|
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$GETQUIW
Returns information about queues and jobs initiated from those queues.
The $SNDJBC service is the major interface to the Job Controller, which
is the queue and accounting manager. For a discussion of the different
types of job and queue, see the Description section of $SNDJBC.
The $GETQUIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller with the requested information. For asynchronous completion,
use the Get Queue Information ($GETQUI) service; $GETQUI returns to the
caller after queuing the information request, without waiting for the
information to be returned.
In all other respects, $GETQUIW is identical to $GETQUI. For more
information about $GETQUIW, refer to the description of $GETQUI in this
manual.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$GETQUIW [efn] ,func [,context] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getquiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned
int *context, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$GETRMI
Returns system performance information about the local system.
Format
SYS$GETRMI [efn] [,nullarg] [,nullarg] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getrmi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int nullarg, unsigned int
nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of event flag to be set when the $GETRMI request completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $GETRMI uses only the low order byte.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information is to be returned about the
local node. The itmlst argument is the address of a
list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. The list of descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.
The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETRMI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the
item code field. If the buffer length is too small, $GETRMI truncates
the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied code specifying the item of
information that $GETRMI is to return. The RMIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the item codes
section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a buffer in which
$GETRMI returns the requested information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which
$GETRMI writes the length in bytes of the information returned.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O
status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETRMI completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument.
Item Codes
RMI$_ACCESS
Returns the count of file name lookup operations in file directories.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ACCLCK
Returns the systemwide count of access locks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ALLOC
Returns the number of QIO requests that caused allocation of disk space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ARRLOCPK
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of arriving local DECnet
packets.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ARRTRAPK
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of arriving transit DECnet
packets.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BADFLTS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of bad-list faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BLKIN
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of blocking ASTs queued that
originated on a remote system and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BLKLOC
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of blocking ASTs queued that
originated and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BLKOUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of blocking ASTs queued that
originated on the local system and were processed on a remote system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BLKAST
Returns the number of blocking ASTs.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFIO
Returns the number of buffered I/Os.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAG
Returns the number of buffer object physical pages currently allocated.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGPEAK
Returns the maximum number of buffer object physical pages currently
allocated.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGS01
Returns the number of buffer object pages currently allocated in S0 and
S1 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGS2
Returns the number of buffer object physical pages currently allocated
in S2 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGMAXS01
Returns the available number of buffer object pages in S0 and S1 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGMAXS2
Returns the available number of buffer object pages in S2 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGPEAKS01
Returns the maximum number of buffer object pages currently allocated
in S0 and S1 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPAGPEAKS2
Returns the maximum number of buffer object pages currently allocated
in S2 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPGLTMAXS01
Returns the available number of buffer object pagelets in S0 and S1
space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFOBJPGLTMAXS2
Returns the available number of buffer object pagelets in S2 space.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CEF
Returns the number of processes in the common event flag wait state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_COLPG
Returns the number of processes in the collided page wait state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_COM
Returns the number of processes in the computable state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_COMO
Returns the number of outswapped processes in the computable state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUEXEC
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in executive mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUID
Returns the primary CPU ID.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUIDLE
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in idle mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUINTSTK
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in processing interrupts.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUKERNEL
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in kernel mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUMPSYNCH
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by the
primary CPU in synchronization mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUSUPER
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in supervisor mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CPUUSER
Returns the amount of time, in 10-millisecond units, spent by all CPUs
in user mode.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_CUR
Returns the number of currently-executing processes.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSBYTESIN
Returns the number of clusterwide process services (CWPS) message bytes
received by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSBYTESOUT
Returns the number of CWPS message bytes sent by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSJPISIN
Returns the number of CWPS $GETJPI requests received by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSJPISOUT
Returns the number of CWPS $GETJPI requests sent by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSMSGSIN
Returns the number of CWPS messages received by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSMSGSOUT
Returns the number of CWPS messages sent by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSPCNTRLIN
Returns the number of CWPS PCNTRL requests received by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSPCNTRLOUT
Returns the number of CWPS PCNTRL requests sent by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSRSRCIN
Returns the number of CWPS resource-fail messages received by the
system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_CWPSRSRCOUT
Returns the number of CWPS resource-fail messages sent by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_ABORTS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions aborted
(planned and unplanned).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_ADDS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transaction branches added
on the local node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BAD_LINKS
Returns the total number of bad message links received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BAD_PARTS
Returns the number of invalid part IDs found.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BAD_TYPECODE
Returns the total number of bad message type codes received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BRANCHS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transaction branches
started on the local node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS1
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of less than 1 second.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS2
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of 1 to 2 (1.99) seconds.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS3
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of 2 to 3 (2.99) seconds.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS4
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of 3 to 4 (3.99) seconds.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS5
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of 4 to 5 (4.99) seconds.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_BUCKETS6
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions with a
duration of at least 5 seconds.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_DECLARES
Returns the total number of $DECLARE_RMs.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_DISC_COMP
Returns the number of disconnected complete events.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_ENDS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions ended.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_FOR_UNLINKS
Returns the number of forced unlinks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_FORGETS
Returns the total number of $FORGET_RMs.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_JOINS
Returns the total number of $JOIN_RMs.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_LOG_COMMITS
Returns the total number of commit records written.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_LOG_FORGETS
Returns the total number of forget records written.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_LOG_PREPARES
Returns the total number of prepare records written.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_ONE_PHASE
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 1-phase commit events
initiated.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_PREPARES
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions that have been
prepared.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_SEQNO
Returns the total number of XCBs created.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_STARTS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transactions successfully
started.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_ACKRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit ACK messages
received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_ACKSNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit ACK messages
sent.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_CANRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit cancel
messages received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_CANSNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit cancel
messages sent.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_COMMITS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit events
initiated.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_RDYRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit ready
messages received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_RDYSNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit ready
messages sent.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_REQRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit requests
received.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_TWOPHASE_REQSNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of 2-phase commit requests
sent.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_VOL_UNLINKS
Returns the number of voluntary unlinks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_WRITES_FORKED
Returns the total number of forked writes.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DDTM_WRITES_STARTED
Returns the total number of writes started.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEPLOCPK
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of departing local DECnet
packets.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEQ
Returns the number of DEQ operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEQIN
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of unlock (dequeue) lock
requests that originated on a remote system and were processed on the
local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEQLOC
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of unlock (dequeue) requests
that originated and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEQOUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of unlock (dequeue) requests
that originated on the local system and were processed on a remote
system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRDATA_HIT
Returns the systemwide count of directory data cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRDATA_MISS
Returns the systemwide count of directory data cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRFCB_HIT
Returns the systemwide count of directory FCB cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRFCB_MISS
Returns the systemwide count of directory FCB cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRIN
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of directory operations
serviced by the local system that originated on remote systems.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIROUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of directory operations that
originated on the local system and were serviced by remote systems.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRIO
Returns the number of direct I/Os.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCK_INCMPLT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of incomplete deadlock
searches.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKFND
Returns the number of deadlocks found.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKMSGS_IN
Returns the systemwide count of incoming deadlock detection messages.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKMSGS_OUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of outgoing deadlock detection
messages.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKSRCH
Returns the number of deadlock searches.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DZROFLTS
Returns the number of demand zero page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQCVT
Returns the number of ENQ conversion operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQCVTIN
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock conversion requests
that originated on a remote system and were processed on the local
system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQCVTLOC
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock conversion requests
that originated and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQCVTOUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock conversion requests
that originated on the local system and were processed on a remote
system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNEW
Returns the number of new ENQ operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNEWIN
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of new lock requests that
originated on a remote system and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNEWLOC
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of new lock requests that
originated and were processed on the local system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNEWOUT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of new lock requests that
originated on the local system and were processed on a remote system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNOTQD
Returns the number of ENQ operations not queued.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQWAIT
Returns the number of ENQ operations forced to wait.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_EXEFAULTS
Returns the number of execute page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_EXTHIT
Returns the systemwide count of extent cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_EXTMISS
Returns the systemwide count of extent cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FAULTS
Returns the number of page faults since last system initialization.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCACHE
Returns the total number of cache hits by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCALLS
Returns the total number of calls to the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCPU
Returns the total number of CPU tics used by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCREATE
Returns the number of new files created since the system was booted.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPERASE
Returns the number of erase I/O operations issued.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPFAULT
Returns the number of FCP page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPHIT
Returns the total number of file I/O transfers for which no disk access
was required.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPREAD
Returns the total number of disk reads by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPSPLIT
Returns the number of split transfers performed by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPTURN
Returns the number of file-map window misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPWRITE
Returns the total number of disk writes by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FIDHIT
Returns the systemwide count of File ID cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FIDMISS
Returns the systemwide count of File ID cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FILHDR_HIT
Returns the systemwide count of file header cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FILHDR_MISS
Returns the systemwide count of file header cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FPG
Returns the number of processes in the free page wait state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FREFLTS
Returns the number of page faults from the free list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FRLIST
Returns the number of pages on the free list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_CURMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of global pages currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_CURMAP_GRP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of group global pages currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_CURMAP_GRPWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable group global pages currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_CURMAP_SYS - Alpha Only
Returns the count of system global pages currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_CURMAP_SYSWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable system global pages currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBP_MAXMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the maximum count of global pages simultaneously mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_CURMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of global sections currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_CURMAP_GRP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of group global sections currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_CURMAP_GRPWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable group global sections currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_CURMAP_SYS - Alpha Only
Returns the count of system global sections currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_CURMAP_SYSWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable system global sections currently mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_MAXMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the maximum count of global sections simultaneously mapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GBS_NOREF - Alpha Only
Returns the current count of global sections not mapped to a process
(reference count is 0).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GVALFLTS
Returns the number of global valid page faults.
