 |
HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference
Manual
SHOW LAN_DEVICE
Displays PEdriver device data. Each device is a local LAN device on the
system, which can be used for NISCA communications.
Format
SHOW LAN_DEVICE landevicename
Parameter
landevicename[,...]
Includes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the /EXCLUDE qualifier to exclude LAN devices.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
Qualifiers
/ALL
Includes all device data.
/COUNTERS
Includes device counters data maintained by PEdriver and counters data
maintained by the LAN drivers.
/EXCLUDE=(landevicename[,...])
Excludes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
/INTERVAL
For the /COUNTERS display, displays the changes to counters since the
last SHOW command.
/n
Displays the nth page. To select a particular page of a
multipage display, specify the number of the page you want to display.
/OUTPUT=filespec
Creates the specified file and directs output to it.
/SDA
Includes LAN device data displayed in SDA format, with all the data
collected in one display for one LAN device.
/SUMMARY
Includes device summary data. This is the default if /ALL, /COUNTERS,
and /SDA qualifiers are not specified.
Example
|
SCACP> SHOW LAN_DEVICE/COUNTERS
|
The command in this example displays device counters.
|
SCACP> SHOW LAN_DEVICE/COUNTERS/INTERVAL
SCACP> SPAWN WAIT 0:0:10
SCACP> SHOW LAN_DEVICE/COUNTERS/INTERVAL
|
The first command in this example displays device counters since the
last SHOW command. The SPAWN command tells the DCL WAIT command to
insert a 10-second delay. The second SHOW command displays counters
after the 10-second period.
|
SCACP> SHOW LAN_DEVICE/COUNTERS
|
The following is a snapshot of the output for SHOW LAN/ALL command.
Figure 21-6 Sample SHOW LAN/ALL output
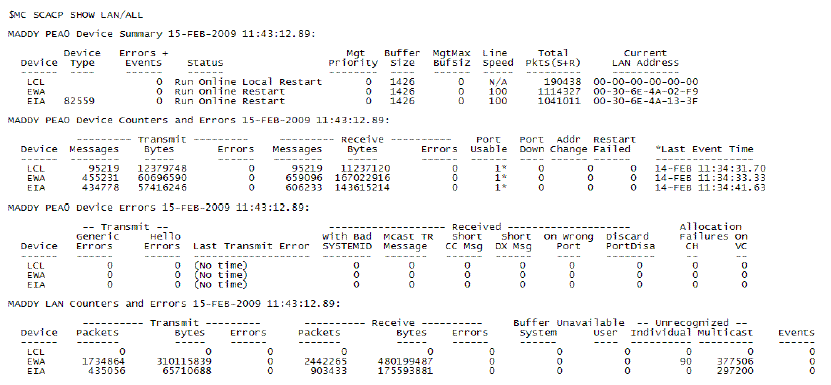
For list of all LAN errors, see Table 21-3.
Displays information about selected SCA ports.
Format
SHOW PORT portname
Parameter
portname[,...]
Displays information about specific SCA ports, which you can use
wildcards to specify. If no portname is specified, all ports on the
node are displayed.
Qualifiers
/EXCLUDE=(portname[,...])
Excludes specific port names from the display. You cannot use wildcards
to specify port names.
/OUTPUT=filespec
Creates the specified file and directs the output of the command to
this file.
Example
The command in this example produces output similar to the following:
Port data for CLUIO2 at 06-DEC 15:01:25.82
Port Mgt Msgs Msgs Dgrams Dgrams
Name Prio Sent Rcvd Sent Rcvd
------ ---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
PEA0 0 64582 92237 0 0
PIB0 0 95276 148937 0 0
PIA0 0 0 0 0 0
PIC0 0 62030 115148 0 0
|
SHOW TRACE
Displays PEdriver tracing data and parameters.
Note
This command is reserved for use by HP Services and OpenVMS Engineering
only. Trace commands and output are subject to change from release to
release.
|
Format
SHOW TRACE nodename
Parameter
nodename[,...]
Includes channels to specific nodes, which you can use wildcards to
specify.
Each node name can be accompanied by optional qualifiers to specify
local and remote device names. If no local or remote device name is
specified, all channels associated with the specified node are included.
Use the SHOW CHANNEL command to display node names and local and remote
device names.
Qualifiers
/CONTEXT
Displays only PEdriver trace settings and the event definition. If this
qualifier is not included, trace event data is displayed.
/EVENT=(event1[,...])
Enables tracing on specific events, which you can use wildcards to
specify. The default is all of the events that are in the trace buffer.
Use the SHOW TRACE/CONTEXT command to display event names.
/EXCLUDE[=(nodename[,...])
Excludes channels to specific nodes, which you can use wildcards to
specify. Each node name can be accompanied by optional qualifiers to
specify local and remote device names.
If no local or remote device name is specified, all channels associated
with the specified node are included.
/GLOBAL (default when no nodes are specified)
/NOGLOBAL (default when nodes are specified)
Specifies whether or not global trace data is to be returned.
/INPUT=filename
Reads trace data from the specified file and displays it.
/LOCAL_DEVICE=(landevicename[,...])
Includes specific LAN devices that identify the local end of the
channel. You can use wildcards to specify LAN devices.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
/OUTPUT=filename
Creates the specified file and directs output to it. If the filename
extension is .DMP, the trace data is written to a dump file so that you
can use the /INPUT qualifier to display it later.
/REMOTE_DEVICE=(landevicename[,...])
Includes specific LAN devices which identify the remote end of the
channel, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
/SORT
/NOSORT (default)
Returns trace data sorted across channels, VCs, and the global trace
buffer by sequence number. The default is trace data returned for
channels and VCs one at a time, in order, for the channel or VC, but
not across channels and VCs.
Examples
| #1 |
SCACP> SHOW TRACE/CONTEXT
|
The command in this example displays trace settings and definition.
| #2 |
SCACP> SHOW TRACE/OUTPUT=NODE10.TRC
|
The command in this example displays trace data and writes it to the
specified file.
An example of the screen output of a SHOW TRACE/CONTEXT command follows.
SYS999 Trace Context 31-JAN-2001 10:59:28.25:
Trace buffer size requested 2048 bytes
Trace buffer total allocated 92160 bytes
Trace buffer allocations 45 successful
Trace buffer allocations 0 failed
Current trace sequence number 812286047
System cycle counter 404196 cps
Stop tracing 0 events after stop event
Trace Stop Default Event
----- ---- ------- -----
Active Y Error
Active Penalize_ch
Active Timer
Active Listen_timr
Active Handsh_timr
Active Size_probe
Active Delay_msmt
Active Verf_vack
Active Y CC_event
Active Y CC_state
Active Y Path_state
Active Y ECS_state
Active ACK_process
Active Y Chan_update
Active Rcvd_CC_msg
Active Rcvd_TR_msg
Active Send_TR_msg
Active Xmt_failed
Active Y VC_state
Active ACK_timeout
Active Y TMO_listen
Y No_path
Channel Selection:
Local Dev Remote Dev Remote Node Name Selection
--------- ---------- ---------------- ---------
All channels and VCs selected
|
SHOW VC
Displays PEdriver virtual circuit data. Each VC is an SCACP
communications path between the local system and a remote system
comprised of a set of channels.
Use the SHOW CHANNEL or SHOW VC commands to display node names, which
are simply the names of the remote nodes.
Format
SHOW VC nodename
Parameter
nodename[,...]
Includes specific nodes, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Qualifiers
/ALL
Includes all VC data.
/COUNTERS
Includes VC counter data.
/EXCLUDE=(nodename[,...])
Excludes specific nodes, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the SHOW CHANNEL or SHOW VC commands to display VC names, which are
simply the names of the remote nodes.
/INTERVAL
For the /COUNTERS display, displays the changes to counters since the
last SHOW command.
/n
Displays the nth page. To select a particular page of a
multipage display, specify the number of the page you want to display.
/OUTPUT=filespec
Creates the specified file and directs output to it.
/SDA
Includes VC data displayed in SDA format.
/SUMMARY
Includes VC summary data. This is the default if /ALL, /COUNTERS, and
/SDA qualifiers are not specified.
