 |
HP OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual
SHOW PARAMETER
Displays the name, location, and value of one or more SYSGEN parameters
currently in use or at the time that the system dump was taken.
Format
SHOW PARAMETER [sysgen_parameter]
[/ACP] [/ALL] [/CLUSTER]
[/DYNAMIC] [/GALAXY] [/GEN] [/JOB] [/LGI] [/MAJOR] [/MULTIPROCESSING]
[/OBSOLETE] [/PQL] [/RMS] [/SCS] [/SPECIAL] [/SYS] [/STARTUP] [/TTY]
Parameter
sysgen_parameter
The name of a specific parameter to be displayed. The name can include
wildcards. However, a truncated name is not recognized, unlike with the
equivalent SYSGEN and SYSMAN commands.
Qualifiers
/ACP
Displays all Files-11 ACP parameters.
/ALL
Displays the values of all parameters except the special control
parameters.
/CLUSTER
Displays all parameters specific to clusters.
/DYNAMIC
Displays all parameters that can be changed on a running system.
/GALAXY
Displays all parameters specific to Galaxy systems.
/GEN
Displays all general parameters.
/JOB
Displays all Job Controller parameters.
/LGI
Displays all LOGIN security control parameters.
/MAJOR
Displays the most important parameters.
/MULTIPROCESSING
Displays parameters specific to multiprocessing.
/OBSOLETE
Displays all obsolete system parameters. SDA displays obsolete
parameters only if they are named explicitly (no wildcards) or if
/OBSOLETE is given.
/PQL
Displays the parameters for all default and minimum process quotas.
/RMS
Displays all parameters specific to OpenVMS Record Management Services
(RMS).
/SCS
Displays all parameters specific to OpenVMS Cluster System
Communications Services.
/SPECIAL
Displays all special control parameters.
/STARTUP
Displays the name of the site-independent startup procedure.
/SYS
Displays all active system parameters.
/TTY
Displays all parameters for terminal drivers.
Description
The SHOW PARAMETER command displays the name, location, and value of
one or more SYSGEN parameters at the time that the system dump is
taken. You can specify either a parameter name, or one or more
qualifiers, but not both a parameter and qualifiers. If you do not
specify a parameter or qualifiers, then the last parameter displayed is
displayed again.
The qualifiers are the equivalent to those available for the SHOW
[parameter] command in the SYSGEN utility and the PARAMETERS SHOW
command in the SYSMAN utility. See the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for more
information about these two commands. You can combine qualifiers, and
all appropriate SYSGEN parameters are displayed.
Note
To see the entire set of parameters, use the SDA command SHOW PARAMETER
/ALL /SPECIAL /STARTUP /OBSOLETE.
|
Examples
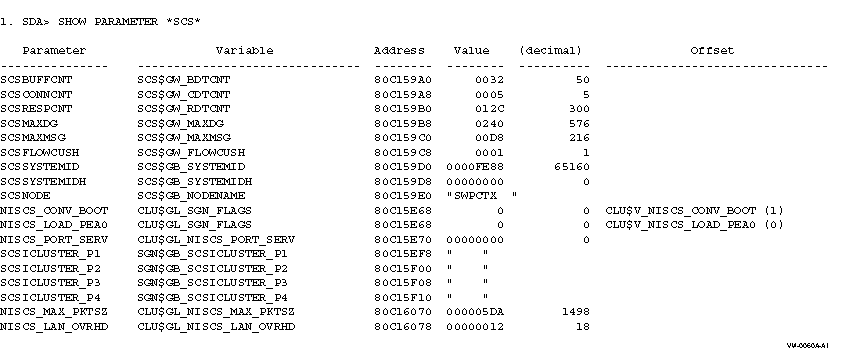
This example shows all parameters that have the string "SCS" in their
name. For parameters defined as a single bit, the name and value of the
bit offset within the location used for the parameter are also given.

This example shows all parameters whose names begin with the string
"WS". For parameters that have both an external value (pagelets) and an
internal value (pages), both are displayed.
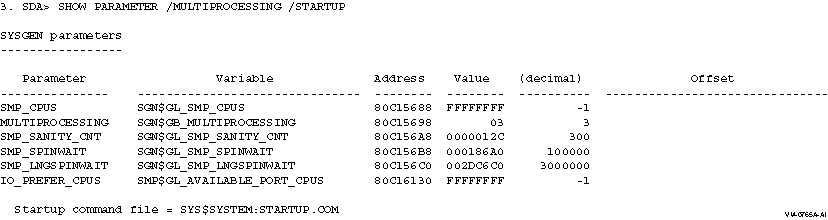
This example shows all the parameters specific to multiprocessing, plus
the name of the site-independent startup command procedure.
SHOW PFN_DATA
Displays information that is contained in the page lists and PFN
database.
Format
SHOW PFN_DATA { [/qualifier] | pfn [{:end-pfn|;length}] }
or
SHOW PFN_DATA/MAP
Parameters
pfn
Page frame number (PFN) of the physical page for which information is
to be displayed.
end-pfn
Last PFN to be displayed. When you specify the end-pfn
parameter, a range of PFNs is displayed. This range starts at the PFN
specified by the pfn parameter and ends with the PFN
specified by the end-pfn parameter.
length
Length of the PFN list to be displayed. When you specify the
length parameter, a range of PFNs is displayed. This
range starts at the PFN specified by the pfn parameter
and contains the number of entries specified by the
length parameter.
Qualifiers
/ADDRESS=PFN-entry-address
Displays the PFN database entry at the address specified. The address
specified is rounded to the nearest entry address, so if you have an
address that points to one of the fields of the entry, the correct
database entry will still be found.
/ALL
Displays the following lists:
Free page list
Zeroed free page list
Modified page list
Bad page list
Untested page list
Private page lists, if any
Per-color or per-RAD free and zeroed free page lists
Entire database in order by page frame number
This is the default behavior of the SHOW PFN_DATA command. SDA precedes
each list with a count of the pages it contains and its low and high
limits.
/BAD
Displays the bad page list. SDA precedes the list with a count of the
pages it contains, its low limit, and its high limit.
/COLOR [= {n|ALL} ]
Displays data on page coloring. Table 4-14 shows the command options
available with the COLOR and RAD qualifiers, which are functionally
equivalent.
Table 4-14 Command Options with the /COLOR and /RAD Qualifiers
| Options |
Meaning |
|
/COLOR
1 with no value
|
Displays a summary of the lengths of the color
1 page lists for both free pages and zeroed pages.
|
|
/COLOR=
n where
n is a color number
|
Displays the data in the PFN lists (for the specified color) for both
free and zeroed pages.
|
|
/COLOR=ALL
|
Displays the data in the PFN lists (for all colors), for both free and
zeroed free pages.
|
|
/COLOR=
n or /COLOR=ALL with /FREE or /ZERO
|
Displays only the data in the PFN list (for the specified color or all
colors), for either free or zeroed free pages as appropriate. The
qualifiers /BAD and /MODIFIED are ignored with /COLOR=
n and /COLOR=ALL.
|
|
/COLOR without an option specified together with one or more of /FREE,
/ZERO, /BAD, or /MODIFIED
|
Displays the color summary in addition to the display of the requested
list.
|
1Wherever COLOR is used in this table, RAD is equally
applicable, both in the qualifier name and the meaning.
For more information on page coloring, see HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual: M--Z.
/FREE
Displays the free page list. SDA precedes the list with a count of the
pages it contains, its low limit, and its high limit.
/MAP
Displays the contents of the PFN memory map. On platforms that support
it, the I/O space map is also displayed. You cannot combine the /MAP
qualifier with any parameters or other qualifiers.
/MODIFIED
Displays the modified page list. SDA precedes the list with a count of
the pages it contains, its low limit, and its high limit.
/PRIVATE [=address]
Displays private PFN lists. If no address is given, all private PFN
lists are displayed; if an address is given, only the PFN list whose
head is at the given address is displayed.