Because this number is a longword the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_HDRINSWAPS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of process header inswap
operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_HDROUTSWAPS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of process header outswap
operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_HIB
Returns the number of processes in the hibernate state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_HIBO
Returns the number of outswapped processes in the hibernate state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_IOPAGCNT
Returns the systemwide count of pages in transit to disk from the
modified page list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ISWPCNT
Returns the number of process inswaps.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ISWPCNTPG
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of pages inswapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_CPU
Returns the ID of the CPU on which the lock manager process runs.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_PID
Returns the PID of the lock manager process.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_REQCNT
Returns the accumulated count of requests handled by the lock manager.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_REQTIME
Returns the accumulated time spent by the lock manager servicing
requests.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_SPINCNT
Returns the accumulated count of times the lock manager entered a spin
loop.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_LCKMGR_SPINTIME
Returns the accumulated spin time, in cycles, of the lock manager.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_LEF
Returns the number of processes in the local event flag wait state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LEFO
Returns the number of outswapped processes in the local event flag wait
state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LOCK_MAX
Returns the lock ID table length.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LOGNAM
Returns the number of logical name translations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_ALLOC2
Returns the number of allocations from other than the first page of the
lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_ALLOCF
Returns the number of failed allocations from the lock manager's pool
zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_EMPTY
Returns the number of empty pages in the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_EXPCNT
Returns the accumulated number of expansions of the lock manager's pool
zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_HITS
Returns the number of hits for the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_MAXPAG
Returns the maximum number of pages in the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_MISSES
Returns the number of misses for the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_PAGCNT
Returns the number of pages currently in the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LPZ_PAKSIZ
Returns the packet size for the lock manager's pool zone.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MBREADS
Returns the number of mailbox reads.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MBWRITES
Returns the number of mailbox writes.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MCHKERRS
Returns the accumulated count of machine checks since the system was
booted.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MEMERRS
Returns the accumulated count of memory errors since the system was
booted.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MODLIST
Returns the number of pages on the modified page list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MSCP_EVERYTHING
Returns all the performance data items in the following order:
|
MSCP_BUFAVL
|
Current number of free MSCP buffers
|
|
MSCP_BUFSMALL
|
Smallest MSCP buffer size allowed
|
|
MSCP_BUFWAITCUR
|
Number of requests currently queued waiting for MSCP buffer memory
|
|
MSCP_BUFWAITPEAK
|
Maximum number of requests simultaneously queued waiting for MSCP buffer
|
|
MSCP_DSKSRV
|
Number of MSCP served disks
|
|
MSCP_HSTSRV
|
Number of MSCP served hosts
|
|
MSCP_LB_FAILCNT
|
MSCP server's count of failed load-balancing requests
|
|
MSCP_LB_INITCNT
|
MSCP server's count of load-balancing requests sent
|
|
MSCP_LB_LMLOAD1
|
MSCP server's previous interval's load 1 value
|
|
MSCP_LB_LMLOAD2
|
MSCP server's previous interval's load 2 value
|
|
MSCP_LB_LMLOAD3
|
MSCP server's previous interval's load 3 value
|
|
MSCP_LB_LMLOAD4
|
MSCP server's previous interval's load 4 value
|
|
MSCP_LB_LOAD
|
MSCP server's target load for load-balancing requests
|
|
MSCP_LB_LOAD_AVAIL
|
MSCP server's current load available value
|
|
MSCP_LB_LOAD_CAP
|
MSCP server's load capacity value
|
|
MSCP_LB_MONINT
|
MSCP server's load-monitoring interval size
|
|
MSCP_LB_MONTIME
|
The time that the last load-balancing monitor pass was made
|
|
MSCP_LB_REQCNT
|
MSCP server's count of load-balancing requests received from other
servers
|
|
MSCP_LB_REQTIME
|
The time that the last load-balancing request was sent
|
|
MSCP_LB_RESPCNT
|
MSCP server's count of load-balancing requests to which it responded
|
|
MSCP_LB_RESP
|
MSCP server's load available from another server
|
|
MSCP_OPCOUNT
|
Count of I/O transfer requests by remote processors
|
|
MSCP_VCFAIL
|
Count of virtual cache failures on MSCP-served requests
|
|
MSCP_READ
|
Count of Read I/O transfer requests by remote processors
|
|
MSCP_WRITE
|
Count of Write I/O transfer requests by remote processors
|
|
MSCP_FRAGMENT
|
Count of extra fragments issued by the MSCP server
|
|
MSCP_SPLITXFER
|
Count of fragmented requests issued by the MSCP server
|
|
MSCP_BUFWAIT
|
Count of requests that had to wait for MSCP buffer memory
|
|
MSCP_SIZE1
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 1 block
|
|
MSCP_SIZE2
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 2-3 blocks
|
|
MSCP_SIZE3
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 4-7 blocks
|
|
MSCP_SIZE4
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 8-15 blocks
|
|
MSCP_SIZE5
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 16-31 blocks
|
|
MSCP_SIZE6
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 32-63 blocks
|
|
MSCP_SIZE7
|
Count of MSCP-served I/O requests with a length of 64 or more blocks
|
Because this an array of 35 longwords, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 times 35 (bytes).