Examples
| #1 |
SCACP> SHOW VC/COUNTERS NODE10
|
The command in this example displays VC counters for all VCs whose name
(that is, remote node name) starts with NODE10.
| #2 |
SCACP> SHOW VC/COUNTERS/INTERVAL
SCACP> SPAWN WAIT 0:0:10
SCACP> SHOW VC/COUNTERS/INTERVAL
|
The first command in this example displays VC counters since the last
SHOW command. The SPAWN command tells the DCL WAIT command to insert a
10-second delay. The second SHOW VC command displays counters after the
10-second period.
SPAWN
Creates a subprocess of the current process. The SPAWN command copies
the context of the subprocess from the current process.
Format
SPAWN [command-string]
Parameter
command-string
A string of commands to be executed in the context of the created
subprocess. After the command string is executed, control returns to
SCACP.
Qualifiers
None.
Example
|
SCACP> SPAWN SHOW TIME
24-AUG-2005 15:22:39
SCACP>
|
The command in this example creates a subprocess of the current process
and displays the time.
START IP_INTERFACE
Directs PEdriver to start using the specified IP interface.
Format
START IP_INTERFACE ipinterface
Parameter
ipinterface[,...]
Includes specific IP interfaces, which you can use wildcards to specify.
- Use the /EXCLUDE qualifier to exclude IP interfaces.
- Use the SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display IP interfaces.
Qualifiers
/EXCLUDE=(ipinterface[,...])
Excludes specific IP interface, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display IP interface names.
Example
|
SCACP> START IP_INTERFACE WE0
|
This command starts PEdriver on the IP interface WE0.
START LAN_DEVICE
Directs PEdriver to start using the specified LAN device. The original
(and still supported) way to start PEdriver on a LAN device is
SYS$EXAMPLES:LAVC$START_BUS.
Format
START LAN_DEVICE landevicename
Parameter
landevicename[,...]
Includes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the /EXCLUDE qualifier to exclude LAN devices.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
Qualifiers
/EXCLUDE=(landevicename[,...])
Excludes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
Example
|
SCACP> START LAN_DEVICE EWA
|
This command starts PEdriver on the LAN device EWA.
START TRACE
Starts or resumes PEdriver tracing, optionally setting tracing options.
Note
This command is reserved for use by HP Services and OpenVMS Engineering
only. Trace commands, their qualifiers, and output are subject to
change from release to release.
|
Format
START TRACE nodename
Parameter
nodename[,...]
Includes information about communications with specific nodes, which
you can use wildcards to specify. Each node name can be accompanied by
optional qualifiers to specify local and remote device names.
If no local or remote device name is specified, the VC and all channels
associated with the specified node are included.
Use the SHOW CHANNEL command to display node names and local and remote
device names.
Qualifiers
/AFTER=n
After the trace stop condition has been satisfied, continues tracing
for n events, and then stops. If you do not specify /AFTER,
tracing does not continue after the trace stop event. n can be
any value between 0 and FFFFFFF.
/DEFAULT
Sets the trace context back to the default settings, which are:
channelname=*
/AFTER=0
/EVENT=default settings
/STOP
/SIZE=512
|
/EVENT=(event1[,...])
Enables tracing on specific events, which you can use wildcards to
specify. The default is a subset of the events, which includes most
errors and state changes.
Use the SHOW TRACE/CONTEXT command to display event names.
/EXCLUDE=(landevicename/IPinterface[,...])
Excludes specific LAN devices/IP interfaces, which you can use
wildcards to specify.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE/SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display device
names.
/LOCAL_DEVICE=(landevicename/IPinterface[,...])
Includes specific LAN devices that identify the local end of the
channel. You can use wildcards to specify LAN devices/IP interfaces.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE/SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display device
names.
/REMOTE_DEVICE=(landevicename/IPinterface[,...])
Includes specific LAN devices that identify the remote end of the
channel. You can use wildcards to specify LAN devices/IP interfaces.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE/SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display device
names.
/STOP=(event[,...])
Stops tracing on specific events, which you can use wildcards to
specify. The default is to stop no events.