/RAD [= {n|ALL} ]
Displays data on the disposition of pages among the Resource Affinity
Domains (RADs) on applicable systems. /RAD is functionally equivalent
to /COLOR. See Table 4-14 for the command options available with
/RAD.
/SUMMARY[=(option,...)]
By default, displays a summary of all pages in the system, totaling
pages by page location (Free List, Modified List, Active, and so on)
and by page type (Process, System, Global, and so on). Also, provides a
breakdown of active system pages by their virtual address (S0/S1, S2,
and so on).
Additional information is displayed if one or more options are given.
If multiple options are given, they must be separated by commas and
enclosed in parentheses. Available options are:
- /SUMMARY=PROCESS
Displays a breakdown of active process pages
for each process by virtual address (P0, P1, and so on), and of
non-active process pages by page location.
- /SUMMARY=GLOBAL
Displays a breakdown for each global section
of its in-memory pages by page location.
- /SUMMARY=RAD
If RADs are enabled on the system, displays a
breakdown for each RAD of its in-memory pages by location and type.
- /SUMMARY=ALL
Equivalent to /SUMMARY=(PROCESS,GLOBAL,RAD)
You cannot combine the /SUMMARY qualifier with any other qualifiers,
but you can specify a range.
/SYSTEM
Displays the entire PFN database in order by page frame number,
starting at PFN 0000.
/UNTESTED
Displays the state of the untested PFN list that was set up for
deferred memory testing.
/ZERO
Displays the contents of the zeroed free page list.
Description
For each page frame number it displays, the SHOW PFN_DATA command lists
information used in translating physical page addresses to virtual page
addresses.
The display contains two or three lines: Table 4-15 shows the fields
in line one, Table 4-16 shows the fields in line two, and
Table 4-17 shows the fields in line three, displayed only if
relevant (page table page or non-zero flags).
Table 4-15 PFN Data---Fields in Line One
| Item |
Contents |
|
PFN
|
Page frame number.
|
|
DB ADDRESS
|
Address of PFN structure for this page.
|
|
PT PFN
|
PFN of the page table page that maps this page.
|
|
BAK
|
Place to find information on this page when all links to this PTE are
broken: either an index into a process section table or the number of a
virtual block in the paging file.
|
|
FLINK
|
Forward link within PFN database that points to the next physical page
(if the page is on one of the lists: FREE, MODIFIED, BAD, or ZEROED);
this longword also acts as the count of the number of processes that
are sharing this global section.
|
|
BLINK
|
Backward link within PFN database (if the page is on one of the lists:
FREE, MODIFIED, BAD, or ZEROED); also acts as an index into the working
set list.
|
|
SWP/BO
|
Either a swap file page number or a buffer object reference count,
depending on a flag set in the page state field.
|
|
LOC
|
Location of the page within the system. Table 4-13 shows the
possible locations with their meaning.
|
Table 4-16 PFN Data---Fields in Line Two
| Item |
Contents |
|
(Blank)
|
First field of line two is left blank.
|
|
PTE ADDRESS
|
Virtual address of the page table entry that describes the virtual page
mapped into this physical page. If no virtual page is mapped into this
physical page then "<no backpointer>" is displayed, and the next
three fields are left blank.
|
|
PTE Type
|
If a virtual page is mapped into this physical page, a description of
the type of PTE is provided across the next three fields: one of
"System-space PTE", "Global PTE (section index
nnnn)", "Process PTE (process index
nnnn)". If no virtual page is mapped into this physical page,
these fields are left blank.
|
|
REFCNT
|
Number of references being made to this page.
|
|
PAGETYP
|
Type of physical page. See Table 4-12 for the types of physical
pages and their meanings.
|
Table 4-17 PFN Data---Fields in Line Three
| Item |
Contents |
|
COUNTS
|
If the page is a page table page, then the contents of the
PRN$W_PT_VAL_CNT, PFN$W_PT_LCK_CNT, and PFN$W_PT_WIN_CNT fields are
displayed. The format is as follows:
VALCNT =
nnnn LCKCNT =
nnnn WINCNT =
nnnn
|
|
FLAGS
|
The flags in text form that are set in page state. Table 4-18 shows
the possible flags and their meaning.