RMI$_MWAIT
Returns the number of processes in the miscellaneous resource wait
state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NP_POOL_ALLOC
Returns the accumulated count of nonpaged pool allocation requests.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NP_POOL_ALLOCF
Returns the accumulated count of unsuccessful nonpaged pool allocation
requests.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NP_POOL_EXP
Returns the accumulated count of successful expansions of nonpaged pool.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NP_POOL_EXPF
Returns the accumulated count of unsuccessful attempts to expand
nonpaged pool.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NUMLOCKS
Returns the total number of locks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NUMRES
Returns the total number of resources.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_OPENS
Returns the systemwide count of files opened.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_OSWPCNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of process outswap operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_OSWPCNTPG
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of pages outswapped.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PFW
Returns the number of processes in the page fault wait state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PG_POOL_ALLOC
Returns the accumulated count of paged pool allocation requests.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PG_POOL_ALLOCF
Returns the accumulated count of unsuccessful paged pool allocation
requests.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PG_POOL_EXPF
Returns the accumulated count of paged pool failures.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PREADIO
Returns physical page read I/Os.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PREADS
Returns the number of pages read.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCBALSETCNT
Returns the number of processes in the balance set.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCBATCNT
Returns the number of batch processes known to the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCCNTMAX
Returns the maximum number of concurrent processes seen by the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCINTCNT
Returns the number of interactive processes known to the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCLOADCNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of process context load
operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCNETCNT
Returns the number of network processes known to the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCS
Returns the number of processes currently known to the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PROCSWITCHCNT
Returns the number of switches from the currently-executing process.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PWRITES
Returns the number of pages written.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PWRITIO
Returns physical page write I/Os.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_QUOHIT
Returns the systemwide count of quota cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_QUOMISS
Returns the systemwide count of quota cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RCVBUFFL
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of DECnet receiver buffer
failures.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RDFAULTS
Returns the number of fault-on-read page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_ACQUIRE
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock trees moved to this
node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_BETTER
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock trees moved from this
node to a cluster node with a higher value for the system parameter
LOCKDIRWT.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_MORE_ACT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock trees moved from this
node due to higher locking activity on another node in the cluster.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_MSGRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster messages received
by this node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_MSGSENT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster messages sent from
this node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_NOQUOTA
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster operations that
failed due to a lack of quota.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_NOTAKER
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster operations that
were proposed and declined.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_OPCNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster operations that
have been completed.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_RBLDMSGRCV
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster rebuild messages
received by this node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_RBLDMSGSENT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of remaster rebuild messages
sent from this node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_SINGLE
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock trees moved from this
node to another cluster node because that node is the only one with
locks remaining on the tree.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_RML_UNLOAD
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of lock trees moved from this
node.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMP_CURMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of global pages currently mapped for Galaxy shared
memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMP_CURMAP_GRP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of group global pages currently mapped for Galaxy
shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMP_CURMAP_GRPWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable group global pages currently mapped for
Galaxy shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMP_CURMAP_SYS - Alpha Only
Returns the count of system global pages currently mapped for Galaxy
shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMP_CURMAP_SYSWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable system global pages currently mapped for
Galaxy shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_CURMAP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of global sections currently mapped for Galaxy shared
memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_CURMAP_GRP - Alpha Only
Returns the count of group global sections currently mapped for Galaxy
shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_CURMAP_GRPWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable group global sections currently mapped
for Galaxy shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_CURMAP_SYS - Alpha Only
Returns the count of system global sections currently mapped for Galaxy
shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_CURMAP_SYSWRT - Alpha Only
Returns the count of writable system global sections currently mapped
for Galaxy shared memory.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SMS_NOREF - Alpha Only
Returns the current count of global sections for Galaxy shared memory
that are not mapped to a process (reference count is 0).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_STORAGMAP_HIT
Returns the systemwide count of storage bitmap cache hits.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_STORAGMAP_MISS
Returns the systemwide count of storage bitmap cache misses.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SUSP
Returns the number of processes in the suspended state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SUSPO
Returns the number of outswapped processes in the suspended state.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SYNCHLCK
Returns the systemwide count of directory- or file-synch locks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SYNCHWAIT
Returns the systemwide count of times the XQP waited for a directory-
or file-synch lock.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SYSFAULTS
Returns the number of system page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TMSCP_EVERYTHING
Returns all the performance data items in the following order:
|
TMSCP_BUFWAIT
|
Count of requests that had to wait for TMSCP buffer memory
|
|
TMSCP_HSTSRV
|
Number of TMSCP served hosts
|
|
TMSCP_TAPSRV
|
Number of TMSCP served tapes
|
|
TMSCP_OPCOUNT
|
Total operations count
|
|
TMSCP_ABORTCNT
|
Total abort operations count
|
|
TMSCP_BUFAVAIL
|
Free TMSCP pool bytes
|
|
TMSCP_ONLINCNT
|
Count of online tapes
|
|
TMSCP_ACCESSCNT
|
Total access count
|
|
TMSCP_FLUSHCNT
|
Total flush count
|
|
TMSCP_RDCOUNT
|
Count of read I/O requests by remote processors
|
|
TMSCP_WRCOUNT
|
Count of write I/O requests by remote processors
|
|
TMSCP_VCFAIL
|
Number of virtual cache failures on TMSCP served requests in location 23
|
|
TMSCP_FRAGMENT
|
Extra fragments
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE1
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 1 block
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE2
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 2-3 blocks
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE3
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 4-7 blocks
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE4
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 8-15 blocks
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE5
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 16-31 blocks
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE6
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 32-63 blocks
|
|
TMSCP_SIZE7
|
Count of TMSCP served I/O requests with a length of 64 or more blocks
|
Because this is an array of 20 longwords, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 4 times 20 (bytes).
RMI$_TQESYSUB
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of timer requests made by the
OpenVMS operating system.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_TQETOTAL
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of timer requests.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_TQEUSRTIMR
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of timer requests made by
application programs through the SYS$SETIMR system service.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_TQEUSRWAKE
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of timer requests made by
application programs through the SYS$SCHDWK system service.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
RMI$_TRANSFLTS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of transition (release pending
or read-in-progress) faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TRCNGLOS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of DECnet packets lost due to
transit congestion.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TTREADCNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of characters read from
terminals.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TTREADS
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of reads from terminals.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TTWRITECNT
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of characters written to
terminals.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_TTWRITES
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of writes to terminals.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_USERPAGES
Returns the number of pages available for use by applications.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_VCPUTICKS - VAX Only
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of virtual balance slot clock
ticks (10-millisecond units).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_VMSPAGES
Returns the number of pages actually allocated to OpenVMS.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_VOLLCK
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of volume-synch locks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_VOLWAIT
Returns the number of times the XQP entered a wait state due to volume
lock contention.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_VRBS_TRAN - VAX Only
Returns the accumulated systemwide count of faults from virtual balance
slots to real balance slots.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_WRTFAULTS
Returns the number of fault-on-write page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_WRTINPROG
Returns the number of page faults from a write in progress.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_XQPCACHEWAIT
Returns the systemwide count of times the XQP waited for free space in
a cache.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Description
The Get Resource Monitor Information service returns performance
information about the local system.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
This service uses the process's AST limit quota (ASTLM).
Related Services
None.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The caller cannot read the item list, cannot write to the buffer
specified by the buffer address field in the item descriptor, or cannot
write to the return length address field in an item descriptor.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
|
$GETSYI
Returns information about the local system or about other systems in an
OpenVMS Cluster system. The $GETSYI service completes asynchronously;
for synchronous completion, use the Get Systemwide Information and Wait
($GETSYIW) service.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETSYI [efn] ,[csidadr] ,[nodename] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getsyi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *csidadr, void
*nodename, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64 astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the $GETSYI request completes.
The efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $GETSYI uses only the low-order byte.
Upon request initiation, $GETSYI clears the specified event flag (or
event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the
request completes, the specified event flag (or event flag 0) is set.
csidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
OpenVMS Cluster system identification of the node about which $GETSYI
is to return information. The csidadr argument is the
32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a longword containing this identification value.
The cluster-connection software assigns the OpenVMS Cluster system
identification of a node. You can obtain this information by using the
DCL command SHOW CLUSTER. The value of the cluster system
identification for a node is not permanent; a new value is assigned to
a node whenever it joins or rejoins the cluster.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the
nodename argument. If you specify
csidadr, you need not specify
nodename, and vice versa. If you specify both, they
must identify the same node. If you specify neither argument, $GETSYI
returns information about the local node; however, for wildcard
operations, you must use the csidadr argument.
If you specify csidadr as --1, $GETSYI assumes a
wildcard operation and returns the requested information for each node
in the cluster, one node per call. In this case, the program should
test for the condition value SS$_NOMORENODE after each call to $GETSYI
and should stop calling $GETSYI when SS$_NOMORENODE is returned.
nodename
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the node about which $GETSYI is to return information. The
nodename argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
The node name string must contain from 1 to 15 characters and must
correspond exactly to the node name; no trailing blanks or
abbreviations are permitted.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the
csidadr argument. See the description of
csidadr.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for
64-bit |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Item list specifying which information is to be returned about the node
or nodes. The itmlst argument is the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a
list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword
of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0.
