 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$AUDIT_EVENTW
Determines whether a security-related event should be reported. If the
event should be reported, the service sends the event report to the
audit server.
The $AUDIT_EVENTW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns
only after receiving an explicit confirmation from the audit server
that the associated audit, if enabled, has been performed.
For asynchronous completion, use the Audit Event ($AUDIT_EVENT)
service. In all other respects, $AUDIT_EVENTW is identical to
$AUDIT_EVENT. For additional information about $AUDIT_EVENTW, refer to
the $AUDIT_EVENT service.
Format
SYS$AUDIT_EVENTW efn ,[flags] ,itmlst ,audsts ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$audit_eventw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, void
*itmlst, unsigned int *audsts, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int
astprm);
$AVOID_PREEMPT
Requests that the EXEC avoid preempting the calling process or thread.
Format
SYS$AVOID_PREEMPT enable
C Prototype
int sys$avoid_preempt (int enable);
Arguments
enable
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Enables or disables preemption avoidance. If the
enable argument is set to 1, preemption avoidance is
enabled; if 0, preemption avoidance is disabled.
Description
The Avoid Process Preemption service is a caller's mode service that
sets a thread-specific bit that informs the scheduler that this thread
desires to avoid preemption. Before setting the bit, it checks if the
process or thread has already benefited from preemption avoidance
during this time on the processor, and if it has, calls the $RESCHED
system service to give up the processor.
If quantum end is reached when this bit is set, the scheduler will
"borrow" the next quantum for this process or thread. It will
give the process or thread another quantum immediately and allow it to
resume execution. The next time that the process or thread is eligible
for scheduling, it will be placed at the end of the scheduling queue
without any execution time, skipping its next quantum.
If another process or thread of the same base priority attempts to
preempt a process or thread that has this bit set, this preemption can
be avoided if the process had the ALTPRI privilege when the
$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT service was called. In this case, the priority of
the current thread is boosted to the same level as the thread
attempting preemption, denying the attempted preemption.
Required Access or Privileges
ALTPRI
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$RESCHED, $SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
$BINTIM
Converts an ASCII string to an absolute or delta time value in the
system 64-bit time format suitable for input to the Set Timer ($SETIMR)
or Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$BINTIM timbuf ,timadr
C Prototype
int sys$bintim (void *timbuf, struct _generic_64 *timadr);
Arguments
timbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
time_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Buffer that holds the ASCII time to be converted. The
timbuf argument specifies the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character
string descriptor pointing to the time string. The time string
specifies the absolute or delta time to be converted by $BINTIM. The
data type table describes the time string.
timadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Time value that $BINTIM has converted. The timadr
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of the quadword system time, which receives
the converted time.
Description
The Convert ASCII String to Binary Time service converts an ASCII
string to an absolute or delta time value in the system 64-bit time
format suitable for input to the Set Timer ($SETIMR) or Schedule Wakeup
($SCHDWK) service. The service executes at the access mode of the
caller and does not check whether address arguments are accessible
before it executes. Therefore, an access violation causes an exception
condition if the input buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read or
the output buffer cannot be written.
This service does not check the length of the argument list and
therefore cannot return the SS$_INSFARG (insufficient arguments) error
status code. If the service does not receive enough arguments (for
example, if you omit required commas in the call), errors can result.
The required ASCII input strings have the following format:
- Absolute Time: dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss.cc
- Delta Time: dddd hh:mm:ss.cc
The following table lists the length (in bytes), contents, and range of
values for each field in the absolute time and delta time formats:
| Field |
Length
(Bytes) |
Contents |
Range of Values |
|
dd
|
2
|
Day of month
|
1--31
|
|
--
|
1
|
Hyphen
|
Required syntax
|
|
mmm
|
3
|
Month
|
JAN, FEB, MAR, APR, MAY, JUN, JUL, AUG, SEP, OCT, NOV, DEC
|
|
--
|
1
|
Hyphen
|
Required syntax
|
|
yyyy
|
4
|
Year
|
1858--9999
|
|
blank
|
n
|
Blank
|
Required syntax
|
|
hh
|
2
|
Hour
|
00--23
|
|
:
|
1
|
Colon
|
Required syntax
|
|
mm
|
2
|
Minutes
|
00--59
|
|
:
|
1
|
Colon
|
Required syntax
|
|
ss
|
2
|
Seconds
|
00--59
|
|
.
|
1
|
Period
|
Required syntax
|
|
cc
|
2
|
Hundredths of a second
|
00--99
|
|
dddd
|
4
|
Number of days (in 24-hour units)
|
000--9999
|
Month abbreviations must be uppercase.
The hundredths-of-second field represents a true fraction. For example,
the string .1 represents ten-hundredths of a second (one-tenth of a
second) and the string .01 represents one-hundredth of a second. Also,
you can add a third digit to the hundredths-of-second field; this
thousandths-of-second digit is used to round the hundredths-of-second
value. Digits beyond the thousandths-of-second digit are ignored.
The following two syntax rules apply to specifying the ASCII input
string:
- You can omit any of the date and time fields.
For absolute time
values, the $BINTIM service supplies the current system date and time
for nonspecified fields. Trailing fields can be truncated. If leading
fields are omitted, you must specify the punctuation (hyphens, blanks,
colons, periods). For example, the following string results in an
absolute time of 12:00 on the current day:
For delta time values, the $BINTIM service uses a default value of
0 for unspecified hours, minutes, and seconds fields. Trailing fields
can be truncated. If you omit leading fields from the time value, you
must specify the punctuation (blanks, colons, periods). If the number
of days in the delta time is 0, you must specify a 0. For example, the
following string results in a delta time of 10 seconds:
Note the space between the 0 in the day field and the two colons.
- For both absolute and delta time values, there can be any number of
leading blanks, and any number of blanks between fields normally
delimited by blanks; however, there can be no embedded blanks within
either the date or time field.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_IVTIME
|
The syntax of the specified ASCII string is invalid, or the time
component is out of range.
|
Example
Column 1 of the following table lists legal input strings to the
$BINTIM service; column 2 lists the $BINTIM output of these strings
translated through the Convert Binary Time to ASCII String ($ASCTIM)
system service. The current date is assumed to be 30-DEC-1994
04:15:28.00.
| Input to $BINTIM |
$ASCTIM Output String |
|
-- :50
|
30-DEC-1994 04:50:28.00
|
|
-- 1994 0:0:0.0
|
29-DEC-1994 00:00:00.00
|
|
30-DEC-1994 12:32:1.1161
|
30-DEC-1994 12:32:01.12
|
|
29-DEC-1994 16:35:0.0
|
29-DEC-1994 16:35:00.00
|
|
0 ::.1
|
0 00:00:00.10
|
|
0 ::.06
|
0 00:00:00.06
|
|
5 3:18:32.068
|
5 03:18:32:07
|
|
20 12:
|
20 12:00:00.00
|
|
0 5
|
0 05:00:00.00
|
$BINUTC
Converts an ASCII string to an absolute time value in the 128-bit UTC
format.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$BINUTC timbuf ,utcadr
C Prototype
int sys$binutc (void *timbuf, unsigned int *utcadr [4]);
Arguments
timbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
time_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Buffer that holds the ASCII time to be converted. The
timbuf argument specifies the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character
string descriptor pointing to a local time string. The time string
specifies the absolute time to be converted by $BINUTC.
utcadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
coordinated universal time |
| type: |
utc_date_time |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Time value that $BINUTC has converted. The utcadr
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a 16-byte location to receive the
converted time.
Description
The Convert ASCII String to UTC Binary Time service converts an ASCII
string to an absolute time in the 128-bit UTC format. The service
executes at the access mode of the caller and does not check whether
address arguments are accessible before it executes. Therefore, an
access violation causes an exception condition if the input buffer or
buffer descriptor cannot be read or the output buffer cannot be written.
This service does not check the length of the argument list and
therefore cannot return the SS$_INSFARG (insufficient arguments) error
status code. If the service does not receive enough arguments (for
example, if you omit required commas in the call), errors can result.
$BINUTC uses the time zone differential factor of the local system to
encode the 128-bit UTC.
The required ASCII input strings have the following format:
- Absolute Time: dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss.cc
The following table lists the length (in bytes), contents, and range of
values for each field in the absolute time format:
| Field |
Length
(Bytes) |
Contents |
Range of Values |
|
dd
|
2
|
Day of month
|
1--31
|
|
--
|
1
|
Hyphen
|
Required syntax
|
|
mmm
|
3
|
Month
|
JAN, FEB, MAR, APR, MAY, JUN, JUL, AUG, SEP, OCT, NOV, DEC
|
|
--
|
1
|
Hyphen
|
Required syntax
|
|
yyyy
|
4
|
Year
|
1858--9999
|
|
blank
|
n
|
Blank
|
Required syntax
|
|
hh
|
2
|
Hour
|
00--23
|
|
:
|
1
|
Colon
|
Required syntax
|
|
mm
|
2
|
Minutes
|
00--59
|
|
:
|
1
|
Colon
|
Required syntax
|
|
ss
|
2
|
Seconds
|
00--59
|
|
.
|
1
|
Period
|
Required syntax
|
|
cc
|
2
|
Hundredths of a second
|
00--99
|
Note that month abbreviations must be uppercase and that the
hundredths-of-second field represents a true fraction. For example, the
string .1 represents ten-hundredths of a second (one-tenth of a second)
and the string .01 represents one-hundredth of a second. Note also that
you can add a third digit to the hundredths-of-second field; this
thousandths-of-second digit is used to round the hundredths-of-second
value. Digits beyond the thousandths-of-second digit are ignored.
The following two syntax rules apply to specifying the ASCII input
string:
- You can omit any of the date and time fields.
For absolute time
values, the $BINUTC service supplies the current system date and time
for nonspecified fields. Trailing fields can be truncated. If leading
fields are omitted, you must specify the punctuation (hyphens, blanks,
colons, periods). For example, the following string results in an
absolute time of 12:00 on the current day:
- For absolute time values, there can be any number of leading
blanks, and any number of blanks between fields normally delimited by
blanks; however, there can be no embedded blanks within either the date
or time field.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCUTC, $GETUTC, $NUMUTC, $TIMCON
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_IVTIME
|
The syntax of the specified ASCII string is invalid, the specified time
is a delta time, or the time component is out of range.
|
$BRKTHRU
Sends a message to one or more terminals. The $BRKTHRU service
completes asynchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after
queuing the message request, without waiting for the message to be
written to the specified terminals.
For synchronous completion, use the Breakthrough and Wait ($BRKTHRUW)
service. The $BRKTHRUW service is identical to the $BRKTHRU service in
every way except that $BRKTHRUW returns to the caller after the message
is written to the specified terminals.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
The $BRKTHRU service supersedes the Broadcast ($BRDCST) service. When
writing new programs, you should use $BRKTHRU instead of $BRDCST. When
updating old programs, you should change all uses of $BRDCST to
$BRKTHRU.
Format
SYS$BRKTHRU [efn] ,msgbuf [,sendto] [,sndtyp] [,iosb] [,carcon]
[,flags] [,reqid] [,timout] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$brkthru (unsigned int efn, void *msgbuf, void *sendto, unsigned
int sndtyp, struct _iosb *iosb, unsigned int carcon, unsigned int
flags, unsigned int reqid, unsigned int timout, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the message has been written to
the specified terminals. The efn argument is a
longword containing this number; however, $BRKTHRU uses only the
low-order byte.
When the message request is queued, $BRKTHRU clears the specified event
flag (or event flag 0 if efn is not specified). Then,
after the message is sent, $BRKTHRU sets the specified event flag (or
event flag 0).
msgbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Message text to be sent to the specified terminals. The
msgbuf argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to this message text.
The $BRKTHRU service allows the message text to be as long as 16,350
bytes; however, both the system parameter MAXBUF and the caller's
available process space can affect the maximum length of the message
text.
sendto
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of a single device (terminal) or single user name to which the
message is to be sent. The sendto argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to this name.
The sendto argument is used in conjunction with the
sndtyp argument. When sndtyp
specifies BRK$C_DEVICE or BRK$C_USERNAME, the sendto
argument is required.
If you do not specify sndtyp or if
sndtyp does not specify BRK$C_DEVICE or
BRK$C_USERNAME, you should not specify sendto; if
sendto is specified, $BRKTHRU ignores it.
sndtyp
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Terminal type to which $BRKTHRU is to send the message. The
sndtyp argument is a longword value specifying the
terminal type.
Each terminal type has a symbolic name, which is defined by the $BRKDEF
macro. The following table describes each terminal type:
| Terminal Type |
Description |
|
BRK$C_ALLTERMS
|
When specified, $BRKTHRU sends the message to all terminals at which
users are logged in and to all other terminals that are connected to
the system except those with the AUTOBAUD characteristic set.
|
|
BRK$C_ALLUSERS
|
When specified, $BRKTHRU sends the message to all users who are
currently logged in to the system.
|
|
BRK$C_DEVICE
|
When specified, $BRKTHRU sends the message to a single terminal; you
must specify the name of the terminal by using the
sendto argument.
|
|
BRK$C_USERNAME
|
When specified, $BRKTHRU sends the message to a user with a specified
user name; you must specify the user name by using the
sendto argument.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of this quadword block.
When the iosb argument is specified, $BRKTHRU sets the
quadword to 0 when it queues the message request. Then, after the
message is sent to the specified terminals, $BRKTHRU returns four
informational items, one item per word, in the quadword I/O status
block.
These informational items indicate the status of the messages sent only
to terminals and mailboxes on the local node; these items do not
include the status of messages sent to terminals and mailboxes on other
nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system.
The following table shows each word of the quadword block and the
informational item it contains:
| Word |
Informational Item |
|
1
|
A condition value describing the final completion status.
|
|
2
|
A decimal number indicating the number of terminals and mailboxes to
which $BRKTHRU successfully sent the message.
|
|
3
|
A decimal number indicating the number of terminals to which $BRKTHRU
failed to send the message because the write to the terminals timed out.
|
|
4
|
A decimal number indicating the number of terminals to which $BRKTHRU
failed to send the message because the terminals were set to the
NOBROADCAST characteristic (by using the DCL command SET
TERMINAL/NOBROADCAST).
|
carcon
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Carriage control specifier indicating the carriage control sequence to
follow the message that $BRKTHRU sends to the terminals. The
carcon argument is a longword containing the carriage
control specifier.
For a list of the carriage control specifiers that you can use in the
carcon argument, refer to the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
If you do not specify the carcon argument, $BRKTHRU
uses a default value of 32, which represents a space in the ASCII
character set. The message format resulting from this default value is
a line feed, the message text, and a carriage return.
The carcon argument has no effect on message
formatting specified by the BRK$M_SCREEN flag in the
flags argument. See the description of the
flags argument.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag bit mask specifying options for the $BRKTHRU operation. The
flags argument is a longword value that is the logical
OR of each desired flag option.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $BRKDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
BRK$V_ERASE_LINES
|
When specified with the BRK$M_SCREEN flag, BRK$V_ERASE_LINES causes a
specified number of lines to be cleared from the screen before the
message is displayed. When BRK$M_SCREEN is not also specified,
BRK$V_ERASE_LINES is ignored.
Unlike the other Boolean flags, BRK$V_ERASE_LINES specifies a
1-byte integer in the range 0 to 24. It occupies the first byte in the
longword flag mask. In coding the call to $BRKTHRU, specify the desired
integer value in the OR operation with any other desired flags.
|
|
BRK$M_SCREEN
|
When specified, $BRKTHRU sends screen-formatted messages as well as
messages formatted through the use of the
carcon argument. $BRKTHRU sends screen-formatted
messages to terminals with the DEC_CRT characteristic, and it sends
messages formatted by
carcon to those without the DEC_CRT characteristic.
You set the DEC_CRT characteristic for the terminal by using the DCL
command SET TERMINAL/DEC_CRT.
A screen-formatted message is displayed at the top of the terminal
screen, and the cursor is repositioned at the point it was prior to the
broadcast message. However, the BRK$V_ERASE_LINES and BRK$M_BOTTOM
flags also affect the display.
|
|
BRK$M_BOTTOM
|
When BRK$M_BOTTOM is specified and BRK$M_SCREEN is also specified,
$BRKTHRU writes the message to the bottom of the terminal screen
instead of the top. BRK$M_BOTTOM is ignored if the BRK$M_SCREEN flag is
not set.
|
|
BRK$M_NOREFRESH
|
When BRK$M_NOREFRESH is specified, $BRKTHRU, after writing the message
to the screen, does not redisplay the last line of a read operation
that was interrupted by the broadcast message. This flag is useful only
when the BRK$M_SCREEN flag is not specified, because BRK$M_NOREFRESH is
the default for screen-formatted messages.
|
|
BRK$M_CLUSTER
|
Specifying BRK$M_CLUSTER enables $BRKTHRU to send the message to
terminals or mailboxes on other nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system. If
BRK$M_CLUSTER is not specified, $BRKTHRU sends messages only to
terminals or mailboxes on the local node.
|
reqid
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Class requester identification, which identifies to $BRKTHRU the
application (or image) that is calling $BRKTHRU. The
reqid argument is this longword identification value.
The reqid argument is used by several images that send
messages to terminals and can be used by as many as 16 different user
images as well.
When such an image calls $BRKTHRU, specifying reqid,
$BRKTHRU notifies the terminal that this image wants to write to the
terminal. This makes it possible for you to allow the image to write or
prevent it from writing to the terminal.
To prevent a particular image from writing to your terminal, you use
the image's name in the DCL command SET
TERMINAL/NOBROADCAST=image-name. Note that image-name
in this DCL command is the same as the value of the
reqid argument that the image passed to $BRKTHRU.
For example, you can prevent the Mail utility (which is an image) from
writing to the terminal by entering the DCL command SET
BROADCAST=NOMAIL.
The $BRKDEF macro defines class names that are used by several OpenVMS
components. These components specify their class names by using the
reqid argument in calls to $BRKTHRU. The $BRKDEF macro
also defines 16 class names (BRK$C_USER1 through BRK$C_USER16) for the
use of user images that call $BRKTHRU. The class names and the
components to which they correspond are as follows:
| Class Name |
Component |
|
BRK$C_GENERAL
|
This class name is used by the image invoked by the DCL command REPLY
and the callers of the $BRKTHRU service. This is the default if the
reqid argument is not specified.
|
|
BRK$C_PHONE
|
This class name is used by the OpenVMS Phone utility.
|
|
BRK$C_MAIL
|
This class name is used by the OpenVMS Mail utility.
|
|
BRK$C_DCL
|
This class name is used by the DIGITAL Command Language (DCL)
interpreter for the Ctrl/T command, which displays the process status.
|
|
BRK$C_QUEUE
|
This class name is used by the queue manager, which manages print and
batch jobs.
|
|
BRK$C_SHUTDOWN
|
This class name is used by the system shutdown image, which is invoked
by the DCL command REPLY/ID=SHUTDOWN.
|
|
BRK$C_URGENT
|
This class name is used by the image invoked by the DCL command
REPLY/ID=URGENT.
|
BRK$C_USER1
through BRK$C_USER16
|
These class names can be used by user-written images.
|
timout
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Timeout value, which is the number of seconds that must elapse before
an attempted write by $BRKTHRU to a terminal is considered to have
failed. The timout argument is this longword value (in
seconds).
Because $BRKTHRU calls the $QIO service to perform write operations to
the terminal, the timeout value specifies the number of seconds
allotted to $QIO to perform a single write operation to the terminal.
If you do not specify the timout argument, $BRKTHRU
uses a default value of 0 seconds, which specifies infinite time (no
timeout occurs).
The value specified by timout can be 0 or any number
greater than 4; the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 are illegal.
When you press Ctrl/S or the No Scroll key, $BRKTHRU cannot send a
message to the terminal. In such a case, the value of
timout is usually exceeded and the attempted write to
the terminal fails.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed after $BRKTHRU has sent the message
to the specified terminals. The astadr argument is the
address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of $BRKTHRU.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
specifies this longword parameter.
Description
The Breakthrough service sends a message to one or more terminals. The
$BRKTHRU service completes asynchronously; that is, it returns to the
caller after queuing the message request without waiting for the
message to be written to the specified terminals.
The $BRKTHRU service operates by assigning a channel (by using the
$ASSIGN service) to the terminal and then writing to the terminal (by
using the $QIO service). When calling $QIO, $BRKTHRU specifies the
IO$_WRITEVBLK function code, together with the IO$M_BREAKTHRU,
IO$M_CANCTRLO, and (optionally) IO$M_REFRESH function modifiers.
The current state of the terminal determines if and when the broadcast
message is displayed on the screen. For example:
- If the terminal is performing a read operation when $BRKTHRU sends
the message, the read operation is suspended, the message is displayed,
and then the line that was being read when the read operation was
suspended is redisplayed (equivalent to the action produced by Ctrl/R).
- If the terminal is performing a write operation when $BRKTHRU sends
the message, the message is displayed after the current write operation
has completed.
- If the terminal has the NOBROADCAST characteristic set for all
images, or if you have disabled the receiving of messages from the
image that is issuing the $BRKTHRU call (see the description of the
reqid argument), the message is not displayed.
After the message is displayed, the terminal is returned to the state
it was in prior to receiving the message.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have OPER privilege for the following
conditions:
- To send a message to more than one terminal
- To send a message to a terminal that is allocated to another user
- To send a message to a specific user that has a different user name
than the current process
To send a message to a specific user that is the same as your process
requires no privileges.
Required Quota
The $BRKTHRU service allows the message text to be as long as 16,350
bytes; however, both the system parameter MAXBUF and the caller's
available process buffered I/O byte count limit (BYTLM) quota must be
sufficient to handle the message.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN,
$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The message buffer, message buffer descriptor, device name string, or
device name string descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The message length exceeds 16,350 bytes; the process's buffered I/O
byte count limit (BYTLM) quota is insufficient; the message length
exceeds the value specified by the system parameter MAXBUF; the value
of the TIMOUT parameter is nonzero and less than 4 seconds; the value
of the REQID is outside the range 0 to 63; or the value of the SNDTYP
is not one of the legal ones listed.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its buffer space quota and has disabled
resource wait mode with the Set Resource Wait Mode ($SETRWM) service.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the request
and the process has disabled resource wait mode with the Set Resource
Wait Mode ($SETRWM) service.
|
|
SS$_NONLOCAL
|
The device is on a remote node.
|
|
SS$_NOOPER
|
The process does not have the necessary OPER privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified terminal does not exist, or it cannot receive the message.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
Any condition values returned by the $ASSIGN, $FAO, $GETDVI, $GETJPI,
or $QIO service.
$BRKTHRUW
Sends a message to one or more terminals. The $BRKTHRUW service
operates synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after the
message has been sent to the specified terminals.
For asynchronous operations, use the Breakthrough ($BRKTHRU) service;
$BRKTHRU returns to the caller after queuing the message request,
without waiting for the message to be delivered.
Aside from the preceding, $BRKTHRUW is identical to $BRKTHRU. For all
other information about the $BRKTHRUW service, refer to the description
of $BRKTHRU.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the documentation of the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
The $BRKTHRU and $BRKTHRUW services supersede the Broadcast ($BRDCST)
service. When writing new programs, you should use $BRKTHRU or
$BRKTHRUW instead of $BRDCST. When updating old programs, you should
change all uses of $BRDCST to $BRKTHRU or $BRKTHRUW. $BRDCST is now an
obsolete system service and is no longer being enhanced.
Format
SYS$BRKTHRUW [efn] ,msgbuf [,sendto] [,sndtyp] [,iosb] [,carcon]
[,flags] [,reqid] [,timout] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$brkthruw (unsigned int efn, void *msgbuf, void *sendto,
unsigned int sndtyp, struct _iosb *iosb, unsigned int carcon, unsigned
int flags, unsigned int reqid, unsigned int timout, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params),int astprm);
$CANCEL
Cancels all pending I/O requests on a specified channel. In general,
this includes all I/O requests that are queued, as well as the request
currently in progress.
Format
SYS$CANCEL chan
C Prototype
int sys$cancel (unsigned short int chan);
Argument
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
I/O channel on which I/O is to be canceled. The chan
argument is a word containing the channel number.
Description
The Cancel I/O on Channel service cancels all pending I/O requests on a
specified channel. In general, this includes all I/O requests that are
queued, as well as the request currently in progress.
When you cancel a request currently in progress, the driver is notified
immediately. The actual cancellation might occur immediately, depending
on the logical state of the driver. When cancellation does occur, the
following action for I/O in progress, similar to that for queued
requests, takes place:
- The specified event flag is set.
- The first word of the I/O status block, if specified, is set to
SS$_CANCEL if the I/O request is queued, or to SS$_ABORT if the I/O is
in progress.
- The AST, if specified, is queued.
Proper synchronization between this service and the actual canceling of
I/O requests requires the issuing process to wait for I/O completion in
the normal manner and then note that the I/O has been canceled.
If the I/O operation is a virtual I/O operation involving a disk or
tape ancilliary control process (ACP), the I/O cannot be canceled. In
the case of a magnetic tape, however, cancellation might occur if the
device driver is hung.
Outstanding I/O requests are automatically canceled at image exit.
Required Access or Privileges
To cancel I/O on a channel, the access mode of the calling process must
be equal to or more privileged than the access mode that the process
had when it originally made the channel assignment.
Required Quota
The $CANCEL service requires system dynamic memory and uses the
process's buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) quota.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN,
$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its buffered I/O limit (BIOLM) quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for canceling the I/O.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel, that is, a channel number of 0 or a
number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
$CANEXH
Deletes an exit control block from the list of control blocks for the
calling access mode. Exit control blocks are declared by the Declare
Exit Handler ($DCLEXH) service and are queued according to access mode
in a last-in first-out order.
Format
SYS$CANEXH [desblk]
C Prototype
int sys$canexh (void *desblk);
Argument
desblk
| OpenVMS usage: |
exit_handler_block |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Control block describing the exit handler to be canceled. If you do not
specify the desblk argument or specify it as 0, all
exit control blocks are canceled for the current access mode. The
desblk argument is the address of this control block.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The first longword of the exit control block or the first longword of a
previous exit control block in the list cannot be read by the caller,
or the first longword of the preceding control block cannot be written
by the caller.
|
|
SS$_IVSSRQ
|
The call to the service is invalid because it was made from kernel mode.
|
|
SS$_NOHANDLER
|
The specified exit handler does not exist.
|
$CANTIM
Cancels all or a selected subset of the Set Timer requests previously
issued by the current image executing in a process. Cancellation is
based on the request identification specified in the Set Timer
($SETIMR) service. If you give the same request identification to more
than one timer request, all requests with that request identification
are canceled.
Format
SYS$CANTIM [reqidt] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$cantim (unsigned __int64 reqidt, unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
reqidt
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Request identification of the timer requests to be canceled. If you
specify it as 0 (the default), all timer requests are canceled. The
reqidt argument is a longword containing this
identification.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode of the requests to be canceled. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Description
The Cancel Timer service cancels all or a selected subset of the Set
Timer requests previously issued by the current image executing in a
process. Cancellation is based on the request identification specified
in the Set Timer ($SETIMR) service. If you give the same request
identification to more than one timer request, all requests with that
request identification are canceled.
Outstanding timer requests are automatically canceled at image exit.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process can cancel only timer requests that are issued by a
process whose access mode is equal to or less privileged than that of
the calling process.
Required Quota
Canceled timer requests are restored to the process's quota for timer
queue entries (TQELM quota).
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANWAK, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
$CANWAK
Removes all scheduled wakeup requests for a process from the timer
queue, including those made by the caller or by other processes. The
Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service makes scheduled wakeup requests.
Format
SYS$CANWAK [pidadr] ,[prcnam]
C Prototype
int sys$canwak (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process for which wakeups are to be
canceled. The pidadr argument is the address of a
longword specifying the PID. The pidadr argument can
refer to a process running on the local node or a process running on
another node in the OpenVMS Cluster system.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the process for which wakeups are to be canceled. The
prcnam argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the process name string.
A process running on the local node can be identified with a 1- to
15-character string. To identify a process on a specific node in a
cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as
well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23
characters.
The operating system interprets the UIC group number of the calling
process as part of the process name; the names of processes are unique
to UIC groups. Because of this, you can use the prcnam
argument only on behalf of processes in the same group as the calling
process.
Description
The Cancel Wakeup service removes from the timer queue all scheduled
wakeup requests for a process, including those made by the caller or by
other processes. The Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service makes scheduled
wakeup requests.
If the longword at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the
target process is returned.
If you specify neither the pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, scheduled wakeup requests for the
calling process are canceled.
Pending wakeup requests issued by the current image are automatically
canceled at image exit.
This service cancels only wakeup requests that have been scheduled; it
does not cancel wakeup requests made with the Wake Process from
Hibernation ($WAKE) service.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
listed privileges to use $CANWAK:
- You need GROUP privilege to cancel wakeups for processes in the
same group that do not have the same UIC.
- You need WORLD privilege to cancel wakeups for any process in the
system.
Required Quota
Canceled wakeup requests are restored to the process's AST limit
(ASTLM) quota.
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $GETTIM, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or you specified an invalid
process identification.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to cancel wakeups for the
specified process.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
$CHECK_ACCESS
Determines on behalf of a third-party user whether a named user can
access the object specified.
Format
SYS$CHECK_ACCESS [objtyp], [objnam], [usrnam], itmlst, [contxt],
[clsnam], [objpro], [usrpro]
C Prototype
int sys$check_access (unsigned int *objtyp, void *objnam, void *usrnam,
void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, void *clsnam, void *objpro, void
*usrpro);
Arguments
objtyp
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Type of object being accessed. The objtyp argument is
the address of a longword containing a value specifying the type of
object.
The appropriate symbols are listed in the following table and are
defined in the system macro $ACLDEF library:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
ACL$C_CAPABILITY
|
Object is a restricted resource; use the reserved name VECTOR.
|
|
ACL$C_DEVICE
|
Object is a device.
|
|
ACL$C_FILE
|
Object is a Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 file.
|
|
ACL$C_GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Object is a group global section.
|
|
ACL$C_JOBCTL_QUEUE
|
Object is a batch, print, or server queue.
|
|
ACL$C_LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
Object is a logical name table.
|
|
ACL$C_SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Object is a system global section.
|
For further information about these symbols, see the description of the
clsnam argument.
objnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the object being accessed. The objnam argument
is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the object
name.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the user attempting access. The usrnam
argument is the address of a descriptor that points to a character
string that contains the name of the user attempting to gain access to
the specified object. The user name string can contain a maximum of 12
alphanumeric characters.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes describing how the object is to be accessed and information
returned after $CHECK_ACCESS performs the protection check (for
instance, security alarm information).
For each item code, you must include a set of four elements and end the
list with a longword containing the value 0 (CHP$_END). This is shown
in the following diagram:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the associated buffer. The length of the buffer needed
depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item
descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service
truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information in the associated buffer.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word in which $CHECK_ACCESS
writes the number of bytes written to the buffer pointed to by
bufadr. If the buffer pointed to by
bufadr is used to pass information to $CHECK_ACCESS,
retlenadr is ignored but must be included.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read-write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword used to maintain the user authorization file (UAF) context.
The contxt argument is the address of a longword to
receive a UAI context longword. On the initial call, this longword
should contain the value --1. On subsequent calls, the value of the
contxt argument from the previous call should be
passed back in.
Using the contxt argument keeps the UAF open across
all calls, thereby improving the performance of the system on
subsequent calls. To close the UAF, you must run down the image.
The resulting contxt value from a $CHECK_ACCESS call
can also be used as the input contxt argument to the
$GETUAI system service, and vice versa.
clsnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Object class name associated with the protected object. The
clsnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to the name of the object class associated with the object
specified by either the objnam or the
objpro argument. The clsnam and
objtyp arguments are mutually exclusive. The
clsnam argument is the preferred argument to
$CHECK_ACCESS. The following object class names are valid:
|
CAPABILITY
|
QUEUE
|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
|
DEVICE
|
SECURITY_CLASS
|
|
FILE
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
VOLUME
|
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
|
objpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream or object handle |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing an object security profile or object handle. The
objpro argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a buffer that contains an encoded object security profile
or the address of a descriptor pointing to an object handle.
Object handles vary according to the associated security object class.
Currently, the only supported object handles are for the file and
device class objects where the object handle is a word or longword
channel.
The objpro and objnam arguments are
mutually exclusive unless the objpro argument is a
simple object handle. The objpro and
usrpro arguments are also mutually exclusive unless
the objpro argument is an object handle.
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing a user security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer that
contains an encoded user security profile.
The $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service can be used to construct a user
security profile. The usrpro and
usrnam arguments are mutually exclusive. The
objpro and usrpro arguments are also
mutually exclusive unless the objpro argument is an
object handle.
The item codes used with $CHECK_ACCESS are described in the following
list and are defined in the $CHPDEF system macro library.
Item Codes
CHP$_ACCESS
A longword bit mask that represents the desired access ($ARMDEF). Only
those bits set in CHP$_ACCESS are checked against the protection of the
object to determine whether access is granted.
The default for CHP$_ACCESS is read. Symbolic representations for the
access types associated with the built-in protected classes are found
in the $ARMDEF macro.
For example, ARM$M_MANAGE specifies Manage access for the queue class
object. Access type names are object class specific and vary from class
to class. Because $CHECK_ACCESS performs only a bitwise comparison of
access desired to object protection, the original Read, Write, Execute,
and Delete names can also be used to specify the first four access
types for any object class.
The following table shows the access types available and lists their
common interpretations. These symbols are defined in the $ARMDEF system
macro library. For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
| Access Type |
Access Permitted |
|
ARM$M_READ
|
Allows holders to read an object, perform wildcard directory lookups,
display jobs in a queue, or use an associated vector processor.
|
|
ARM$M_WRITE
|
Allows holders to alter the contents of an object, remove a directory
entry, write or extend existing files on a volume, or submit a job to a
queue.
|
|
ARM$M_EXECUTE
|
Allows holders to run an image or command procedure, perform exact
directory lookups, issue physical I/O requests to a device, create new
files on a volume, or act as operator for a queue.
|
|
ARM$M_DELETE
|
Allows holders to delete an object, perform logical I/O to a device, or
delete a job in a queue.
|
|
ARM$M_CONTROL
|
Allows holders to display or alter the security characteristics of an
object.
|
CHP$_ACMODE
A byte that defines the accessor's processor access mode ($PSLDEF). The
following access modes and their symbols are defined in the system
macro library ($PSLDEF). Objects supported by the operating system do
not consider access mode in determining object access.
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
If CHP$_ACMODE is not specified, access mode is not used to determine
access.
CHP$_ALARMNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the alarm name from any Alarm ACE
contained in the object's ACL. Currently, if a matching Alarm ACE
exists, the string SECURITY will be returned. The string returned by
CHP$_ALARMNAME can be used as input to the $AUDIT_EVENT system service,
using the NSA$_ALARM_NAME item code.
CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
A list containing information to be added to any resulting security
audit. The bufadr argument points to the beginning of
an $AUDIT_EVENT item list. See the itmlst argument of
the $AUDIT_EVENT system service for a list of valid security auditing
item codes. Note that the NSA$_EVENT_TYPE and NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE items
are ignored when auditing with $CHECK_ACCESS. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag must
be specified.
CHP$_AUDITNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the audit name from any Audit ACE
contained in the object's ACL. Currently, if a matching Audit ACE
exists, the string SECURITY will be returned. The string returned by
CHP$_AUDITNAME can be used as input to the $AUDIT_EVENT system service,
using the NSA$_AUDIT_NAME item code.
CHP$_FLAG
A longword that controls various aspects of the protection check. The
symbols in the following table are offsets to the bits within the
longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate
bit set by using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. These symbols are
defined in the system macro library ($CHPDEF).
| Symbol |
Access |
|
CHP$V_ALTER
|
Accessor desires write access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_AUDIT
|
Access audit requested.
|
|
CHP$V_CREATE
|
Perform the audit as an object creation event.
|
|
CHP$V_DELETE
|
Perform the audit as an object deletion event.
|
|
CHP$V_FLUSH
|
Force audit buffer flush.
|
|
CHP$V_INTERNAL
|
Audit on behalf of the Trusted Computing Base (TCB). Reserved to HP.
|
|
CHP$V_MANDATORY
|
Force the object access event to be audited.
|
|
CHP$V_NOFAILAUD
|
Do not perform audits for failed access.
|
|
CHP$V_NOSUCCAUD
|
Do not perform audits for successful access.
|
|
CHP$V_OBSERVE
|
Accessor desires read access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_SERVER
|
Audit on behalf of a TCB server process.
|
|
CHP$V_USEREADALL
|
Accessor is eligible for READALL privilege.
|
The default for CHP$_FLAG is CHP$V_OBSERVE.
The primary purpose of the CHP$V_OBSERVE and CHP$V_ALTER flags is as
latent support for a mandatory (lattice) security policy, such as that
provided by the Security Enhanced VMS (SEVMS) offering.
CHP$_MATCHEDACE
A variable-length data structure containing the first Identifier ACE in
the ACL that granted or denied access to the object. The $FORMAT_ACL
system service describes the format of an Identifier ACE.
CHP$_PRIVUSED
A longword mask of flags that represent the privileges used to gain
access.
You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set by
using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The symbols are defined in
the system macro library ($CHPDEF). The following symbols are offsets
to the bits within the longword:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
CHP$V_SYSPRV
|
SYSPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPPRV
|
GRPPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_BYPASS
|
BYPASS was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_READALL
|
READALL was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_OPER
|
OPER was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPNAM
|
GRPNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_SYSNAM
|
SYSNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GROUP
|
GROUP was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_WORLD
|
WORLD was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_PRMCEB
|
PRMCEB was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_UPGRADE
|
UPGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_DOWNGRADE
|
DOWNGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
Description
The Check Access service invokes the operating system control
protection check mechanism, $CHKPRO, to determine whether a named user
is allowed the described access to the named object. A file server, for
example, might check the access attributes of a user who attempts to
access a file (the object).
If the user can access the object, $CHECK_ACCESS returns the SS$_NORMAL
status code; otherwise, $CHECK_ACCESS returns SS$_NOPRIV.
The arguments accepted by this service specify the name and class of
object being accessed, the name of the user requesting access to the
object, the type of access desired, and the type of information to be
returned.
The caller can also request that an object access audit be performed if
security auditing has been enabled for the object class or if Audit
ACEs are contained in the object's ACL. Auditing ACEs include both
Alarm ACEs and Audit ACEs. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag requests an access
audit. This requires that the caller be in executive or kernel mode or
possess the AUDIT privilege.
Normally, $CHECK_ACCESS generates an object access audit when an audit
is required. The caller can specify the CHP$V_CREATE flag to force an
object creation audit instead of an object access audit. Similarly, the
CHP$V_DELETE flag forces an object deletion audit. The CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
item code can be used to specify additional information to be included
in any resulting audit records.
With certain types of devices, $CHECK_ACCESS can return a false
negative, but never a false positive. This is due to additional LOG_IO
and PHY_IO privilege checking in the $QIO system service that might
override an otherwise unsuccessful access attempt. These privilege
checks are not mirrored by the $CHECK_ACCESS system service. The
affected devices are those that are non-file-structured or mounted
foreign and also either spooled, file-oriented, or shareable. For
example, mailbox devices fall into this category because they are
non-file-structured and shareable. To accurately duplicate the result
that would be obtained if the user had issued a read or write against
these devices, it might be necessary to test for these additional
privileges using the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE system service. Refer to the
HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for further information on access requirements for devices.
Required Access or Privileges
Access to SYSUAF.DAT and RIGHTSLIST.DAT is required. AUDIT privilege is
required when requesting a user mode audit.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CHKPRO, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE, $FORMAT_ACL
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, one of the buffers
specified in the item list cannot be written by the caller, or one of
the arguments could not be read or written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid or conflicting combination of parameters.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Insufficient information to identify object or user.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient process memory to execute service.
|
|
SS$_NOAUDIT
|
Caller lacks privilege to request audit.
|
|
SS$_NOCALLPRIV
|
Caller lacks privilege to access authorization database.
|
|
SS$_NOCLASS
|
No matching object class was located.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The desired access is not granted.
|
|
SS$_UNSUPPORTED
|
Operations on remote object are not supported.
|
If CHP$V_AUDIT is specified, any error from the $AUDIT_EVENT system
service can also be returned.
$CHECK_FEN (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, indicates whether floating point is enabled for the
current image.
Format
SYS$CHECK_FEN
C Prototype
int sys$check_fen (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Check Floating Point service returns a Boolean value in R0
indicating whether floating point is enabled for the current image.
The $CHECK_FEN service returns a value of 1 if the floating point is
enabled for the current image. A value of 0 is returned if the floating
point is disabled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE
Determines whether the caller has the specified privileges or
identifier. In addition to checking for a privilege or an identifier,
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE determines if the caller's use of privilege needs to
be audited.
Format
SYS$CHECK_PRIVILEGE [efn] ,prvadr ,[altprv] ,[flags] ,[itmlst]
,[audsts] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$check_privilege (unsigned int efn, struct _generic_64 *prvadr,
struct _generic_64 *altprv, unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned
int *audsts, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the audit completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing the number of
the event flag; however, $CHECK_PRIVILEGE uses only the low-order byte.
If efn is not specified, event flag 0 is used.
Upon request initiation, $CHECK_PRIVILEGE clears the specified event
flag.
prvadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The privilege, privileges, or identifier that the calling process must
possess.
The prvadr argument is either the address of a
quadword bit array, where each bit corresponds to a privilege, or the
address of a quadword identifier.
When the array lists privileges, each bit has a symbolic name. The
$PRVDEF macro defines these names. You form the bit array by specifying
the symbolic name of each desired privilege in a logical OR operation.
See the $SETPRV system service for the symbolic name and description of
each privilege.
If the caller passes an identifier, the caller must set the
NSA$M_IDENTIFIER bit in the flags longword. The
identifier structure is defined by the $KGBDEF macro. The identifier
attributes (KGB$) are reserved for future use and should be set to 0.
altprv
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Alternate privilege mask to check against. The altprv
argument is the address of a quadword privilege mask, where each bit
corresponds to a privilege. This argument and the flags NSA$M_AUTHPRIV,
NSA$M_IDENTIFIER, and NSA$M_PROCPRIV are mutually exclusive.
With this argument, $CHECK_PRIVILEGE uses the supplied set of
privileges instead of the current, active privileges. Each bit in the
mask has a symbolic name, defined by the $PRVDEF macro. You form the
bit array by specifying the symbolic name of each desired privilege in
a logical OR operation. See the $SETPRV system service for the symbolic
name and description of each privilege.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags that specify options for the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE operation. The
flags argument is a longword bit mask, where each bit
corresponds to an option.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $NSADEF macro defines the
following symbolic names. Be aware that the flags NSA$M_AUTHPRIV,
NSA$M_IDENTIFIER, and NSA$M_PROCPRIV are mutually exclusive; therefore,
you can specify only one of these flag options.
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
NSA$M_AUTHPRIV
|
Checks the authorized privileges of the process instead of the current
(active) privileges.
|
|
NSA$M_FLUSH
|
Specifies that all messages in the audit server buffer be written to
the audit log file.
|
|
NSA$M_IDENTIFIER
|
Interprets the
prvadr argument as the address of an identifier
instead of a privilege mask.
|
|
NSA$M_INTERNAL
|
Specifies that the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE call originates in the context of a
trusted computing base (TCB) component. The auditing components use
this flag to indicate that internal auditing failures should result in
a SECAUDTCB bugcheck. This flag is reserved to HP.
|
|
NSA$M_MANDATORY
|
Specifies that an audit is to be performed, regardless of system alarm
and audit settings.
|
|
NSA$M_PROCPRIV
|
Checks the permanent privileges of the process, instead of the
privileges in the current (active) mask.
|
|
NSA$M_SERVER
|
Indicates that the call originates in a TCB server process and that the
event should be audited regardless of the state of a process-specific
no-audit bit.
Trusted servers use this flag to override the no-audit bit when
they want to perform explicit auditing on behalf of a client process.
This flag is reserved to HP.
|
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying additional security auditing information to be
included in any security audit that is generated by the service. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item
descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The list
of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.
The item list is a standard format item list. The following diagram
depicts the format of a single item descriptor.

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length of the buffer in bytes. The buffer
supplies information to be used by $CHECK_PRIVILEGE. The required
length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified; each
item code description specifies the required length.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the
information currently in the buffer or to be returned in the buffer.
The location of the buffer is pointed to by the buffer address field.
Each item code has a symbolic name.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies or
receives the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
Not currently used; this field is reserved to HP. You should specify 0.
|
All item codes listed in the Item Codes section of the $AUDIT_EVENT
service are valid within the item list used by the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE
service except for the NSA$_EVENT_TYPE and NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE item
codes, which are supplied internally by the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE service.
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE should be called with an item list identifying the
alarm and audit journals, and does not need to use the NSA$_PRIVS_USED
item code. NSA$_PRIVS_USED is supplied automatically by the
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE service. Note that $CHECK_PRIVILEGE returns
SS$_BADPARAM if you supply either NSA$_EVENT_TYPE or
NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE. These items are supplied internally by
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE.
audsts
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value_type |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword condition value that receives a final completion status from
the operation. If a security audit is required, the final completion
status represents either the successful completion of the resulting
security audit or any failing status that occurred while the security
audit was performed within the AUDIT_SERVER process.
The audsts argument is valid only when the service
returns success and the status is not SS$_EVTNOTENAB. In addition, the
caller must either make use of the astadr argument or
use the $CHECK_PRIVILEGEW service before attempting to access
audsts.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Asynchronous system trap (AST) routine to be executed after the
audsts argument is written. The
astadr argument, which is the address of a longword
value, is the procedure value of the AST routine.
The AST routine executes in the access mode of the caller of
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Asynchronous system trap (AST) parameter passed to the AST service
routine. The astprm argument is a longword value
containing the AST parameter.
Description
The Check Privilege service determines whether a user has the
privileges or identifier that an operation requires. In addition,
$CHECK_PRIVILEGE audits the use of privilege if privilege auditing has
been enabled by the site security administrator. The caller does not
need to determine whether privilege auditing has been enabled.
Required Access or Privileges
AUDIT privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$AUDIT_EVENT, $SETPRV
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The specified parameter of the item list buffer is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFADR
|
The buffer address is invalid or not readable.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The specified buffer length is invalid or out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADCHAIN
|
The address of the next item list to be processed, as identified in the
buffer address field, is either not readable or points to itself.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
The specified item code is invalid or out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified list entry is invalid or out of range.
|
|
SS$_EVTNOTENAB
|
No audit required; privilege granted.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
The argument list contains too few arguments for the service.
|
|
SS$_INVAJLNAM
|
The alarm or audit journal name is invalid.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
The specified system service flags are invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOAUDIT
|
The caller does not have the required privilege to perform the audit.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The subject does not have the required privileges or identifier.
|
|
SS$_NO[privilege-name]
|
The subject does not have a specific privilege.
|
|
SS$_OVRMAXAUD
|
There is insufficient memory to perform the audit.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYAJL
|
Too many alarm or audit journals were specified.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
An unassociated event flag cluster was specified.
|
$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW
Determines whether the caller has the specified privileges or
identifier. In addition to checking for a privilege or an identifier,
the Check Privilege and Wait service determines if the caller's use of
privilege needs to be audited.
$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW completes synchronously; that is, it returns the
final status to the caller only after receiving an explicit
confirmation from the audit server that the associated audit, if
enabled, has been performed.
Format
SYS$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW efn ,prvadr ,[altprv] ,[flags] ,[itmlst] ,audsts
,[astadr] ,[astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$check_privilegew (unsigned int efn, struct _generic_64 *prvadr,
struct _generic_64 *altprv, unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned
int *audsts, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$CHKPRO
Determines whether an accessor with the specified rights and privileges
can access an object with the specified attributes.
Format
SYS$CHKPRO itmlst ,[objpro] ,[usrpro]
C Prototype
int sys$chkpro (void *itmlst, void *objpro, void *usrpro);
Argument
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Protection attributes of the object and the rights and privileges of
the accessor. The itmlst argument is the address of an
item list of descriptors used to specify the protection attributes of
the object and the rights and privileges of the accessor.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the associated buffer. The length of the buffer needed
depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item
descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service
truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information in the associated buffer. The item codes are defined in the
$ACLDEF system macro library.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword that normally contains the user-supplied address of a word
in which the service writes the length in bytes of the information it
returned. This is not used by $CHKPRO and should contain a 0.
|
Specifying any specific protection attribute causes that protection
check to be made; any protection attribute not specified is not
checked. Rights and privileges specified are used as needed. If a
protection check requires any right or privilege not specified in the
item list, the right or privilege of the caller's process is used.
objpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing an object security profile. The
objpro argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a buffer that contains an encoded object security profile.
The objpro argument eliminates the need to supply all
of the component object protection attributes with the $CHKPRO item
list. The objpro argument is currently reserved to HP.
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing a user security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer that
contains an encoded user security profile. The usrpro
argument eliminates the need to supply all of the component user
security attributes with the $CHKPRO item list.
The $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service can be used to construct a user
security profile. When the usrpro argument is
specified, any component user profile attributes specified in the
$CHKPRO item list replace those contained in the user security profile.
The item codes used with $CHKPRO are described in the following list
and are defined in the $CHPDEF system macro library.
Item Codes
CHP$_ACCESS
A longword bit mask representing the type of access desired ($ARMDEF).
Be aware that the $CHKPRO service does not interpret the bits in the
access mask; instead, it compares them to the object's protection mask
(CHP$_PROT). Any bits not specified by CHP$_ACCESS or CHP$_PROT are
assumed to be clear, which grants access.
CHP$_ACL
A vector that points to an object's access control list. The buffer
address, bufadr, specifies a buffer containing one or
more ACEs. The number that specifies the length of the CHP$_ACL buffer,
buflen, must be equal to the sum of all ACE lengths.
The format of the ACE structure depends on the value of the second byte
in the structure, which specifies the ACE type. The $FORMAT_ACL system
service description describes each ACE type and its format.
You can specify the CHP$_ACL item multiple times to point to multiple
segments of an access control list. You can specify a maximum of 20
segments. The segments are processed in the order specified.
CHP$_ACMODE
A byte that defines the accessor's processor access mode. The following
access modes and their symbols are defined in the $PSLDEF macro:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
If CHP$_ACMODE is not specified, access mode is not used to determine
access.
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS
A vector that points to an additional rights list segment to be
appended to the existing rights list. Each entry of the rights list is
a quadword data structure consisting of a longword containing the
identifier value, followed by a longword containing a mask identifying
the attributes of the holder. The $CHKPRO service ignores the
attributes.
A maximum of 11 rights descriptors is allowed. If you specify
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS without specifying CHP$_RIGHTS, the accessor's rights
list consists of the rights list specified by the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item
codes and the rights list of the current process.
If you specify CHP$_RIGHTS and CHP$_ADDRIGHTS, you should be aware of
the following:
- CHP$_RIGHTS must come first.
- The accessor's UIC is the identifier of the first entry in the
rights list specified by the CHP$_RIGHTS item code.
- The accessor's rights list consists of the rights list specified by
the CHP$_RIGHTS item code and the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item codes.
CHP$_ALARMNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the alarm name from any Alarm ACE
contained in the object's ACL. If the object does not have security
alarms enabled, $CHKPRO returns retlenadr as 0. If a
matching Alarm ACE exists, the string SECURITY will be returned.
CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
A security auditing item list containing additional information to be
included in any resulting security audit. The bufadr
argument points to the beginning of an $AUDIT_EVENT item list. See the
itmlst argument of the $AUDIT_EVENT system service for
a list of valid security auditing item codes. Note that the
NSA$_EVENT_TYPE and NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE items are ignored when auditing
with $CHKPRO. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag must be specified.
CHP$_AUDITNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the audit name from any Audit ACE
contained in the object's ACL. If the object does not have auditing
enabled, $CHKPRO returns retlenadr as 0. If a matching
Audit ACE exists, the string SECURITY will be returned.
CHP$_FLAGS
A longword that defines various aspects of the protection check. The
symbols in the following table are offsets to the bits within the
longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate
bit set by using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The following
symbols are defined only in the system macro library ($CHPDEF):
| Symbol |
Access |
|
CHP$V_ALTER
|
Accessor desires write access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_AUDIT
|
Access audit requested.
|
|
CHP$V_CREATE
|
Perform the audit as an object creation event.
|
|
CHP$V_DELETE
|
Perform the audit as an object deletion event.
|
|
CHP$V_FLUSH
|
Force audit buffer flush.
|
|
CHP$V_INTERNAL
|
Audit on behalf of the Trusted Computing Base (TCB). Reserved to HP.
|
|
CHP$V_MANDATORY
|
Force the object access event to be audited.
|
|
CHP$V_NOFAILAUD
|
Do not perform audits for failed access.
|
|
CHP$V_NOSUCCAUD
|
Do not perform audits for successful access.
|
|
CHP$V_OBSERVE
|
Accessor desires read access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_SERVER
|
Audit on behalf of a TCB server process.
|
|
CHP$V_USEREADALL
|
Accessor is eligible for READALL privilege.
|
The default for CHP$_FLAG is CHP$M_OBSERVE and CHP$M_ALTER.
The primary purpose of the CHP$V_OBSERVE and CHP$V_ALTER flags is as
latent support for a mandatory (lattice) security policy, such as that
provided by the Security Enhanced VMS (SEVMS) offering.
CHP$_MATCHEDACE
This output item is a variable-length data structure containing the
first Identifier ACE in the object's ACL that allowed or denied the
accessor to access the object. See the $FORMAT_ACL system service for a
description of an Identifier ACE format.
CHP$_MODE
A byte that defines the object's owner access mode. The following
access modes of the object's owner and their symbols are defined in the
system macro library ($PSLDEF):
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
CHP$_MODES
A quadword that defines the object's access mode protection. You
specify a 2-bit access mode as shown in CHP$_MODE for each possible
access type. The following diagram illustrates the format of an access
mode vector for bit numbers:
Each pair of bits in the access mode vector represents the access mode
for the specific type of access. For example, bits <6:7>
represent the access mode value used to check for delete access.
CHP$_OBJECT_CLASS
A character string containing the protected object class associated
with the object. The object class string is used to determine whether
any security auditing is enabled for the object access event. This item
code is required when the CHP$_AUDIT flag is specified.
CHP$_OBJECT_NAME
A character string containing the object name associated with the
protection check. The object name string is included in any resulting
security audit. If an object name string is not specified, the string
"<not available>" is substituted in any security audit
for all protected object classes other than FILE. For FILE class
audits, it is assumed that the caller has supplied an object name by
using the auditing item list (NSA$_OBJECT_NAME).
CHP$_OWNER
A longword describing the object's owner identifier (UIC or general
identifier). This might be either a UIC format identifier or a general
identifier.
Note
CHP$_OWNER is used in conjunction with the CHP$_PROT item code.
|
CHP$_PRIV
A quadword that defines an accessor's privilege mask. Each bit in the
mask has a symbolic name, defined by the $PRVDEF macro. You form the
bit array by specifying the symbolic name of each privilege in a
logical OR operation. See the $SETPRV system service for the symbolic
name and description of each privilege.
CHP$_PRIVUSED
A longword mask of flags representing privileges used to gain the
requested access.
You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set by
using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The symbols are defined in
the system macro library ($CHPDEF). The following symbols are used as
offsets to the bits within the longword:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
CHP$V_SYSPRV
|
SYSPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPPRV
|
GRPPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_BYPASS
|
BYPASS was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_READALL
|
READALL was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_OPER
|
OPER was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPNAM
|
GRPNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_SYSNAM
|
SYSNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GROUP
|
GROUP was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_WORLD
|
WORLD was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_PRMCEB
|
PRMCEB was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_UPGRADE
|
UPGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_DOWNGRADE
|
DOWNGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
CHP$_PROT
A vector describing the object's SOGW protection mask. The following
diagram depicts the format for describing the object's protection:
The first word contains the first four protection bits for each field,
the second word the next four protection bits, and so on. If a bit is
clear, access is granted. By convention, the first five protection bits
are (from right to left in each field of the first word) read, write,
execute, delete, and (in the low-order bit in each field of the second
word) control access. You can specify the CHP$_PROT item in increments
of words; if a short buffer is given, zeros are assumed for the
remainder.
The $CHKPRO service compares the low-order four bits of CHP$_ACCESS
against one of the 4-bit fields in the low-order word of CHP$_PROT, the
next four bits of CHP$_ACCESS against one of the 4-bit fields in the
next word of CHP$_PROT, and so on. The $CHKPRO service chooses a field
of CHP$_PROT based on the privileges specified for the accessor
(CHP$_PRIV), the UICs of the accessor (CHP$_RIGHTS or CHP$_ADDRIGHTS,
or both), and the object's owner (CHP$_OWNER).
You must also specify the identifier of the object's owner with
CHP$_OWNER when you use CHP$_PROT.
CHP$_RIGHTS
A vector that points to an accessor's rights list. The accessor's UIC
is the identifier of the first entry in the rights list. The accessor's
rights list consists of the rights list specified by CHP$_RIGHTS and,
optionally, the rights list specified by the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item codes.
CHP$_UIC
A longword specifying the accessor's owner UIC. This item code can be
used to avoid having to pass an entire rights list segment via the
CHP$_RIGHTS item code. If CHP$_RIGHTS and then CHP$_UIC are specified,
in that order, $CHKPRO initializes the local rights list and then
replaces just the owner UIC with the value of CHP$_UIC.
Description
The Check Access Protection service determines whether an accessor with
the specified rights and privileges can access an object with the
specified attributes. The service invokes the system's access
protection check, which permits layered products and other subsystems
to build protected structures that are consistent with the protection
facilities provided by the base operating system. The service also
allows a privileged subsystem to perform protection checks on behalf of
a requester.
If the accessor can access the object, $CHKPRO returns the SS$_NORMAL
status code; otherwise, $CHKPRO returns SS$_NOPRIV.
The item list arguments accepted by this service permit you to specify
the protection of the object being accessed, the rights and privileges
of the accessor, and the type of access desired.
At minimum, the following item codes should be specified to perform a
third-party protection check:
CHP$_ACCESS
CHP$_OWNER
CHP$_PRIV
CHP$_PROT
CHP$_UIC
The default for information relating to the subject is to use the
current process information (for example, privileges). The default for
missing object information is a representation of 0.
The caller can also request that an object access audit be performed if
security auditing has been enabled for the object class or if auditing
ACEs are contained in the object's ACL. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag requests
an access audit. This requires that the caller be in executive or
kernel mode or possess the AUDIT privilege.
Normally, $CHKPRO generates an object access audit when an audit is
required. The caller can specify the CHP$V_CREATE flag to force an
object creation audit instead of an object access audit. Similarly, the
CHP$V_DELETE flag forces an object deletion audit. The CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
item code can be used to specify additional information to be included
in any resulting audit records.
Required Access or Privileges
AUDIT privilege is required when requesting an audit.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$AUDIT_EVENT, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE, $FORMAT_ACL
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or one of the buffers
specified in the item list cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ACLFULL
|
More than 20 CHP$_ACL items were given.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The argument is invalid.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The output buffer is too small and the protection check succeeded.
|
|
SS$_IVACL
|
You supplied an invalid ACL segment with the CHP$_ACL item.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The output buffer is too small and the protection check failed.
|
|
SS$_NOAUDIT
|
Caller lacks privilege to request audit.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The desired access is not granted.
|
|
SS$_RIGHTSFULL
|
More than 11 CHP$_ADDRIGHTS items were given.
|
$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT (Alpha Only)
Removes one or more notification requiests previously established by a
call to $SET_SYSTEM_EVENT.
This service does not allow you to specify a handle and an event. You
must pass a zero as one of these parameters. You can either clear by
handle or request that all events for the user be cleared.
Format
SYS$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT [handle] ,[acmode] ,event
C Prototype
int sys$clear_system_event (struct _generic_64 * handle, unsigned int
acmode, unsigned int event);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification of the AST request to be cleared. The
handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is
returned when the $SET_SYSTEM_EVENT service is called. The
handle argument may be omitted by specifying a zero
address.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode of the system event to be cleared. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The value of the access mode is maximized with the access mode of
the caller.
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The event argument is a value indicating the type of
system event to be cleared. SYSEVT$C_ALL_EVENTS may be specified to
clear all event types.
Description
The Clear System Event service removes one or more event types or
notification objects previously established by a call to the
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT service.
A valid request specifies either the handle for a
specific notification request, or is a wildcard clear of all
notification objects whose is access mode is greater than or equal to
acmode.
If the handle argument is specified, caller's access
mode must be less than or equal to the access mode of the object to be
cleared.
If SYSEVT$C_ALL_EVENTS is specified, or the set of events enabled for
the object(s) becomes empty, the notification object is deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the location specified by the handle.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments has an invalid value, such as an invalid handle.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
No request was found that matches the description supplied.
|
$CLOSE
The Close service terminates file processing and closes the file. This
service performs an implicit Disconnect service for all record streams
associated with the file.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this service.
$CLRAST
Clears the "AST active" status.
This enables delivery of asynchronous system traps (ASTs) for the
access mode from which the service call was issued, while an AST
routine is active.
Note
The explicit use of $CLRAST is strongly discouraged, as it complicates
synchronization issues and may lead to the unbounded consumption of
stack space.
|
Format
SYS$CLRAST
Arguments
None.
Description
Normally, AST delivery for a particular access mode is deferred while
an AST routine is executing in that access mode. When the AST routine
returns, an implicit call is made to $CLRAST to re-enable AST delivery.
Explicitly calling $CLRAST within an AST routine allows the delivery of
ASTs for the access mode from which the service call was issued, prior
to completion of the active AST routine.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SETAST
Condition Values Returned
|
None
|
The return value is undefined.
|
$CLRCLUEVT
Removes one or more notification requests previously established by a
call to SYS$SETCLUEVT.
Format
SYS$CLRCLUEVT [handle] ,[acmode] ,[event]
C Prototype
int sys$clrcluevt (struct _cluevthndl *handle, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int event);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification of the AST request to be canceled. The
handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is
returned when the $SETCLUEVT service is called.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode of the cluster configuration event to be canceled. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
Each access mode has a symbolic name. The $PSLDEF macro defines the
following symbols for the four access types:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event code indicating the type of cluster configuration event for which
an AST is no longer to be delivered. The event
argument is a value indicating which type of event is no longer of
interest.
Each event type has a symbolic name. The $CLUEVTDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CLUEVT$C_ADD
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system.
|
|
CLUEVT$C_REMOVE
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster
system.
|
Description
The Clear Cluster Event service removes one or more notification
requests previously established by a call to the $SETCLUEVT service.
$CLRCLUEVT verifies that the parameters specify a valid request, and
dequeues and deallocates the request.
A valid request specifies either the handle argument
or the event argument. If the handle
argument is specified, the acmode argument must match
the value recorded when $SETCLUEVT was called. If the
event argument is specified, all requests matching the
access mode are canceled, provided that the access mode is not greater
than the caller's mode. If the access mode parameter is more privileged
than the mode of the caller, the mode of the caller will be used.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SETCLUEVT, $TSTCLUEVT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
There is an unsatisfactory combination of event and handle parameters,
or the event was specified incorrectly.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
No request was found that matches the description supplied.
|
$CLREF
Clears (sets to 0) an event flag in a local or common event flag
cluster.
Format
SYS$CLREF efn
C Prototype
int sys$clref (unsigned int efn);
Argument
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be cleared. The efn
argument is a longword containing this number; however, $CLREF uses
only the low-order byte.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag was
previously 0. Note that this is also the same value as SS$_NORMAL.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. The specified event flag was
previously 1. Note that while the message id is the same as SS$_ACCVIO,
the severity bits are different.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
$CMEXEC
Changes the access mode of the calling process to executive mode.
Format
SYS$CMEXEC routin ,[arglst]
C Prototype
int sys$cmexec (int (*routin)(__unknown_params), unsigned int *arglst);
Arguments
routin
| OpenVMS usage: |
procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Routine to be executed while the process is in executive mode. The
routin argument is the address of this routine.
arglst
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Argument list to be passed to the routine specified by the
routin argument. The arglst argument
is the address of this argument list.
If the arglst value is nonzero and is not accessible
as an address or if the routine is inaccessible, the service returns
SS$_ACCVIO.
Alpha systems require a pointer to a valid argument list or a value of
0 in the arglst argument. This means that the
arglst argument must contain an accessible virtual
address for an argument list, the first longword of which must be a
valid list size.
Description
The Change to Executive Mode service allows a process to change its
access mode to executive, execute a specified routine, and then return
to the access mode in effect before the call was issued.
The $CMEXEC service uses standard procedure calling conventions to pass
control to the specified routine.
On Alpha systems, to conform to the OpenVMS calling standard, you must
not omit the arglst argument.
On VAX systems, if no argument list is specified, the argument pointer
(AP) contains a 0. However, to conform to the OpenVMS calling standard,
you must not omit the arglst argument.
On Alpha and VAX systems, when you use the $CMEXEC service, the system
service dispatcher modifies the registers before entry into the target
routine. The specified routine must exit with a RET instruction and
should place a status value in R0 before returning.
All of the Change Mode system services are intended to allow for the
execution of a routine at an access mode more (not less) privileged
than the access mode from which the call is made. If $CMEXEC is called
while a process is executing in kernel mode, the routine specified by
the routin argument executes in kernel mode, not
executive mode.
Required Access or Privileges
To call this service, the process must either have CMEXEC or CMKRNL
privilege or be currently executing in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
arglst or routine argument is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The routine specified is in a translated image.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to change mode to executive.
|
|
All other values
|
The routine executed returns all other values.
|
$CMEXEC_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, changes the access mode of the calling process to
executive mode.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CMEXEC_64 routin_64 ,arglst_64
C Prototype
int sys$cmexec_64 (int (*routin_64)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64
*arglst_64);
Arguments
routin_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Routine to be executed while the process is in executive mode. The
routin_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of
this routine.
arglst_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Argument list to be passed to the routine specified by the
routin_64 argument. The arglst_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of this argument list.
If the arglst value is nonzero and is not accessible
as an address or if the routine is inaccessible, the service returns
SS$_ACCVIO.
Alpha systems require a pointer to a valid argument list or a value of
0 in the arglst_64 argument. This means that the
arglst_64 argument, if nonzero, must contain an
accessible virtual address for an argument list, the first quadword of
which must be a number between 0 and 255 specifying the number of
quadwords that follow it on the list.
Description
The Change to Executive Mode with Quadword Argument List service allows
a process to change its access mode to executive, execute a specified
routine, and then return to the access mode in effect before the call
was issued.
The $CMEXEC_64 service uses standard procedure-calling conventions to
pass control to the specified routine.
When you use the $CMEXEC_64 service, the system modifies the registers
before entry into the target routine. The specified routine must exit
with a RET instruction.
All of the Change Mode system services are intended to allow for the
execution of a routine at an access mode more (not less) privileged
than the access mode from which the call is made. If $CMEXEC_64 is
called while a process is executing in kernel mode, the routine
specified by the routin_64 argument executes in kernel
mode, not executive mode.
Required Access or Privileges
To call this service, the process must either have CMEXEC or CMKRNL
privilege or be currently executing in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CMEXEC, $CMKRNL, $CMKRNL_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
arglst argument or routine is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The routine specified is in a translated image.
|
|
SS$_NOCMEXEC
|
The process does not have the privilege to change mode to executive.
|
|
All other values
|
The routine executed returns all other values.
|
$CMKRNL
Changes the access mode of the calling process to kernel mode. This
service allows a process to change its access mode to kernel, execute a
specified routine, and then return to the access mode in effect before
the call was issued.
Format
SYS$CMKRNL routin ,[arglst]
C Prototype
int sys$cmkrnl (int (*routin)(__unknown_params), unsigned int *arglst);
Arguments
routin
| OpenVMS usage: |
procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Routine to be executed while the process is in kernel mode. The
routin argument is the address of this routine.
arglst
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Argument list to be passed to the routine specified by the
routin argument. The arglst argument
is the address of this argument list.
If the arglst value is nonzero and is not accessible
as an address or if the routine is inaccessible, the service returns
SS$_ACCVIO.
Alpha systems require a pointer to a valid argument list or a value of
0 in the arglst argument. This means that the
arglst argument must contain an accessible virtual
address for an argument list, the first longword of which must be a
valid list size.
Description
The Change Mode to Kernel ($CMKRNL) and the Change Mode to Executive
($CMEXEC) system services provide a simple and secure path for
applications to execute code in the privileged kernel and executive
processor modes. These services first check for the necessary CMKRNL or
CMEXEC privileges, and then call the routine specified in the argument
list in the specified processor mode.
When code is executing in a privileged processor mode, such as
executive or kernel mode, the code executes with full OpenVMS
privileges. Furthermore, specific protection checks can also be
bypassed. For example, $CMKRNL bypasses the check for CMKRNL privilege
that is normally required when $CMKRNL is called from executive mode,
and $SETPRV calls are processed without SETPRV privilege when called
from executive or kernel mode.
The condition value returned from the procedure specified in the
argument list is used as the return status from the $CMKRNL or $CMEXEC
system service call. Based on the OpenVMS calling standard, this
condition value is returned by register R0, using a language-specific
mechanism.
Note
The $CMKRNL and $CMEXEC system services are typically used to access
privileged or internal OpenVMS routines or data structures. The code to
access these data structures can be OpenVMS version-dependent,
particularly if the internal routines or data structures change. Errors
that occur in code executing in a privileged processor mode can lead to
one or more possible situations: data corruptions, process deletions,
or system crashes.
The particular library routines and libraries that can be called from
code executing in executive or kernel mode can also be limited, because
not all library routines accessible from user mode can be called from
kernel mode.
|
Code Example
The following code example shows how to call a specified routine in
kernel mode using this service:
/*
// cmkrnl.c
//
// OpenVMS example of calling a specified routine in kernel mode,
// using the SYS$CMKRNL system service.
//
// Requires CMKRNL privilege.
//
// Errors in kernel-mode code can corrupt critical data structures,
// can cause process deletions, and can potentially crash the OpenVMS
// operating system.
//
// To build:
//
// $ CC/DECC CMKRNL
// $ LINK CMKRNL
// $ RUN CMKRNL
*/
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stsdef.h>
/*
// The KernelRoutine routine executes in kernel mode, but does
// absolutely nothing useful.
*/
int KernelRoutine( int *UsrArg1, int *UsrArg2)
{
return SS$_NORMAL;
}
main()
{
int RetStat;
int ArgList[3];
int i = 0;
printf("OpenVMS Alpha example of calling sys$cmkrnl\n");
/*
// Build the routine argument list in an array -- the KernelRoutine
// call expects two arguments, necessitating an array containing the
// count and the two arguments.
*/
ArgList[++i] = 1;
ArgList[++i] = 2;
ArgList[0] = i;
/*
// Now invoke the KernelRoutine in kernel mode...
*/
RetStat = sys$cmkrnl( KernelRoutine, ArgList );
if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( RetStat ))
return RetStat;
printf("Now successfully back in user mode.\n");
return SS$_NORMAL;
}
|
Required Access or Privileges
To call the $CMKRNL service, a process must either have CMKRNL
privilege or be currently executing in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CMEXEC, $CMEXEC_64, $CMKRNL_64, $SETPRV
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
arglst argument or routine is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The routine specified is in a translated image.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
The process does not have the privilege to change mode to kernel.
|
|
All other values
|
The routine executed returns all other values.
|
$CMKRNL_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, changes the access mode of the calling process to
kernel mode. This service allows a process to change its access mode to
kernel, execute a specified routine, and then return to the access mode
in effect before the call was issued.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CMKRNL_64 routin_64 ,arglst_64
C Prototype
int sys$cmkrnl_64 (int (*routin_64)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64
*arglst_64);
Arguments
routin_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Routine to be executed while the process is in kernel mode. The
routin_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of
this routine.
arglst_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
arg_list |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Quadword argument list to be passed to the routine specified by the
routin_64 argument. The routin_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of this routine.
If the arglst value is nonzero and is not accessible
as an address or if the routine is inaccessible, the service returns
SS$_ACCVIO.
Alpha systems require a pointer to a valid argument list or a value of
0 in the arglst_64 argument. This means that the
arglst_64 argument, if nonzero, must contain an
accessible virtual address for an argument list, the first quadword of
which must be a number between 0 and 255 specifying the number of
quadwords that follow it on the list.
Description
The Change to Kernel Mode with Quadword Argument List service allows a
process to change its access mode to kernel, execute a specified
routine, and then return to the access mode in effect before the call
was issued.
The $CMKRNL_64 service uses standard procedure calling conventions to
pass control to the specified routine.
When you use the $CMKRNL_64 service, the system modifies the registers
before entry into the target routine. The system loads R4 with the
address of the process control block (PCB). The specified routine (if
programmed in MACRO-32) must exit with a RET instruction.
Required Access or Privileges
To call the $CMKRNL_64 service, a process must either have CMKRNL
privilege or be currently executing in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CMEXEC, $CMEXEC_64, $CMKRNL, $SETPRV
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
arglst argument or routine is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The routine specified is in a translated image.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
The process does not have the privilege to change mode to kernel.
|
|
All other values
|
The routine executed returns all other values.
|
$CONNECT
The Connect service establishes a record stream by associating and
connecting a RAB with a FAB. You can invoke the Connect service only
for files that are already open.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this service.
$CPU_CAPABILITIES (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows modification of the user capability set for a
specified CPU, or for the global user capability CPU default.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CPU_CAPABILITIES cpu_id [,select_mask] [,modify_mask] [,prev_mask]
[,flags]
C Prototype
int sys$cpu_capabilities (int cpu_id, struct _generic_64 *select_mask,
struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct
_generic_64 *flags);
Arguments
cpu_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Identifier of the CPU whose user capability mask is to be modified or
returned. The cpu_id argument is a longword containing
this number, which is in the supported range of individual CPUs from 0
to SYI$_MAX_CPUS - 1 .
Specifying the constant CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS applies the current
modification operation to all CPUs currently in the active set, and to
the default CPU initialization context in SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP. If
the prev_mask argument is also supplied, the previous
default CPU initialization context in SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP will be
returned rather than any specific CPU state.
To modify only the user capabilities in SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP, the
flags argument has a bit constant
CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY. When this bit is set, all service operations
are performed on the global cell rather than on an individual CPU
specified in the cpu_id argument. This bit does not
supersede the CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS constant, however. If both
constants are specified, CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS take precedence;
nevertheless, the operations to SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU are identical
because that function is a direct subset of the other.
select_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying which bits of the specified CPU's user capability mask
are to be modified. The select_mask argument is the
32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set,
specifies that the corresponding user capability is to be modified.
The individual user capability bits in select_mask can
be referenced by their symbolic constant names, CAP$M_USER1 through
CAP$M_USER16. These constants (not zero-relative) specify the position
in the mask quadword that corresponds to the bit name. Multiple
capabilities can be selected by connecting the appropriate bits with a
logical OR operation.
The constant CAP$K_ALL_USER, when specified in the
select_mask argument, selects all user capability bits.
modify_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying the settings for those capabilities selected in the
select_mask argument. The modify_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein
a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding user capability is to
be added to the specified CPU; when clear, the corresponding user
capability is to be removed from the specified CPU.
The bit constants CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16 can be used to
modify the appropriate bit position in modify_mask.
Multiple capabilities can be modified by connecting the appropriate
bits with OR.
To add a specific user capability to the specified CPU, that bit
position must be set in both select_mask and
modify_mask. To remove a specific user capability from
the specified CPU, that bit position must be set in
select_mask and cleared in
modify_mask.
The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_ADD, when specified in
modify_mask, indicates that all capabilities specified
in select_mask are to be added to the current user
capability set. The constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_REMOVE indicates that all
capabilities specified are to be cleared from the set.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous user capability mask for the specified CPU before execution of
this call to $CPU_CAPABILITIES. The prev_mask argument
is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword into which $CPU_CAPABILITIES
writes a quadword bit mask specifying the previous user capabilities.
If this argument is specified in conjunction with CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS
as the cpu_id selection constant or with
CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY, the user capability portion of the default
boot initialization state context SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP will be
returned.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability modification. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified in the following
table are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and
must be 0.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined by the $CAPDEF macro.
The flags argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY
|
Indicates that the specified operations are to be performed on the
global context cell instead of on a specific CPU. This bit supersedes
any individual CPU specified in
cpu_id but does not override the all active set
behavior (CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS). Specifying this bit constant applies
this operation to the default startup capabilities for all CPUs booted
for the first time.
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
|
Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a nonrunnable state
under some circumstances. No operation of this service allows a
transition from a runnable to blocked state; however, if the kernel
thread is already at a blocked state, this bit determines whether the
result of the operation must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
is set or
flags is not specified, the kernel thread is checked
to ensure that it can safely run on one of the CPUs in the active set.
If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU is not set, any state operations on kernel
threads already in a blocked state are allowed.
|
Description
The Modify CPU User Capabilities system service, based on the arguments
select_mask and modify_mask, adds or
removes user capabilities for the specified cpu_id. If
specified, the previous capability mask is returned in
prev_mask. With the modify_mask
argument, multiple user capabilities for a CPU can be added or removed
in the same system service call.
Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or
both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask
is specified, select_mask must be specified as an
argument. If modify_mask is not specified, no
modifications are made to the user capability mask for the specified
CPU. In this case, select_mask is ignored. If
prev_mask is not specified, no previous mask is
returned.
No service state changes that will place any currently runnable kernel
thread into a blocked state are allowed.
If CAP$K_ALL_ACTIVE_CPUS is specified in cpu_id, the
user capability modifications are performed on all CPUs currently in
the active set, as well as the global initialization cell. If the bit
constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the flags
argument, the user capability modifications are made only to the global
initialization cell, regardless of what individual CPU is specified in
cpu_id.
Required Access or Privileges
The caller must have both ALTPRI and WORLD privileges to call
SYS$CPU_CAPABILITIES to modify CPU user capabilities.
No privileges are required if SYS$CPU_CAPABILITIES is called only to
retrieve the current user capabilities mask from the specified CPU or
global default.
Related Services
$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments has an invalid value, or the specified CPU is not
in the configuration.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_CPUCAP
|
Attempted operation would place one or more processes in an unrunnable
state.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified, or no
operation was specified.
|
$CPU_TRANSITION (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, changes the current processing state of a CPU in the
configure set of the current system or an unassigned CPU in an OpenVMS
Galaxy configuration. This service completes asynchronously. For
synchronous completion, use the $CPU_TRANSITIONW service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses. Parameter and bit definitions
are resolved in $CSTDEF in the appropriate STARLET library.
Refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide for more information.
Format
SYS$CPU_TRANSITION tran_code ,cpu_id ,nodename ,node_id ,flags ,efn
,iosb ,astadr_64 ,astprm_64
C Prototype
int sys$cpu_transition (int tran_code, int cpu_id,
dsc64$descriptor_s_pq nodename, int node_id, uint32 flags, int efn,
IOSB *iosb, VOID_PQ astadr, uint64 astprm, uint32 timout);
Arguments
tran_code
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Identifier specifying the type of state change to be initiated on the
target CPU. The tran_code argument is a longword
containing one of the following values:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CST$K_CPU_STOP
|
The target CPU is to be removed from the active set and halted into
console mode. It remains in the configure set of the current partition.
|
|
CST$K_CPU_MIGRATE
|
The target CPU is removed from the configure set of the local partition
and the console is requested to add it to the configure set of the
partition specified in node_id. If the CPU is currently in the active
set, it is automatically brought to console mode through the
CST$K_CPU_STOP function first.
|
|
CST$K_CPU_START
|
The target CPU is requested to exit console mode and join the active
set of the current partition. The CPU must already be part of the
configure set.
|
|
CST$K_CPU_FAILOVER
|
The CPU is assigned a default target partition where it will
automatically migrate on system failure. This assignment persists until
it is superseded. To remove an assignment or partition name, the
current partition ID should be specified.
|
|
CST$K_CPU_POWER_OFF
|
The requested operation is initiated on the target CPU to bring the
electrical power to the OFF state. If the CPU is currently in the
active set, it is automatically brought to console mode through the
CST$K_CPU_STOP function first.
|
|
CST$K_CPU_POWER_ON
|
The requested operation is initiated on the target CPU to bring the
electrical power to the ON state.
|
Each $K code represents an end state operation, each of which has a
specific start state that the CPU must be in, in order to initiate the
transition.
This service may automatically initiate a successful completion of the
requested operation by initiating one or more transparent transitions.
This operation takes place if the CPU is not in that specific start
state, and there are an obvious and unique set of transitions that can
be initiated prior to the specified end state.
Multiple transitions can also be initiated simultaneously through the
system service tran_code parameter. Each transition
code has a $M form as shown in the following list, that can be or'd
with a specific end state $K code:
- CST$M_CPU_STOP
- CST$M_CPU_MIGRATE
- CST$M_CPU_START
- CST$M_CPU_FAILOVER
- CST$M_CPU_POWER_OFF
- CST$M_CPU_POWER_ON
Any legal combination of transitions can be specified with the $M form,
however no more than one $K code is allowed.
cpu_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Identifier of the CPU whose state is to be modified. The
cpu_id argument is a longword number in the supported
range of individual CPUs from 0 to SYI$_MAX_CPUS - 1.
Generic identifiers can also be used to allow OpenVMS to select the
most appropriate resource. The following table lists these codes:
| Code |
Description |
|
CST$K_ANY_OWNED_CPU
|
Any CPU in the configure set, regardless of the active set state
|
|
CST$K_ANY_ACTIVE_CPU
|
Any CPU in the active set
|
|
CST$K_ANY_STOPPED_CPU
|
Any CPU in the configure set, but not the active set
|
node_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Identifier of the target Galaxy partition in CST$K_CPU_ASSIGN,
CST$K_CPU_FAILOVER, or CST$K_CPU_MIGRATE transition. The
node_id argument is a longword containing a number in
the supported range of IDs provided by the console for the current
hardware platform. If the nodename parameter is
specified, node_id is ignored.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_mask |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Options selected for the CPU state transition. The
flags argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified below are used; the
remainder of the longword bits are reserved and must be 0.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name. The flags
argument is constructed by performing a logical OR operation using the
symbolic names of the following options:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CST$V_CPU_DEFAULT_CAPABILITIES
|
At the completion of the transition, the CPU's user capabilities are
set back to the default system value. If this option is not specified,
modified user capabilities are maintained across STOP and START
transitions as long as the CPU remains in the local partition configure
set.
|
|
CST$V_CPU_ALLOW_ORPHANS
|
The transition is to be allowed even though it will leave at least one
thread in the system unable to execute on any CPU in the active set.
|
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The event flag to be set when the state transition attempt has
completed. The efn argument is a longword specifying
the number of the event flag; however, this service only uses the
low-order byte.
When you invoke $CPU_TRANSITION, the specified event flag is cleared;
when the operation is complete, the event flag is set.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_area |
| type: |
IOSB structure |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
The I/O status area to receive the final completion status of the
transition operation. The iosb argument is the 32-bit
or 64-bit virtual address of the I/O status area. The I/O status area
structure is 32 bytes in length; its definition can be found in
$IOSBDEF in STARLET.MLB for macro and in the file IOSBDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB for C.
When you call $CPU_TRANSITION, the I/O status area is cleared. After
the transition operation is complete, the block is modified as follows:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
iosb$w_status
|
The first word contains the condition value return, indicating the
final completion status of the operation.
|
|
|
The first bit in the second word of the IOSB is set only if an error
occurred during the operation; the remaining bits are zeroes.
|
astadr_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
The AST routine to be executed when the requested transition attempt
has completed. The astadr_64 argument is the 32-bit or
64-bit virtual address of this routine. If you specify the
astadr_64 argument, the AST routine executes at the
access mode from which the state transition was requested.
astprm_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The quadword AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
Description
The state transition in tran_id is requested for the
target cpu_id.
A CPU currently in the active set can transition:
- To the STOPPED state; removed from the active set and left in the
configure set, halted in console mode.
A CPU in the configure set can transition:
- To the UNASSIGNED state by STOPPING it and then DEASSIGNING it back
to the console.
- To the ACTIVE state; warm rebooted and a full member of the
symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) active set on the requesting partition.
- To another partition through MIGRATION; the target CPU is removed
from the configure set and added to the configure set of the partition
specified by node_id.
A CPU in the Galaxy unassigned state (not in the configure set of any
partition in the platform) can transition:
- To the ASSIGNED state; in the configure set of the partition.
specified by node_id. Any partition can make the
assignment, but the CPU must be unassigned.
CPU state transition is a two-phase operation in the OpenVMS scheduling
model. This service initiates the request in the process context of the
caller and returns the setup status in the service condition value.
Phase 2 proceeds asynchronously; the efn and
iosb arguments can be used to indicate the completion
of the transition through the standard wait system services. Additional
notification of the completion can be made through the OpenVMS AST
mechanisms using a routine specified in astadr_64 and
a user-supplied parameter in astprm_64.
Required Privileges
The caller must have the CMKRNL privilege to call SYS$CPU_TRANSITION to
modify CPU states.
Related Services
$CPU_TRANSITIONW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One of more arguments has an invalid value or the specified CPU is not
in the configuration.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
Caller does not have CMKRNL privilege needed to complete operation.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no
operation was specified.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
More arguments were specified than are allowed by the service.
|
|
SS$_INVCOMPID
|
The target partition ID is not valid in this configuration.
|
|
SS$_CPUNOTACT
|
The specified CPU is not part of the current partition's active set.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHCPU
|
The specified CPU does not exist in the current hardware configuration,
or is not in the configure set of the local partition.
|
|
SS$_CPUSTARTD
|
The specified CPU is already in the local active set, or is in the
process of joining it.
|
|
SS$_CPUSTOPPING
|
The specified CPU is already STOPPED or in the processing of leaving
the active set.
|
$CPU_TRANSITIONW (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, changes the current processing state of a CPU in the
configure set or an unassigned CPU in a Galaxy configuration. This
service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller only
after the final completion status of the operation is known.
In all other respects, $CPU_TRANSITIONW is identical to
$CPU_TRANSITION. For all other information about the $CPU_TRANSITIONW
service, refer to the description of $CPU_TRANSITION in this manual.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide for more information.
Format
SYS$CPU_TRANSITIONW tran_id ,cpu_id ,nodename ,node_id ,flags ,efn
,iosb ,astadr_64 ,astprm_64
C Prototype
int sys$cpu_transitionw (int tran_code, int cpu_id,
dsc64$descriptor_s_pq nodename, int node_id, uint32 flags, int efn,
IOSB *iosb, UINT64_PQ astadr, uint64 astprm, uint32 timout);
$CREATE
The Create service constructs a new file according to the attributes
you specify in the FAB. If any XABs are chained to the FAB, then the
characteristics described in the XABs are applied to the file. This
service performs implicit Open and Display services.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this service.
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a buffer object out of a range of pages.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,flags
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 ,buffer_handle_64
C Prototype
int sys$create_bufobj_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64
length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void
*(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64, struct
_generic_64 *buffer_handle_64);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Starting virtual address of the pages to be included in the buffer
object. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a
CPU-specific page boundary.
The virtual address space must already exist.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be included in the buffer
object. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page
boundary such that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested
range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
For the $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 service to complete successfully, the
resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the
access mode already associated with the pages in the specified input
range.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the request options. The flags
argument is a longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a
flag. The $CBODEF macro in STARLET.MLB and CBODEF.H file in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define a symbolic name for each flag.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 service:
| Flag |
Value |
Description |
|
CBO$M_RETSVA
|
1
|
If set, returns the system virtual address in the
return_va_64 argument instead of the process virtual
address range. (Valid for inner mode callers only.)
|
|
CBO$M_SVA_32
|
4
|
If set, creates the buffer object window in 32-bit S0/S1 space. (By
default, this service creates the window in 64-bit S2 space.)
|
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages in the buffer object.
The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range in the buffer object. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
buffer_handle_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
handle |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which a buffer handle is returned to be used when referencing the
created buffer object.
Description
The Create Buffer Object service creates a buffer object for use by the
I/O subsystem. The pages that constitute the buffer object are
permanently locked into physical memory (but not the process's working
set) and double mapped into system space. The net effect is the
following:
- I/O can be initiated to or from the buffer without the need to
probe or lock the buffer pages.
- The process is still fully swappable.
If the condition value, SS$_ACCVIO, is returned by this service, a
value cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by
the return_va_64, return_length_64,
and buffer_handle_64 arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
made part of the buffer object before the error occurred. If no pages
were made part of the buffer object, the return_va_64
argument will contain the value -1, and a value is not
returned in the memory location pointed to by the
return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
No privileges are required if calling $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 from an inner
mode. If calling from user mode, the process must hold the rights
identifier VMS$BUFFER_OBJECT_USER at the time of the call. This
identifier is normally granted by the system administrator via the
Authorize utility.
Required Quota
No process quota is charged, but the number of pages is limited by the
system parameter MAXBOBMEM.
Related Services
$CRETVA_64, $DELETE_BUFOBJ, $EXPREG_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64,
return_length_64, or
buffer_handle_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid flags options specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBUFOBJLM
|
Buffer object cannot be created because it would bring the total number
of buffer object pages above the systemwide limit MAXBOBMEM.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient dynamic memory.
|
|
SS$_INSFSPTS
|
Insufficient system page table entries.
|
|
SS$_NOBUFOBJID
|
The process attempted to create a buffer object from user mode but was
not holding required rights identifier VMS$BUFFER_OBJECT_USER.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Valid flag options were specified but from user mode.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTWRITE
|
A page within the address range is not writable.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
The pages could not be put into the buffer object because the access
mode associated with the call to $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 was less privileged
than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK (Alpha Only)
Allocates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock block from a lock table created with
the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE service.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment.
For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system
services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK lcktbl_handle ,name ,size ,timeout ,ipl ,rank
,handle
C Prototype
int sys$create_galaxy_lock (unsigned int lcktbl_handle, void *name,
unsigned int size, unsigned int timeout, unsigned int ipl, unsigned int
rank, unsigned __int64 *lock_handle);
Arguments
lcktbl_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
lock table handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The 32-bit lock table handle that identifies the lock table in which to
create the lock. This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE.
name
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
ASCID string |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by reference |
The name parameter is a pointer to an ASCID string
(passed by descriptor). The name can be a maximum of 15 characters.
Lock names are not checked for uniqueness; therefore, multiple locks
can be created with the same name.
timeout
| OpenVMS usage: |
wait timeout |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The 32-bit wait or spin timeout specified in 10 microsecond units. If
not specified, the timeout defaults to 10 microseconds.
size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The size of the galaxy lock in bytes. Galaxy locks have two legal
sizes. These values are returned by SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE. The value
passed to SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK must be equal to the value passed to
the call to SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE.
ipl
| OpenVMS usage: |
IPL of lock |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
For galaxy locks acquired in kernel mode, the IPL to raise to while the
lock is held. This parameter is ignored for all other access mode.
rank
| OpenVMS usage: |
rank of lock |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
Rank applied to a galaxy lock. Ranking is used to detect potential
deadlocks. This parameter is currently ignored.
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
The handle parameter is a pointer to a quadword. The value returned is
a 64-bit handle that uniquely identifies the lock galaxy-wide.
Description
This service allocates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock block from a lock table
created with the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE service.
Required Access or Privileges
For System Lock: CMKRNL, SHMEM
For User Lock: SHMEM
Write access to Lock Table
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO,
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADLCKTBL
|
OpenVMS Galaxy lock table is corrupt.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKID
|
Invalid lock id.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKTBL
|
Invalid lock table.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient memory in lock table.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
Operation requires CMKRNL privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOSHMEM
|
Operation requires SHMEM privilege.
|
$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE (Alpha Only)
Allocates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock table.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment.
For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system
services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE name ,accmode ,section_size ,section_type
,prot ,lock_size ,lcktbl_handle
C Prototype
int sys$create_galaxy_lock_table (void *name, unsigned int accmode,
unsigned __int64 section_size, unsigned int section_type, unsigned int
prot, unsigned int lock_size, unsigned int *lcktbl_handle);
Arguments
name
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
ASCID string |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by reference |
The name parameter is a pointer to an ASCID string (passed by
descriptor). The name is given to the global section that is created to
contain the galaxy locks.
accmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The accmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
section_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
Length of the global section to be created, in bytes. The size must be
specified as a multiple of the CPU-specific page size. A size of zero
is illegal.
section_type
| OpenVMS usage: |
bit mask |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
Used to control where in virtual memory the global section is created.
If GLCKTBL$C_PROCESS is specified, the section is created in P2
(process) space. If GLCKTBL$C_SYSTEM is specified, the section is
created in S0/S1 (system) space. These constants are defined in the
GLOCKDEF macro.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
Protection to be applied to the global section.
The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left
in each field. The following diagram depicts the mask:
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user.
Only read and write access are meaningful for lock section protection.
Delete access bits are ignored.
lock_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The size of the galaxy lock in bytes. Galaxy locks have two sizes. The
legal values are returned by SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE.
lcktbl_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is a 32-bit handle that
uniquely identifies the lock table galaxy-wide.
Description
This service allocates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock table. This structure is
used to maintain information about a shared memory section, which this
service also creates. The first caller of the service with a unique
lock table name creates the section. Additional callers map it. This
shared memory section contains a set of Galaxy locks. All locks
residing in the section are of the same size. Once the lock table is
created, the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK service can be used to create and
allocate a lock from the table.
The flags GLCKTBL$C_PROCESS and GLCKTBL$C_SYSTEM specify whether the
shared memory region is mapped into system space or process space.
Creation of process space sections requires the SHMEM privilege.
Creation of system space sections requires the SHMEM and CMKRNL
privileges.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL, SHMEM
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO,
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
File or section did not exist; has been created.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKID
|
Invalid lock id.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
No privilege for attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
Operation requires CMKRNL privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOSHMEM
|
Operation requires SHMEM privilege.
|
$CREATE_GDZRO (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a permanent, memory-resident, global
demand-zero section to which processes can map. Shared page table
sections can also be created.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GDZRO gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64 ,acmode ,flags
[,reserved_length_64] [,rad_mask]
C Prototype
int sys$create_gdzro (void *gs_name_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int flags,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of the global
section. The ident_64 argument is a quadword
containing three fields. The ident_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that
contains the identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. Their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global demand-zero section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If 0 is specified, read
access and write access are granted to all users.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global demand-zero section to be created. The
length_64 argument must be specified as a multiple of
the CPU-specific page size. A length of 0 cannot be specified.
Note
Creating a memory-resident global section with shared page tables does
not imply that the global section must have a length that is an even
multiple of CPU-specific page table pages. The global section might not
fully use the last shared page table page.
|
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
If the memory-resident global section is created with shared page
tables, this is the access mode that is stored in the owner, read, and
write fields of the corresponding shared page table entries (PTEs).
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of global section to be created as well
as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_GDZRO service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_MRES
|
Pages form a memory-resident section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_RAD_HINT
|
When set, the argument
rad_mask is used as a mask of RADs from which to
allocate memory. See the
rad_mask argument description for more information.
|
|
SEC$M_READ_ONLY_SHPT
|
Create shared table pages for the section that allow read access only.
|
|
SEC$M_SHMGS
|
Create a shared-memory global section.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set.
reserved_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
32- or 64-bit reference |
Length, in bytes, of the global section as currently registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry. The reserved_length_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned
quadword into which the service returns the reserved length.
If reserved_length_64 is not specified or is specified
as 0, no reserved length is returned to the caller.
If the memory-resident global section is not registered,
reserved_length_64 is written with the value 0.
rad_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Use the rad_mask argument to specify from which RADs
to allocate memory. Currently only one bit may be set. The specified
RAD must contain memory. This argument is only a hint. Memory may be
obtained from other RADs if no free memory is available at the time of
allocation.
The rad_mask argument is considered only if the
SEC$M_RAD_HINT flag is specified. Otherwise, this argument is ignored.
On a system that does not support resource affinity domains (RADs),
specifying 1 for the rad_mask argument is allowed.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Demand-Zero Section service allows a
process to create a permanent, memory-resident, global demand-zero
section. If you set the SEC$M_SHMGS flag, the section is created as a
Galaxy-wide global demand-zero section in shared memory.
You must call either the $CREATE_GDZRO service or the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64
service on each instance where the Galaxy shared memory will be
accessed.
Memory-resident or Galaxy-wide global sections contain demand-zero
allocation pages that are writable and memory resident. All pages in
these types of global section are shared by all processes that map to
the global section.
The pages are always resident in memory and are not backed up by any
file on any disk. The pages are not placed into the process's working
set list when the process maps to the global section and the virtual
memory is referenced by the process. The pages are also not charged
against the process's working set quota or against any page-file quota.
To create a memory-resident section, the process must have the rights
identifier, VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER. The error status, SS$_NOMEMRESID, is
returned if the caller has not been granted this identifier. To create
a Galaxy-wide shared section, the process must have the SHMEM privilege.
Only memory-resident sections can be registered with the Reserved
Memory Registry in the SYSMAN facility. Memory for Galaxy-wide shared
sections is reserved through appropriate settings of the console
environment parameters.
If the section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, or if
the /NOALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was
registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, invalid global PTEs are
written to the global page table. When the global section is mapped,
invalid page table entries are placed in the process page table.
Physical memory is not allocated until the pages are referenced.
If the global section is registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,
the size of the global section need not match the reserved size. If the
global section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, or if
the reserved size is smaller than the size of the global section, the
error status SS$_INSFLPGS is returned if there are not enough fluid
pages in the system to satisfy the request.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was
registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, contiguous, aligned,
physical pages are preallocated during system initialization for this
global section. Valid page table entries are placed in the global page
table and when the global section is mapped, valid page table entries
are placed in the process page table. With the proper virtual
alignment, granularity hints (GH) are used to map to the global pages.
If the global section is not registered in the Reserved Memory
Registry, or if the /PAGE_TABLES qualifier was specified when the
global section was registered, shared page tables are created for the
memory-resident global section.
If the /ALLOCATE and /PAGE_TABLE qualifiers were specified when the
global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,
contiguous, aligned physical pages are preallocated during system
initialization for this global section, and granularity hints are used
to map to the shared page table sections.
The following table lists the factors affecting the creation of shared
page tables for memory-resident global sections. The /ALLOCATE and the
/PAGE_TABLES qualifiers pertain to the Reserved Memory Registry command
RESERVED_MEMORY ADD entered for the memory-resident global section
being created. For more information about using the SYSMAN utility to
create entries to the Reserved Memory Registry, refer to the
HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
| /ALLOCATE |
/PAGE_TABLES |
Outcome |
|
Not registered
|
Not registered
|
Shared page tables created.
Shared page tables cannot use GH.
Returns SS$_CREATED_SHPT.
|
|
No
|
No
|
No shared page tables created.
Returns SS$_CREATED.
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
Shared page tables created.
Shared page tables cannot use GH.
Returns SS$CREATED_SHPT.
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
No shared page tables created.
Returns SS$_CREATED.
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Shared page tables created.
Shared page tables can use GH.
Returns SS$_CREATED_SHPT.
|
Shared page tables are always created for Galaxy-wide shared sections
of at least 128 pages.
Shared page tables consume the same internal OpenVMS data structures as
global sections. The system parameters GBLPAGES and GBLSECTIONS must
account for the additional global pages and the additional global
section.
Note that only one set of shared page tables can be associated with any
memory-resident or Galaxy-wide section. By default, shared page tables
will allow write access. To create shared page tables that allow only
read access, you must set the READ_ONLY_SHPT flag. A process that
requires write access to a section where the shared page tables only
allow read access must use private page tables to map the section.
To use the shared page tables associated with a memory-resident global
section, a process must first create a shared page table region (with
$CREATE_REGION_64). Additionally, a subsequent request to map to the
memory-resident global section must do the following:
- Specify a shared page table region to the mapping request (see
Table SYS-22 for additional information).
- Specify the same access mode as specified by the
acmode argument to this service.
- Set the flag SEC$M_WRT in the mapping request only if shared page
tables allow write access.
- Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG in the mapping request or provide a
CPU-specific page table page aligned virtual address. (See the
description of the CREATE_REGION_64 service for information about
calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specific page
table page boundary.)
If a shared page table region is not specified, process-private page
tables are used to map to the global section.
If the service returns an error status value that is neither
SS$_INSFLPGS nor SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL, a value is not returned in the
reserved_length_64 argument.
If the service returns a successful condition value or if SS$_INSFLPGS
or SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the
reserved_length_64 argument is specified as a nonzero
address, the length in bytes of the global section as registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry is returned in the
reserved_length_64 argument.
To map a Galaxy shared section or a memory resident section, see the
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service.
Refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide for additional information.
Required Privileges
To create a permanent memory-resident global DZRO section, the process
must have the following privileges or rights identifiers:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER rights identifier to create a memory-resident
section
- SHMEM privilege on OpenVMS Galaxy systems to create an object in
Galaxy shared memory.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
A Galaxy-wide section already existed and has been made available.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
Global section has been created.
|
|
SS$_CREATED_SHPT
|
Global section has been created with shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or
the
reserved_length_64 argument was specified as a nonzero
value and cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADRAD
|
The specified RAD contains no memory, or if the specified RAD is
greater than or equal to the maximum number of RADs on the system.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the global section or for the shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_INSFLPGS
|
Insufficient fluid pages available.
|
|
SS$_INSFRPGS
|
Insufficient free shared pages or private pages.
|
|
SS$_INV_SHMEM
|
Shared memory is not valid.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVPROTECT
|
The protection argument format is invalid.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages.
|
|
SS$_LOCK_TIMEOUT
|
An OpenVMS Galaxy lock timed out.
|
|
SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL
|
Preallocated, contiguous, aligned physical memory specified in the
Reserved Memory Registry is smaller than the length specified for the
global section by the
length_64 argument.
|
|
SS$_NOBREAK
|
An OpenVMS Galaxy lock is held by another node and was not broken.
|
|
SS$_NOMEMRESID
|
The process attempted to create a memory-resident section but was not
holding the correct identifier (VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER).
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table for
the global section or for the shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_GFILE (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a permanent global disk file section to which
processes can map.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GFILE gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,file_offset_64 ,length_64 ,chan
,acmode ,flags ,return_length_64 [,fault_cluster]
C Prototype
int sys$create_gfile (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned __int64 file_offset_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned
short int chan, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, unsigned
__int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit string
descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword and contains two fields: a
minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major
identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign values for
these fields by installation convention to differentiate versions of
global sections. If no version number is specified when a section is
created, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot
access the global section.
file_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Byte offset into the file that marks the beginning of the section. The
file_offset_64 argument is a quadword containing this
number. If you do not specify the file_offset_64
argument or specify it as 0, the section is created beginning with the
first byte in the file.
The file_offset_64 argument must be a multiple of
virtual disk blocks.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global disk file section to be created. The
length specified must be 0 or a multiple of virtual disk blocks. If the
length specified is 0 or extends beyond end-of-file (EOF), the global
disk file section is created up to and including the virtual block
number that contains EOF.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. The
chan argument is a longword containing this number.
The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to or
less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
You can use the OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) macro $OPEN to
access a file; the file options parameter in the file access block must
indicate a user file open (UFO keyword).
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of global section to be created as well
as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CREATE_GFILE service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Pages are copy-on-reference. By default, pages are shared.
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when
copied.
Note that SEC$M_DZRO and SEC$M_CRF cannot both be set and that
SEC$M_DZRO set and SEC$M_WRT clear is an invalid combination.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the global section created. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the global section in bytes.
fault_cluster
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Page fault cluster in byte units indicating how many pages are to be
brought into memory when a page fault occurs for a single page. The
fault cluster specified is rounded up to a multiple of CPU-specific
pages.
If this argument is specified as 0, the system default page fault
cluster is used. If this argument is specified as more than the maximum
allowed for the system, no error is returned. The systemwide maximum is
used.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Disk File Section service allows a process
to create a permanent global disk file section.
Creating a global disk file section involves defining all or part of a
disk file as a section. The global section is created as entire pages;
however, the last page in the section might correspond to less than a
full page of virtual disk blocks. Only the number of virtual disk
blocks specified by the length_64 argument, or as many
as exist in the disk file, will be associated with the disk file
section.
Upon successful completion of this service, the
return_length_64 argument will contain the length of
the global section created in even multiples of virtual disk blocks.
The security profile of the file is used to determine access to the
global section. For a global disk file section to allow write access to
the file during the mapping of the global section, the channel used to
open the file must allow write access to the file.
Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the following
privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_CHANVIO
|
The specified channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The
file_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
Process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to map
the requested file.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
was 0 or a channel that is unassigned.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
The channel number specified is currently active, or there are no files
opened on the specified channel.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
is larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLVEC
|
The specified section was not installed using the /PROTECT qualifier.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk
blocks.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device.
|
|
SS$_NOWRT
|
The file is read only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set.
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTBLKALGN
|
The
file_offset_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual
disk blocks.
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_GPFILE (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a permanent global page file section to which
processes can map.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GPFILE gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64 ,acmode ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$create_gpfile (void *gs_name_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int flags);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. Their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If 0 is specified, read
access and write access are granted to all users.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global page file section to be created. The
length_64 argument must be specified as a multiple of
the CPU-specific page size. A length of 0 cannot be specified.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of global section to be created as well
as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_GPFILE service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Pages form a global page-file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies
SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Page File Section service allows a process
to create a permanent global page file section. Global page file
sections contain demand-zero allocation pages that are writable and
backed up by the system page file. All pages in the global page file
section are shared by all processes that map to the global section.
Required Privileges
To create a permanent global page file section, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
The systemwide number of global page file pages is limited by the
system parameter GBLPAGFIL.
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages or was specified as 0.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_GPFN (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a permanent page frame section to which
processes can map.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GPFN gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,start_pfn ,page_count
,acmode ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$create_gpfn (void *gs_name_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned int start_pfn, unsigned int page_count,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two
bits.
The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified, and
their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page frame section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,
read access and write access are granted to all users.
start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: |
page frame number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins in memory.
page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the page frame section to
be created. The flags argument is a longword bit
vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and
the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct
the flags argument by performing a logical OR
operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_GPFN service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global page frame section. By default, pages form a
group global page frame section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Page Frame Section service allows a process
to create a global page frame section. All global page frame sections
are permanent. Pages mapped to a global page frame section are not
included in or charged against the process's working set; they are
always valid.
Do not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET_64; this
can result in a machine check if they are in I/O space.
Required Privileges
To create a permanent global page frame section, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_RDB
Initializes a rights database.
Format
SYS$CREATE_RDB [sysid]
C Prototype
int sys$create_rdb (struct _generic_64 *sysid);
Argument
sysid
| OpenVMS usage: |
system_access_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
System identification value associated with the rights database when
$CREATE_RDB completes execution. The sysid argument is
the address of a quadword containing the system identification value.
If you omit sysid, the current system time in 64-bit
format is used.
Description
The Create Rights Database service initializes a rights database. The
database name is the file equated to the logical name RIGHTSLIST, which
must be defined as a system logical name from executive mode. If the
logical name does not exist, the database is created in
SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE] with the file name RIGHTSLIST.DAT. If the database
already exists, $CREATE_RDB fails with the error RMS$_FEX.
The rights database is created with an owner of [1,4] and a protection
of (RWED, RWED, R).
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the directory in which the file is being created is
required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER,
$FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $GRANTID, $GET_SECURITY, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
sysid argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
RMS$_FEX
|
A rights database already exists. To create a new one, you must
explicitly delete or rename the old one.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to SYS$SYSTEM.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$CREATE_REGION_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, creates a virtual region within the process's private
address space.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_REGION_64 length_64 ,region_prot ,flags ,return_region_id_64
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]
C Prototype
int sys$create_region_64 ( unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int
region_prot, unsigned int flags, struct _generic_64 *return_region_id,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual region to be created. The length specified must
be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. This length is fixed at the time
the region is created.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, this length is rounded up to
include an even multiple of CPU-specific pages mapped by a page table
page.
region_prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
region_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Region protection to be associated with the region to be created. The
region_prot argument is a longword containing the
create and owner mode.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define the following symbols for valid combinations of
create and owner modes:
| Symbol |
Create and Owner Modes |
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_UOWN
|
User create mode and user owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_SOWN
|
User create mode and supervisor owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_EOWN
|
User create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_KOWN
|
User create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_SOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and supervisor owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_EOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_KOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_ECREATE_EOWN
|
Executive create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_ECREATE_KOWN
|
Executive create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_KCREATE_KOWN
|
Kernel create mode and kernel owner mode
|
For both create and owner mode, the $CREATE_REGION_64 service uses
whichever of the following two access modes is least privileged:
- Access mode specified by the acmode argument
- Access mode of the caller
A subsequent call to any system service that created address space
within a region must be made from an access mode that is the same or
more privileged than the create mode associated with the region.
A subsequent call to $DELETE_REGION_64 to delete the region must be
made from an access mode that is the same or more privileged than the
owner mode associated with the region.
All regions created by $CREATE_REGION_64 are automatically deleted when
the image is run down on image exit.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the region to be created.
The flags argument is a longword bit vector in which
each bit corresponds to a flag. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB
and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_REGION_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
VA$M_DESCEND
|
Created region is a descending region; that is, allocation occurs
toward decreasing virtual addresses. If VA$M_DESCEND is not specified,
the region allocation occurs toward increasing virtual addresses.
|
|
VA$M_SHARED_PTS
|
Created region requires the virtual address space created within it to
be capable of using shared page tables. If this flag is not specified,
the virtual address space created within the region is mapped by
process-private page tables only. By default, the region does not allow
the use of shared page tables.
|
|
VA$M_P0_SPACE
|
Create region in P0 space. This flag cannot be set if VA$M_P1_SPACE is
set.
|
|
VA$M_P1_SPACE
|
Create region in P1 space. This flag cannot be set if VA$M_P0_SPACE is
set.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP. The condition value SS$_IVREGFLG is returned if any
undefined bits are set.
return_region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the created region. The
return_region_id_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the region ID.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
return address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the region. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the lowest virtual address of the region.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the returned virtual address is
aligned to a CPU-specific page table page boundary. If the global
section mapped by this shared page table region is large enough that
multiple page table pages are required to map the global section, the
page tables themselves can be mapped with granularity hints; therefore,
the alignment of the returned virtual address can be even greater than
that of a single CPU-specific page table page boundary.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the region actually created. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the region in bytes.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the returned length is the input
length rounded up to an even multiple of bytes mapped by a single
CPU-specific page table page.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting address for the created virtual region. The specified
virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the start_va_64 argument is not specified or is
specified as 0, the region can be created anywhere within the following
address spaces:
- P2 space (if the flags VA$M_P0_SPACE and VA$M_P1_SPACE are clear)
- P0 space (if the flag VA$M_P0_SPACE is set and VA$M_P1_SPACE is
clear)
- P1 space (if the flag VA$M_P1_SPACE is set and VA$M_P0_SPACE is
clear)
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set and this argument is specified, the
specified starting address must be aligned to a natural page table page
boundary or an error is returned.
Description
The Create Virtual Region service allows a process to create a virtual
region within its P0, P1, or P2 address space. Once a virtual region
has been created, virtual address space can be created within it using
the system services that accept a region identifier argument. Note that
the virtual region is simply a reservation of virtual address space. No
physical memory is occupied for a virtual region until virtual address
space is created within the region.
If the VA$M_SHARED_PTS flag is set in the flags
argument, only memory-resident global sections can be mapped into the
virtual region. The $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 and $MGBLSC_64 system services are
available for mapping to memory-resident global sections. If a
memory-resident global section was not created with shared page tables,
private page tables are used to map to the global section.
If a memory-resident global section with shared page tables is mapped
into a virtual region that does not have the shared page table
attribute, the global section is mapped with process private page
tables. Other address-space creation services (see Table SYS-18) are
not allowed to create address space into a shared page table region
because they have an implicit dependency on process-private page
tables.
Table SYS-18 Services That Do Not Accept Shared Page Table Regions
| Service |
Description |
|
$CRETVA[_64]
|
Adds a range of demand-zero allocation pages to a process's virtual
address space for the execution of the current image. The new pages are
added at the virtual address specified by the caller.
|
|
$CRMPSC
|
Allows a process to create a private or global section and to map a
section of its address space to the private or global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_FILE_64
|
Allows a process to map a section of its address space to a specified
portion of a file. This service maps a private disk file section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64
|
Allows a process to create a global disk file section and to map a
section of its address space to the global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64
|
Allows a process to create a global page file section and to map a
section of its address space to the global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64
|
Allows a process to create a permanent global page frame section and to
map a section of its address space to the global page frame section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_PFN_64
|
Allows a process to map a section of its address space to a specified
physical address range represented by page frame numbers. This service
creates and maps a private page frame section.
|
|
$DELTVA
|
Deletes a specified number of pages from a process's virtual address
space.
|
|
$EXPREG_[64]
1
|
Adds a specified number of demand-zero allocation pages to a process's
virtual address space for the execution of the current image. Expansion
occurs at the next free available address within the specified region.
|
|
$MGBLSC
|
Establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space
of the process and the pages occupied by a global section.
|
|
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64
|
Establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space
of the process and the pages occupied by a global page frame section.
|
1$EXPREG can specify only the P0 or P1 region and thus
cannot specify a shared page table region.
$CREATE_REGION_64 creates the virtual region on a CPU-specific page
aligned boundary; however, if the VA$M_SHARED_PTS flag is set in the
flags argument, the virtual region is created on a
CPU-specific page table page aligned boundary.
HP recommends that you not specify the start_va_64
argument when creating a shared page table region due to the particular
alignment that must prevail for virtual addresses created within the
virtual region to exploit page table sharing. If the
start_va_64 argument does not contain the proper
alignment, $CREATE_REGION_64 returns SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN.
If a starting virtual address must be specified for a shared page table
region, use the following steps to compute a properly aligned
start_va_64:
- Determine the CPU-specific page size by using the $GETSYI system
service and specifying the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code.
- Determine the number of CPU-specific pages mapped by a single page
table page by using the $GETSYI system service and specifying the
SYI$_PTES_PER_PAGE item code.
- Multiply the CPU-specific page size by the number of pages mapped
by a page table page. The product represents the minimum virtual
alignment required for a shared page table region. It also represents
the number of bytes mapped by a single CPU-specific page table page.
Assuming a system with an 8 kilobyte page size, the alignment of the
start_va_64 argument must be an even multiple of
8,388,608 (8 megabytes). The virtual address, therefore, must have 23
low-order zero bits.
- If the shared page tables are to be mapped with granularity hints
(GH), the address computed in the previous step should to be adjusted
to account for the granularity hint factor. The Alpha architecture
provides three granularity hint factors: 8, 64, and 512 pages.
The virtual address alignment factors required for shared page table
regions (and mappings using shared page tables) are more stringent than
the simple CPU-specific page alignment. Global pages provide a level of
data sharing in which the unit is a single CPU-specific page or, on
today's systems, 8 kilobytes (KB). Shared page tables increase the
level of sharing by an order of magnitude, such that the unit of
sharing is a CPU-specific page table page or, on today's systems, 8
megabytes (MB); therefore, virtual regions that are to be used for
shared page tables and mappings that use shared page tables require an
alignment of at least 8 MB.
Table SYS-19 highlights the values $CREATE_REGION_64 returns for
various region lengths. When the length_64 argument is not an even
multiple of 8 MB, the returned length is rounded up to an even multiple
of 8 MB. This must occur so that a shared page table region ends on an
even CPU-specific page table page boundary.
Note
The requirement for CPU-specific page table page multiples for shared
page table regions does not imply that memory-resident global sections
must also be sized at even CPU-specific page table page multiples.
Memory-resident global sections must be specified in single
CPU-specific page multiples as is the case for global page file
sections.
|
The virtual alignment of the returned address is further biased by the
ability to map the shared page tables with granularity hints. All
values listed are based upon an 8 KB page size. All of the virtual
addresses in the return_va_64 column accommodate the
maximum GH factor for 8 KB page table pages.
Table SYS-19 Sample Returned Values from$CREATE_REGION_64
| length_64 |
return_va_64 |
return_length_64 |
Comments |
|
1,048,576 (1 MB)
|
FFFFFFFB00800000 at least 23 zero bits
|
8,388,608 (8 MB)
|
GH not possible for shared page table pages. Region occupies 1 page
table page.
|
|
67,108,864 (64 MB)
|
FFFFFFFBFC000000 at least 26 zero bits
|
67,108,864 (64 MB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 8 for shared page table pages.
|
|
73,400,320 (70 MB)
|
FFFFFFFBF8000000 at least 26 zero bits
|
75,497,472 (72 MB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 8 for shared page table pages.
Region occupies 9 page table pages. Only the first 8 can be mapped with
GH.
|
|
1,073,741,824 (1 GB)
|
FFFFFFFBC0000000 at least 30 zero bits
|
1,073,741,824 (1 GB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 64 for shared page table pages.
Region occupies 128 page table pages. In this case, there would be two
GH regions, each containing 64 page table pages.
|
If the returned value of the service is not a successful condition
value, a value is not returned in the memory locations pointed to by
the return_region_id_64,
return_va_64, or return_size_64
arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_GDZRO, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,
$DELTVA_64, $EXPREG_64, $GET_REGION_INFO, $MGBLSC_64, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_region_id_64 argument, the
return_va_64 argument, or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_IVREGFLG
|
One or more of the reserved bits in the
flags argument is set, or an illegal combination of
flags bits are set.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The process private address space is full, or no space is available in
the process private address space for a region of the specified size.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified virtual address range is within another virtual
region or is otherwise inaccessible.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned;
or, if the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table
page aligned.
|
$CREATE_UID
Generates a universally unique identifier (UID).
Format
SYS$CREATE_UID uid
C Prototype
int sys$create_uid (unsigned int uid [4]);
Arguments
uid
| OpenVMS usage: |
uid |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the unique identifier is returned to
the calling process.
Description
Generates a identifier that is unique across all computer systems.
Note
To access this service, DECdtm must be running. For information on
enabling and disabling DECdtm services, refer to the chapter on
managing DECdtm services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
|
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The request was successful.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE
Returns an encoded security profile for the specified user.
Format
SYS$CREATE_USER_PROFILE usrnam ,[itmlst] ,[flags] ,usrpro ,usrprolen
,[contxt]
C Prototype
int sys$create_user_profile (void *usrnam, void *itmlst, unsigned int
flags, void *usrpro, unsigned int *usrprolen, unsigned int *contxt);
Arguments
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the user whose security profile is to be returned. The
usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a text string containing the user name. The user name
string can contain a maximum of 12 alphanumeric characters.
For more information about user names, refer to the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying the portions of the user's security profile to be
replaced or augmented.
The item list is a standard format item list. The following figure
depicts the general format of an item descriptor. See the Item Codes
section for a list of valid item codes for $CREATE_USER_PROFILE.

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer from which the service is to read the information.
The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in
the item code field of the item descriptor.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword that normally contains the user-supplied address of a word
in which the service writes the length (in bytes) of the information it
returned. This is not used by $CREATE_USER_PROFILE and should contain a
0.
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The flags argument is used to control the behavior of
the $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service. This argument does not accept ISS$
mask values; therefore, continue to use the CHP$ mask values for this
argument.
The following table describes each flag:
| Symbol |
Description |
|
CHP$M_DEFCLASS
|
By default, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE initializes the security profile with
the user's maximum authorized classification. When this flag is set,
the service initializes the security profile from the user's default
classification instead. This flag is reserved to HP.
|
|
CHP$M_DEFPRIV
|
By default, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE initializes the security profile with
the user's authorized privilege mask. When this flag is set, the
service initializes the security profile from the user's default
privilege mask instead.
|
|
CHP$M_NOACCESS
|
Instructs the service not to access the user authorization file
(SYSUAF.DAT) or rights database (RIGHTSLIST.DAT) to build the security
profile. This flag can be used as an optimization when all the
information necessary to build the security profile is known to the
caller.
|
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Buffer to receive the security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a buffer to receive the encoded security
profile. If an address of 0 is specified, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns
the size of the buffer needed in the usrprolen
argument.
usrprolen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Word to receive the full size of the security profile. On input, the
usrprolen argument specifies the length of the buffer
pointed to by the usrpro argument. The
usrprolen argument is the address of a word to which
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE writes the actual length of the security profile.
If the caller specifies a usrpro address of 0,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns the anticipated size, in bytes, of the
buffer needed to hold the user's security profile in the
usrprolen argument.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword used to maintain authorization file context. The
contxt argument is the address of a longword to
receive a $GETUAI context value. On the initial call, this longword
should contain the value --1. On subsequent calls, the value of the
contxt argument from the previous call should be
passed back in.
Using the contxt argument keeps the UAF open across
all calls, thereby improving the performance of the system on
subsequent calls. To close the UAF, you must run down the image.
The resulting context value from a $CREATE_USER_PROFILE call can also
be used as the input contxt argument to the $GETUAI
system service, and vice versa.
Item Codes
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS
A rights list segment containing additional identifiers to be appended
to the set of identifiers held by the user. A rights list segment is a
list of quadword identifier/attributes pairs, each containing a
longword identifier value, followed by a longword mask identifying the
attributes of the holder. The buflen argument should
be set to the total size, in bytes, of the rights list segment. The
bufadr argument points to a descriptor that points to
the first byte in the rights list segment (that is, the first byte of
the first identifier value).
This item code can be repeated to add up to 256 additional rights list
segments. If more than 256 identifiers are granted to the user,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns SS$_INSFMEM.
CHP$_CLASS
The classification to be associated with the created security profile.
This item code is reserved to HP.
CHP$_PRIV
A quadword privilege mask specifying the user's privileges. The $PRVDEF
macro defines the list of available privileges.
CHP$_UIC
A longword describing the user identification code (UIC).
ISS$_ACCOUNT
Variable-length buffer containing the account name. The maximum size of
this buffer is 32 bytes.
ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS
A rights list segment containing additional identifiers to be appended
to the set of identifiers held by the user. A rights list segment is a
list of quadword identifier/attributes pairs, each containing a
longword identifier value, followed by a longword mask identifying the
attributes of the holder. The buflen argument should
be set to the total size, in bytes, of the rights list segment. The
bufadr argument points to a descriptor that points to
the first byte in the rights list segment (that is, the first byte of
the first identifier value).
This item code can be repeated to add up to 256 additional rights list
segments. If more than 256 identifiers are granted to the user,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns SS$_INSFMEM.
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
Quadword containing the authorized privileges. See $PRVDEF macro for
definitions.
ISS$_FLAGS
Longword containing user flags. The following flag is supported:
ISS$M_FLAG_SECAUDIT - Mandatory audit flag.
ISS$_MAXCLASS
Buffer containing the maximum classification. The maximum size of this
buffer is CLS$K_LENGTH. This item code is reserved to HP. See the
$CLSDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_MINCLASS
Buffer containing the minimum classification. The maximum size of this
buffer is CLS$K_LENGTH. This item code is reserved to HP. See the
$CLSDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_MODE
Longword containing the access mode. See $PSLDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_PERMPRIV
Quadword containing the permanent privileges. See $PRVDEF macro for
definitions.
ISS$_RIGHTS
Descriptor pointing to a vector of quadwords containing
identifier/attribute pairs used to initialize the rights identifier
list. See the $KGBDEF macro for definitions. Any identifiers specified
by the ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS item code will be added to this list.
The format of this vector is as follows:

ISS$_UIC
A longword describing the user identification code (UIC).
ISS$_WORKCLASS
The classification to be associated with the created security profile.
This item code is reserved to HP.
ISS$_WORKPRIV
A quadword privilege mask specifying the user's privileges. The $PRVDEF
macro defines the list of available privileges.
Description
The Create User Profile service returns a security profile for a user.
This profile can be generated in two ways:
- If the caller does not specify the CHP$_NOACCESS flag in the
flags argument, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE accesses the
system authorization database (SYSUAF.DAT) or the rights database
(RIGHTSLIST.DAT) for the specified user name and builds a
representation of the privileges and rights granted to that user. The
security profile is returned as an opaque byte stream.
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns a representation of the security
profile that the user would have when logged in at the highest
authorized classification with all authorized privileges enabled.
- When the caller specifies the CHP$M_NOACCESS flag in the
flags argument, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE creates a
security profile without accessing the user authorization file
(SYSUAF.DAT) or the rights database (RIGHTSLIST.DAT). When
CHP$M_NOACCESS is specified, all of the information is obtained from
the item list. The caller must supply the CHP$_PRIV and CHP$_UIC items.
In addition, an address of 0 can be specified for the
usrnam argument.
In either case, the newly created security profile can be passed as
input to the $CHKPRO and $CHECK_ACCESS system services using the
usrpro argument.
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns the set of identifiers associated with the
user's owner identifier. The CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item code can be used to
add additional identifiers to this set.
Required Access or Privileges
Access to SYSUAF.DAT and RIGHTSLIST.DAT is required unless you are
constructing the security profile for your own user name.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $FIND_HELD, $FINISH_RDB, $GETUAI
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Profile created successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
Item list code is invalid.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
Size specified for item is invalid.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Buffer address is invalid or inaccessible.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Insufficient call arguments.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient memory.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
Invalid system service flags specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Caller lacks privilege to access UAF.
|
|
RMS$_RNF
|
User name is not in UAF.
|
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE can also return any error returned by the $GETUAI
or $FIND_HELD services.
$CRELNM
Creates a logical name and specifies its equivalence names.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRELNM [attr] ,tabnam ,lognam ,[acmode] ,[itmlst]
C Prototype
int sys$crelnm (unsigned int *attr, void *tabnam, void *lognam,
unsigned char *acmode, void *itmlst);
Arguments
attr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Attributes to be associated with the logical name. The
attr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword bit mask
specifying these attributes.
Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic
name. These symbolic names are defined by the $LNMDEF macro. To specify
an attribute, specify its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit.
The longword bit mask is the logical OR of all desired attributes. All
undefined bits in the longword must be 0.
If you do not specify this argument or specify it as 0 (no bits set),
no attributes are associated with the logical name.
The attributes are as follows:
| Attribute |
Description |
|
LNM$M_CONFINE
|
If set, the logical name is not copied from the process to its spawned
subprocesses. You create a subprocess with the DCL command SPAWN or the
LIB$SPAWN Run-Time Library routine. If the logical name is placed into
a process-private table that has the CONFINE attribute, the CONFINE
attribute is automatically associated with the logical name. This
applies only to process-private logical names.
|
|
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS
|
If set, the logical name cannot be duplicated in this table at an outer
access mode. If another logical name with the same name already exists
in the table at an outer access mode, it is deleted.
|
tabnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the table in which to create the logical name. The
tabnam argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a descriptor that
points to the name of this table. This argument is required and must be
specified in uppercase.
The name must be entered in uppercase letters. (This requirement
differs from the $CRELNT system service, which automatically changes
tabnam to uppercase.)
If tabnam is not the name of a logical name table, it
is assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively until
either the name of a logical name table is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. If
tabnam translates to a list of logical name tables,
the logical name is entered into the first table in the list.
lognam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the logical name to be created. The lognam
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a descriptor that points to the logical
name string.
Logical name strings of logical names created within either the system
or process directory table must consist of uppercase alphanumeric
characters, dollar signs ($), hyphens (-), and underscores (_); the
maximum length is 31 characters. The maximum length of logical name
strings created within other tables is 255 characters with no
restrictions on the types of characters that can be used. This argument
is required.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Access mode to be associated with the logical name. The
acmode argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a byte that
specifies the access mode.
The access mode associated with the logical name is determined by
maximizing the access mode of the caller with the access mode
specified by the acmode argument, which means that the
less privileged of the two is used. Symbols for the four access modes
are defined by the $PSLDEF macro.
You cannot specify an access mode more privileged than that of the
containing table. However, if the caller has SYSNAM privilege, then the
specified access mode is associated with the logical name regardless of
the access mode of the caller.
If you omit this argument or specify it as 0, the access mode of the
caller is associated with the logical name.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list 64b |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for
64-bit |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Item list describing the equivalence names to be defined for the
logical name and information to be returned to the caller. The
itmlst argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a list of item
descriptors, each of which specifies information about an equivalence
name. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0;
an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All
items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or
64-bit.
Note that it is possible to create a logical that has no equivalence
names. This is done by either omitting the itmlst
argument to $CRELNM, or by not including the LNM$_STRING item code to
the itmlst data structure that is passed into $CRELNM.
It is not possible to create this kind of logical using DCL.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item
descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by the
buffer address field. The length of the buffer needed depends on the
item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If
the value of buffer length is too small, the service truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the
buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by
the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the 32-bit address of the buffer that receives or
passes information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the 32-bit address of a word specifying the
actual length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM in the
buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The return length
address field is used only when the item code specified is LNM$_TABLE.
Although this field is ignored for all other item codes, it must
nevertheless be present as a placeholder in each item descriptor.
|
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
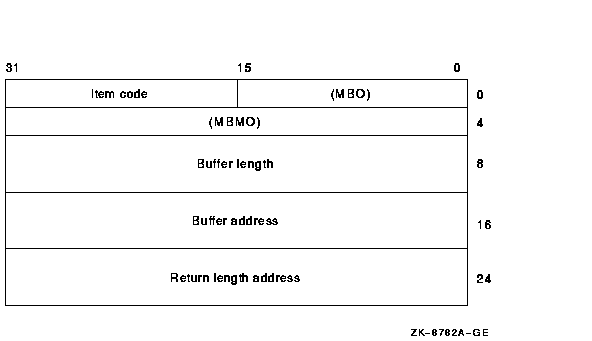
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
MBO
|
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the
buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by
the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
MBMO
|
The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Buffer length
|
A quadword specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by
the buffer address field. The length of the buffer needed depends on
the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor.
If the value of buffer length is too small, the service truncates the
data.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of the buffer that receives or
passes information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of a word specifying the
actual length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM in the
buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The return length
address field is used only when the item code specified is LNM$_TABLE.
Although this field is ignored for all other item codes, it must
nevertheless be present as a placeholder in each item descriptor.
|
Item Codes
LNM$_ATTRIBUTES
When you specify LNM$_ATTRIBUTES, the buffer address field of the item
descriptor points to a longword bit mask that specifies the current
translation attributes for the logical name. The current translation
attributes are applied to all subsequently specified equivalence
strings until another LNM$_ATTRIBUTES item descriptor is encountered in
the item list. The symbolic names for these attributes are defined by
the $LNMDEF macro. The symbolic name and description of each attribute
are as follows:
| Attribute |
Description |
|
LNM$M_CONCEALED
|
If set, OpenVMS RMS interprets the equivalence name as a device name or
logical name with the LNM$M_CONCEALED attribute.
|
|
LNM$M_TERMINAL
|
If set, further iterative logical name translation on the equivalence
name is not to be performed.
|
LNM$_CHAIN
When you specify LNM$_CHAIN, the buffer address field of the item
descriptor points to another item list that $CRELNM is to process
immediately after it has processed the current item list.
If you specify the LNM$_CHAIN item code, it must be the last item code
in the current item list.
You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
LNM$_STRING
When you specify LNM$_STRING, the buffer address field of the item
descriptor points to a buffer containing a user-specified equivalence
name for the logical name. The maximum length of the equivalence string
is 255 characters.
When $CRELNM encounters an item descriptor with the item code
LNM$_STRING, it creates an equivalence name entry for the logical name
using the most recently specified values for LNM$_ATTRIBUTES. The
equivalence name entry includes the following information:
- Name specified by LNM$_STRING.
- Next available index value. Each equivalence is assigned a unique
value from 0 to 127.
- Attributes specified by the most recently encountered item
descriptor with item code LNM$_ATTRIBUTES (if these are present in the
item list).
Therefore, you should construct the item list so that the
LNM$_ATTRIBUTES item codes immediately precede the LNM$_STRING item
code or codes to which they apply.
Note that it is possible to create a logical that has no equivalence
names. This is done by either omitting the itmlst
argument to $CRELNM, or by not including the LNM$_STRING item code to
the itmlst data structure that is passed into $CRELNM.
It is not possible to create this kind of logical using DCL.
LNM$_TABLE
When you specify LNM$_TABLE, the buffer address field of the item
descriptor points to a buffer in which $CRELNM writes the name of the
logical name table in which it entered the logical name. The return
length address field points to a word that contains a buffer that
specifies the length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM.
The maximum length of the name of a logical name table is 31 characters.
This item code can appear anywhere in the item list.
Description
The Create Logical Name service creates a logical name and specifies
its equivalence name. Note that logical names are case sensitive.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have the following:
- Write access to shareable tables to create logical names in those
tables
- GRPNAM or GRPPRV privilege to enter a logical name into the group
logical name table
- SYSNAM or SYSPRV privilege to enter a logical name into the system
logical name table
Required Quota
The quota for the specified logical name table must be sufficient for
the creation of the logical name.
Related Services
$CRELNT, $DELLNM, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the logical name has been created.