|
Table 4-18 Flags Set in Page State
| Flag |
Meaning |
|
BUFOBJ
|
Set if any buffer objects reference this page
|
|
COLLISION
|
Indicates an empty collision queue when page read is complete
|
|
BADPAG
|
Indicates a bad page
|
|
RPTEVT
|
Indicates a report event on I/O completion
|
|
DELCON
|
Indicates a delete PFN when REFCNT=0
|
|
MODIFY
|
Indicates a dirty page (modified)
|
|
UNAVAILABLE
|
Indicates PFN is unavailable; most likely a console page
|
|
SWPPAG_VALID
|
Indicated swap file page number is valid
|
|
TOP_LEVEL_PT
|
Level one (1) page table
|
|
SLOT
|
Page is part of process's balance set
|
|
SHARED
|
Shared memory page
|
|
ZEROED
|
Shared memory page that has been zeroed
|
Examples
| #1 |
SDA> SHOW PFN_DATA/MAP
System Memory Map
-----------------
Start PFN PFN count Flags
--------- --------- -----
00000000 000000FA 0009 Console Base
000000FA 00003306 000A OpenVMS Base
00003C00 000003FF 000A OpenVMS Base
00003FFF 00000001 0009 Console Base
00003400 00000800 0010 Galaxy_Shared
|
This example shows the output when you invoke the SHOW PFN/MAP command.
| #2 |
SDA> SHOW PFN 598:59f
PFN data base for PFN range
---------------------------
PFN DB ADDRESS PT PFN BAK FLINK BLINK SWP/BO LOC
PTE ADDRESS REFCNT PAGETYP
----------------- ----------------- ----------------- ----------------- ----------------- ----------------- ------ -------
00000000.00000598 FFFFF802.06C16600 00000000.000001D7 FFFFFFFF.84D6F700 00000000.00000000 00000000.00000000 ---- ACTIVE
FFFFF801.FFD072A0 System-space PTE 0001 SYSTEM
00000000.00000599 FFFFF802.06C16640 00000000.00000000 00000000.0001DBD9 00000000.0001DBD9 00000000.000081B6 ---- FRELST
<no backpointer> 0000 SYSTEM
00000000.0000059A FFFFF802.06C16680 00000000.00000565 FF000000.00000000 00000000.00000000 00000000.000000D4 ---- ACTIVE
000007FF.FF700000 Process PTE (process index 001A) 0001 PROCESS
FLAGS = Modify
00000000.0000059B FFFFF802.06C166C0 00000000.0000493A 000000FD.00010000 00000000.00000003 00000000.00000000 ---- ACTIVE
FFFFF802.0F641680 Global PTE (section index 00FD) 0001 GLOBAL
00000000.0000059C FFFFF802.06C16700 00000000.000005E3 FF000000.00000000 00000000.00000000 00000000.00000136 ---- ACTIVE
000007FE.00001C30 Process PTE (process index 000F) 0001 PROCESS
00000000.0000059D FFFFF802.06C16740 00000000.0000059D 00000000.8705A000 00000000.00000002 00000000.00000001 ---- ACTIVE
000007FF.FFFFFFF8 Process PTE (process index 0005) 0001 PPT(L1)
VALCNT = 0002 LCKCNT = FFFF WINCNT = FFFF FLAGS = Modify,Top_Level_PT
00000000.0000059E FFFFF802.06C16780 00000000.000001D7 FFFFFFFF.84D6F700 00000000.00000000 00000000.00000000 ---- ACTIVE
FFFFF801.FFD07420 System-space PTE 0001 SYSTEM
00000000.0000059F FFFFF802.06C167C0 00000000.000001D7 FFFFFFFF.84D6F700 00000000.00000000 00000000.00000000 ---- ACTIVE
FFFFF801.FFD07428 System-space PTE 0001 SYSTEM
|
This example shows the output from SHOW PFN for a range of pages.
|