All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or
64-bit.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item
descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length field is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of the buffer
into which $GETSYI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of a word in
which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually
returned.
|
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
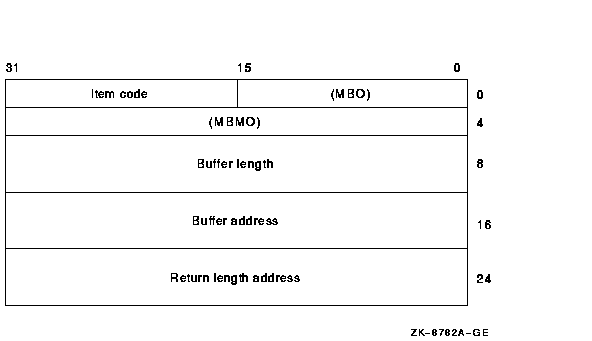
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
MBO
|
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
MBMO
|
The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Buffer length
|
A quadword containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of the buffer
into which $GETSYI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of a word in
which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually
returned.
|
See the Item Codes section for a description of the various $GETSYI
item codes.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of the quadword I/O
status block.
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETSYI sets the
quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a
condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword
is reserved for future use.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $GETSYI service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$GETSYI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETSYI completes. The
astadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of the $GETSYI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is the longword parameter.
Item Codes
SYI$_ACTIVE_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed
bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with
that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's active set - those
currently participating in the OpenVMS SMP scheduling activities.
SYI$_ACTIVECPU_CNT
Returns a count of the CPUs actively participating in the current boot
of the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ARCHFLAG
Returns the architecture flags for the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ARCH_NAME
Returns, as a character string, the name of the CPU architecture on
which the process is executing. Currently, either of two strings is
returned: "Alpha" for Alpha or "VAX" for VAX.
Because this name can include up to 15 characters, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 15 (bytes).
SYI$_ARCH_TYPE
Returns the type of CPU architecture on which the process is executing.
SYI$_ARCH_TYPE returns 1 on VAX or 2 on Alpha.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_AVAIL_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed
bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with
that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's configure set - those
owned by the partition and controlled by the issuing instance.
SYI$_AVAILCPU_CNT
Returns the number of CPUs available in the current boot of the
symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_BOOTTIME
Returns the time when the node was booted.
Because the returned time is in the standard 64-bit absolute time
format, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8
(bytes).
SYI$_CHARACTER_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the character string instructions are emulated
on the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_CLUSTER_EVOTES
Returns the number of votes expected to be found in the OpenVMS Cluster
system. The cluster determines this value by selecting the highest
number from all of the following: each node's system parameter
EXPECTED_VOTES, the sum of the votes currently in the cluster, and the
previous value for the number of expected votes.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_CLUSTER_FSYSID
Returns the system identification of the founding node, which is the
first node in the OpenVMS Cluster system to boot.
The cluster management software assigns this system identification to
the node. You can obtain this information by using the DCL command SHOW
CLUSTER. Because the system identification is a 6-byte hexadecimal
number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 6
(bytes).
SYI$_CLUSTER_FTIME
Returns the time when the founding node is booted. The founding node is
the first node in the OpenVMS Cluster system to boot.
Because the returned time is in the standard 64-bit absolute time
format, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8
(bytes).
SYI$_CLUSTER_MEMBER
Returns the membership status of the node in the OpenVMS Cluster
system. The membership status specifies whether the node is currently a
member of the cluster.
Because the membership status of a node is described in a 1-byte bit
field, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1
(byte). If bit 0 in the bit field is set, the node is a member of the
cluster; if it is clear, then it is not a member of the cluster.
SYI$_CLUSTER_NODES
Returns the number (in decimal) of nodes currently in the OpenVMS
Cluster system.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_CLUSTER_QUORUM
Returns the number (in decimal) that is the total of the quorum values
held by all nodes in the OpenVMS Cluster system. Each node's quorum
value is derived from its system parameter EXPECTED_VOTES.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_CLUSTER_VOTES
Returns the total number of votes held by all nodes in the OpenVMS
Cluster system. The number of votes held by any one node is determined
by that node's system parameter VOTES.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_COMMUNITY_ID
On Alpha systems, returns the hardware community ID for the issuing
instance within the hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer
systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_CONTIG_GBLPAGES
Returns the maximum number of free, contiguous global CPU-specific
pages. This number is the largest size global section that can be
created.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_CPU
On VAX systems, returns the CPU processor type, as represented in the
processor's system identification (SID) register.
For example, the integer 1 represents a VAX--11/780 system and the
integer 6 represents a VAX 8530, VAX 8550, VAX 8700, or VAX 8800 system.
Because the processor type is a longword decimal number, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
The $PRDEF macro defines the following symbols for the processor types:
| Processor |
Symbol |
|
VAX-11/730
|
PR$_SID_TYP730
|
|
VAX-11/750
|
PR$_SID_TYP750
|
|
VAX-11/780, 785
|
PR$_SID_TYP780
|
|
VAXstation II, II/GPX, and MicroVAX II
|
PR$_SID_TYPUV2
|
|
VAXstation 2000/MicroVAX 2000
|
PR$_SID_TYP410
|
|
VAX 8200, 8250, 8300, 8350
|
PR$_SID_TYP8SS
|
|
VAX 8530, 8550, 8810 (8700), and 8820-N (8800)
|
PR$_SID_TYP8NN
|
|
VAX 8600, 8650
|
PR$_SID_TYP790
|
|
VAX 8820, 8830, 8840
|
PR$_SID_TYP8PS
|
|
VAXft 3000 Model 310
|
PR$_SID_TYP520
|
|
VAXstation, MicroVAX 3100 series
|
PR$_SID_TYP420
|
|
MicroVAX 3300, 3400, 3500, 3600, 3800, 3900
|
PR$_SID_TYP650
|
|
VAXstation 3520, 3540
|
PR$_SID_TYP60
|
|
VAX 4000-300
|
PR$_SID_TYP670
|
|
VAX 6000-200, 6000-300 series
|
PR$_SID_TYP9CC
|
|
VAX 6000-400 series
|
PR$_SID_TYP9RR
|
|
VAX 9000-200, 9000-400 series
|
PR$_SID_TYP9AQ
|
On Alpha systems, $GETSYI returns PR$_SID_TYP_NOTAVAX.
For information about extended processor type codes, see the
description for the SYI$_XCPU item code.
SYI$_CPU_AUTOSTART
On Alpha systems, returns a list of zeroes and ones, separated by
commands and indexed by CPU ID. Any entry with a value of one indicates
that specific CPU will be brought into the OpenVMS active set if it
transitions into the current instance from outside, or is powered up
while already owned.
SYI$_CPU_FAILOVER
Returns list of numeric partition IDs, separated by commas and indexed
by CPU ID, that define the destination of the processor if the current
instance should crash. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that
support partitioning.
SYI$_CPUCAP_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns an array of quadword user capability masks
for all CPUs in the system. This array is indexed by CPU ID and
contains as many elements as the amount of space specified by the
buffer length field in the item descriptor.
To minimize wasted space, a prior call to $GETSYI with SYI$_MAX_CPUS
will provide the number of CPUs that need to be retrieved. Multiplying
that value by 8 bytes for each quadword provides the value to be
written in the buffer length field of the item descriptor.
SYI$_CPUCONF
On Alpha systems, returns the CPU Configuration bit mask: 0 through 31.
SYI$_CPUTYPE
On Alpha systems, returns the processor type, as stored in the hardware
restart parameter block (HWRPB).
For example, the value of 2 represents a DECchip 21064 processor.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
The following table shows the processor codes and processors:
| Processor Code |
Processor |
|
2
|
21064
|
|
4
|
21066, 21068, 21066A, 21068A
|
|
5
|
21164
|
|
6
|
21064A
|
|
7
|
21164A
|
|
8
|
21264
|
|
11
|
21264A
|
|
12
|
21264C
|
|
13
|
21264B
|
|
14
|
21264D
|
|
15
|
21364
|
|
16
|
21364
|
SYI$_CWLOGICALS
Returns the number 1 if the clusterwide logical name database has been
initialized on the CPU, or the value 0 if it has not been initialized.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_DAY_OVERRIDE
Returns the number 1 if the SET DAY command has been used to override
the default primary and secondary day types in the user authorization
file that are used to control user logins. $GETSYI returns the number 0
if no override is currently in effect, and the contents of user
authorization file records for each user are being honored.
SYI$_DAY_SECONDARY
Returns the number 1 if any override with the SET DAY command has been
used to specify that the current day is to be considered a Secondary
day for user login purposes. $GETSYI returns the number 0 if any
override with the SET DAY command has been used to specify that the
current day is to be considered a Primary day for user login purposes.
If $GETSYI returns the number 0 for SYI$_DAY_OVERRIDE, the number
returned for SYI$_DAY_SECONDARY is meaningless.
SYI$_DECIMAL_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the decimal string instructions are emulated on
the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_DECNET_FULLNAME
Returns, as a character string, the DECnet for OpenVMS full name of the
node.
Because the DECnet for OpenVMS full name of a node can contain up to
255 characters, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should
specify 255 (bytes).
SYI$_D_FLOAT_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the D_floating instructions are emulated on the
CPU and 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MAX
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum priority for the default
scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_DEF_PRIO_MIN
On Alpha systems, returns the minimum priority for the default
scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ERLBUFFERPAGES
Returns the number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha
systems) in an error log buffer.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ERRORLOGBUFFERS
Returns the number of system pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on
Alpha systems) in use as buffers for the error logger.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_F_FLOAT_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the F_floating instructions are emulated on the
CPU and 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_FREE_GBLPAGES
Returns the current number of free global pages. The system parameter
GBLPAGES sets the number of global pages that can exist systemwide.
Because the current number is a longword, the buffer length in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_FREE_GBLSECTS
Returns the current number of free global section table entries. The
system parameter GBLSECTIONS sets the maximum number of global sections
that can exist systemwide.
Because the current number is a longword, the buffer length in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_G_FLOAT_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the G_floating instructions are emulated on the
CPU and the value 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_GALAXY_ID
On Alpha systems, returns the 128-bit Galaxy ID. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GALAXY_MEMBER
On Alpha systems, returns 1 if you are member of a Galaxy sharing
community, 0 if you are not a member. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GALAXY_PLATFORM
On Alpha systems, returns 1 if you are running on a Galaxy platform, 0
if you are not running on a Galaxy platform. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GALAXY_SHMEMSIZE
On Alpha systems, returns the number of shared memory pages. If the
current instance is not a member of a Galaxy, no shared memory is
reported. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GH_RSRVPGCNT
On Alpha systems, returns the number of pages covered by granularity
hints to reserve for use by the Install utility after system startup
has completed.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_GLX_FORMATION
On Alpha systems, returns the a time-stamp string when the Galaxy
configuration, of which this instance is a member, was created.
Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GLX_MAX_MEMBERS
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum count of instances that may join
the current Galaxy configuration. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GLX_MBR_MEMBER
On Alpha systems, returns the 64-byte integer. Each 8 bytes represents
a Galaxy member number, listed from 7 to 0. The value is 1 if the
instance is currently a member, 0 if not a member. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GLX_MBR_NAME
On Alpha systems, returns a string indicating the names which are known
in the Galaxy membership. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_GLX_TERMINATION
On Alpha systems, returns a time-stamp string when the Galaxy
configuration, of which this instance last was a member, was
terminated. Supported only on AlphaServer GS series systems.
SYI$_H_FLOAT_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the H_floating instructions are emulated on the
CPU and the value 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_HP_ACTIVE_CPU_CNT
Returns the number of active CPUs in this hard partition that are not
currently in firmware console mode. For OpenVMS, this implies that the
CPU is in, or in the process of joining, the active set in one of the
instances in the hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_HP_ACTIVE_SP_CNT
Returns the count of active operating system instances currently
executing within the hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_HP_CONFIG_SBB_CNT
Returns a count of the existing system building blocks within the
current hard partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_HP_CONFIG_SP_CNT
Returns the maximum count of soft partitions within the current hard
partition. This count does not imply that an operating system instance
is currently running within any given soft partition. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_HW_MODEL
Returns a small integer that can be used to identify the model type of
the node.
An integer greater than 1023 indicates an Alpha node.
An integer less than or equal to 1023 indicates a VAX node.
The $ALPHADEF and $VAXDEF macros in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET define the
model type integers. See the tables under the SYI$_HW_NAME item code
for the VAX processor names and the corresponding model types.
Because SYI$_HW_MODEL is a word, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_HW_NAME
Returns the model name string of the node. The model name is a
character string that describes the model of the node (such as VAX
8800, MicroVAX II). The model name usually corresponds to the nameplate
that appears on the outside of the CPU cabinet.
Because SYI$_HW_NAME can include up to 60 characters plus one for the
byte count, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should
specify 61 (bytes).
The following table lists the Alpha model processor names and the
corresponding model types:
| Alpha Model Processor Name |
Alpha Model Type |
|
DEC 3000 400
|
ALPHA$K_A3000_400W
|
|
DEC 3000 400S
|
ALPHA$K_A3000_400S
|
|
DEC 3000 500
|
ALPHA$K_A3000_500W
|
|
DEC 3000 500S
|
ALPHA$K_A3000_500S
|
|
DEC 4000 610
|
ALPHA$K_A4000_610
|
|
DEC 4000 620
|
ALPHA$K_A4000_620
|
|
DEC 4000 630
|
ALPHA$K_A4000_630
|
|
DEC 4000 640
|
ALPHA$K_A4000_640
|
|
DEC 7000 Model 610
|
ALPHA$K_A7000_610
|
|
DEC 7000 Model 620
|
ALPHA$K_A7000_620
|
|
DEC 7000 Model 630
|
ALPHA$K_A7000_630
|
|
DEC 7000 Model 640
|
ALPHA$K_A7000_640
|
|
DEC 10000 Model 610
|
ALPHA$K_A10000_610
|
|
DEC 10000 Model 620
|
ALPHA$K_A10000_620
|
|
DEC 10000 Model 630
|
ALPHA$K_A10000_630
|
|
DEC 10000 Model 640
|
ALPHA$K_A10000_640
|
The following table lists the VAX model processor names and the
corresponding model types:
| VAX Model Processor Name |
VAX Model Type |
|
VAX-11/730
|
VAX$K_V730
|
|
VAX-11/750
|
VAX$K_V750
|
|
VAX-11/780
|
VAX$K_V780
|
|
VAX-11/785
|
VAX$K_V785
|
|
MicroVAX II
|
VAX$K_VUV2
|
|
VAXstation II
|
VAX$K_VWS2
|
|
VAXstation II/GPX
|
VAX$K_VWSD
|
|
VAXstation 2000
|
VAX$K_VWS2000
|
|
MicroVAX 2000
|
VAX$K_VUV2000
|
|
VAXstation 2000/GPX
|
VAX$K_VWSD2000
|
|
VAX 8200
|
VAX$K_V8200
|
|
VAX 8250
|
VAX$K_V8250
|
|
VAX 8300
|
VAX$K_V8300
|
|
VAX 8350
|
VAX$K_V8350
|
|
VAX 8530
|
VAX$K_V8500
|
|
VAX 8550
|
VAX$K_V8550
|
|
VAX 8600
|
VAX$K_V8600
|
|
VAX 8650
|
VAX$K_V8650
|
|
VAX 8810 (8700)
|
VAX$K_V8700
|
|
VAX 8820-N (8800)
|
VAX$K_V8800
|
|
VAX 8820, 8830, or 8840 with one CPU enabled
|
VAX$K_V8810
|
|
VAX 8820
|
VAX$K_V8820
|
|
VAX 8830
|
VAX$K_V8830
|
|
VAX 8840
|
VAX$K_V8840
|
|
VAXft 3000 Model 310
|
VAX$K_V520FT
|
|
VAXstation 3520
|
VAX$K_V3520L
|
|
VAXstation 3540
|
VAX$K_V3540L
|
|
VAX 4000-300 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V670
|
|
VAX 4000-300 server
|
VAX$K_V670_S
|
|
VAX 6000-210 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6210_T
|
|
VAX 6000-220 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6220_T
|
|
VAX 6000-230 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6230_T
|
|
VAX 6000-240 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6240_T
|
|
VAX 6000-250 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6250_T
|
|
VAX 6000-260 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6260_T
|
|
VAX 6000-210 server
|
VAX$K_V6210_S
|
|
VAX 6000-220 server
|
VAX$K_V6220_S
|
|
VAX 6000-310 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6310_T
|
|
VAX 6000-320 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6320_T
|
|
VAX 6000-330 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6330_T
|
|
VAX 6000-340 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6340_T
|
|
VAX 6000-350 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6350_T
|
|
VAX 6000-360 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V6360_T
|
|
VAX 6000-310 server
|
VAX$K_V6310_S
|
|
VAX 6000-320 server
|
VAX$K_V6320_S
|
|
VAX 6000-410 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR10_T
|
|
VAX 6000-420 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR20_T
|
|
VAX 6000-430 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR30_T
|
|
VAX 6000-440 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR40_T
|
|
VAX 6000-450 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR50_T
|
|
VAX 6000-460 timeshare
|
VAX$K_V9RR60_T
|
|
VAX 6000-410 server
|
VAX$K_V9RR10_S
|
|
VAX 6000-420 server
|
VAX$K_V9RR20_S
|
|
VAX 9000-210
|
VAX$K_V9AR10
|
|
VAX 9000-410
|
VAX$K_V9AQ10
|
|
VAX 9000-420
|
VAX$K_V9AQ20
|
|
VAX 9000-430
|
VAX$K_V9AQ30
|
|
VAX 9000-440
|
VAX$K_V9AQ40
|
SYI$_IO_PREFER_CPU
On Alpha systems, returns the bit mask of CPUs available to be Fast
Path preferred CPUs.
SYI$_ITB_ENTRIES
On Alpha systems, returns the number of instruction stream translation
buffer entries that support granularity hints to be allocated for
resident code.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_MAX_CPUS
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum number of CPUs that could be
recognized by this instance.
SYI$_MAX_PFN
Returns the highest numbered PFN in use by the operating system. The
highest numbered PFN used by OpenVMS is influenced by the
PHYSICAL_MEMORY system parameter.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_MEMSIZE
Returns the total number of pages of physical memory in the system
configuration.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_AREA
Returns the DECnet area of the node.
Because the DECnet area is a longword decimal number, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_CSID
Returns the OpenVMS Cluster system ID (CSID) of the node. The CSID is a
longword hexadecimal number assigned to the node by the cluster
management software.
Because the CSID is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_EVOTES
Returns the number of votes the node expects to find in the OpenVMS
Cluster system. This number is determined by the system parameter
EXPECTED_VOTES.
Because the number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_HWVERS
Returns the platform-specific hardware version information associated
with the node. The high word of the buffer contains the CPU type. The
$VAXDEF and $ALPHADEF macros define the CPU model types for VAX and
Alpha systems, respectively. (HP recommends acquiring the model type
using the SYI$_HW_MODEL item code.)
Because the hardware version is a 12-byte hexadecimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 12 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_NUMBER
Returns the DECnet for OpenVMS number of the node.
Because the DECnet for OpenVMS number is a longword decimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_QUORUM
Returns the value (in decimal) of the quorum held by the node. This
number is derived from the node's system parameter EXPECTED_VOTES.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_SWINCARN
Returns the software incarnation of the node.
Because the software incarnation of the node is an 8-byte hexadecimal
number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8
(bytes).
SYI$_NODE_SWTYPE
Returns the software type of the node. The software type indicates
whether the node is a VAX system, an Alpha system, or an HSC storage
controller.
Because the software type is a 4-byte ASCII string, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_SWVERS
Returns the software version of the node.
Because the software version is a 4-byte ASCII string, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_SYSTEMID
Returns the system identification of the node.
The OpenVMS Cluster management software assigns this system
identification to the node. You can obtain this information by using
the DCL command SHOW CLUSTER. Because the system identification is a
6-byte hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 6 (bytes).
SYI$_NODE_VOTES
Returns the number (in decimal) of votes held by the node. This number
is determined by the node's system parameter VOTES.
Because this number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
SYI$_NODENAME
Returns, as a character string, the name of the node in the buffer
specified in the item list.
Because this name can include up to 15 characters, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 15 (bytes).
SYI$_PAGEFILE_FREE
Returns the number of free pages in the currently installed page files.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PAGEFILE_PAGE
Returns the number of pages in the currently installed page files.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PAGE_SIZE
Returns the number of CPU-specific bytes per page in the system.
On VAX systems, $GETSYI always returns 512.
On Alpha systems, CPU page size varies from system to system.
On Alpha and VAX systems, because this number is a longword, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PARTITION_ID
On Alpha systems, returns the soft partition ID. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP
Returns a map describing the system's use of physical memory. The
following figure shows an example of a physical memory map:
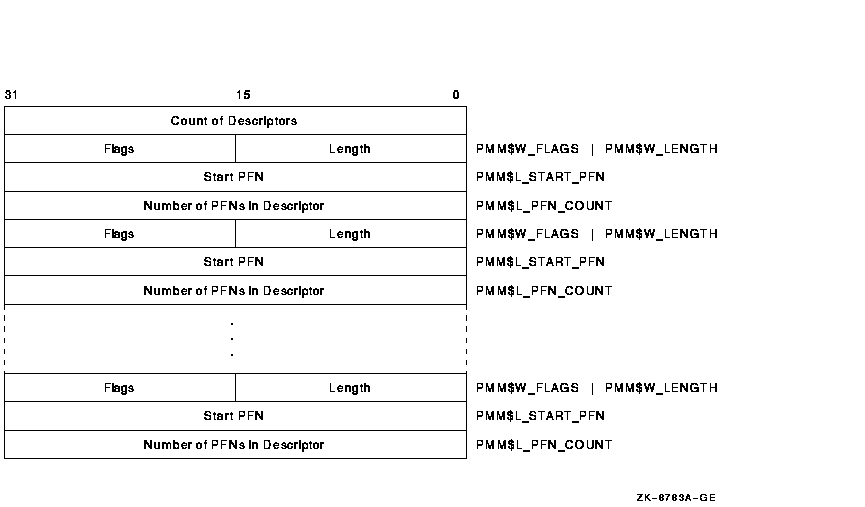
The first longword of the physical memory contains a count of
descriptors. This number is equal to the value returned when the
SYI$_PMD_COUNT item code is specified.
Each descriptor contains at least 3 longwords: a word containing the
length of the descriptor (always use PMM$C_LENGTH when determining
descriptor size); a flags word (whose bits are defined in the following
table); and the starting PFN for that physical memory cluster and the
number of PFNs in that cluster.
| Bit |
Meaning When Set |
|
PMM$V_CONSOLE
|
The physical memory descriptor is in use by the console (hardware).
|
|
PMM$V_OPENVMS
|
The physical memory descriptor is in use by OpenVMS.
|
|
PMM$V_AVAILABLE
|
The physical descriptor is not in use by either the console (hardware)
or OpenVMS.
|
|
Remaining bits
|
The remaining bits in the PMM$W_FLAGS word are reserved for HP.
|
The structure definition for the physical memory descriptor resides in
PMMDEF.H.
Because the size of the physical memory map returned by $GETSYI can
vary from system to system, HP recommends using the following steps
when using this item code:
- Call $GETSYI first using the SYI$_PMD_COUNT to obtain the number of
physical memory descriptors.
