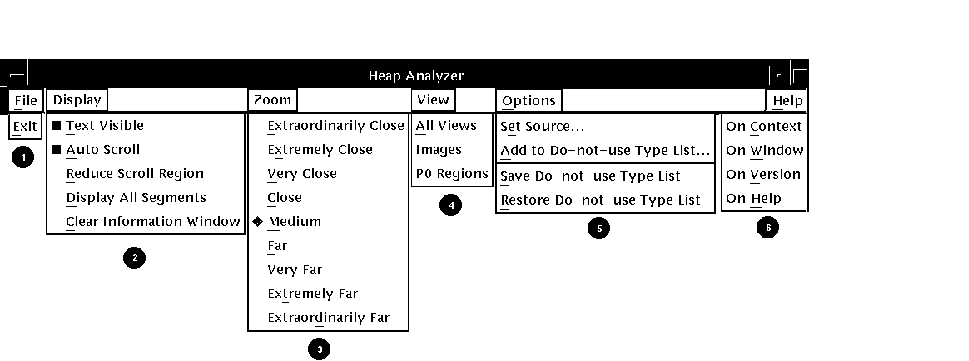
| 1. File Menu | Allows you to exit from the Heap Analyzer |
| 2. Display Menu | Allows you to adjust the Memory Map display and to clear the Information window |
| 3. Zoom Menu | Provides a closer or further view of the Memory Map |
| 4. View Menu | Lets you select the granularity of the display |
| 5. Options Menu | Allows you to indicate a search directory list or to adjust the Do-not-use Type List |
| 6. Help Menu | Provides context-sensitive or task-oriented online help |
Figure 12-3 Heap Analyzer Context-Sensitive Pop-Up Menus
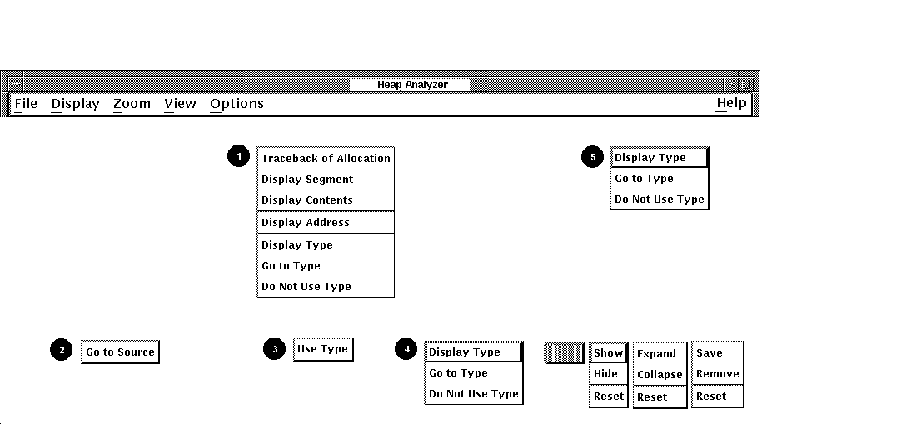
| 1. Memory Map Pop-Up | Provides additional information on segments displayed in the Memory Map, allows you to jump to a segment's type in the Views-and-Types Display, or adds a segment's type to the Do-not-Use Type List. |
| 2. Information Window Pop-Up | Allows you to jump from a line of traceback displayed in the Information window to the related source code in the Source window. |
| 3. Do-not-use Type List Pop-Up | Deletes a segment's type from the Do-not-Use Type List. |
| 4. Views-and-Types Display Pop-Up |
Left side: Provides additional information on segment types listed,
highlights a segment type within the Views-and-Types Display, or adds a
segment type to the Do-not-Use Type List.
Right side: Allows you to adjust display characteristics for the segment type highlighted in the left side of the Views-and-Types Display. |
| 5. Type Histogram Pop-Up | Provides additional information on segment types listed, highlights a segment type in the Type Histogram, or adds the segment type to the Do-not-Use Type List. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |