 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$CREPRC
Creates, on behalf of the calling process, a subprocess or detached
process on the current node, or a detached process on another OpenVMS
Cluster node.
Format
SYS$CREPRC [pidadr] ,[image] ,[input] ,[output] ,[error] ,[prvadr]
,[quota] ,[prcnam] ,[baspri] ,[uic] ,[mbxunt] ,[stsflg] ,[itmlst]
,[node] ,[home_rad]
C Prototype
int sys$creprc (unsigned int *pidadr, void *image, void *input, void
*output, void *error, struct _generic_64 *prvadr, unsigned int *quota,
void *prcnam, unsigned int baspri, unsigned int uic, unsigned short int
mbxunt, unsigned int stsflg,...);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the newly created process. The
pidadr argument is the address of a longword into
which $CREPRC writes the PID.
image
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the image to be activated in the newly created process. The
image argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the file specification of the image.
The image name can have a maximum of 63 characters. If the image name
contains a logical name, the logical name is translated in the created
process and must therefore be in a logical name table that it can
access.
To create a process that will run under the control of a command
language interpreter (CLI), specify SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE as the
image name.
input
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$INPUT in
the logical name table of the created process. The
input argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.
output
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$OUTPUT in
the logical name table of the created process. The
output argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.
error
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$ERROR in
the logical name table of the created process. The
error argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.
Note that the error argument is ignored if the
image argument specifies SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE; in
this case, SYS$ERROR has the same equivalence name as SYS$OUTPUT.
prvadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_privileges |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Privileges to be given to the created process. The
prvadr argument is the address of a quadword bit mask
wherein each bit corresponds to a privilege; setting a bit gives the
privilege. If the prvadr argument is not specified,
the current privileges are used.
Each bit has a symbolic name; the $PRVDEF macro defines these names.
You form the bit mask by specifying the symbolic name of each desired
privilege in a logical OR operation.
Table SYS-20 gives the symbolic name and description of each privilege.
Table SYS-20 User Privileges
| Privilege |
Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
ACNT
|
PRV$M_ACNT
|
Create processes for which no accounting is done
|
|
ALLSPOOL
|
PRV$M_ALLSPOOL
|
Allocate a spooled device
|
|
ALTPRI
|
PRV$M_ALTPRI
|
Set (alter) any process priority
|
|
AUDIT
|
PRV$M_AUDIT
|
Generate audit records
|
|
BUGCHK
|
PRV$M_BUGCHK
|
Make bugcheck error log entries
|
|
BYPASS
|
PRV$M_BYPASS
|
Bypass UIC-based protection
|
|
CMEXEC
|
PRV$M_CMEXEC
|
Change mode to executive
|
|
CMKRNL
|
PRV$M_CMKRNL
|
Change mode to kernel
|
|
DIAGNOSE
|
PRV$M_DIAGNOSE
|
Can diagnose devices
|
|
DOWNGRADE
|
PRV$M_DOWNGRADE
|
Can downgrade classification
|
|
EXQUOTA
|
PRV$M_EXQUOTA
|
Can exceed quotas
|
|
GROUP
|
PRV$M_GROUP
|
Group process control
|
|
GRPNAM
|
PRV$M_GRPNAM
|
Place name in group logical name table
|
|
GRPPRV
|
PRV$M_GRPPRV
|
Group access via system protection field
|
|
IMPERSONATE
1
|
PRV$M_IMPERSONATE
|
Can create detached processes under another UIC
|
|
IMPORT
|
PRV$M_IMPORT
|
Mount a nonlabeled tape volume
|
|
LOG_IO
|
PRV$M_LOG_IO
|
Perform logical I/O operations
|
|
MOUNT
|
PRV$M_MOUNT
|
Issue mount volume QIO
|
|
NETMBX
|
PRV$M_NETMBX
|
Create a network device
|
|
OPER
|
PRV$M_OPER
|
All operator privileges
|
|
PFNMAP
|
PRV$M_PFNMAP
|
Map to section by physical page frame number
|
|
PHY_IO
|
PRV$M_PHY_IO
|
Perform physical I/O operations
|
|
PRMCEB
|
PRV$M_PRMCEB
|
Create permanent common event flag clusters
|
|
PRMGBL
|
PRV$M_PRMGBL
|
Create permanent global sections
|
|
PRMMBX
|
PRV$M_PRMMBX
|
Create permanent mailboxes
|
|
PSWAPM
|
PRV$M_PSWAPM
|
Change process swap mode
|
|
READALL
|
PRV$M_READALL
|
Possess read access to everything
|
|
SECURITY
|
PRV$M_SECURITY
|
Can perform security functions
|
|
SETPRV
|
PRV$M_SETPRV
|
Set any process privileges
|
|
SHARE
|
PRV$M_SHARE
|
Can assign a channel to a nonshared device
|
|
SYSGBL
|
PRV$M_SYSGBL
|
Create system global sections
|
|
SYSLCK
|
PRV$M_SYSLCK
|
Queue systemwide locks
|
|
SYSNAM
|
PRV$M_SYSNAM
|
Place name in system logical name table
|
|
SYSPRV
|
PRV$M_SYSPRV
|
Access files and other resources as if you have a system UIC
|
|
TMPMBX
|
PRV$M_TMPMBX
|
Create temporary mailboxes
|
|
UPGRADE
|
PRV$M_UPGRADE
|
Can upgrade classification
|
|
VOLPRO
|
PRV$M_VOLPRO
|
Override volume protection
|
|
WORLD
|
PRV$M_WORLD
|
World process control
|
1This privilege replaces the DETACH privilege; however, the
prior mask, PRV$M_DETACH, is still valid for existing programs.
You need the user privilege SETPRV to grant a process any privileges
other than your own. If the caller does not have this privilege, the
mask is minimized with the current privileges of the creating process;
any privileges the creating process does not have are not granted, but
no error status code is returned.
quota
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_quota_list |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process quotas to be established for the created process. These quotas
limit the created process's use of system resources. The
quota argument is the address of a list of quota
descriptors, where each quota descriptor consists of a 1-byte quota
name followed by a longword that specifies the desired value for that
quota. The list of quota descriptors is terminated by the symbolic name
PQL$_LISTEND.
If you do not specify the quota argument or specify it
as 0, the operating system supplies a default value for each quota.
For example, in MACRO you can specify a quota list, as follows:
QLIST: .BYTE PQL$_PRCLM ; Limit number of subprocesses
.LONG 2 ; Max = 2 subprocesses
.BYTE PQL$_ASTLM ; Limit number of asts
.LONG 6 ; Max = 6 outstanding asts
.BYTE PQL$_LISTEND ; End of quota list
|
The $PQLDEF macro defines symbolic names for quotas.
In C you can specify a quota list, as follows:
#include <pqldef.h>
...
#pragma member_alignment save
#pragma nomember_alignment
typedef struct
{
char Quota;
int Value;
} QUOTA_ENTRY_T;
#pragma member_alignment restore
...
QUOTA_ENTRY_T QuotaArray[] =
{{PQL$_PRCLM, 2}, {PQL$_ASTLM, 6}, {PQL$_LISTEND, 0}};
|
Individual Quota Descriptions
A description of each quota follows. The description of each quota
lists its minimum value (a system parameter), its default value (a
system parameter), and whether it is deductible, nondeductible, or
pooled. These terms have the following meaning:
|
Minimum value
|
A process cannot be created with a quota less than this minimum. Any
quota value you specify is maximized against this minimum. You obtain
the minimum value for a quota by running SYSGEN to display the
corresponding system parameter.
|
|
Default value
|
If the quota list does not specify a value for a particular quota, the
system assigns the process this default value. You obtain the default
value by running SYSGEN to display the corresponding system parameter.
|
|
Deductible quota
|
When you create a subprocess, the value for a deductible quota is
subtracted from the creating process's current quota and is returned to
the creating process when the subprocess is deleted. There is currently
only one deductible quota, the CPU time limit. Note that quotas are
never deducted from the creating process when a detached process is
created.
|
|
Nondeductible quota
|
Nondeductible quotas are established and maintained separately for each
process and subprocess.
|
|
Pooled quota
|
Pooled quotas are established when a detached process is created, and
they are shared by that process and all its descendent subprocesses.
Charges against pooled quota values are subtracted from the current
available totals as they are used and are added back to the total when
they are not being used.
|
To run SYSGEN to determine the minimum and default values of a quota,
enter the following sequence of commands:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGEN
SYSGEN> SHOW/PQL
|
Minimum values are named PQL_Mxxxxx, where xxxxx are
the characters of the quota name that follow "PQL$_" in the
quota name.
Default values are named PQL_Dxxxxx, where xxxxx are
the characters of the quota name that follow "PQL$_" in the
quota name.
Individual Quotas
PQL$_ASTLM
Asynchronous system trap (AST) limit. This quota restricts both the
number of outstanding AST routines specified in system service calls
that accept an AST address and the number of scheduled wakeup requests
that can be issued.
Minimum: PQL_MASTLM
Default: PQL_DASTLM
Nondeductible
PQL$_BIOLM
Buffered I/O limit. This quota limits the number of outstanding
system-buffered I/O operations. A buffered I/O operation is one that
uses an intermediate buffer from the system pool rather than a buffer
specified in a process's $QIO request.
Minimum: PQL_MBIOLM
Default: PQL_DBIOLM
Nondeductible
PQL$_BYTLM
Buffered I/O byte count quota. This quota limits the amount of system
space that can be used to buffer I/O operations or to create temporary
mailboxes.
Minimum: PQL_MBYTLM
Default: PQL_DBYTLM
Pooled
PQL$_CPULM
CPU time limit, specified in units of 10 milliseconds. This quota
limits the total amount of CPU time that a created process can use.
When it has exhausted its CPU time limit quota, the created process is
deleted and the status code SS$_EXCPUTIM is returned.
If you do not specify this quota and the created process is a detached
process, the detached process receives a default value of 0, that is,
unlimited CPU time.
If you do not specify this quota and the created process is a
subprocess, the subprocess receives half the CPU time limit quota of
the creating process.
If you specify this quota as 0, the created process has unlimited CPU
time, provided the creating process also has unlimited CPU time. If,
however, the creating process does not have unlimited CPU time, the
created process receives half the CPU time limit quota of the creating
process.
The CPU time limit quota is a consumable quota; that is, the amount of
CPU time used by the created process is not returned to the creating
process when the created process is deleted.
Minimum: PQL_MCPULM
Default: PQL_DCPULM
Deductible
PQL$_DIOLM
Direct I/O quota. This quota limits the number of outstanding direct
I/O operations. A direct I/O operation is one for which the system
locks the pages containing the associated I/O buffer in memory for the
duration of the I/O operation.
Minimum: PQL_MDIOLM
Default: PQL_DDIOLM
Nondeductible
PQL$_ENQLM
Lock request quota. This quota limits the number of lock requests that
a process can queue.
Minimum: PQL_MENQLM
Default: PQL_DENQLM
Pooled
PQL$_FILLM
Open file quota. This quota limits the number of files that a process
can have open at one time.
Minimum: PQL_MFILLM
Default: PQL_DFILLM
Pooled
PQL$_JTQUOTA
Job table quota. This quota limits the number of bytes of system paged
pool used for the job logical name table. If the process being created
is a subprocess, this item is ignored.
A value of 0 represents an unlimited number of bytes.
Minimum: PQL_MJTQUOTA
Default: PQL_DJTQUOTA
Nondeductible
PQL$_PGFLQUOTA
Paging file quota. This quota limits the number of pages (on VAX
systems) or pagelets (adjusted up or down to represent CPU-specific
pages on Alpha systems) that can be used to provide secondary storage
in the paging file for the execution of a process.
Minimum: PQL_MPGFLQUOTA
Default: PQL_DPGFLQUOTA
Pooled
PQL$_PRCLM
Subprocess quota. This quota limits the number of subprocesses a
process can create.
Minimum: PQL_MPRCLM
Default: PQL_DPRCLM
Pooled
PQL$_TQELM
Timer queue entry quota. This quota limits both the number of timer
queue requests a process can have outstanding and the creation of
temporary common event flag clusters.
Minimum: PQL_MTQELM
Default: PQL_DTQELM
Pooled
PQL$_WSDEFAULT
Default working set size. This quota defines the number of pages (on
VAX systems) or pagelets (adjusted up or down to represent CPU-specific
pages on Alpha systems) in the default working set for any image the
process executes. The working set size quota determines the maximum
size you can specify for this quota.
Minimum: PQL_MWSDEFAULT
Default: PQL_DWSDEFAULT
Nondeductible
PQL$_WSEXTENT
Working set expansion quota. This quota limits the maximum size to
which an image can expand its working set size with the Adjust Working
Set Limit ($ADJWSL) system service.
Minimum: PQL_MWSEXTENT
Default: PQL_DWSEXTENT
Nondeductible
PQL$_WSQUOTA
Working set size quota. This quota limits the maximum size to which an
image can lock pages in its working set with the Lock Pages in Memory
($LCKPAG) system service.
Minimum: PQL_MWSQUOTA
Default: PQL_DWSQUOTA
Nondeductible
Use of the Quota List
The values specified in the quota list are not necessarily the quotas
that are actually assigned to the created process. The $CREPRC service
performs the following steps to determine the quota values that are
assigned when you create a process on the same node:
- It constructs a default quota list for the process being created,
assigning it the default values for all quotas. Default values are
system parameters and so might vary from system to system.
- It reads the specified quota list, if any, and updates the
corresponding items in the default list. If the quota list contains
multiple entries for a quota, only the last specification is used.
- For each item in the updated quota list, it compares the quota
value with the minimum value required (also a system parameter) and
uses the larger value. Then, the following occurs:
- If a subprocess is being created or if a detached process is being
created and the creating process does not have IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL
privilege, the resulting value is compared with the current value of
the corresponding quota of the creating process and the lesser value is
used.
Then, if the quota is a deductible quota, that value is
deducted from the creating process's quota, and a check is performed to
ensure that the creating process will still have at least the minimum
quota required. If not, the condition value SS$_EXQUOTA is returned and
the subprocess or detached process is not created.
Pooled quota
values are ignored.
- If a detached process is being created and the creating process has
IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege, the resulting value is not compared
with the current value of the corresponding quota of the creating
process and the resulting value is not deducted from the creating
process's quota. A process with IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege is
allowed to create a detached process with quota values larger than it
has.
When you create a detached process on another OpenVMS Cluster node, the
quotas assigned to the process are determined in the following way:
- The $CREPRC service reads the specified quota list, if any. If it
contains multiple entries for a quota, only the last specification is
used. If the process does not have IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege, the
service compares each value in the list with the current value of the
corresponding quota of the creating process and uses the lesser value.
It sends the resulting quota list to the node on which the new process
is to be created.
- On that node, the $CREPRC service constructs a default quota list
for the process being created, assigning it default values for all
quotas based on that node's system parameters.
- It updates the default list with the corresponding values from the
quota list.
- For each item in the updated quota list, it compares the quota
value with the minimum value required based on that node's system
parameters and uses the larger value.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name to be assigned to the created process. The
prcnam argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to a process name string.
If a subprocess is being created, the process name is implicitly
qualified by the UIC group number of the creating process. If a
detached process is being created, the process name is qualified by the
group number specified in the uic argument.
baspri
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Base priority to be assigned to the created process. The
baspri argument is a longword value.
The OpenVMS VAX range is 0 to 31, where 31 is the highest priority and
0 is the lowest. Usual priorities are in the range 0 to 15, and
real-time priorities are in the range 16 to 31.
The OpenVMS Alpha range is 0 to 63, with real-time priorities in the
range 32 to 63.
If you want a created process to have a higher priority than its
creating process, you must have ALTPRI privilege to raise the priority
level. If the caller does not have this privilege, the specified base
priority is compared with the caller's priority and the lower of the
two values is used.
A process with ALTPRI privilege running on a VAX node can create a
process with a priority greater than 31 on an Alpha node.
If the baspri argument is not specified, the priority
defaults to 2 for VAX MACRO and VAX BLISS--32 and to 0 for all other
languages.
uic
| OpenVMS usage: |
uic |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
User identification code (UIC) to be assigned to the created process.
The uic argument is a longword value containing the
UIC.
If you do not specify the uic argument or specify it
as 0 (the default), $CREPRC creates a process and assigns it the UIC of
the creating process.
If you specify a nonzero value for the uic argument,
$CREPRC creates a detached process. This value is interpreted as a
32-bit octal number, with two 16-bit fields:
bits 0--15---member number
bits 16--31---group number
You need IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege to create a detached process
with a UIC that is different from the UIC of the creating process.
If the image argument specifies the
SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE, the UIC of the created process will be the UIC
of the caller of $CREPRC, and the UIC parameter is ignored.
mbxunt
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Unit number of a mailbox to receive a termination message when the
created process is deleted. The mbxunt argument is a
word containing this number.
If you do not specify the mbxunt argument or specify
it as 0 (the default), the operating system sends no termination
message when it deletes the process.
The Get Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) service can be used to
obtain the unit number of the mailbox.
If you specify the mbxunt argument, the mailbox is
used when the created process actually terminates. At that time, the
$ASSIGN service is issued for the mailbox in the context of the
terminating process and an accounting message is sent to the mailbox.
If the mailbox no longer exists, cannot be assigned, or is full, the
error is treated as if no mailbox had been specified.
If you specify this argument when you create a process on another node,
an accounting message will be written to the mailbox when the process
terminates. If the node is removed from the cluster before the created
process terminates, an accounting message will be simulated. The
simulated message will contain the created process's PID and name and a
final status of SS$_NODELEAVE, but will lack execution statistics.
Note that two processes on different nodes cannot use the termination
mailbox for general interprocess communication.
The accounting message is sent before process rundown is initiated but
after the process name has been set to null. Thus, a significant
interval of time can occur between the sending of the accounting
message and the final deletion of the process.
To receive the accounting message, the caller must issue a read to the
mailbox. When the I/O completes, the second longword of the I/O status
block, if one is specified, contains the process identification of the
deleted process.
The $ACCDEF macro defines symbolic names for offsets of fields within
the accounting message. The offsets, their symbolic names, and the
contents of each field are shown in the following table. Unless stated
otherwise, the length of the field is 4 bytes.
| Offset |
Symbolic Name |
Contents |
|
0
|
ACC$W_MSGTYP
|
MSG$_DELPROC (2 bytes)
|
|
2
|
|
Not used (2 bytes)
|
|
4
|
ACC$L_FINALSTS
|
Exit status code
|
|
8
|
ACC$L_PID
|
External process identification
|
|
12
|
|
Not used (4 bytes)
|
|
16
|
ACC$Q_TERMTIME
|
Current time in system format at process termination (8 bytes)
|
|
24
|
ACC$T_ACCOUNT
|
Account name for process, blank filled (8 bytes)
|
|
32
|
ACC$T_USERNAME
|
User name, blank filled (12 bytes)
|
|
44
|
ACC$L_CPUTIM
|
CPU time used by the process, in 10-millisecond units
|
|
48
|
ACC$L_PAGEFLTS
|
Number of page faults incurred by the process
|
|
52
|
ACC$L_PGFLPEAK
|
Peak paging file usage
|
|
56
|
ACC$L_WSPEAK
|
Peak working set size
|
|
60
|
ACC$L_BIOCNT
|
Count of buffered I/O operations performed by the process
|
|
64
|
ACC$L_DIOCNT
|
Count of direct I/O operations performed by the process
|
|
68
|
ACC$L_VOLUMES
|
Count of volumes mounted by the process
|
|
72
|
ACC$Q_LOGIN
|
Time, in system format, that process logged in (8 bytes)
|
|
80
|
ACC$L_OWNER
|
Process identification of owner
|
The length of the termination message is equated to the constant
ACC$K_TERMLEN.
stsflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Options selected for the created process. The stsflg
argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an
option. Only bits 0 to 22 are used; the others are reserved and must be
0.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $PRCDEF macro defines.
You construct the stsflg argument by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
PRC$M_BATCH
|
Create a batch process. IMPERSONATE privilege is required.
|
|
PRC$M_IMPERSONATE
|
Create a detached process under another UIC.
|
|
PRC$M_DISAWS
|
Disable system-initiated working set adjustment.
|
|
PRC$M_HIBER
|
Force process to hibernate before it executes the image.
|
|
PRC$M_HOME_RAD
|
Assign process to specified home resource affinity domain (RAD).
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
|
|
PRC$M_IMGDMP
|
Enable image dump facility. If an image terminates due to an unhandled
condition, the image dump facility writes the contents of the address
space to a file in your current default directory. The file name is the
same as the name of the terminated image. The file type is .DMP.
|
|
PRC$M_INTER
|
Create an interactive process. This option is meaningful only if the
image argument specifies SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. The
purpose of this option is to provide you with information about the
process. When you specify this option, it identifies the process as one
that is in communication with another user (an interactive process).
For example, if you use the DCL lexical function F$MODE to make an
inquiry about a process that has specified the PRC$M_INTER option,
F$MODE returns the value INTERACTIVE.
|
|
PRC$M_NETWRK
|
Create a process that is a network connect object. IMPERSONATE
privilege required.
|
|
PRC$M_NOACNT
|
Do not perform accounting. ACNT privilege is required.
|
|
PRC$M_NOPASSWORD
|
Do not display the
Username: and
Password: prompts if the process is interactive and detached
and the image is SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. If you specify this option in
your call to $CREPRC, the process created by the call is logged in
under the user name associated with the creating process. If you do not
specify this option for an interactive process, SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE
prompts you for the user name and password to be associated with the
process. The prompts are displayed at the SYS$INPUT device.
|
|
PRC$M_NOUAF
|
Do not check authorization file if the process is detached and the
image is SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. You should not specify this option if
a subprocess is being created.
In previous versions of the operating system, the symbolic name of
this option was PRC$M_LOGIN. The symbolic name has been changed to more
accurately denote the effect of setting this bit. For compatibility
with existing user programs, you can still specify this bit as
PRC$M_LOGIN.
This flag prevents the loading of the new process's security
profile from the contents of the UAF record associated with the
specified user name. Restrictions are still enforced on the UAF record,
if it exists, for account disuser, account expiration, and
primary/secondary days/hours.
|
|
PRC$M_PARSE_EXTENDED
|
Sets the PARSE_STYLE_PERM and the PARSE_STYLE_IMAGE properties for the
new process to EXTENDED.
|
|
PRC$M_PSWAPM
|
Inhibit process swapping. PSWAPM privilege is required.
|
|
PRC$M_SSFEXCU
|
Enable system service failure exception mode.
|
|
PRC$M_SSRWAIT
|
Disable resource wait mode.
|
|
PRC$M_SUBSYSTEM
|
Inherit any protected subsystem identifiers. The default is that the
new process does not inherit subsystem identifiers.
|
|
PRC$M_TCB
|
Mark a process as part of the trusted computing base (TCB). As such, it
is expected to perform its own auditing. IMPERSONATE privilege is
required.
|
Note that options PRC$M_BATCH, PRC$M_INTER, PRC$M_NOUAF, PRC$M_NETWRK,
and PRC$M_NOPASSWORD are intended for use by HP software.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
reserved |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
|
The itmlst argument is reserved by HP.
node
| OpenVMS usage: |
SCS_nodename |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the OpenVMS Cluster node on which the process is to be created.
The node argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to a 1- to 6-character SCS node name string. If the
argument is present but zero or if the string is zero length, the
process is created on the current node.
home_rad
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Sets the home resource affinity domain (RAD) of a process.
The home RAD is determined by the operating system, unless you
explicitly request one. If bit PRC$M_HOME_RAD in the
stsflg is set, home_rad is the RAD on
which the process is to start. Note that you may set this bit to 0 on
non-RAD systems.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Description
The Create Process service creates a subprocess or detached process on
behalf of the calling process. A subprocess can be created only on the
current OpenVMS Cluster node. A detached process can be created on the
current OpenVMS Cluster node or on the node specified with the
node argument.
A detached process is a fully independent process. For example, the
process that the system creates when you log in is a detached process.
A subprocess, on the other hand, is related to its creating process in
a treelike structure; it receives a portion of the creating process's
resource quotas and must terminate before the creating process. Any
subprocesses that still exist when their creator is being deleted are
automatically deleted.
The presence of the uic argument,
node argument, or the PRC$M_IMPERSONATE flag specifies
that the created process is detached.
Creating a process is synchronous in that the process has actually been
created and its PID determined before control returns to the program
that requested the system service. Note, however, that the new process
has not necessarily begun to execute at that point. Some error
conditions are not detected until the created process executes. These
conditions include an invalid or nonexistent image; invalid SYS$INPUT,
SYS$OUTPUT, or SYS$ERROR logical name equivalence; inadequate quotas;
or insufficient privilege to execute the requested image.
In creating a detached or subprocess, you can specify that the process
run the image SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. During interactive logins,
LOGINOUT performs the following functions:
- It validates user name and password.
- It reads the system authorization file record associated with that
user and redefines the process environment based on information from
the record.
- It maps a command language interpreter (CLI) into the process and
passes control to it.
The CLI reads a command from SYS$INPUT, processes it, and reads another
command. The presence of the CLI enables the process to execute
multiple images. It also enables an image running in the process to use
Run-Time Library procedures, such as LIB$SPAWN, LIB$DO_COMMAND, and
LIB$SET_LOGICAL, that require a CLI.
Running in the context of a process you create through $CREPRC,
LOGINOUT can perform some or all of the preceding steps, depending on
whether the process is a subprocess or a detached process and on the
values of PRC$M_NOPASSWORD and PRC$M_NOUAF in the
stsflg argument.
Certain characteristics of a created process can be specified
explicitly through $CREPRC system service arguments, while other
characteristics are propagated implicitly from the $CREPRC caller.
Implicit characteristics include the following:
- Current default directory
- Creator's equivalence name for SYS$DISK
- User and account names
- Command language interpreter (CLI) name and command table file name
Note, however, that after the process has been created, if it runs
LOGINOUT and LOGINOUT redefines the process environment, those
characteristics will be overridden by information from the system
authorization file.
Several process characteristics are relevant to the creation of a
process on another OpenVMS Cluster node, in particular, process quotas,
default directory, SYS$DISK equivalence name, CLI name, and CLI command
table name.
Quotas for a process created on another OpenVMS Cluster node are
calculated as previously described in the section on the use of the
quota list; namely, they are based on explicit values passed by the
creator and system parameters on the other OpenVMS Cluster node. If the
other node has its own authorization file with node-specific quotas,
you might want to specify in the $CREPRC request that the process run
LOGINOUT so it can redefine the process environment based on that
node's quotas for the user.
Unless overridden by LOGINOUT, the new process will use its creator's
default disk and directory. If the disk is not mounted clusterwide, the
created process might need to redefine SYS$DISK with an equivalence
name that specifies a disk accessible from that node.
When you set the PRC$M_NOUAF flag in the stsflg
argument and create a process running LOGINOUT, LOGINOUT will attempt
to map a CLI and command table with the same file names as those
running in your process. The CLI and command table images must
therefore have already been installed by the system manager on the
other node. Problems can arise when you are using something other than
the DCL CLI and its standard command tables. For example, if you are
running on a VAX node with MCR as your current CLI, LOGINOUT will be
unable to map that CLI on an Alpha node. The new process will be
created but then aborted by LOGINOUT.
A detached process is considered an interactive process only if (1) the
process is created with the PRC$M_INTER option specified and (2)
SYS$INPUT is not defined as a file-oriented device.
The $CREPRC service requires system dynamic memory.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have the following:
- IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege to create any of the following
types of process:
- A detached process with a UIC that is different from the UIC of the
calling process
- A detached process with a larger value specified for some quota
than is authorized for the caller
- A detached process on another node if the system parameter
CWCREPRC_ENABLE has a value of 0
- IMPERSONATE privilege to create any of the following types of
process:
- A batch process
- A network process
- A trusted computing base process
- ALTPRI privilege to create a subprocess with a higher base priority
than the calling process
- SETPRV privilege to create a process with privileges that the
calling process does not have
- PSWAPM privilege to create a process with process swap mode disabled
- ACNT privilege to create a process with accounting functions
disabled
- OPER privilege to create a detached process on another OpenVMS
Cluster node on which interactive logins have not yet been enabled
Required Quota
The number of subprocesses that a process can create is controlled by
the subprocess (PRCLM) quota; this quota is returned when a subprocess
is deleted.
The number of detached processes on any one OpenVMS Cluster node that a
process can create with the same user name is controlled by the
MAXDETACH entry in the user authorization file (UAF).
When a subprocess is created, the value of any deductible quota is
subtracted from the total value the creating process has available, and
when the subprocess is deleted, the unused portion of any deductible
quota is added back to the total available to the creating process. Any
pooled quota value is shared by the creating process and all its
subprocesses.
Related Services
$CANEXH, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,
$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,
$WAKE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The caller cannot read a specified input string or string descriptor,
the privilege list, or the quota list; or the caller cannot write the
process identification.
|
|
SS$_BADRAD
|
The specified RAD contains no memory or contains no active CPUs, or the
specified RAD is greater than or equal to the maximum number of RADs on
the system. Use the $GETSYI item code RAD_MAX_RADS to determine the
maximum number of RADs on the system.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
The specified process name duplicates one already specified within that
group.
|
|
SS$_EXPRCLM
|
The creation of a detached process failed because the creating process
already reached its limit for the creation of detached processes. This
limit is established by the MAXDETACH quota in the user authorization
file (UAF) of the creating process.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
At least one of the following conditions is true:
- The process has exceeded its quota for the creation of subprocesses.
- A quota value specified for the creation of a subprocess exceeds
the creating process's corresponding quota.
- The quota is deductible and the remaining quota for the creating
process would be less than the minimum.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system, namely, one that does not support remote process creation.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for the requested operation.
|
|
SS$_INVARG
|
An invalid argument was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
At least one of the following two conditions is true:
- The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
- The specified image name, input name, output name, or error name
has more than 255 characters.
|
|
SS$_IVQUOTAL
|
The quota list is not in the proper format.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
A reserved status flag was specified.
|
|
SS$_NODELEAVE
|
The specified node was removed from the OpenVMS Cluster during the
$CREPRC service's execution.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller violated one of the privilege restrictions.
|
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_NOSLOT
|
No process control block is available; in other words, the maximum
number of processes that can exist concurrently in the system has been
reached.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The specified node is not currently a member of the cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.
|
$CRETVA
Adds a range of demand-zero allocation pages (on VAX systems) or
pagelets (on Alpha systems) to a process's virtual address space for
the execution of the current image.
Format
SYS$CRETVA inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$cretva (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a 2-longword array containing the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the pages to be created. If the starting and
ending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is created. The
addresses are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific page
boundaries. Only the virtual page number portion of the virtual address
is used; the low order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference--array reference or descriptor |
Address of a 2-longword array to receive the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the pages created.
On Alpha systems, the retadr argument should be
checked by programs for actual allocation. Because the Alpha
architecture defines more than one page size, more space might be
created than was specified in the inadr argument.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode and protection for the new pages. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The protection of the pages is read/write for the resultant access mode
and those more privileged.
Description
The Create Virtual Address Space service adds a range of demand-zero
allocation pages to a process's virtual address space for the execution
of the current image.
Pages are created starting at the address contained in the first
longword of the location addressed by the inadr
argument and ending with the second longword. The ending address can be
lower than the starting address. The retadr argument
indicates the byte addresses of the pages created.
If an error occurs while pages are being created, the
retadr argument, if specified, indicates the pages
that were successfully created before the error occurred. If no pages
were created, both longwords of the retadr argument
contain the value --1.
If $CRETVA creates pages that already exist, the service deletes those
pages if they are not owned by a more privileged access mode than that
of the caller. Any such deleted pages are reinitialized as demand-zero
pages. For this reason, it is important to use the
retadr argument to capture the address range actually
created. Because the Alpha architecture has a larger page size than the
VAX architecture, more space is potentially affected on Alpha systems.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
The paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,
$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
The Expand Program/Control Region ($EXPREG) service also adds pages to
a process's virtual address space.
Note
Do not use the $CRETVA system service in conjunction with other
user-written procedures or procedures supplied by HP (including
Run-Time Library procedures). This system service provides no means to
communicate a change in virtual address space with other routines. HP
recommends that you use either $EXPREG or the Run-Time Library
procedure Allocate Virtual Memory (LIB$GET_VM) to get memory. You can
find documentation on LIB$GET_VM in the OpenVMS RTL Library (LIB$) Manual. When using
$DELTVA, you should take care to delete only pages that you have
specifically created.
|
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
inadr argument cannot be read by the caller, or the
retadr argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its paging file quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased size of the virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted
because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the
caller.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The process's virtual address space is full; no space is available in
the page tables for the requested pages.
|
$CRETVA_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, adds a range of demand-zero allocation pages to a
process's virtual address space for the execution of the current image.
The new pages are added at the virtual address specified by the caller.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRETVA_64 region_id_64 ,start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,flags
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$cretva_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, void *start_va_64,
unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);
Arguments
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to create the virtual address
range. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified. Also, given a particular virtual address, the region ID for
the region it is in can be obtained by calling the $GET_REGION_INFO
system service specifying the VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA function.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting address for the created virtual address range. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be created. The length specified
must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $CRETVA_64. The access mode
determines the owner mode of the pages as well as the read and write
protection on the pages. The acmode argument is a
longword containing the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The $CRETVA_64 service uses whichever of the following access modes is
least privileged:
- Access mode specified by the acmode argument
- Access mode of the caller
The protection of the pages is read/write for the resultant access mode
and those more privileged.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask controlling the characteristics of the demand-zero pages
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $VADEF macro and the
VADEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flag that is valid for the $CRETVA_64
service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
VA$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future use by HP
and should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVVAFLG is
returned if any undefined bits are set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the created virtual address
range. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range created. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Create Virtual Address Space service is a kernel mode service that
can be called from any mode. The service adds a range of demand-zero
allocation pages, starting at the virtual address specified by the
start_va_64 argument. The pages are added to a
process's virtual address space for the execution of the current image.
Expansion occurs at the next free available address within the
specified region if the range of addresses is beyond the next free
available address.
The new pages, which were previously inaccessible to the process, are
created as demand-zero pages.
The returned address is always the lowest virtual address in the range
of pages created. The returned length is always an unsigned byte count
indicating the length of the range of pages created.
Successful return status from $CRETVA means that the specified address
space was created of the size specified in the
length_64 argument.
If $CRETVA_64 creates pages that already exist, the service deletes
those pages if they are not owned by a more privileged access mode than
that of the caller. Any such deleted pages are reinitialized as
demand-zero pages.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If an address within the specified address range is not within the
bounds of the specified region, the condition value SS$_PAGNOTINREG is
returned.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
added before the error occurred. If no pages were added, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
The process's paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA) must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64, $CREATE_REGION_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,
$EXPREG_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64,
$ULWSET_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its paging file quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
An invalid region ID was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVVAFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted
because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the
caller.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified range is already mapped, and the
VA$M_NO_OVERLAP flag was set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$CRMPSC
Allows a process to associate (map) a section of its address space with
either a specified section of a file (a disk file section) or specified
physical addresses represented by page frame numbers (a page frame
section). This service also allows the process to create either type of
section and to specify that the section be available only to the
creating process (private section) or to all processes that map to it
(global section).
Format
SYS$CRMPSC [inadr] ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[flags] ,[gsdnam] ,[ident]
,[relpag] ,[chan] ,[pagcnt] ,[vbn] ,[prot] ,[pfc]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, unsigned int
relpag, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int pagcnt, unsigned int vbn,
unsigned int prot,unsigned int pfc);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses into which the section is to be
mapped. The inadr argument is the address of a
2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process
virtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual
address is used to specify which pages are to be mapped; the low-order
byte-within-page bits are ignored for this purpose.
The interpretation of the inadr argument depends on
the setting of SEC$M_EXPREG in the flags argument and
on whether you are using an Alpha or a VAX system. The two system types
are discussed separately in this section.
Alpha System Usage
On Alpha systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the
inadr argument specifies the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space
are not allowed. The addresses must be aligned on CPU-specific pages;
no rounding to CPU-specific pages occurs. The lower address of the
inadr argument must be on a CPU-specific page boundary
and the higher address of the inadr argument must be 1
less than a CPU-specific boundary, thus forming a range, from lowest to
highest, of address bytes. You can use the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code in
the $GETSYI system service to set the inadr argument
to the proper values. You do this to avoid programming errors that
might arise because of incorrect programming assumptions about page
sizes.
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,
indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available
space in a particular region, the inadr argument is
used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or
the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must
be executed with extreme care. Because the user stack is mapped in P1,
it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently
read or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.
|
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr
longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword is used to determine the
region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,
P1 is chosen. On Alpha systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword must be 0. To ensure
compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,
HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadr
longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
In general, the inadr argument should be specified;
however, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanent
global sections, you can omit the inadr argument, or
specify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped.
Such a request will be granted regardless of the setting of the
SEC$M_EXPREG flag; however, to ensure compatibility between VAX and
Alpha systems, HP recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear when
the inadr argument is omitted.
VAX System Usage
On VAX systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the
inadr argument specifies the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space
are not allowed. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the
same, a single page is mapped.
Note
If the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is not set, HP recommends that the
inadr argument always specify the entire virtual
address range, from starting byte address to ending byte address. This
ensures compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems.
|
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,
indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available
space in a particular region, the inadr argument is
used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or
the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must
be executed with extreme care. Because the user stack is mapped in P1,
it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently
read or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.
|
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr
longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword is used to determine the
region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,
P1 is chosen. On VAX systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of the
first inadr longword is ignored. To ensure
compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,
HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadr
longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
In general, the inadr argument should be specified;
however, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanent
global sections, you can omit the inadr argument, or
specify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped.
You must also ensure that SEC$M_EXPREG is not set in the
flags argument. Omitting the inadr
argument with SEC$M_EXPREG set is interpreted by VAX systems as a
request to map with no region preference. This latter combination of
argument settings is strongly discouraged, as the chosen region is
indeterminate. To ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems,
HP recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear when the
inadr argument is omitted.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference--array reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses into which the section
was actually mapped by $CRMPSC. The retadr argument is
the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting
and ending process virtual addresses.
On Alpha systems, the retadr argument returns starting
and ending addresses of the usable range of addresses. This
might differ from the total amount mapped. The retadr
argument is required when the relpag argument is
specified. If the section being mapped does not completely fill the
last page used to map the section, the retadr argument
indicates the highest address that actually maps the section. If the
relpag argument is used to specify an offset into the
section, the retadr argument reflects the offset.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of section to be created or mapped to, as
well as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector wherein each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF
macro defines a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag and the default value that it
supersedes:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. The default is private section.
|
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Pages are copy-on-reference. By default, pages are shared.
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when
copied. For page file sections, the default is demand zero.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space. By default, pages are
mapped into the range specified by the
inadr argument.
See the
inadr argument description for a complete explanation
of how to set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section. For page file sections, the default is writeable.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, pages form a disk file
section. Pages mapped by SEC$M_PFNMAP are not included in or charged
against the process's working set; they are always valid. Do not lock
these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a
machine check if they are in I/O space.
++On Alpha systems, when the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag is set, the
pagcnt and
relpag arguments are interpreted in CPU-specific pages,
not as pagelets.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Pages form a global page file section. By default, pages form a disk
file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO.
|
|
SEC$M_EXECUTE
|
Pages are mapped if the caller has execute access. This flag takes
effect only (1) when specified from executive or kernel mode, (2) when
the SEC$M_GBL flag is also specified, and (3) when SEC$M_WRT is not
specified. By default $CRMPSC performs a read access check against the
section.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. Note that, by default,
pages can overmap existing address space.
|
++Alpha specific
gsdnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gsdnam argument is the
address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the UIC
group as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global
sections are unique to UIC groups.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section
and, for processes mapping to an existing global section, the criteria
for matching the identification. The ident argument is
the address of a quadword structure containing three fields.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
The first longword specifies, in its low-order two bits, the matching
criteria. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be
specified, and their meanings are as follows:
| Value/Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0 SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1 SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2 SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored.
If you do not specify the ident argument or specify it
as 0 (the default), the version number and match control fields default
to 0.
relpag
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Relative page number within the global section of the first page in the
section to be mapped. The relpag argument is a
longword containing this page number.
On Alpha systems, the relpag argument is interpreted
as an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for a
file-backed section or in CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section.
On Alpha and VAX systems, you use this argument only for global
sections. If you do not specify the relpag argument or
specify it as 0 (the default), the global section is mapped beginning
with the first virtual block in the file.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. The
chan argument is a word containing this number.
The file must have been accessed with the OpenVMS RMS macro $OPEN; the
file options parameter (FOP) in the FAB must indicate a user file open
(UFO keyword). The access mode at which the channel was opened must be
equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
pagcnt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems) in the
section. The pagcnt argument is a longword containing
this number.
On Alpha systems, the smallest allocation is an Alpha page, which is
8192 bytes. When requesting pagelets, the size requested is a multiple
of 512 bytes, but the actual allocation is rounded to 8192. For
example, when requesting 17 pagelets, the allocation is for two Alpha
pages, 16384 bytes.
On Alpha systems, if the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag bit is set, the
pagcnt argument is interpreted as CPU-specific pages,
not as pagelets.
On Alpha and VAX systems, the specified page count is compared with the
number of blocks in the section file; if they are different, the lower
value is used. If you do not specify the page count or specify it as 0
(the default), the size of the section file is used. However, for
physical page frame sections, this argument must not be 0.
vbn
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Virtual block number in the file that marks the beginning of the
section. The vbn argument is a longword containing
this number. If you do not specify the vbn argument or
specify it as 0 (the default), the section is created beginning with
the first virtual block in the file.
If you specified page frame number mapping (by setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP
flag), the vbn argument specifies the CPU-specific
page frame number where the section begins in memory.
Table SYS-21 shows which arguments are required and which are optional
for three different uses of the $CRMPSC service.
Table SYS-21 Required and Optional Arguments for the$CRMPSC Service
| Argument |
Create/Map
Global Section |
Map Global1
Section |
Create/Map
Private Section |
|
inadr
|
Optional
2
|
Required
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
retadr
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
acmode
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
flags
|
|
|
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Required
|
Ignored
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_CRF
3
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
3
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Optional
2
|
Not used
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gsdnam
|
Required
|
Required
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ident
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
relpag
3
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
chan
3
|
Required
|
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pagcnt
|
Required
|
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vbn
3
|
Optional
|
|
Optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
prot
|
Optional
|
|
Not used
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pfc
3
|
Optional
|
|
Optional
|
1The Map Global Section ($MGBLSC) service maps an existing
global section.
2See the description of inadr for the rules
governing the omission of the argument.
3For physical page frame sections: vbn
specifies the starting page frame number; chan must be
0; pfc is not used; and the SEC$M_CRF and SEC$M_DZRO
flag bit settings are invalid. For page file sections,
chan must be 0 and pfc not used.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file and PFN sections. For
file-backed sections, the protection is taken from the backing file and
the prot argument is ignored.
The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left
in each field.
The following diagram depicts the mask:
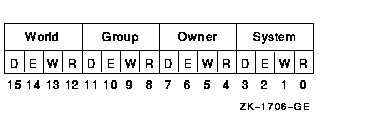
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user.
Only read, write, and execute access are meaningful for section
protection. Delete access bits are ignored. Read access also grants
execute access for those situations where execute access applies.
Protection is taken from the system or group global section template
for page file or PFN global sections if the prot
argument is not specified.
pfc
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Page fault cluster size indicating how many pages (on VAX systems) or
pagelets (on Alpha systems) are to be brought into memory when a page
fault occurs for a single page.
On Alpha systems, this argument is not used for page file sections or
physical page frame sections. The pfc argument is
rounded up to CPU-specific pages. That is, at least 16 pagelets (on an
Alpha system with an 8KB page size) will be mapped for each physical
page. The system cannot map less than one physical page.
On VAX systems, this argument is not used for page file sections or
physical page frame sections.
Description
The Create and Map Section service allows a process to associate (map)
a section of its address space with (1) a specified section of a file
(a disk file section) or (2) specified physical addresses represented
by page frame numbers (a page frame section). This service also allows
the process to create either type of section and to specify that the
section be available only to the creating process (private section) or
to all processes that map to it (global section).
Creating a disk file section involves defining all or part of a disk
file as a section. Mapping a disk file section involves making a
correspondence between virtual blocks in the file and pages (on VAX
systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems) in the caller's virtual address
space. If the $CRMPSC service specifies a global section that already
exists, the service maps it.
Any section created is created as entire pages. Refer to the memory
management section in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Depending on the actual operation requested, certain arguments are
required or optional. Table SYS-21 summarizes how the $CRMPSC service
interprets the arguments passed to it and under what circumstances it
requires or ignores arguments.
The $CRMPSC service returns the virtual addresses of the virtual
address space created in the retadr argument, if
specified. The section is mapped from a low address to a high address,
whether the section is mapped in the program or control region.
If an error occurs during the mapping of a global section, the
retadr argument, if specified, indicates the pages
that were successfully mapped when the error occurred. If no pages were
mapped, the value of the longwords is indeterminate. In this case,
either both longwords of the retadr argument will
contain the value --1, or the value of the longwords will be unaltered.
The SEC$M_PFNMAP flag setting identifies the memory for the section as
starting at the page frame number specified in the vbn
argument and extending for the number of CPU-specific pages specified
in the pagcnt argument. Setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag
places restrictions on the following arguments:
| Argument |
Restriction |
|
chan
|
Must be 0
|
|
pagcnt
|
Must be specified; cannot be 0
|
|
vbn
|
Specifies first page frame to be mapped
|
|
pfc
|
Does not apply
|
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Must be 1 if the flags SEC$M_GBL or SEC$M_SYSGBL are set
|
Setting the SEC$M_PAGFIL flag places the following restrictions on the
following flags:
| Flag |
Restriction |
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Assumed to be 0
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Must be 1
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Must be 0
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Assumed to be 0
|
The flags argument bits 4 through 13 and 18 through 31
must be 0.
If the global section is mapped to a file (neither SEC$M_PAGFIL nor
SEC$M_PFNMAP is set), the security profile of the file is used to
determine access to the global section.
On VAX systems, by default, the initial security profile created for a
page file or PFN global section is taken from the group global section
template. If the SEC$M_SYSGBL flag is set, the profile is taken from
the system global section template. The owner is then set to the
process UIC. If the prot argument is nonzero, it
replaces the protection mask from the template.
On Alpha and VAX systems, the flag bit SEC$M_WRT applies only to the
way in which the newly created section is mapped. For a file to be made
writable, the channel used to open the file must allow write access to
the file.
If the flag bit SEC$M_SYSGBL is set, the flag bit SEC$M_GBL must be set
also.
Required Access or Privileges
If $CRMPSC specifies a global section and the SS$_NOPRIV condition
value is returned, the process does not have the required privilege to
create that section. To create global sections, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
- SHMEM privilege to create a global section in memory shared by
multiple processors (VAX only)
Note that you do not need PFNMAP privilege to map an existing page
frame section.
Required Quota
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). The systemwide number of
global page file pages is limited by the system parameter GBLPAGFIL.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,
$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
inadr argument,
gsdnam argument, or name descriptor cannot be read by
the caller; the
inadr argument was omitted; or the
retadr argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The starting virtual block number specified is beyond the logical
end-of-file, or the value in the
relpag argument is greater than or equal to the actual
size of the global section.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to
map the requested file.
|
|
SS$_EXGBLPAGFIL
|
The process has exceeded the systemwide limit on global page file
pages; no part of the section was mapped.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota while creating
copy-on-reference or page file backing store pages.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_ILLPAGCNT
|
The page count value is negative or is 0 for a physical page frame
section.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough pages are available in the specified shared memory to create
the section.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased size of the address space.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified, that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
The channel number specified is currently active.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLVEC
|
The specified section was not installed using the /PROTECT qualifier.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, a flag requiring a privilege you
lack, or an invalid combination of flags was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privileges to create a system global
section (SYSGBL) or a permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
The process does not have the privilege to create a section
starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP).
The process does not have the privilege to create a global section
in memory shared by multiple processors (SHMEM).
A page in the input address range is in the system address space.
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device.
|
|
SS$_NOWRT
|
The section cannot be written to because the flag bit SEC$M_WRT is set,
the file is read only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table or in
the process section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gsdnam argument exceeded the allowed depth.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped, and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The process's virtual address space is full; no space is available in
the page tables for the pages created to contain the mapped global
section.
|
$CRMPSC_FILE_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to map a section of its address
space to a specified portion of a file. This service creates and maps a
private disk file section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_FILE_64 region_id_64 ,file_offset_64 ,length_64 ,chan
,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,fault_cluster
[,start_va_64]]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_file_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned
__int64 file_offset_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned short int
chan, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)),
unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the private disk file
section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
file_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Byte offset into the file that marks the beginning of the section. The
file_offset_64 argument is a quadword containing this
number. If you specify the file_offset_64 argument as
0, the section is created beginning with the first byte in the file.
The file_offset_64 argument must be a multiple of
virtual disk blocks.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
value |
Length, in bytes, of the private disk file section to be created and
mapped to. The length specified must be 0 or a multiple of virtual disk
blocks. If the length specified is 0 or extends beyond end-of-file
(EOF), the disk file is mapped up to and including the virtual block
number that contains EOF.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. The
chan argument is a longword containing this number.
The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to or
less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
Use the OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) macro $OPEN to access
a file; the file options parameter in the file access block must
indicate a user file open (UFO) keyword.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by
an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the
calling process.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the private section to be
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CRMPSC_FILE_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Pages are copy-on-reference.
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when
copied.
Note that SEC$M_DZRO and SEC$M_CRF cannot both be set and that
SEC$M_DZRO set and SEC$M_WRT clear is an invalid combination.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the private disk file
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the usable virtual address
range mapped in bytes. This length might differ from the total amount
mapped. If the section being mapped does not completely fill the last
page used to map the section, the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments indicate the highest
address that actually maps the section.
fault_cluster
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Page fault cluster in byte units indicating how many pages are to be
brought into memory when a page fault occurs for a single page. The
fault cluster specified will be rounded up to a multiple of
CPU-specific pages.
If this argument is specified as 0, the process default page fault
cluster will be used. If this argument is specified as more than the
maximum allowed for the system, no condition value will be returned.
The systemwide maximum will be used.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the private disk file section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
Description
The Create and Map Private Disk File Section service allows a process
to create a map to a private disk file section. Creating a private disk
file section involves mapping all or part of a disk file as a section.
The section is mapped from a low address to a high address whether the
section is mapped in a region that grows from low to high addresses or
from high to low addresses.
The flag SEC$M_WRT applies only to the way in which the newly created
section is mapped. For a file to be made writable, the channel used to
open the file must allow write access to the file.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
The process must have sufficient byte count quota to satisfy the
request.
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,
$LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64,
$UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_CHANVIO
|
The specified channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The
file_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to
map the requested file.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
was 0 or a channel that is unassigned.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
The channel number specified is currently active, or there are no files
opened on the specified channel.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
is larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk
blocks.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device.
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTBLKALGN
|
The
file_offset_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual
disk blocks.
|
|
SS$_NOWRT
|
The file is read-only, the flag bit SEC$M_WRT was set, and the flag bit
SEC$M_CRF is not set.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted
because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the
caller.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a memory-resident global
demand-zero section and to map a section of its address space to the
global section. Shared page table sections can also be created.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64 ,region_id_64
,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
[[[[,start_va_64] ,map_length_64] ,reserved_length_64] ,rad_mask]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_gdzro_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, struct _generic_64
*region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,
the version number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global demand-zero section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,
read access and write access are granted to all users.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global demand-zero section to be created. The
length_64 must be specified as a multiple of the
CPU-specific page size. A length of 0 cannot be specified.
Note
Creating a memory-resident global section with shared page table does
not imply that the global section must have an even multiple of
CPU-specific page table pages. The global section might not fully use
the last page table page.
|
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page file
section.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process's
virtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple of a
CPU-specific page size.
If a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument,
section_offset_64 must be an even multiple of the
number of bytes that can be mapped by a CPU-specific page table page.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. This access mode is also the read access mode and the write
access mode. The acmode argument is a longword
containing the access mode.
If the memory-resident global section is created with shared page
tables, this is the access mode that is stored in the owner, read, and
write fields of the corresponding shared page table entries (PTEs).
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by
an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the
calling process.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of the global section to be created as
well as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section
was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, virtually aligned
addresses after the first available space are chosen for the mapping.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent.
|
|
SEC$M_RAD_HINT
|
When set, the argument
rad_mask is used as a mask of RADs from which to
allocate memory. See the
rad_mask argument description for more information.
|
|
SEC$M_READ_ONLY_SHPT
|
Create shared table pages for the section that allow read access only.
|
|
SEC$M_SHMGS
|
Create a shared-memory global section.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_MRES
|
Pages form a memory-resident section. By default, this page is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalid
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global demand-zero
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
If a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument and the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is
set, the returned virtual address is aligned to a CPU-specific page
table page boundary.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range
mapped in bytes.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the memory-resident global section.
The specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned
address. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the
start_va_64 argument must not be specified or must be
specified as 0. If SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the
start_va_64 argument is nonzero, the condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
If SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, start_va_64 is nonzero, and
a shared page table region is specified, the specified starting address
must be aligned to a natural page table page boundary; otherwise, the
condition value SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN is returned.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the memory-resident
global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry and
start_va_64 is aligned to a multiple of CPU-specific
pages appropriate for taking advantage of granularity hints (8, 64, or
512 pages), then granularity hints are used to map to the global
section.
map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the memory-resident global section to be mapped. The length
specified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. If this argument is
not specified or is specified as zero, the global file section is
mapped up to and including the last page in that section.
If a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, map_length_64
must be an even multiple of the number of bytes that can be mapped by a
CPU-specific page table page or must include the last page within the
global section.
reserved_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
32- or 64-bit reference |
Length, in bytes, of the global section as currently registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry. The reserved_length_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned
quadword into which the service returns the reserved length.
If reserved_length_64 is not specified or is specified
as 0, no reserved length is returned to the caller.
If the memory-resident global section is not registered,
reserved_length_64 is written with the value 0.
rad_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Use the rad_mask argument to specify from which RADs
to allocate memory. Currently only one bit may be set. The specified
RAD must contain memory. This argument is only a hint. Memory may be
obtained from other RADs if no free memory is available at the time of
allocation.
The rad_mask argument is considered only if the
SEC$M_RAD_HINT flag is specified. Otherwise, this argument is ignored.
On a system that does not support resource affinity domains (RADs),
specifying 1 for the rad_mask argument is allowed.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Description
The Create and Map to Global Demand-Zero Section service allows a
process to create and map to a memory-resident global demand-zero
section. If you set the SEC$M_SHMGS flag, the section is created as a
Galaxy-wide global demand-zero section in shared memory.
You must call either the $CREATE_GDZRO service or the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64
service on each instance where the Galaxy shared memory will be
accessed.
Memory-resident or Galaxy-wide global sections contain demand-zero
allocation pages that are writable and memory resident. All pages in
these types of global section are shared by all processes that map to
the global section.
If the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service specifies a global section that already
exists, the service maps to it only if it is a memory-resident global
section. All pages in the memory-resident global section are shared by
all processes that map to the global section.
The global demand-zero pages are always resident in memory and are not
backed up by any file on any disk. The global pages are not charged
against any page file quota. The process must have the rights
identifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER to create a memory-resident global
section; otherwise, the error status SS$_NOMEMRESID is returned.
The pages are always resident in memory and are not backed up by any
file on any disk. The pages are not placed into the process's working
set list when the process maps to the global section and the virtual
memory is referenced by the process. The pages are also not charged
against the process's working set quota or against any page-file quota.
Only memory-resident sections can be registered with the Reserved
Memory Registry in the SYSMAN facility. Memory for Galaxy-wide shared
sections is reserved through appropriate settings of the console
environment parameters.
If the memory-resident global section is either not registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry or if the /NOALLOCATE qualifier was specified
when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,
invalid global PTEs are written to the global page table and invalid
PTEs are placed in the process page table. Physical memory is not
allocated until the virtual memory is referenced.
If the global section is registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,
the size of the global section need not match the reserved size. If the
global section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or if
the reserved size is smaller than the size of the global section, the
error status SS$_INSFLPGS is returned if there are not enough fluid
pages in the system to satisfy the request.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was
registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, contiguous, aligned
physical pages are preallocated during system initialization for this
global section. Valid page table entries are placed in the global page
table and in the process page table. If the reserved preallocated
memory is smaller than the size of the global section, the error
SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the global section is not created.
If the memory-resident global section is not registered in the Reserved
Memory Registry or if the /PAGE_TABLES qualifier was specified when the
global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, shared
page tables are created for the global section.
For more information about using the SYSMAN utility to create entries
to the Reserved Memory Registry, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Shared page tables consume the same internal OpenVMS data structures as
a global section. The system parameters GBLPAGES and GBLSECTIONS must
account for the additional global pages and the additional global
section.
To use the shared page tables associated with a memory-resident global
section, you must first create a shared page-table region (with
$CREATE_REGION_64). To map to the memory-resident global section using
the shared page tables, you must do the following:
- Specify a shared page-table region in the
region_id_64 argument.
- Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG or provide a CPU-specific page table page
aligned virtual address in the start_va_64 argument.
- Specify a value for the section_offset_64 argument
that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table
page or zero.
- Specify a value for the map_length_64 argument
that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table
page or zero, or include the last page of the section.
See the description of the $CREATE_REGION_64 service for information
about calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specific
page table page boundary.
The memory-resident global section can be mapped with shared page
tables or private page tables. The following table lists the factors
associated with determining whether the mapping occurs with shared page
tables or with private page tables:
| Global Section Created with Shared Page Tables |
Shared Page Table Region Specified by region_id_64 |
Type of Page Tables Used in Mapping |
|
No
|
No
|
Private
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
Private
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
Private
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Shared
|
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual
address within the specified region is used to map to the global
section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the region_id_64
argument indicates a shared page table region, the first free virtual
address within the specified region is rounded up to a CPU-specific
page table page boundary and used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and if the /ALLOCATE qualifier was
specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for the
memory-resident global section, the first free virtual address within
the specified region is rounded up to the same virtual alignment as the
physical alignment of the preallocated pages and used to map to the
global section. Granularity hints are set appropriately for each
process private PTE.
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the virtual address in
the start_va_64 argument is used to map to the global
section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the value specified in the
start_va_64 argument can determine if the mapping is
possible and if granularity hints are used in the private page tables.
If a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the virtual address specified
by the start_va_64 argument must be on an even
CPU-specific page table page boundary or an error is returned by this
service. If the region_id_64 argument does not specify
a shared page table region and /ALLOCATE was specified with the SYSMAN
command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for this global section, granularity hints
are used only if the virtual alignment of start_va_64
is appropriate for the use of granularity hints (either 8-page,
64-page, or 512-page alignment).
Whenever granularity hints are being used within the mapping of a
memory-resident global section, if the length_64
argument is not an exact multiple of the alignment factor, lower
granularity hints factors are used as appropriate at the higher
addressed portion of the global section. If the
section_offset_64 argument is specified, a lower
granularity hint factor can be used throughout the mapping of the
global section to match the physical alignment of the first page mapped.
When you map a Galaxy shared section or a memory resident section that
has an associated shared page table section, you have the following
options for accessing data:
Table SYS-22 Shared Page Tables
| Shared Page Tables |
Read Only |
Read and Write |
|
None created
|
Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request.
Private page tables will always be used, even if you are specifying
a shared page table region into which to map the section.
|
Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request.
Private page tables will always be used, even if you are specifying
a shared page table region into which to map the section.
|
|
Write access
|
Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request.
Ensure that private page tables will be used. Do not specify a
shared page table region into which to map the section. If you do, the
error status SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
|
Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request.
The shared page table section will be used for mapping if you
specify a shared page table region into which to map the section.
|
|
Read access
|
Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. The shared page table
section will be used for mapping if you specify a shared page table
region into which to map the section.
|
Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. Ensure that private page
tables will be used. Do not specify a shared page table region into
which to map the section. If you do, the error status SS$_IVSECFLG is
returned.
|
Notes
Shared page tables for Galaxy shared sections are also implemented as
Galaxy shared sections. This implies that they allow either read access
only on all OpenVMS instances connected to this section or read and
write access on all instances. The setting of the SEC$M_READ_ONLY_SHPT
flag as requested by the first instance to create the section is used
on all instances.
Using the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service always implies that the SEC$M_WRT
flag is set and that you want to map the section for writing. If you
want to use this service to create a section with shared page tables
for read only access, you must use private page tables and you cannot
specify a shared page table region into which to map the section.
|
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments and, if specified as a nonzero value, the
reserved_length_64 argument.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument contains the value --1.
If the service returns an error status value other than SS$_INSFLPGS or
SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL, a value is not returned in the
reserved_length_64 argument.
If the service returns a successful condition value or if SS$_INSFLPGS
or SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the
reserved_length_64 argument is specified as a nonzero
address, the length in bytes of the global section as registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry is returned in the
reserved_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the following
privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER rights identifier to create a memory-resident
section
- SHMEM privilege on OpenVMS Galaxy systems to create an object in
Galaxy shared memory
Required Quota
If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident global
section, the working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be
sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables
required by the increase in virtual address space.
If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident global
section, the page file quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be
sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables
required by the increase in virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_GDZRO, $CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC,
$CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64,
$DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64,
$MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64,
$UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The global section has been created.
|
|
SS$_CREATED_SHPT
|
Global section has been created with shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_BADRAD
|
The specified RAD contains no memory, or if the specified RAD is
greater than or equal to the maximum number of RADs on the system.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process's page file quota is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it is not a memory-resident section.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the global section or for the shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_INSFLPGS
|
Insufficient fluid pages available.
|
|
SS$_INSFRPGS
|
Insufficient free shared pages or private pages.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_INV_SHMEM
|
Shared memory is not valid.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The specified access mode is greater than PSL$_USER, or the caller's
mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVPROTECT
|
The protection argument format is invalid.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
An invalid region ID was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specified
pages. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the
map_length_64 argument is not a multiple of
CPU-specific page table pages.
|
|
SS$_LOCK_TIMEOUT
|
An OpenVMS Galaxy lock timed out.
|
|
SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL
|
Preallocated, contiguous, aligned physical memory specified in the
Reserved Memory Registry is smaller than the length specified for the
memory-resident global section by the
length_64 argument.
|
|
SS$_NOBREAK
|
An OpenVMS Galaxy lock is held by another node and was not broken.
|
|
SS$_NOMEMRESID
|
The process attempted to create a memory-resident section, but was not
holding the right identifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page
aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the
section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page
table page aligned.
|
|
SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG
|
The
section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified input address range is not within the specified
region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table for
the global section or for the shared page tables.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or a page in the specified input address
range is in another region, in system space, or inaccessible; or, the
existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table
page aligned.
|
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a global disk file section
and to map a section of its address space to the global section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,file_offset_64 ,length_64
,chan ,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64
,return_length_64 [,fault_cluster
[,start_va_64 [,map_length_64]]]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_gfile_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned __int64 file_offset_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned
short int chan, struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned __int64
section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void
*(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,
the version number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
file_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Byte offset into the file that marks the beginning of the section. The
file_offset_64 argument is a quadword containing this
number. If you specify the file_offset_64 argument as
0, the section is created beginning with the first byte in the file.
The file offset specified must be a multiple of virtual disk blocks.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global disk file section to be created. The
length specified must be 0 or a multiple of virtual disk blocks. If the
length specified is 0 or extends beyond the end-of-file (EOF), the
global disk file section is created up to and including the virtual
block number that contains EOF.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. The
chan argument is a longword containing this number.
The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to or
less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
You can use the OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) macro $OPEN to
access a file; the file options parameter in the file access block must
indicate a user file open (UFO) keyword.
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64 bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region in which to map the global
disk file section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF
macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three
default regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process's
virtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple of
virtual disk blocks.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to be
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_CRF
|
Pages are copy-on-reference.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when
copied.
Note that SEC$M_DZRO and SEC$M_CRF cannot both be set and that
SEC$M_DZRO set and SEC$M_WRT clear is an invalid combination.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global disk file
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
Upon successful completion of this service, if the
section_offset_64 argument was specified, the virtual
address returned in return_va_64 reflects the offset
into the global section mapped such that the virtual address returned
cannot be aligned on a CPU-specific page boundary. The virtual address
returned will always be on an even virtual disk block boundary.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range
mapped in bytes.
Upon successful completion of this service, the value in the
return_length_64 argument indicates the amount of
created address space backed by the section file.
If the number of disk blocks mapped does not represent an exact
multiple of CPU-specific pages, the last page in the mapped address
space will not be completely mapped by the section file. In this case,
modifying memory beyond the amount indicated by
return_length_64 can result in the loss of this data.
Unlike the return_length_64 argument for the
$CREATE_GFILE service, upon successful completion of this service, the
return_length_64 argument does not represent the total
length of the global section created if the
section_offset_64 argument was specified as nonzero.
The value in the section_offset_64 argument plus the
value in the return_length_64 argument is the total
length of the global disk file section created.
fault_cluster
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Page fault cluster in byte units indicating how many pages are to be
brought into memory when a page fault occurs for a single page. The
fault cluster specified will be rounded up to a multiple of
CPU-specific pages.
If this argument is specified as 0, the system default page fault
cluster will be used. If this argument is specified as more than the
maximum allowed for the system, no error will be returned. The
systemwide maximum will be used.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global disk file section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, this argument will not be used.
If SEC$M_EXPREG is clear and the start_va_64 argument
is not specified or is specified as 0, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG
will be returned.
Always refer to the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments to determine the usable
range of virtual addresses mapped.
map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword unsigned |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the global disk file section to be mapped. The length
specified must be a multiple of virtual disk blocks. If this argument
is not specified as zero, the global disk section is mapped up to and
including the last disk block in the section.
Description
The Create and Map Global Disk File Section service allows a process to
create and map to a global disk file section.
Creating a global disk file section involves defining all or part of a
disk file as a section. The section is mapped from a low address to a
high address whether the section is mapped in a region that grows from
low to high addresses or from high to low addresses. If the
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 service specifies a global disk file section that
already exists, the service maps it.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
The flag SEC$M_WRT applies only to the way in which the newly created
section is mapped. For a file to be made writable, the channel used to
open the file must allow write access to the file.
Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the following
privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,
$DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64,
$ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_CHANVIO
|
The specified channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The
file_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to
map the requested file.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference
pages.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it was not a global disk file section.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
was 0 or a channel that is unassigned.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
The channel number specified is currently active or there are no files
opened on the specified channel.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified
is larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT
|
The
length_64 or the
map_length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual
disk blocks.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device.
|
|
SS$_NOWRT
|
The file is read-only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set.
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTBLKALGN
|
The
file_offset_64 or
section_offset_64 argument is not virtual disk block
aligned.
|
|
SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG
|
The
section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a global page file section
and to map a section of its address space to the global section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64
,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64
,return_length_64 [,start_va_64 [,map_length_64]]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_gpfile_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, struct _generic_64
*region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode,
unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,
the version number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,
read access and write access are granted to all users.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global page file section to be created. The
length specified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. A length of
0 cannot be specified.
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page file
section.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process's
virtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple of
virtual disk blocks.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by
an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the
calling process.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to be
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region. SEC$M_EXPREG cannot be specified with the
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP flag.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space. SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP cannot be specified
with the SEC$M_EXPREG flag.
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Pages form a global page file section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalid
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page file
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range
mapped in bytes.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global page file section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
Always refer to the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments to determine the range of
virtual addresses mapped.
map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the global page file section to be mapped. The length
specified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. If this argument is
not specified or is specified as zero, the global file section is
mapped up to and including the last page in that section.
Description
The Create and Map Global Page File Section service allows a process to
create a map to global page file section. Creating a global page file
section involves defining a global section backed up by the system page
file. The section is mapped from a low address to a high address
whether the section is mapped in a region that grows from low to high
addresses or from high to low addresses. If the $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64
service specifies a global section that already exists, the service
maps it.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the following
privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
Because the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
The working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient
to accommodate the increased size of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space when the section is mapped.
Related Services
$CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,
$DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS,
$SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_EXGBLPAGFIL
|
The process has exceeded the systemwide limit on global page file
pages; no part of the section was mapped.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference
pages.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it is not a global disk or page file section.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specified
pages or was specified as 0.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOWRTACC
|
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not
allow write access.
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page
aligned if a map to a global page file section was requested
(SEC$M_PAGFIL is set in the flags argument).
|
|
SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG
|
The
section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a permanent global page
frame section and to map a section of its address space to the global
page frame section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_GPFN_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,start_pfn ,page_count
,region_id_64 ,relative_page ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64
,return_length_64 [,start_va_64 [,map_page_count]]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_gpfn_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned int start_pfn, unsigned int page_count,
struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int relative_page, unsigned
int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned
__int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is
ignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,
the version number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file section.
The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left
in each field. The following diagram depicts the mask:

Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,
read access and write access are granted to all users.
start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: |
page frame number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins.
page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page frame
section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
relative_page
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Relative CPU-specific page number within the global section to start
mapping.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to be
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page frame
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the
service returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range
mapped in bytes.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global page frame section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page-aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
Always refer to the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments to determine the range of
virtual addresses mapped.
map_page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the global page frame section to be mapped in CPU-specific
pages.
Description
The Create and Map Global Page Frame Section service allows a process
to create and map to a global page frame section. Creating a global
page frame section involves defining certain physical page frame
numbers (PFNs) as a section.
All global page frame sections are permanent. Pages mapped to a global
page frame section are not included in or charged against the process's
working set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in the
working set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a machine check if
they are in I/O space.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
To create a global page frame section, the process must have the
following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section (if flag
SEC$M_PERM is set)
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_GPFN, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,
$DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section
already exists and has been mapped.
|
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it was not a global disk file section.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_ILLRELPAG
|
The specified relative page argument is either larger than the highest
page number within the section or is not a valid 32-bit physical page
frame number.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPFNMAP
|
The process does not have the privilege to create or delete a section
starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP).
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
A virtual address within a shared page-table region was specified, or
the region ID of a shared page-table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOWRTACC
|
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not
allow write access.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page-aligned.
|
$CRMPSC_PFN_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows a process to map a section of its address
space to a specified physical address range represented by page frame
numbers. This service creates and maps a private page frame section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CRMPSC_PFN_64 region_id_64 ,start_pfn ,page_count ,acmode ,flags
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]
C Prototype
int sys$crmpsc_pfn_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int
start_pfn, unsigned int page_count, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int
flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the private page frame
section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: |
page frame number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins in memory.
page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by
an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the
calling process.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the private section to be
created. The flags argument is a longword bit vector
in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the
SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$CRMPSC_PFN_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can
overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalid
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the private page frame
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range mapped. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the private page frame section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVESCFLG is returned.
Description
The Create and Map Private Page Frame Section service allows a process
to create a map to a private page frame section. Creating a private
page frame section involves defining certain physical page numbers
(PFNs) as a section. The section is mapped from a low address to a high
address whether the section is mapped in a region that grows from low
to high addresses or from high to low addresses.
All global page frame sections are permanent. Pages mapped by
SEC$M_PFNMAP are not included in or charged against the process's
working set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in the
working set by using $LKWSET_64; this can result in a machine check if
they are in I/O space.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and
a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to
by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
PFNMAP privilege is required to create a page frame section.
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
and arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPFNMAP
|
The process does not have the privilege to create a section starting at
a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP).
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be
deleted because it is associated with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$CVT_FILENAME (Alpha Only)
Converts a string from RMS format to file-system (ACP-QIO) format or
from file-system (ACP-QIO) format to RMS format.
Format
SYS$CVT_FILENAME cvttyp ,srcstr ,inflags ,outbuf ,outlen ,outflags
C Prototype
int sys$cvt_filename (unsigned int cvttyp, void *srcstr, unsigned int
inflags, void *outbuf, unsigned short int *outlen, unsigned int
*outflags);
Arguments
cvttyp
| OpenVMS usage: |
unsigned_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword value that indicates whether the conversion is from RMS format
to ACP-QIO format or vice versa.
There are two legal values for this parameter, represented by the
symbols CVTFNM$C_ACPQIO_TO_RMS and CVTFNM$C_RMS_TO_ACPQIO, that are
defined by the $CVTFNMDEF macro.
srcstr
| OpenVMS usage: |
string of bytes or words |
| type: |
string of bytes or words |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
String to be converted by the service.
If the conversion is from RMS format to ACP-QIO format,
srcstr is an ISO-Latin-1 or
VTF-7-encoded character string. If the conversion is from ACP-QIO
format to RMS format, srcstr is a string of byte-width
or word-width characters.
The descriptor length field indicates the length of the input string in
bytes, whether the characters are byte-width or word-width.
The srcstr argument is the 32-bit address of a
descriptor that points to this string.
inflags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword flag mask indicating the characteristics of the input string.
For conversion from RMS format to ACP-QIO format, only the
CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS flag is valid.
For conversion from ACP-QIO format to RMS format, legal flags are
CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS and CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS (defined by the
$CVTFNMDEF macro).
| Flag |
Description |
|
CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS
|
Input source string contains word-width UCS-2 characters (ACPQIO_TO_RMS
conversion only).
|
|
CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS
|
Input source string should be treated as an arbitrary string (such as a
subdirectory name) rather than as a file name that contains (or should
contain) dots or semicolons as type and version delimiters.
|
|
CVTFNM$V_FORCE_UPCASE
|
Causes this system service to convert each character to uppercase.
(ACPQIO_TO_RMS conversion only).
|
outbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
string of bytes or words |
| type: |
string of bytes or words |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
The buffer into which the converted string is to be written.
If the conversion is from RMS format to ACP-QIO format, the string may
consist of byte-width ISO Latin-1 characters or word-width UCS-2
characters, depending on the characters in the source string. (If any
character in the source string must be converted to UCS-2, then all
characters in the output buffer will be converted to UCS-2.)
If the conversion is from ACP-QIO format to RMS format, then the output
string will consist of ISO Latin-1 and
VTF-7 characters in RMS canonical form. (Refer to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications.)
For ACPQIO_TO_RMS conversion, if the output string contains word-width
characters, the CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS flag in the
outflags flag mask will be set.
The outbuf argument is the 32-bit address of a
descriptor pointing to a buffer writable in the access mode of the
caller.
outlen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference |
The outlen argument is the 32-bit address of a
(16-bit) word writable in the access mode of the caller.
outflags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference |
Longword flag mask in which the service sets or clears flags to
indicate characteristics of the output string.
For an RMS_TO_ACPQIO conversion, SYS$CVT_FILENAME sets the bit
corresponding to CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS (defined by the $CVTFNMDEF macro)
if the characters of the converted string are one-word wide rather than
one-byte wide. If the characters of the converted string are one-byte
wide, the service clears the CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS bit. All other bits
are cleared by an RMS_TO_ACPQIO conversion.
The outflags argument is the 32-bit address of a
32-bit flag mask writable in the access mode of the caller.
Description
This service is intended to provide the conversion of a file name or a
subdirectory name between the RMS format (as seen at the RMS interface)
and the ACP-QIO format (as stored on disk). A file name consists of a
file name, a file type, and a file version; and a subdirectory name is
a string to which ".DIR;1" can be appended to form a directory file
name, as stored on disk.
Prior to Version 7.2, these representations were the same. This is not
necessarily the case for extended (ODS-5) file names. (Refer to the
Guide to OpenVMS File Applications for details on ODS-5 file specifications.)