- Dynamically create a buffer to which $GETSYI can copy the physical
memory map. The size of the buffer can be computed with the following
formula:
map_buffer_size = (PMM$C_LENGTH * ret-val) + 4
|
where:
- PMM$C_LENGTH is the size of an individual physical memory
descriptor.
- ret-val is the return value from a call to $GETSYI specifying the
SYI$_PMD_COUNT item code.
- 4 is the number of bytes occupied by the descriptor count in the
physical memory map.
SYI$_PHYSICALPAGES
Returns the total number of PFNs that exist between the first PFN
(typically PFN 0) and the highest numbered PFN.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PMD_COUNT
Returns the total number of physical memory descriptors defined by the
system. The return value of this parameter can be used to determine the
buffer size to use when specifying the SYI$_PFN_MEMORY_MAP item code.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_POTENTIAL_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed
bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with
that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's potential set. A CPU in
the potential set implies that it could actively join the OpenVMS
active set for this instance if it is ever owned by it. To meet this
rule the CPU's characteristics must match hardware and software
compatibility rules defined particularly for that instance.
SYI$_POTENTIALCPU_CNT
On Alpha systems, returns the count of CPUs in the hard partition that
are members of the potential set for this instance. A CPU in the
potential set implies that it could actively join the OpenVMS active
set for this instance if it is ever owned by it. To meet this rule the
CPU's characteristics must match hardware and software compatibility
rules defined particularly for that instance.
SYI$_POWERED_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed
bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with
that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's powered set - those
CPUs physically existing within the hard partition and powered up for
operation.
SYI$_POWEREDCPU_CNT
On Alpha systems, returns the count of CPUs in the hard partition that
are physically powered up.
SYI$_PRESENT_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed
bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with
that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's present set - those
CPUs physically existing within the hard partition. Being in the
present set does not imply that it is part of the powered set.
SYI$_PRESENTCPU_CNT
On Alpha systems, returns the count of CPUs in the hard partition that
physically reside in a hardware slot.
SYI$_PRIMARY_CPUID
On Alpha systems, returns the CPU ID of the primary processor for this
OpenVMS instance.
SYI$_PROCESS_SPACE_LIMIT
On Alpha systems, this item code returns the 64-bit virtual address
succeeding the last available process private address. The value
returned is the upper bound on the process private address space. The
value returned is the same for every process on the system.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
SYI$_PSXFIFO_PRIO_MAX
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum priority for the POSIX FIFO
scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PSXFIFO_PRIO_MIN
On Alpha systems, returns the minimum priority for the POSIX FIFO
scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PSXRR_PRIO_MAX
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum priority for the POSIX
round-robin scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PSXRR_PRIO_MIN
On Alpha systems, returns the minimum priority for the POSIX
round-robin scheduling policy.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_PT_BASE
On Alpha systems, returns the 64-bit virtual address of the base of the
page tables. The value returned is the same for every process on the
system.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
SYI$_PTES_PER_PAGE
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum number of CPU-specific pages that
can be mapped by one page table page.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_RAD_CPUS
On Alpha systems, returns a longword array of RAD/CPU pairs that can
potentially be in this operating system instance. If there is no RAD
support, all potential CPUs are in RAD 0. The array is terminated with
a -1,-1 pair.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
SYI$_RAD_MEMSIZE
On Alpha systems, returns a longword array of RAD/page count pairs. The
number of pages of private memory is returned. If there is no RAD
support, all memory is reported in RAD 0. The array is terminated with
a -1,-1 pair.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
SYI$_RAD_MAX_RAD
On Alpha systems, returns the maximum number of RADs possible on this
platform. If there is no RAD support, 1 is returned.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
SYI$_RAD_SHMEMSIZE
On Alpha systems, returns a longword array of RAD/page count pairs. The
number of pages of shared memory is returned. If there is no RAD
support, all shared memory is reported in RAD 0. If the current
instance is not a member of a Galaxy, no shared memory is reported. The
array is terminated with a -1,-1 pair.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
SYI$_REAL_CPUTYPE
Returns the actual CPU type of the primary CPU of the system.
See the SYI$_CPUTYPE item code for a list of symbols and processors.
SYI$_SCSNODE
Returns the Galaxy instance name. Supported only on AlphaServer systems that support partitioning.
SYI$_SCS_EXISTS
Returns a longword value that is interpreted as Boolean. If the value
is 1, the System Communication Subsystem (SCS) is currently loaded on
the node; if the value is 0, the SCS is not currently loaded.
SYI$_SERIAL_NUMBER
Returns the system serial number from out of the Hardware Restart
Parameter Block (HWRPB).
SYI$_SHARED_VA_PTES
On Alpha systems, returns the 64-bit virtual address of the PTE that
marks the boundary between process-private PTEs and system-shared PTEs.
The value returned is the same for every process on the system.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
SYI$_SID
Returns the contents of the system identification register of the node.
On Alpha systems, SYI$_SID returns a value in which all fields are 0
except the CPU-type field, which always contains the value 256.
Because the value of this register is a longword hexadecimal number,
the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_SWAPFILE_FREE
Returns the number of free pages in the currently installed swapping
files.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_SWAPFILE_PAGE
Returns the number of pages in the currently installed swapping files.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_SYSTEM_RIGHTS
Returns the system rights list as an array of quadword identifiers.
Each entry consists of a longword identifier value and the following
longword identifier attributes:
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
Allocate a buffer that is sufficient to hold the system rights list,
because $GETSYI returns only as much of the list as will fit in the
buffer.
SYI$_SYSTYPE
On Alpha systems, returns the name of the family or system hardware
platform. For example, the integer 2 represents a DEC 4000 processor,
the integer 3 represents a DEC 7000 or DEC 10000 processor, and the
integer 4 represents a DEC 3000 processor.
SYI$_VERSION
Returns, as a character string, the software version number of the
OpenVMS operating system running on the node.
Because the version number is 8-byte blank-filled, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
SYI$_VECTOR_EMULATOR
Returns a byte, the low-order bit of which, when set, indicates the
presence of the Vector Instruction Emulator facility (VVIEF) in the
system.
SYI$_VP_MASK
Returns a longword mask, the bits of which, when set, indicate which
processors in the system have vector coprocessors.
SYI$_VP_NUMBER
Returns an unsigned longword containing the number of vector processors
in the system.
SYI$_XCPU
Returns the extended CPU processor type of the node.
You should obtain the general processor type value first by using the
SYI$_CPU item code. For some of the general processor types, extended
processor type information is provided by the item code, SYI$_XCPU. For
other general processor types, the value returned by the SYI$_XCPU item
code is currently undefined.
Because the processor type is a longword decimal number, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
On VAX systems, the $PRDEF macro defines the following symbols for the
extended processor types:
VAX
Processor
Type Symbol |
Extended
Processor
Type |
Extended
Processor
Symbol |
|
PR$_SID_TYPUV
|
MicroVAX II
VAXstation II
|
PR$_XSID_UV_UV2
|
|
|
MicroVAX 2000
VAXstation 2000
|
PR$_XSID_UV_410
|
|
PR$_SID_TYPCV
|
MicroVAX 3300, 3400, 3500, 3600, 3800, 3900 series
|
PR$_XSID_CV_650
|
|
|
VAX 6000-200, 6000-300 series
|
PR$_XSID_CV_9CC
|
|
|
VAXstation 3520, 3540
|
PR$_XSID_CV_60
|
|
|
VAXstation 3100 series
|
PR$_XSID_CV_420
|
|
|
VAXft 3000 Model 310
|
PR$_XSID_CV_520
|
|
PR$_SID_TYP8NN
|
VAX 8530
|
PRS$_XSID_N8500
|
|
|
VAX 8550
|
PRS$_XSID_N8550
|
|
|
VAX 8810 (8700)
|
PRS$_XSID_N8700
|
|
|
VAX 8820-N (8800)
|
PRS$_XSID_N8800
|
|
PR$_SID_TYPRV
|
VAX 4000-300
|
PR$_XSID_RV_670
|
|
|
VAX 6000-400 series
|
PR$_XSID_RV_9RR
|
SYI$_XSID
Returns processor-specific information. For the MicroVAX II system,
this information is the contents of the system type register of the
node. The system type register contains the full extended information
used in determining the extended system type codes. For other
processors, the data returned by SYI$_XSID is currently undefined.