Use the SHOW TRACE/CONTEXT command to display event names.
/SIZE=n
Specifies a trace buffer size of n bytes to be used by
PEdriver for each trace buffer: one for global PEdriver use, one for
each selected channel, and one for each selected VC. n can be
any value between 0 and FFFFFFF.
Examples
| #1 |
SCACP> START TRACE/EVENT=CC_STATE/SIZE=2000
|
The command in this example changes the Trace Channel Control layer
state with a 2000-byte trace buffer.
| #2 |
SCACP> START TRACE/EVENT=ALL NODE10,NODE20
|
The command in this example traces all events but only for the NODE10
and NODE20 channels.
STOP IP_INTERFACE
Directs PEdriver to stop using the specified IP interface.
Caution
If you use STOP IP_INTERFACE to stop the only connection you have to a
cluster, it results in a system CLUEXIT. If you use STOP IP_INTERFACE
to stop the only the connection, connected to a cluster, the system
will CLUEXIT even when you have another connection that uses a
different cluster port. However, if you stop all the IP_INTERFACE
results in excessive activity. When PEdriver loses access to all of its
IP interfaces, it makes an effort to restore cluster IP interfaces
communications by completely re-initializing itself. After the
displayed retry count is exceeded, PEdriver permanently goes offline.
To disable cluster use of all but one IP interface, enter the following
command:
SCACP> STOP IP_INTERFACE * /EXCLUDE=ipinterface
All IP interfaces are stopped except the excluded interface and
PEdriver does not need to be reset.
|
Format
STOP IP_INTERFACE ipinterface[,...]
Parameter
ipinterface[,...]
Includes specific IP interface, which you can use wildcards to specify.
- Use the /EXCLUDE qualifier to exclude IP interfaces.
- Use the SHOW IP_INTERFACE command to display IP interface names.
Qualifiers
/EXCLUDE=(ipinterface[,...])
Excludes specific IP interface, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Example
|
SCACP> STOP IP_INTERFACE WE0
|
This command stops PEdriver on the IP interface WE0.
STOP LAN_DEVICE
Directs PEdriver to stop using the specified LAN device. The original
(and still supported) way to stop PEdriver on a LAN device is
SYS$EXAMPLES:LAVC$STOP_BUS.
Caution
If you use either STOP LAN_DEVICE or SYS$EXAMPLES:LAVC$STOP_BUS to stop
the only connection you have to a cluster, you cause the system to
CLUEXIT.
Even when you have have another connection using a different cluster
port, stopping all LAN devices results in excessive activity. When
PEdriver loses access to all of its LAN devices, it makes an effort to
restore cluster communications by completely re-initializing itself.
After the last LAN device is stopped, the reinitilization produces an
error message similar to the following:
SCACP> STOP LAN *
;%PEA0, Port is Reinitializing ( 49 Retries Left). Check the Error Log.
|
After the displayed retry count is exceeded, PEdriver permanently goes
offline.
To disable cluster use of all but 1 LAN device, enter the following
command:
SCACP> STOP LAN * /EXCLUDE=landevicename
|
All LAN devices except the excluded device are stopped, and PEdriver
does not need to be reset.
|
Format
STOP LAN_DEVICE landevicename
Parameter
landevicename[,...]
Includes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Use the /EXCLUDE qualifier to exclude LAN devices.
Use the SHOW LAN_DEVICE command to display device names.
Qualifier
/EXCLUDE=(landevicename[,...])
Excludes specific LAN devices, which you can use wildcards to specify.
Example
|
SCACP> STOP LAN_DEVICE EWA
|
This command stops PEdriver on the LAN device EWA.
STOP TRACE
Stops PEDRIVER tracing. You can read the trace data recorded so far
with a SHOW TRACE command.
To revert trace behavior to initial settings, enter the command SET
TRACE/DEFAULT.
Note
This command is reserved for use by HP Services and OpenVMS Engineering
only. Trace commands and output are subject to change from release to
release.
|
Format
STOP TRACE
Parameters
None.
Qualifiers
None.
Example
The command in this example stops PEDRIVER tracing.
|