Depending on the value of cvttyp, the service will
perform a conversion of a string from RMS format to ACP-QIO format or
from ACP-QIO format to RMS format.
The source string is described by the argument srcstr,
the output buffer is described by the argument outbuf,
and the resultant string length is written to the argument
outlen.
If any of the source string falls within the address range of the
output buffer, the output string is unpredictable.
RMS-to-ACPQIO Conversion:
A string described by the srcstr descriptor argument
is converted to an ISO Latin-1 or UCS-2 string with each character
represented in a form that can be passed to the ACP-QIO by the $QIO
service.
If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is not set, the source string
will be scanned and, if necessary, a dot and a semicolon will be
inserted or appended as though a $PARSE were done with no default name,
type, or version fields supplied. If the scan detects any delimiters
indicating the presence of fields other than name (without FID), type,
or version, a syntax error will be returned.
If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is set, individual characters
will be validated and converted to their on-disk form; however, no scan
will be done to determine if the type and version delimiters are
present, and no delimiters will be added.
A percent sign (%) that is not preceded by the escape character (^) is
converted to a question mark. An ISO Latin-1 character that is preceded
by the escape character (^) is converted to the corresponding ISO
Latin-1 character. A
VTF-7 character (for example, ^U1234) that is preceded by the escape
character (^) is converted to a UCS-2 character (for example, 0x1234).
If any character requires UCS-2 (word-width character) representation,
all characters are represented in the output string with UCS-2. If no
character requires word-width character representation, all characters
are represented in the output string with ISO Latin-1 (byte-width)
characters.
Valid characters are those that are legal in an RMS file name (file
name, file type, and file version) or in an RMS subdirectory name. For
example, directory delimiters "[" and "]" are not
legal unless preceded by the escape character (^).
ACPQIO-to-RMS Conversion:
The string described by the srcstr descriptor argument
is converted to the RMS canonical form for that string.
If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is clear, the source string
must contain at least one semicolon and, to the left of the semicolon,
at least one dot. If it does not, RMS$_SYN (syntax error) is returned.
In the output string, all other dots and semicolons are preceded by the
RMS escape character (^).
If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is set, any dot or semicolon
encountered is preceded in the output string by the RMS escape
character (^).
The CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS flag of the inflags argument
indicates whether the input string is to be interpreted as having
byte-width (ISO Latin-1) or word-width (UCS-2) characters. If the
argument indicates word-width characters, but the input length value is
an odd number, a syntax error is returned.
Questions marks are converted to percent signs; percent signs are
preceded by the escape character (^). UCS-2 characters are converted to
VTF-7 characters. All characters are represented in RMS canonical form.
$CVT_FILENAME Usage:
You can use this service to compare two file names using the same
conventions as RMS.
For an example program, refer to: [SYSHLP.EXAMPLES]FILENAME_COMPARE.C.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
None.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Unrecognized conversion type, extraneous input flags set, or
zero-length input string.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Not enough arguments provided.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments provided.
|
|
RMS$_SYN
|
The service could not translate one or more characters in the strings
described by the
srcstr argument. Either the input string has
word-width characters but odd byte-length (ACPQIO_TO_RMS only), or the
CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag was clear, and the input string did
not contain both type and version delimiters.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The output buffer was not large enough to accommodate the converted
string.
|
$DACEFC
Releases the calling process's association with a common event flag
cluster.
Format
SYS$DACEFC efn
C Prototype
int sys$dacefc (unsigned int efn);
Argument
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of any event flag in the common cluster to be disassociated. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $DACEFC uses only the low-order byte. The number must be in
the range of 64 through 95 for cluster 2, and 96 through 127 for
cluster 3.
Description
The Disassociate Common Event Flag Cluster service disassociates the
calling process from a common event flag cluster and decreases the
count of processes associated with the cluster accordingly. When the
image associated with a cluster exits, the system disassociates the
cluster. When the count of processes associated with a temporary
cluster or with a permanent cluster that is marked for deletion reaches
0, the cluster is automatically deleted.
If a process issues this service specifying an event flag cluster with
which it is not associated, the service completes successfully.
Required Access or Privileges
A calling process must have PRMCEB privilege to delete a permanent
common event flag cluster.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLAND, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number. The number must be in the
range of event flags 64 through 127.
|
|
SS$_INTERLOCK
|
The bit map lock for allocating common event flag clusters from the
specified shared memory is locked by another process.
|
$DALLOC
Deallocates a previously allocated device.
Format
SYS$DALLOC [devnam] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$dalloc (void *devnam, unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the device to be deallocated. The devnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
the device name string. The string might be either a physical device
name or a logical name. If it is a logical name, it must translate to a
physical device name.
If you do not specify a device name, all devices allocated by the
process from access modes equal to or less privileged than that
specified are deallocated.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode from which the deallocation is to be performed. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access
modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Description
The Deallocate Device service deallocates a previously allocated
device. The issuing process relinquishes exclusive use of the device,
thus allowing other processes to assign or allocate that device. You
can deallocate an allocated device only from access modes equal to or
more privileged than the access mode from which the original allocation
was made.
This service does not deallocate a device if, at the time of
deallocation, the issuing process has one or more I/O channels assigned
to the device; in such a case, the device remains allocated.
At image exit, the system automatically deallocates all devices that
are allocated at user mode.
If you attempt to deallocate a mailbox, success is returned but no
operation is performed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DASSGN,
$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The device name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_DEVASSIGN
|
The device cannot be deallocated because the process still has channels
assigned to it.
|
|
SS$_DEVNOTALLOC
|
The device is not allocated to the requesting process.
|
|
SS$_IVDEVNAM
|
You did not specify a device name string, or the device name string
contains invalid characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The device name string has a length of 0 or has more than 63 characters.
|
|
SS$_NONLOCAL
|
The device is on a remote node.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The device was allocated from a more privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist in the host system.
|
$DASSGN
Deassigns (releases) an I/O channel previously acquired using the
Assign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN) service.
Format
SYS$DASSGN chan
C Prototype
int sys$dassgn (unsigned short int chan);
Argument
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the I/O channel to be deassigned. The chan
argument is a word containing this number.
Description
The Deassign I/O Channel service deassigns (releases) an I/O channel
that it acquired using the Assign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN) service. You
can deassign an I/O channel only from an access mode equal to or more
privileged than the access mode from which the original channel
assignment was made.
When you deassign a channel, any outstanding I/O requests on the
channel are canceled. If a file is open on the specified channel, the
file is closed.
If a mailbox was associated with the device when the channel was
assigned, the link to the mailbox is cleared.
If the I/O channel was assigned for a network operation, the network
link is disconnected.
If the specified channel is the last channel assigned to a device that
has been marked for dismounting, the device is dismounted.
I/O channels assigned from user mode are automatically deassigned at
image exit.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Note that you should use the SHARE privilege with caution.
Applications, application protocols, and device drivers coded to expect
only exclusive access can encounter unexpected and errant behavior when
access to the device is unexpectedly shared. Unless the SHARE privilege
is explicitly supported by the application, the application protocol,
and the device driver, its use is generally discouraged. Refer to the
OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual for additional information.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_IVCHNLSEC
|
A process section file is currently accessed using the specified
channel number.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
On Alpha systems, you specified an invalid channel number that your
process never assigned.
|
|
SS$_NOICHAN
|
On Alpha systems, you specified a channel number outside of the set of
channel numbers available for your process.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
$DCLAST
Queues an asynchronous system trap (AST) for the calling access mode or
for a less privileged access mode.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$DCLAST astadr ,[astprm] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$dclast (void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64
astprm, unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
AST service routine to be executed. On Alpha systems, the
astadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of this
routine. On VAX systems, the astadr argument is the
32-bit address of this routine.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument. On Alpha sytems, the
astprm argument is a quadword value containing this
parameter. On VAX systems, the astprm argument is a
longword value containing this parameter.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode for which the AST is to be declared. The most privileged
access mode used is the access mode of the caller. The resultant mode
is the access mode for which the AST is declared.
Description
The Declare AST service queues an AST for the calling access mode or
for a less privileged access mode. For example, a routine executing in
supervisor mode can declare an AST for either supervisor or user mode.
The service does not validate the address of the AST service routine.
If you specify an illegal address (such as 0), an access violation
occurs when the AST service routine is given control.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
The $DCLAST service requires system dynamic memory and uses the AST
limit (ASTLM) quota of the process.
Related Services
$SETAST, $SETPRA
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit (ASTLM) quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
$DCLCMH
On Alpha systems, specifies the address of a routine to receive control
when a Change Mode to User or Change Mode to Supervisor instruction
trap occurs.
On VAX systems, specifies the address of a routine to receive control
when a Change Mode to User or Change Mode to Supervisor instruction
trap occurs, or when a compatibility mode fault occurs.
Format
SYS$DCLCMH addres ,[prvhnd] ,[type]
C Prototype
int sys$dclcmh (int (*addres)(__unknown_params), void *(*(prvhnd)),
char type);
Arguments
addres
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Routine to receive control when a change mode trap or a compatibility
mode fault occurs. The addres argument is the
exception handling code in the address space of the calling process.
If you specify the addres argument as 0, $DCLCMH
clears the previously declared handler.
prvhnd
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a previously declared handler. The prvhnd
argument is the address of a longword containing the address of the
previously declared handler.
type
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Handler type indicator. The type argument is a
longword value. The value 0 (the default) indicates that a change mode
handler is to be declared for the access mode at which the request is
issued; the value 1 specifies that a compatibility mode handler is to
be declared.
Description
On Alpha systems, the Declare Change Mode or Compatibility Mode Handler
service calls the change mode handler as a normal procedure (that is,
with a standard procedure call). The change mode handler must exit by
performing a standard procedure return to the change mode dispatcher.
Arguments (for example, the change mode code) passed between the
routine that issued the change mode instruction and the change mode
handler are strictly by agreement between the two procedures.
The following MACRO code example shows a subroutine calling Change Mode
to User. The example is written for Alpha users porting from VAX
systems.
CHG_MD: .CALL_ENTRY
CHMU
RET
|
Call this subroutine from any program that requires a Change Mode to
User instruction to be invoked.
On VAX systems, the $DCLCMH service specifies the address of a routine
to receive control when (1) a Change Mode to User or Change Mode to
Supervisor instruction trap occurs, or (2) a compatibility mode fault
occurs. A change mode handler provides users with a dispatching
mechanism similar to that used for system service calls. It allows a
routine that executes in supervisor mode to be called from user mode.
You declare the change mode handler from supervisor mode; then when the
process executing in user mode issues a Change Mode to Supervisor
instruction, the change mode handler receives control and executes in
supervisor mode.
The top longword of the stack contains the zero-extended change mode
code. The change mode handler must exit by removing the change mode
code from the stack and issuing an REI instruction.
The operating system uses compatibility mode handlers to bypass normal
condition handling procedures when an image executing in compatibility
mode causes a compatibility mode exception. Before transferring control
to the compatibility mode handler, the system saves the compatibility
exception code, the registers R0 through R6, and the PC and PSL in a
10-longword array starting at the location CTL$AL_CMCNTX. Before the
compatibility mode handler exits, it must restore the saved registers
R0 through R6, push the saved PC and PSL onto the stack, and exit by
issuing an REI instruction.
Required Access or Privileges
You can declare a change mode or compatibility mode handler only from
user or supervisor mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SETEXV, $UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The longword to receive the address of the previous change mode handler
cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
++SS$_IVSSRQ
|
The call to the service is invalid because it attempted to declare a
compatibility mode handler on Alpha systems.
|
++Alpha specific
$DCLEXH
Declares an exit handling routine that receives control when an image
exits.
Format
SYS$DCLEXH desblk
C Prototype
int sys$dclexh (void *desblk);
Argument
desblk
| OpenVMS usage: |
exit_handler_block |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Exit handler control block. The desblk argument is the
address of this control block. This control block, which describes the
exit handler, is depicted in the following diagram:

Description
The Declare Exit Handler service declares an exit handler routine that
receives control when an image exits. Image exit normally occurs when
the image currently executing in a process returns control to the
operating system. Image exit might also occur when you call the Exit
($EXIT) or Force Exit ($FORCEX) service. Process exit handlers are not
invoked when a process is deleted (such as using a $DELPRC call, for
example).
Exit handlers are described by exit control blocks. The operating
system maintains a separate list of these control blocks for user,
supervisor, and executive modes, and the $DCLEXH service adds the
description of an exit handler to the front of one of these lists. The
actual list to which the exit control block is added is determined by
the access mode of the $DCLEXH caller.
At image exit, the image context, the image stack pointers, and the
validity of any variables allocated on the stack are all indeterminate.
Accordingly, the exit handler control block and any variables accessed
by each exit handler must all be declared using non-volatile semantics.
Examples of such non-volatile declarations include the BASIC and Fortran
COMMON
construct, and the C
static
storage class.
The declared exit handlers are called from the least-privileged
processor mode to the most-privileged mode, and the exit handler(s) for
each processor mode are called in the reverse order from which they
were originally declared. Each exit handler is executed only once; it
must be explicitly redeclared by the application if it is to be
executed again.
The exit handler routine is called as a normal procedure with the
argument list specified in the third through nth longwords of
the exit control block. The first argument is always the address of a
user-allocated longword to receive the system status code indicating
the reason for the exit; the system always fills in the referenced
longword before calling the exit handler. Accordingly, the exit handler
routine receives a pointer to the status code as its first argument.
Application programmers can append zero or more additional
application-specific longword arguments for use within the exit handler
routine, with the total number of arguments controlled by the value
specified in the argument count field.
You can call this service only from user, supervisor, and executive
modes.
Following is a BASIC programming example for this service. To view a C
example, refer to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
program DCLEXH_EXAMPLE
option type = explicit
external long EXIT_HANDLER
external long function SYS$DCLEXH
external long function SYS$EXIT
external long function LIB$STOP
declare long RETURN_STATUS
record EXIT_DESCRIPTOR
long FORWARD_LINK
long HANDLER_ADDR
long ARG_COUNT
long CONDITION_VALUE_PTR
long RANDOM_EXAMPLE_VALUE
! borrow part of the record structure for data storage...
long CONDITION_VALUE
end record EXIT_DESCRIPTOR
! declare the exit handler block in non-volatile storage
common (SaveBlock) EXIT_DESCRIPTOR EXHBLK
PRINT
PRINT "DCLEXH_EXAMPLE initializing..."
PRINT
EXHBLK::FORWARD_LINK = 0%
EXHBLK::HANDLER_ADDR = loc(EXIT_HANDLER)
EXHBLK::ARG_COUNT = 2%
EXHBLK::CONDITION_VALUE_PTR = loc(EXHBLK::CONDITION_VALUE )
EXHBLK::RANDOM_EXAMPLE_VALUE = 303147%
PRINT "Calling SYS$DCLEXH..."
RETURN_STATUS = SYS$DCLEXH (EXHBLK by ref)
call LIB$STOP (RETURN_STATUS by value) if (RETURN_STATUS and 1%) = 0%
PRINT "SYS$DCLEXH called..."
PRINT "Calling SYS$EXIT..."
call SYS$EXIT(RETURN_STATUS by value)
end
function LONG EXIT_HANDLER(long CONDITION_VALUE, long RANDOM_VALUE by value)
! the exit handler gains control effectively after the main
! program module has exited. Direct access to (or otherwise
! sharing) variables used by the main routine requires explicit
! storage allocation control.
option type = explicit
print "EXIT_HANDLER invoked..."
print "CONDITION_VALUE: ", CONDITION_VALUE
print "RANDOM_VALUE: ", RANDOM_VALUE
PRINT
PRINT "DCLEXH_EXAMPLE done..."
PRINT
end function
|
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,
$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,
$WAKE
The Cancel Exit Handler ($CANEXH) service removes an exit control block
from the list.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The first longword of the exit control block cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_IVSSRQ
|
The call to the service is invalid because it was made from kernel mode.
|
|
SS$_NOHANDLER
|
The exit handler control block address was not specified or was
specified as 0.
|
$DECLARE_RM
Creates a new Resource Manager instance (RMI) in the calling process.
Format
SYS$DECLARE_RM [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
,event_handler ,[part_name] [,[rm_context] ,[acmode] ,[tm_log_id]
,[event_mask]]
C Prototype
int sys$declare_rm unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
*rm_id, void (*event_handler)(__unknown_params),...
;
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags, described in Table SYS-23. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-23 $DECLARE_RM Option Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
|
DDTM$M_VOLATILE
|
Set this flag for the new RMI to be volatile. With this flag set, the
DECdtm transaction manager will not log information about any RM
participants associated with the new RMI. Resource managers that never
perform recovery should set this flag.
If this flag is clear, the new RMI is not volatile. The DECdtm
transaction manager will log the following information about each RM
participant associated with the new RMI:
- The name of the RM participant.
- The identifier (TID) of the transaction in which it is
participating.
If this flag is clear and a recoverable failure occurs, such as a
system crash, the resource manager can use the $GETDTI system service
to query the transaction log to determine the outcome of the
transactions in which it was participating before the failure occurred.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if
SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The astadr argument is
the address of the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed
in the same access mode as that of the caller of the $DECLARE_RM
service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword in which the identifier (RM_ID) of the new RMI is returned.
This identifier is unique within the calling process at any time.
event_handler
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The new RMI's event handler. This routine is called to report an event
to the new RMI or one of its RM participants. The
event_handler argument is the address of the entry
mask of this routine. An event handler must be specified.
This routine is called as an AST delivered by the DECdtm transaction
manager.
The AST is executed in the access mode specified by the
acmode argument. The AST parameter is the address of a
DECdtm event report block that contains an event report.
The DECdtm transaction manager reports events to an RMI and the RM
participants associated with it using ASTs executed in the access mode
specified in the call to $DECLARE_RM that created that RMI.
The DECdtm transaction manager creates an event report block, and
passes its address to the AST routine in the parameter of the AST. Each
event report block contains:
- The identifier of the event report.
- A code that describes the event.
- The identifier (TID) of the transaction.
- The name of the RM participant or RMI.
- The context of the RM participant or RMI.
- Other data that depend on the type of the event.
Table SYS-24 describes the fields in an event report block, in
alphabetical order:
Table SYS-24 Fields in an Event Report Block
| Symbol |
Description |
|
DDTM$A_TID_PTR
|
Address of the identifier (TID) of the transaction.
|
|
DDTM$L_ABORT_REASON
|
Abort reason code (longword).
See the $ACK_EVENT service for a list of possible values. Present
only in abort event reports.
|
|
DDTM$L_EVENT_TYPE
|
A code that identifies the event (longword). The following table lists
the possible values:
| Symbol |
Event |
|
DDTM$K_ABORT
|
Abort
|
|
DDTM$K_COMMIT
|
Commit
|
|
DDTM$K_PREPARE
|
Prepare
|
|
DDTM$K_ONE_PHASE_COMMIT
|
One-phase commit
|
|
DDTM$K_STARTED_DEFAULT
|
Default transaction started
|
|
DDTM$K_STARTED_NONDEFAULT
|
Nondefault transaction started
|
|
|
DDTM$L_REPORT_ID
|
Event report identifier (unsigned longword).
|
|
DDTM$L_RM_CONTEXT
|
The context of the RM participant or RMI to which the event report is
being delivered (unsigned longword).
|
|
DDTM$Q_PART_NAME
|
The name of the RM participant or RMI to which the event report is
being delivered (descriptor).
|
|
DDTM$Q_TX_CLASS
|
The transaction class of the transaction (descriptor).
|
Each event report must be acknowledged by calling $ACK_EVENT,
specifying the identifier of the report. This acknowledgment need not
come from AST context.
The DECdtm transaction manager delivers only one event report at a time
to each RM participant. For example, if a prepare event report has been
delivered to an RM participant, and the transaction is aborted while
the RM participant is doing its prepare processing, then the DECdtm
transaction manager does not deliver an abort event report to that RM
participant until it has acknowledged the prepare event report by a
call to $ACK_EVENT. Note that the DECdtm transaction manager may
deliver multiple reports to an RMI.
After acknowledging the event report, the RMI or RM participant should
no longer access the event report block.
part_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the new RMI. This is:
- The default name of its RM participants, used when a call to
$JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that adds one of these RM participants to a
transaction does not specify the name of the new RM participant.
When an RM participant associated with the new RMI is added to a
transaction by a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that has a zero
part_name argument, then that RM participant inherits
its name from the RMI. The name of that RM participant is the same as
the name of the RMI.
- The string passed in the participant name field of Transaction
Started event reports delivered to the new RMI.
This string must be no longer than 32 characters.
If this argument is omitted, the name of the new RMI is the null string.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
rm_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
userarg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The context of the new RMI. This is:
- The default context of its RM participants, used when a call to
$JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that adds one of these RM participants to a
transaction does not specify the context of the new RM participant.
When an RM participant associated with the new RMI is added to a
transaction by a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that has a zero
rm_context argument, then that RM participant inherits
its context from the RMI. The context of that RM participant is the
same as the context of the RMI.
- The string passed in the context field of Transaction Started event
reports delivered to the new RMI.
If this argument is omitted, the context of the new RMI is 0.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The access mode of the new RMI. This is:
- The access mode at which the ASTs delivered to its event handler
are to be executed.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to call
$ACK_EVENT to acknowledge an event report delivered to the new RMI or
to its RM participants.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to
delete the new RMI by calling $FORGET_RM.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to call
$JOIN_RM to add a new RM participant associated with the new RMI.
- The most privileged access mode of new branches that this RMI is
interested in, if the event_mask argument requests
events of type Transaction Started.
The call to $START_TRANS or
$START_BRANCH that adds a new branch to a transaction specifies the
access mode of that transaction within this process. The DECdtm
transaction manager reports a Transaction Started event to the new RMI
only if the access mode of the transaction is the same as or less
privileged than the access mode of the new RMI.
For example, if the
access mode of the new RMI is supervisor, it will receive a Transaction
Started event when a branch of the calling process is added to a
transaction only if the access mode of that transaction is user or
supervisor.
The access mode of the new RMI is the least privileged of:
- The access mode of the caller.
- The access mode specified by the acmode argument.
If this argument is omitted, the access mode of the new RMI is the same
as the access mode of the caller.
tm_log_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
DECnet_uid |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The globally unique identifier of the transaction log for the local
node. This identifier is used during resource manager recovery to check
that the correct DECdtm transaction manager log is used. See $GETDTI
for more information.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
event_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Requests the types of event to be reported to the new RMI and to its RM
participants. The only type of event that can be reported to the new
RMI is a Transaction Started event (a default or non-default
transaction started event). The following types of event can be
reported to its RM participants:
- Abort events
- Commit events
- One-phase commit events
- Prepare events
The event_mask argument is a longword bit mask that is
the logical OR of each bit set, where each bit corresponds to an event.
The $DDTMDEF module defines a symbolic name for each flag bit.
Table SYS-25 describes the flags. All undefined bits must be 0.
If this argument is omitted, the following events are requested:
- Abort events
- Commit events
- One-phase commit events
- Prepare events
Table SYS-25 $DECLARE_RM Event Selection Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_EV_ABORT
|
Specifies that abort events are to be reported to the RM participants
associated with the new RMI. If this flag is set, when an abort event
occurs for a transaction, the DECdtm transaction manager delivers an
abort event report to each RM participant in the transaction that is
associated with the new RMI.
|
|
DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT
|
Specifies that commit events are to be reported to the RM participants
associated with the new RMI.
If this flag is set, when the DECdtm transaction manager decides
that the outcome of a transaction is commit, it delivers a commit event
report to each RM participant in the transaction that is associated
with the new RMI.
|
|
DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE
|
Specifies that prepare events are to be reported to the RM participants
associated with the new RMI.
If this flag is set, when the DECdtm transaction manager initiates
the commit protocol (in response to a call to $END_TRANS) to determine
the outcome of a transaction, it reports a prepare event to each RM
participant in the transaction that is associated with the new RMI.
The acknowledgment of a prepare event is a vote on the outcome of
the transaction. See $ACK_EVENT for more information.
|
|
DDTM$M_EV_TRANS_START
|
Specifies that events of type Transaction Started are to be reported to
the new RMI. Events of type Transaction Started are:
- Default transaction started events.
- Non-default transaction-started events.
If this flag is set, the DECdtm transaction manager will report one of
these events to the new RMI whenever a new branch in the calling
process is added to a transaction, provided that the access mode of the
new branch is not more privileged than the access mode of the new RMI.
The acknowledgment of that event report may add a new RM participant
associated with the new RMI to that transaction. See the description of
the
acmode argument for a discussion of access modes.
|
Description
The $DECLARE_RM system service creates a new Resource Manager instance
(RMI) in the calling process and returns its identifier.
Preconditions for successful completion of $DECLARE_RM include:
- The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
- The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
When $DECLARE_RM completes successfully, a new RMI is created in the
calling process, and its identifier is returned. The new RMI has no RM
participants. They are added to transactions by subsequent calls to
$JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT.
DECdtm events for the RMI and its RM participants, as specified by
event_mask, are reported to the specified event
handler.
If an RM does not specify DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE, its RM participants do not
have a vote on the outcome of their transactions. The DECdtm
transaction manager assumes that their votes are "yes".
If an RM does not specify DDTM$M_EV_ABORT or DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT, DECdtm
forgets the involvement of the RM participant associated with the RMI
in the transaction when the corresponding event occurs.
A one-phase commit event is reported to an RM participant if:
- Both the DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE and DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT flags are set.
- It is the only RM participant in the transaction.
- It is running in the process that started the transaction (the
process that called $START_TRANS).
The new RMI is deleted from the calling process:
- On termination of the calling process.
- On termination of the current image, if the access mode of the RMI
was user mode.
- On successful completion of a call to $FORGET_RM in the calling
process that passes its identifier.
There is also a wait form of the service, $DECLARE_RMW.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS,
$END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,
$START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Either the options flags were invalid or the event mask flags were
invalid.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_INVBUFLEN
|
The string passed in the
part_name argument was too long.
|
|
SS$_NOLOG
|
The local node did not have a transaction log.
|
|
SS$_TPDISABLED
|
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
|
$DECLARE_RMW
Creates a new Resource Manager instance (RMI) in the calling process.
$DECLARE_RMW always waits for the request to complete before returning
to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $DECLARE_RM.
Format
SYS$DECLARE_RMW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
,event_handler ,[part_name] [,[rm_context] ,[acmode] ,[tm_log_id]
,[event_mask]]
C Prototype
int sys$declare_rmw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
*rm_id, void (*event_handler)(__unknown_params),...);
$DELETE
The Delete service removes an existing record from a relative or
indexed file. You cannot use this service when processing sequential
files.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this service.
$DELETE_BUFOBJ (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, deletes a buffer object previously created by the
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 system service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$DELETE_BUFOBJ buffer_handle_64
C Prototype
int sys$delete_bufobj (struct _generic_64 *buffer_handle_64);
Arguments
buffer_handle_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
handle |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The buffer object to be deleted. The buffer_handle_64
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a 2-longword array previously
returned by a $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 call.
Description
The Delete Buffer Object system service deletes the buffer object
identified by the buffer_handle_64 argument. The
associated memory is made free to be paged, swapped, or deleted.
Buffer objects are also automatically deleted at image rundown.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
buffer_handle_64 argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
buffer_handle_64 argument is not a valid buffer handle.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The buffer object was created by a more privileged access mode than the
caller's access mode.
|
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK (Alpha Only)
Invalidates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock and deletes it.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment.
For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system
services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK handle
C Prototype
int sys$delete_galaxy_lock (unsigned __int64 lock_handle);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
galaxy lock handle |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The 64-bit lock handle that identifies the lock to be deleted. This
value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK.
Description
This service invalidates the OpenVMS Galaxy lock and deletes it. The
memory for the lock is not truly deleted; however, it is put on a free
list for later use.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL, SHMEM
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO,
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_BADLCKTBL
|
Galaxy lock table is corrupt.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKID
|
Invalid lock id.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKTBL
|
Invalid lock table.
|
|
SS$_LOCKINUSE
|
Invalid operation; lock is in use.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
Operation requires CMKRNL privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOSHMEN
|
Operation requires SHMEM privilege.
|
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE (Alpha Only)
Deletes an OpenVMS Galaxy locktable.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS
Galaxy system services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE handle
C Prototype
int sys$delete_galaxy_lock_table (unsigned int *lcktbl_handle);
Arguments
lcktbl_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
lock table handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The 32-bit lock table handle that identifies the table to be deleted.
This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE.
Description
This service deletes an OpenVMS Galaxy lock table. If there are no
longer any mappers of the locktable section, the table is deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL, SHMEM
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE,
$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKID
|
Invalid lock id.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKTBL
|
Invalid lock table.
|
|
SS$_NOCMKRNL
|
Operation requires CMKRNL privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOSHMEM
|
Operation requires SHMEM privilege.
|
$DELETE_INTRUSION
Searches for and deletes all records in the intrusion database matching
the caller's specifications.
Format
SYS$DELETE_INTRUSION user_criteria ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$delete_intrusion (void *user_criteria, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
user_criteria
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string or item_list_3 |
| type: |
character-coded text string or longword
(unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor or by
reference |
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:
The user_criteria argument is the description of
intruder or suspect. This argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to a buffer containing the user criteria to match
an intrusion record's user specification in the intrusion database.
The user_criteria argument is a character string of 1
to 1058 bytes containing characters to match the user specification on
records in the intrusion database.
A user specification is any combination of the suspect's or intruder's
source node name, source user name, source DECnet-Plus address, local
failed user name, or local terminal. The user specification for an
intrusion record is based on the input to the $SCAN_INTRUSION service
and the settings of the LGI system parameter. For more information,
refer to the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Wildcards are allowed for the user_criteria argument.
For example, if you specify an asterisk (*) for the
user_criteria argument, the service deletes all
records in the intrusion database.
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE:
The user_criteria argument is now the address of a
32-bit item list. If the item list is used, one item, the
CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL item, must be present in the item list. The
ITM$L_BUFADR should point to a buffer containing the specified user
criteria.
The following table lists the valid item descriptions for the
user_criteria argument:
| Item |
Description |
|
CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST
|
Address of a list of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which
intrusions are to be deleted.
|
|
CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL
|
Address of a buffer, 1-1058 bytes long, containing the intruder or
suspect.
|
If the CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is present, it is the address of a list
of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which intrusions are to be
deleted. If this item is absent, the service deletes the specified
intrusion records for all nodes in the cluster. Multiple
CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST items are permitted.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Functional specification for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an
option.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $CIADEF macro defines the
following valid names for the $DELETE_INTRUSION service:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CIA$M_IGNORE_RETURN
|
The service should not wait for the return status from the security
server. No return status from the server's function will be returned to
the caller.
|
|
CIA$M_ITEMLIST
|
If FALSE, the
user_criteria argument is a character string. If TRUE,
this argument is a 32-bit item list.
|
Description
The Delete Intrusion Records service deletes from the intrusion
database a set of records matching the criteria you specify in the
user_criteria argument. All records matching the
criteria you specify are deleted. You do not have to call the service
more than once to delete a set of records.
For example, if you specify an asterisk (*) for the
user_criteria argument, the service deletes all
records in the intrusion database with one call.
Required Access or Privileges
$DELETE_INTRUSION requires access to the intrusion database. You must
have SECURITY privilege to access the database.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SCAN_INTRUSION, $SHOW_INTRUSION
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
user_criteria argument cannot be read.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The length of the
user_criteria argument is out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid flag was specified in the
flags argument.
|
|
SS$_NOSECURITY
|
The caller does not have SECURITY privilege.
|
|
|
|
|
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from
the security server:
|
|
|
|
|
SECSRV$_CIADBEMPTY
|
No records in the intrusion database.
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHINTRUDER
|
No records matching the specified criteria were found in the intrusion
database.
|
|
SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
|
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again
later.
|
$DELETE_PROXY
Deletes an existing proxy or removes the default user or a local user
from an existing proxy in the proxy database.
Format
SYS$DELETE_PROXY rem_node ,rem_user ,[local_user] ,[flags]
D Prototype
int sys$delete_proxy (void *rem_node, void *rem_user, void *local_user,
unsigned int flags);
Arguments
rem_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote node name of the proxy to be deleted from or modified in the
proxy database. The rem_node argument is the address
of a character-string descriptor pointing to the remote node name
string.
A remote node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specific
characters, format, or case are required for a remote node name string.
All node names are converted to their DECnet for OpenVMS full name
unless the PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND flag is set with the
flags argument.
Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remote
node specification. If you specify wildcards for the
rem_node argument, the security server searches for an
exact match to the specified remote node first. If it does not find an
exact match, the server performs the requested operations on all of the
matching proxies in the proxy database.
rem_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote user name of the proxy to be deleted from or modified in the
proxy database. The rem_user argument is the address
of a character-string descriptor pointing to the user name string.
A remote user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and brackets ([ ]). Any
lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
The rem_user argument can be specified in user
identification code (UIC) format ([group, member]).
Brackets are allowed only if the remote user name string specifies a
UIC. Group and member are character-string representations of octal
numbers with no leading zeros.
Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remote
user specification. If you specify wildcards for the
rem_user argument, the server searches for an exact
match to the specified remote user first. If it does not find an exact
match, the server performs the requested operations on all of the
matching proxies in the proxy database.
local_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user name to delete from the proxy record specified by the
rem_node and rem_user arguments in
the proxy database. The local_user argument is the
address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the local user
name.
A local user name consists of 0 to 32 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_). If the
local_user argument is not specified or has a length
of 0, the server will delete the entire record or records specified by
the rem_node and rem_user arguments
from the proxy database.
If the local_user argument is specified, the server
will delete only the user name specified by the
local_user argument from the record specified by the
rem_node and rem_user arguments. The
local_user argument can specify either the proxy's
default user or a user name in the proxy's local users list.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Functional specification for the service and type of user the
local_user argument represents. The
flags argument is a longword bit mask wherein each bit
corresponds to an option.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $PRXDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND
|
The service should not convert the node name specified in the
rem_node argument to its corresponding DECnet full
name. If this flag is set, it is the caller's responsibility to ensure
that the fully expanded node name is passed into the service.
|
|
PRX$M_IGNORE_RETURN
|
The service should not wait for a return status from the security
server. No return status from the server's function will be returned to
the caller.
|
|
PRX$M_EXACT
|
The service should match exactly the remote node and remote user and
ignore wildcards.
|
Description
The Delete Proxy service deletes a proxy from, or modifies an existing
proxy in, the proxy database.
Required Access or Privileges
$DELETE_PROXY requires access to the proxy database. To achieve access,
the caller must have either SYSPRV privilege or a UIC group less than
or equal to the MAXSYSGRP system parameter.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_PROXY, $DISPLAY_PROXY, $VERIFY_PROXY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
rem_node,
rem_user,
local_user, or
flags argument cannot be read by the service.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The length of the
rem_node,
rem_user, or
local_user argument was out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid flag was specified in the
flags argument.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSPRV
|
The caller does not have access to the proxy database.
|
|
|
|
|
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from
the security server:
|
|
|
|
|
SECSRV$_BADNODENAMELEN
|
The node name length is out of range.
|
|
SECSRV$_BADREMUSERLEN
|
The remote user name length is out of range.
|
|
SECSRV$_INVALIDDELETE
|
You attempted to remove the last local user with no default user
remaining, or you tried to remove the last default user with no local
user remaining. You must have at least one local user or one default
user.
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHPROXY
|
The proxy specified by the
rem_node and
rem_user arguments does not exist in the proxy
database.
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHUSER
|
The specified local user does not exist in the proxy's local user list,
or is not the proxy's default user.
|
|
SECSRV$_PROXYNOTACTIVE
|
Proxy processing is currently stopped. Try the request again later.
|
|
SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
|
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again
later.
|
$DELETE_REGION_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, deletes a virtual region within the process's address
space, including all created virtual addresses within the region.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$DELETE_REGION_64 region_id_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64
,return_length_64
C Prototype
nt sys$delete_region_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int
acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);
Arguments
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to be deleted. The region ID
specified must be one returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service. You
cannot specify VA$C_P0, VA$C_P1, or VA$C_P2.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $DELETE_REGION_64. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
The caller can delete pages only if those pages are owned by an access
mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
Once all pages are deleted within the region, the region can be deleted
only if the region is owned by an access mode equal to or less
privileged than the access mode of the caller.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages that $DELETE_REGION_64
has successfully deleted. The return_va_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address of the first page
deleted. Virtual addresses are deleted from low address to high
address, regardless of the direction in which virtual addresses expand
for that region.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range that $DELETE_REGION_64 has
successfully deleted. The return_length_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the deleted virtual address
range in bytes.
Description
The Delete a Virtual Region service is a kernel mode service that can
be called from any mode. This service deletes the user-defined region
specified by the region_id_64 argument. You cannot
delete the program (P0), control (P1), or 64-bit program (P2) regions.
The Delete a Virtual Region service also deletes all created virtual
addresses within the specified region before deleting the region itself.
If a page within the region is owned by an access mode more privileged
than the access mode of the caller, the condition value SS$_PAGOWNVIO
is returned. The return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments contain the virtual address
range that was actually deleted by $DELETE_REGION_64. In this case, the
region is not deleted because there are still some pages mapped within
the region.
To delete a virtual region, the caller's access mode must be at least
as privileged as the access mode associated with the region. If the
caller is not privileged enough to delete the region, the condition
value SS$_REGOWNVIO is returned only if all pages were successfully
deleted from within the region.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned, no pages have
been deleted, and the region has not been deleted.
If an error other than SS$_ACCVIO occurs, the returned address and
returned length indicate the pages that were successfully deleted
before the error occurred. If no pages were deleted, the
return_va_64 argument contains the value --1 and a
value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by
the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELTVA_64,
$EXPREG_64, $GET_REGION_INFO, $MGBLSC_64, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Successful completion. All pages within the region have been deleted as
well as the region itself.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified. This condition value is returned if P0,
P1, or P2 space is specified because these regions cannot be deleted,
or if no region exists for the specified ID.
|
|
SS$_REGOWNVIO
|
The region is owned by a more privileged access mode than the access
mode of the caller. All pages within the region have been deleted;
however, the region has not been deleted.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page within the specified region is owned by a more privileged access
mode than the access mode of the caller.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
$DELLNM
Deletes all logical names with the specified name at the specified
access mode or outer access mode, or it deletes all the logical names
with the specified access mode or outer access mode in a specified
table.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$DELLNM tabnam ,[lognam] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$dellnm (void *tabnam, void *lognam, unsigned char *acmode);
Arguments
tabnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of a logical name table or a list of tables to be searched for the
logical name to be deleted. The tabnam argument is the
32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a descriptor that points to the table name. This argument
is required.
If tabnam is not the name of a logical name table, it
is assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively until
either the name of a logical name table is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed.
If tabnam translates to the name of a list of tables,
$DELLNM does the following:
- If you specify the lognam argument, $DELLNM
searches (in order) each table in the list until it finds the first
table that contains the specified logical name. If the logical name is
at the specified access mode, $DELLNM then deletes occurrences of the
logical name at the specified access mode and at outer access modes
within the table.
- If you do not specify the lognam argument, $DELLNM
deletes all of the logical names at the specified access mode or at
outer access modes from the first table in the list whose access mode
is equal to or less privileged than the caller's access mode.
lognam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Logical name to be deleted. The lognam argument is the
32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a descriptor that points to the logical name string.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Access mode to be used in the delete operation. The
acmode argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a byte containing
this access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbolic names for the four
access modes.
You determine the access mode actually used in the delete operation by
maximizing the access mode of the caller with the access mode
specified by the acmode argument; that is, the less
privileged of the two is used.
However, if you have SYSNAM privilege, the delete operation is executed
at the specified access mode regardless of the caller's access mode.
If you omit this argument or specify it as 0, the access mode of the
caller is used in the delete operation. The access mode used in the
delete operation determines which tables are used and which names are
deleted.
Description
The Delete Logical Name service deletes all logical names with the
specified name at the specified access mode or outer access mode, or it
deletes all the logical names with the specified access mode or outer
access mode in a specified table. If any logical names being deleted
are also the names of logical name tables, then all of the logical
names contained within those tables and all of their subtables are also
deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following access or rights privileges to use $DELLNM:
- Write and delete access to the logical name table to delete a
logical name
- Write access to the directory table that contains the table name,
or SYSPRV privilege, to delete a shareable logical name table
- SYSNAM privilege to delete a logical name or table at an inner
access mode
- GRPNAM or SYSPRV privilege to delete a logical name from a group
table
- SYSNAM or SYSPRV privilege to delete a logical name from a system
table
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRELNM, $CRELNT, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table
name was not specified.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There is insufficient dynamic memory to build a message describing the
deletion of a clusterwide name.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The
lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not
in the required range of 1 through 255 characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGTAB
|
The
tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGNAM
|
The specified logical name table does not exist, or a logical name with
an access mode equal to or less privileged than the caller's access
mode does not exist in the logical name table.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGTAB
|
The specified logical name table does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller lacks the necessary privilege to delete the logical name.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable
depth (10 translations).
|
$DELMBX
Marks a permanent mailbox for deletion.
Format
SYS$DELMBX chan
C Prototype
int sys$delmbx (unsigned short int chan);
Argument
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the channel assigned to the mailbox that is to be deleted.
The chan argument is a word containing this number.
Description
The Delete Mailbox service marks a permanent mailbox for deletion. The
actual deletion of the mailbox and of its associated logical name
assignment occurs when no more I/O channels are assigned to the mailbox.
You can delete a mailbox only from an access mode equal to or more
privileged than the access mode from which the mailbox channel was
assigned. Temporary mailboxes are automatically deleted when their
reference count goes to 0.
The $DELMBX service does not deassign the channel assigned by the
caller, if any. The caller must deassign the channel with the Deassign
I/O Channel ($DASSGN) service.
Required Access or Privileges
You need PRMMBX privilege to delete a permanent mailbox.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_DEVNOTMBX
|
The specified channel is not assigned to a mailbox.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel is not assigned to a device; the process does not
have the privilege to delete a permanent mailbox or a mailbox in memory
shared by multiple processors; or the access mode of the caller is less
privileged than the access mode from which the channel was assigned.
|
$DELPRC
Allows a process to delete itself or another process.
Format
SYS$DELPRC [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$delprc (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be deleted. The
pidadr argument is the address of a longword that
contains the PID. The pidadr argument can refer to a
process running on the local node or a process running on another node
in the OpenVMS Cluster system.
You must specify the pidadr argument to delete
processes in other UIC groups.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process to be deleted. The prcnam
is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process
name string. A process running on the local node can be identified with
a 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on a particular node
on a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node
name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up
to 23 characters.
You use the prcnam argument to delete only processes
in the same UIC group as the calling process, because process names are
unique to UIC groups, and the operating system uses the UIC group
number of the calling process to interpret the process name specified
by the prcnam argument.
You must use the pidadr argument to delete processes
in other groups.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The flags argument can be used to control whether exit
handlers are called by $DELPRC. If the flags argument
is not specified or is specified with a zero, the system parameter
DELPRC_EXIT controls what exit handlers, if any, are called by $DELPRC.
The $DELPRCSYMDEF macro defines a symbolic name for EXIT and NOEXIT.
The EXIT flag should be or'd with the access mode defined by the
$PSLDEF macro for the initial exit handler.
The following table describes each flag:
| Flag |
Description |
|
DELPRC$M_EXIT
|
When set, exit handlers as specified by DELPRC$M_MODE are called. This
flag is ignored for a hard suspended process.
|
|
DELPRC$M_MODE
|
2 bit field: values psl$c_kernel, psl$c_exec, psl$c_super, psl$c_user
(from the $PSLDEF macro)
|
|
DELPRC$M_NOEXIT
|
Set to disable any exit handler execution
|
Note
Deleting the current process:
When $DELPRC is used to delete the current process, execution cannot
continue in the mode from which $DELPRC was called. The first exit
handlers that are called will be in the next more privileged mode
relative to the mode from which $DELPRC was called (subject to options
defined). For example:
- $DELPRC called from user mode can call supervisor mode exit
handlers.
- $DELPRC called from exec mode can only execute kernel mode exit
handlers.
- $DELPRC called from kernel mode cannot call exit handlers.
|
Description
The Delete Process service allows a process to delete itself or another
process. If you specify neither the pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, $DELPRC deletes the calling process;
control is not returned. If the longword at address
pidadr is 0, the PID of the target process is
returned. This system service requires system dynamic memory.
When you delete a process or subprocess, a termination message is sent
to its creating process, provided the mailbox to receive the message
still exists and the creating process has access to the mailbox. The
termination message is sent before the final rundown is initiated;
thus, the creating process might receive the message before the process
deletion is complete.
Due to the complexity of the required rundown operations, a significant
time interval occurs between a delete request and the actual deletion
of the process; however, the $DELPRC service returns to the caller
immediately after initiating the rundown operation.
If you issue subsequent delete requests for a process currently being
deleted, the requests return immediately with a successful completion
status.
Process exit handlers are not invoked when a process is deleted. For
details on exit handlers, see the $DCLEXH service.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following privileges to use $DELPRC:
- GROUP privilege to delete processes in the same group that do not
have the same UIC
- WORLD privilege to delete any process in the system
Required Quota
None. Deductible resource quotas granted to subprocesses are returned
to the creating process when the subprocesses are deleted.
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,
$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,
$WAKE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the operation.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have the privilege to delete the specified process.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
|