However, if you attempted to create a new clusterwide logical name with
the same access mode and identical equivalence names and attributes as
an existing clusterwide logical name, this message indicates only that
the service completed successfully. Because an identical clusterwide
logical name already exists, and because a clusterwide update would
adversely affect performance, the name is not created.
|
|
SS$_SUPERSEDE
|
The service completed successfully; the logical name has been created
and a previously existing logical name with the same name has been
deleted.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The service completed successfully; the buffer length field in an item
descriptor specified an insufficient value, so the buffer was not large
enough to hold the requested data.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table
name or logical name was not specified. Or, an item list containing
both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
An attempt was made to create a logical name with the same name as an
already existing logical name, and the existing logical name was
created at a more privileged access mode and with the LNM$M_NO_ALIAS
attribute.
|
|
SS$_EXLNMQUOTA
|
The quota associated with the specified logical name table for the
creation of the logical name is insufficient.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The dynamic memory is insufficient for the creation of the logical
name, or there is insufficient dynamic memory to build a message
describing the creation of a clusterwide name.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The
tabnam argument, the
lognam argument, or the equivalence string specifies a
string whose length is not in the required range of 1 through 255
characters. The
lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not
in the required range of 1 to 31 characters for directory table entries.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGTAB
|
The
tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGTAB
|
Either the specified logical name table does not exist or the logical
name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth of 10
translations.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller lacks the necessary privilege to create the logical name.
|
$CRELNT
Creates a process-private or shareable logical name table.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRELNT [attr] ,[resnam] ,[reslen] ,[quota]
,[promsk] ,[tabnam]
,partab ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$crelnt (unsigned int *attr, void *resnam, unsigned short int
*reslen, unsigned int *quota, unsigned short int *promsk, void *tabnam,
void *partab, unsigned char *acmode);
Arguments
attr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Attributes to affect the creation of the logical name table and to be
associated with the newly created logical name table. The
attr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword bit mask
specifying these attributes.
Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic
name. These symbolic names are defined by the $LNMDEF macro. To specify
an attribute, specify its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit.
The longword bit mask is the logical OR of all desired attributes. All
unused bits in the longword must be 0.
If you do not specify this argument or specify it as 0 (no bits set),
no attributes are associated with the logical name table or affect the
creation of the new table.
The following table describes each attribute:
| Attribute |
Description |
|
LNM$M_CONFINE
|
If set, the logical name table is not copied from the process to its
spawned subprocesses. You create a subprocess with the DCL command
SPAWN or the Run-Time Library LIB$SPAWN routine. You can specify this
attribute only for process-private logical name tables; it is ignored
for shareable tables.
|
|
|
The state of this bit is also propagated from the parent table to the
newly created table and can be overridden only if the parent table does
not have the bit set. Thus, if the parent table has the LNM$M_CONFINE
attribute, the newly created table will also have it, no matter what is
specified in the
attr argument. On the other hand, if the parent table
does not have the LNM$M_CONFINE attribute, the newly created table can
be given this attribute through the
attr argument.
|
|
|
The process-private directory table LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY does not have
the LNM$M_CONFINE attribute.
|
|
LNM$M_CREATE_IF
|
This attribute applies to all types of logical name tables except
clusterwide logical name tables. If set, a new logical name table is
created only if the specified table name is not already entered at the
specified access mode in the appropriate directory table. If the table
name exists, a new table is not created and no modification is made to
the existing table name. This holds true even if the existing name has
differing attributes or quota values, or even if it is not the name of
a logical name table.
If LNM$M_CREATE_IF is not set, the new logical name table will
supersede any existing table name with the same access mode within the
appropriate directory table. Setting this attribute is useful when two
or more users want to create and use the same table but do not want to
synchronize its creation.
Regardless of the setting of LNM$M_CREATE_IF:
- You cannot create a new clusterwide logical name table with the
same name and the same mode as an existing clusterwide logical name
table until you delete the existing one.
- If you specify a new clusterwide logical name table with the same
name and access mode as an existing local logical name table, the new
clusterwide logical name table is created, and the local table and its
logical names are deleted.
|
|
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS
|
If set, the name of the logical name table cannot be duplicated at an
outer access mode within the appropriate directory table. If this name
already exists at an outer access mode, it is deleted.
|
resnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the newly created logical name table, returned by $CRELNT. The
resnam argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a descriptor
pointing to this name. The name is a character string whose maximum
length is 31 characters.
reslen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Length in bytes of the name of the newly created logical name table,
returned by $CRELNT. The reslen argument is the 32-bit
address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a word to receive this length.
quota
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Maximum number of bytes of memory to be allocated for logical names
contained in this logical name table. The quota
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a longword specifying this value.
If you specify no quota value, the logical name table has an infinite
quota. Note that a shareable table created with infinite quota permits
users with write access to that table to consume system dynamic memory
without limit.
promsk
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Protection mask to be associated with the newly created shareable
logical name table. The promsk argument is the 32-bit
address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a word that contains a value that represents four 4-bit
fields. Each field grants or denies the type of access, either delete,
create, write, or read, allowed for system, owner, group, and world
users.
The following diagram depicts these protection bits:

Create access is required to create a shareable table within another
shareable table.
Each field consists of 4 bits specifying protection for the logical
name table. The remaining bits in the protection mask are as follows:
- Read privileges allow access to names in the logical name table.
- Write privileges allow creation and deletion of names within the
logical name table.
- Delete privileges allow deletion of the logical name table.
If a bit is clear, access is granted.
The initial security profile for any shared logical name table is taken
from the logical name table template. The owner is then set to the
process UIC and, if the promsk argument is nonzero,
that value replaces the protection mask.
tabnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
The name of the new logical name table. The tabnam
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a character-string descriptor pointing to
this name string. Table names are contained in either the process or
system directory table (LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY or LNM$SYSTEM_DIRECTORY);
therefore, table names must consist of alphanumeric characters, dollar
signs ($), and underscores (_); the maximum length is 31 characters.
Names of logical name tables must be in uppercase latters. If you
specify a lowercase name, the $CRELNT service automatically changes it
to uppercase.
This argument is required for clusterwide logical name tables. For all
other logical name tables, if you do not specify this argument, a
default name in the format LNM$xxxx is used, where
xxxx is a unique hexadecimal number.
You need SYSPRV privilege or write access to LNM$SYSTEM_DIRECTORY to
specify the name of a shareable logical name table.
partab
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name string for the parent table name. The partab
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to
this name string.
If the parent table is shareable, then the newly created table is
shareable and is entered into the system directory
LNM$SYSTEM_DIRECTORY. If the parent table is process-private, then the
newly created table is process-private and is entered in the process
directory LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY.
You need SYSPRV privilege or write access to the system directory table
to create a named shareable table. This argument is required.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Access mode to be associated with the newly created logical name table.
The acmode argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a byte
containing this access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbolic names
for the four access modes.
If you do not specify the acmode argument or specify
it as 0, the access mode of the caller is associated with the newly
created logical name table.
The access mode associated with the logical name table is determined by
maximizing the access mode of the caller with the access mode
specified by the acmode. The less privileged of the
two access modes is used.
However, if the caller has SYSNAM privilege, then the specified access
mode is associated with the logical name table, regardless of the
access mode of the caller.
Access modes associated with logical name tables govern logical name
table processing and provide a protection mechanism that prevents the
deletion of inner access mode logical name tables by nonprivileged
users. You cannot specify an access mode more privileged than that of
the parent table.
A logical name table with supervisor mode access can contain supervisor
mode and user mode logical names and can be a parent to supervisor mode
and user mode logical name tables, but cannot contain executive or
kernel mode logical names or be a parent to executive or kernel mode
logical name tables.
You need SYSNAM privilege to specify executive or kernel mode access
for a logical name table.
Description
The Create Logical Name Table service creates a process-private or a
shareable logical name table.
The $CRELNT service uses the following system resources:
- System paged dynamic memory to create a shareable logical name table
- Process dynamic memory to create a process-private logical name
table
The parent table governs whether the new table is process-private or
shareable. If the parent table is process-private, so is the new table;
if the parent table is shareable, so is the new table.
Note that logical names are case sensitive.
Required Access or Privileges
Create access to the parent table and either SYSPRV privilege or write
access to the system directory table are required.
You need the SYSNAM privilege to create a table at an access mode more
privileged than that of the calling process.
Required Quota
The parent table must have sufficient quota for the creation of the new
table.
Related Services
$CRELNM, $DELLNM, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the logical name table already
exists.
|
|
SS$_LNMCREATED
|
The service completed successfully; the logical name table was created.
|
|
SS$_SUPERSEDE
|
The service completed successfully; the logical name table was created
and its logical name superseded the already existing logical names in
the directory table.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a parent logical name
table was not specified.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
You attempted to create a logical name table with the same name as an
already existing name within the appropriate directory table, and the
existing name was created at a more privileged access mode with the
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS attribute.
|
|
SS$_EXLNMQUOTA
|
The parent table has insufficient quota for the creation of the new
table.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The dynamic memory is insufficient for the creation of the table, or
there is insufficient dynamic memory to build a message describing the
creation of a clusterwide logical name table.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The
partab argument specifies a string whose length is not
within the required range of 1 to 31 characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGTAB
|
The
tabnam argument is not alphanumeric or specifies a
string whose length is not within the required range of 1 to 31
characters, or the TABNAM argument is omitted from a clusterwide
$CRELNT call.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGTAB
|
The parent logical name table does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller lacks the necessary privilege to create the table.
|
|
SS$_PARENT_DEL
|
The creation of the new table would have resulted in the deletion of
the parent table.
|
|
SS$_RESULTOVF
|
The table name buffer is not large enough to contain the name of the
new table.
|
$CREMBX
Creates a virtual mailbox device named MBAn and assigns an I/O
channel to it. The system provides the unit number n when it
creates the mailbox. If a logical name is specified and a mailbox with
the specified name already exists, the $CREMBX service assigns a
channel to the existing mailbox.
Format
SYS$CREMBX [prmflg] ,chan ,[maxmsg] ,[bufquo] ,[promsk] ,[acmode]
,[lognam] ,[flags] ,[nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$crembx (char prmflg, unsigned short int *chan, unsigned int
maxmsg, unsigned int bufquo, unsigned int promsk, unsigned int acmode,
void *lognam,...);
Arguments
prmflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
boolean |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Indicator specifying whether the created mailbox is to be permanent or
temporary. The prmflg argument is a longword value.
The value 1 specifies a permanent mailbox; the value 0, which is the
default, specifies a temporary mailbox. Any other values result in an
error.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Channel number assigned by $CREMBX to the mailbox. The
chan argument is the address of a word into which
$CREMBX writes the channel number.
maxmsg
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Maximum size (in bytes) of a message that can be sent to the mailbox.
The maxmsg argument is a longword value containing
this size.
The maximum value you can specify for the maxmsg
argument is 65535. If you do not specify a value or specify the value
as 0, the operating system provides a default value from the
DEFMBXBUFQUO system parameter.
bufquo
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of bytes of system dynamic memory that can be used to buffer
messages sent to the mailbox. The bufquo argument is a
value containing this number. If you do not specify the
bufquo argument or specify it as 0, the operating
system provides a default value from the DEFMBXBUFQUO system parameter.
For a temporary mailbox, this value must be less than or equal to the
process buffer quota.
Note that as of Version 7.3-1, the maximum value limit for the
bufquo argument is the amount of available non-paged
pool.
promsk
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection mask to be associated with the created mailbox. The
promsk argument is a longword value that is the
combined value of the bits set in the protection mask. Cleared bits
grant access and set bits deny access to each of the four classes of
user: world, group, owner, and system. The following diagram depicts
these protection bits:
If you do not specify the promsk argument or specify
it as 0, the mailbox template is used.
The logical access bit must be clear for the class of user requiring
access to the mailbox. The access bit must be clear for all categories
of user because logical access is required to read or write to a
mailbox; thus, setting or clearing the read and write access bits is
meaningless unless the logical access bit is also cleared.
The physical access bit is ignored for all categories of user.
Logical access also allows you to queue read or write attention ASTs.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be associated with the channel to which the mailbox is
assigned. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
Numeric Value |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
0
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
1
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
2
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
3
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The specified access mode and the access mode of the caller are
compared. The less privileged (but the higher numeric valued) of the
two access modes becomes the access mode associated with the assigned
channel. I/O operations on the channel can be performed only from equal
or more privileged access modes.
lognam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Logical name to be assigned to the mailbox. The lognam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
the logical name string.
The equivalence name for the mailbox is MBAn. The equivalence
name is marked with the terminal attribute. Processes can use the
logical name to assign other I/O channels to the mailbox.
For permanent mailboxes, the $CREMBX service enters the specified
logical name, if any, in the LNM$PERMANENT_MAILBOX logical name table
and, for temporary mailboxes, into the LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX logical
name table.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The flags argument is used for specifying options for
the assign operation that occurs in $CREMBX. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask that enables the user to specify that
the channel assigned to the mailbox is a READ ONLY or WRITE ONLY
channel. If the flags argument is not specified, then
the default channel behavior is READ/WRITE. The $CMBDEF macro defines a
symbolic name for each flag bit.
The following table describes each flag:
| Flag |
Description |
|
CMB$M_READONLY
|
When this flag is specified, $CREMBX assigns a read-only channel to the
mailbox device. An attempt to issue a QIO WRITE operation on the
mailbox channel results in an illegal I/O operation error.
|
|
CMB$M_WRITEONLY
|
When this flag is specified, $CREMBX assigns a write-only channel to
the mailbox device. An attempt to issue a QIO READ operation on the
mailbox channel results in an illegal I/O operation error.
|
For more information about the flags argument, refer
to the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved by HP.
Description
The Create Mailbox and Assign Channel service creates a virtual mailbox
device named MBAn and assigns an I/O channel to it. The system
provides the unit number n when it creates the mailbox. If a
mailbox with the specified name already exists, the $CREMBX service
assigns a channel to the existing mailbox.
The $CREMBX service uses system dynamic memory to allocate a device
database for the mailbox and for an entry in the logical name table (if
a logical name is specified).
When a temporary mailbox is created, the process's buffered I/O byte
count (BYTLM) quota is reduced by the amount specified in the
bufquo argument. The size of the mailbox unit control
block and the logical name (if specified) are also subtracted from the
quota. The quota is returned to the process when the mailbox is deleted.
The initial security profile created for a mailbox is taken from the
mailbox template for the device class. The owner is then set to the
process UIC and the promsk argument replaces the
protection mask.
After the process creates a mailbox, it and other processes can assign
additional channels to it by calling the Assign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN)
or Create Mailbox ($CREMBX) service. If the mailbox already exists, the
$CREMBX service assigns a channel to that mailbox; in this way,
cooperating processes need not consider which process must execute
first to create the mailbox.
A channel assigned to the mailbox READ ONLY is considered a READER. A
channel assigned to the mailbox WRITE ONLY is considered a WRITER. A
channel assigned to the mailbox READ/WRITE is considered both a WRITER
and READER.
A temporary mailbox is deleted when no more channels are assigned to
it. A permanent mailbox must be explicitly marked for deletion with the
Delete Mailbox ($DELMBX) service; its actual deletion occurs when no
more channels are assigned to it.
A mailbox is treated as a shareable device; it cannot, however, be
mounted or allocated.
The mailbox unit number is determined when the mailbox is created. A
process can obtain the unit number of the created mailbox by calling
the Get Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) service using the channel
returned by $CREMBX.
Mailboxes are assigned sequentially increasing numbers (from 1 to a
maximum of 9999) as they are created. When all unit numbers have been
used, the system starts numbering again at unit 1. Logical names or
mailbox names should be used to identify a mailbox between cooperating
processes.
Default values for the maximum message size and the buffer quota (an
appropriate multiple of the message size) are determined for a specific
system during system generation. The system parameter DEFMBXMXMSG
determines the maximum message size; the system parameter DEFMBXBUFQUO
determines the buffer quota. For termination mailboxes, the maximum
message size must be at least as large as the termination message
(currently 84 bytes).
When you specify a logical name for a temporary mailbox, the $CREMBX
service enters the name into the LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX logical name
table.
Normally, LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX specifies LNM$JOB, the jobwide logical
name table; thus, only processes in the same job as the process that
first creates the mailbox can use the logical name to access the
temporary mailbox. If you want to use the temporary mailbox to enable
communication between processes in different jobs, you must redefine
LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX in the process logical name directory table
(LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY) to specify a logical name table that those
processes can access.
For instance, if you want to use the mailbox as a communication device
for processes in the same group, you must redefine
LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX to specify LNM$GROUP, the group logical name
table. The following DCL command assigns temporary mailbox logical
names to the group logical name table:
$ DEFINE/TABLE=LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX LNM$GROUP
|
When you specify a logical name for a permanent mailbox, the system
enters the name in the logical name table specified by the logical name
table name LNM$PERMANENT_MAILBOX, which normally specifies LNM$SYSTEM,
the system logical name table. If you want the logical name that you
specify for the mailbox to be entered in a logical name table other
than the system logical name table, you must redefine
LNM$PERMANENT_MAILBOX to specify the desired table. For more
information about logical name tables, refer to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
If you redefine either LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX or LNM$PERMANENT_MAILBOX,
be sure that the name of the new table appears in the logical name
table LNM$FILE_DEV. OpenVMS RMS and the I/O system services use
LNM$FILE_DEV to translate I/O device names. If the logical name table
specified by either LNM$TEMPORARY_MAILBOX or LNM$PERMANENT_MAILBOX does
not appear in LNM$FILE_DEV, the system will be unable to translate the
logical name of your mailbox and therefore will be unable to access
your mailbox as an I/O device.
If you redirect a logical name table to point to a process-private
table, then the following occurs:
- Other processes cannot access the mailbox by its name.
- If the creating process issues a second call to $CREMBX, a
different mailbox is created and a channel is assigned to the new
mailbox. (If the creating process issues a second call to $CREMBX using
a shared logical name, a second channel is assigned to the existing
mailbox.)
- The logical name is not deleted when the mailbox disappears.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following privileges to use $CREMBX:
- TMPMBX privilege whenever the prmflg argument is
specified as 0; however, a process that has PRMMBX privilege will also
meet this requirement.
- PRMMBX privilege whenever the prmflg argument is
specified as 1.
- SYSNAM privilege to place a logical name for a mailbox in the
system logical name table.
- GRPNAM privilege to place a logical name for a mailbox in the group
logical name table.
Required Quota
The calling process must have sufficient buffer I/O byte count (BYTLM)
quota to allocate the mailbox unit control block (UCB) or to satisfy
buffer requirements. When a temporary mailbox is created, the process's
buffered I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota is reduced by the amount
specified in the bufquo argument. The size of the
mailbox UCB and the logical name (if specified) are also subtracted
from the quota. The quota is returned to the process when the mailbox
is deleted.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $DALLOC, $DASSGN,
$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The logical name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the channel number cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more of the arguments has an invalid value. One possible problem
is the
flags argument has both the CMB$M_READONLY and
CMB$M_WRITEONLY flags set; however, only one of these values is allowed.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has insufficient buffer I/O byte count (BYTLM) quota to
allocate the mailbox UCB or to satisfy buffer requirements.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_INTERLOCK
|
The bit map lock for allocating mailboxes from the specified shared
memory is locked by another process.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The logical name string has a length of 0 or has more than 255
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
The bit set in the
prmflg argument is undefined; this argument can have a
value of 1 or 0.
|
|
SS$_NOIOCHAN
|
No I/O channel is available for assignment.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to create a temporary mailbox,
a permanent mailbox, a mailbox in memory that is shared by multiple
processors, or a logical name.
|
|
SS$_NOSHMBLOCK
|
No shared memory mailbox UCB is available for use to create a new
mailbox.
|
|
SS$_OPINCOMPL
|
A duplicate unit number was encountered while linking a shared memory
mailbox UCB. If this condition value is returned, contact your HP
support representative.
|
|
SS$_SHMNOTCNCT
|
The shared memory named in the
name argument is not known to the system. This error
can be caused by a spelling error in the string, an improperly assigned
logical name, or the failure to identify the multiport memory as shared
at system generation time.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the string named in the
lognam argument exceeded the allowed depth.
|
|