Because the value of this register is a longword hexadecimal number,
the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_xxxx
Returns the current value of the system parameter named xxxx
for the node.
The buffer must specify a longword into which $GETSYI writes the value
of the specified system parameter. For a list and description of all
system parameters, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Description
The Get Systemwide Information service returns information about the
local system or about other systems in an OpenVMS Cluster configuration.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
This service uses the process's AST limit quota (ASTLM).
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR,
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The caller cannot read the item list, cannot write to the buffer
specified by the buffer address field in an item descriptor, or cannot
write to the return length address field in an item descriptor.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
|
|
SS$_NOMORENODE
|
You requested a wildcard operation, and $GETSYI has returned
information about all available nodes.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The specified node does not exist or is not currently a member of the
OpenVMS Cluster system.
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
Remote node is not currently reachable.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
Same as those returned in R0.
Example
|
/* Defining __NEW_STARLET enables the program to benefit from better type
checking for prototypes and structures provided by OpenVMS. */
#define __NEW_STARLET 1
#include <efndef> /* No Event Flag Event Flag */
#include <iledef> /* Item List Entry Definitions */
#include <iosbdef> /* I/O Status Block Structure Definition */
#include <starlet> /* Function Prototypes for System Services */
#include <stdio> /* C Standard I/O Functions */
#include <string> /* memset Prototype */
#include <syidef> /* $GETSYI Item Code Definitions */
#define NUM_ILE 3
#define BUFFER_SIZE 20
/* Macro to initialize a 32-bit item_list_3. */
#define init_ile32(ile, length, code, bufaddr, retlen_addr) \
{ (ile)->ile3$w_length = (length); \
(ile)->ile3$w_code = (code); \
(ile)->ile3$ps_bufaddr = (bufaddr); \
(ile)->ile3$ps_retlen_addr = (retlen_addr); }
/* Simple status checking macro. */
#define bad_status(status) (((status) & 1) != 1)
main ()
{
char
node_name [BUFFER_SIZE],
version_string [BUFFER_SIZE];
int
status;
unsigned short
node_name_length,
version_string_length;
ILE3
syi_ile [NUM_ILE];
IOSB
iosb;
/* Zeroing the item list has the effect of creating the terminating entry. */
memset (syi_ile, 0, ILE3$K_LENGTH*NUM_ILE);
/* Initialize the item list entries to fetch the operating system version
and the node name. */
init_ile32 (
&syi_ile [0],
BUFFER_SIZE,
SYI$_VERSION,
version_string,
&version_string_length);
init_ile32 (
&syi_ile [1],
BUFFER_SIZE,
SYI$_NODENAME,
node_name,
&node_name_length);
status = sys$getsyiw (
EFN$C_ENF,
NULL,
NULL,
&syi_ile,
&iosb,
NULL,
0);
if (bad_status (status)) return status;
if (bad_status (iosb.iosb$w_status)) return iosb.iosb$w_status;
/* Zero terminate the strings before displaying them. */
version_string [version_string_length] = '\0';
node_name [node_name_length] = '\0';
printf ("Version: %s Node Name: %s\n",
version_string,
node_name);
}
|
This example C program demonstrates how to use $GETSYIW to obtain the
operating system version number string and the node name.
$GETSYIW
Returns information about the local system or about other systems in a
cluster.
The $GETSYIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller with the requested information. For asynchronous completion,
use the Get Systemwide Information ($GETSYI) service; $GETSYI returns
to the caller after queuing the information request, without waiting
for the information to be returned. In all other respects, these
services are identical; refer to the documentation about $GETSYI for
information about the $GETSYIW service.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETSYIW [efn] ,[csidadr] ,[nodename] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getsyiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *csidadr, void
*nodename, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
You must specify either the csidadr or the
nodename argument, but not both. For wildcard
operations, however, you must use the csidadr argument.
$GETTIM
Returns the current system time in a 64-bit format.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETTIM timadr
C Prototype
int sys$gettim (struct _generic_64 *timadr);
Argument
timadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on
VAX systems) of a quadword to receive the current time in 64-bit format.
Description
The Get Time service returns the current system time in 64-bit format.
The quadword is the number of nanoseconds since November 17, 1858.
Based upon system time initialization, all bits in the time quadword
are valid.
On VAX systems, system time is updated every 10 milliseconds.
On Alpha systems, the frequency at which system time is updated varies,
depending on the clock frequency of the Alpha processor, or
approximately 1 millisecond.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME, $SETIMR
For additional information about the system time, refer to the
HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The quadword to receive the time cannot be written by the caller.
|
$GETUAI
Returns authorization information about a specified user.
Format
SYS$GETUAI [nullarg] ,[contxt] ,usrnam ,itmlst ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg]
,[nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$getuai (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *contxt, void *usrnam,
void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int
astprm);
Arguments
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
An optional longword used to maintain an open channel to the
authorization file. The contxt argument is the address
of a longword to receive a $GETUAI context value. If the
contxt argument is specified on the initial call, this
longword should contain the value --1, and on subsequent calls, the
value of the contxt argument from the previous call
should be passed back in.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the user about whom $GETUAI returns authorization information.
The usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a character text string containing the user name. The user
name string can contain a maximum of 12 alphanumeric characters.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information from the specified user's user
authorization file (UAF) record is to be returned. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of one or
more item descriptors, each of which specifies an item code. The item
list is terminated by an item code value of 0 or by a longword value of
0.
The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETUAI
is to write the information. The length of the buffer varies, depending
on the item code specified in the item code field of the item
descriptor, and is given in the description of each item code. If the
value of the buffer length field is too small, $GETUAI truncates the
data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETUAI is to return. The $UAIDEF macro defines these
codes.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which
$GETUAI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which
$GETUAI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually
returned.
|
The symbolic codes have the following format:
See the Item Codes section for descriptions of the various $GETUAI item
codes.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
Item Codes
UAI$_ACCOUNT
Returns, as a blank-filled 32-character string, the account name of the
user.
An account name can include up to 8 characters. Because the account
name is a blank-filled string, however, the buffer length field of the
item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_ASTLM
Returns the AST queue limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch
access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour
period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch
access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a
1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BIOLM
Returns the buffered I/O count.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BYTLM
Returns the buffered I/O byte limit.
Because the buffered I/O byte limit is a longword decimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_CLITABLES
Returns, as a character string, the name of the user-defined CLI table
for the account, if any.
Because the CLI table name can include up to 31 characters in addition
to a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor
should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_CPUTIM
Returns the maximum CPU time limit (per session) for the process in
10-millisecond units.
Because the maximum CPU time limit is a longword decimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFCLI
Returns, as an RMS file name component, the name of the command
language interpreter used to execute the specified batch job. The file
specification returned assumes the device name and directory SYS$SYSTEM
and the file type .EXE.
Because a file name can include up to 31 characters in addition to a
size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should
specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDEV
Returns, as a 1- to 31-character string, the name of the default device.
Because the device name string can include up to 31 characters in
addition to a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDIR
Returns, as a 1- to 63-character string, the name of the default
directory.
Because the directory name string can include up to 63 characters in
addition to a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
UAI$_DEF_PRIV
Returns the default privileges for the user.
Because the default privileges are returned as a quadword value, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_DFWSCNT
Returns the default working set size in pages (on VAX systems) or
pagelets (on Alpha systems).
Because the default working set size is a longword decimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DIOLM
Returns the direct I/O count limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup
access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour
period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is allowed. For
each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup
access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a
1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is allowed. For
each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_ENCRYPT
Returns one of the values shown in the following table, identifying the
encryption algorithm for the primary password.
Because the encryption algorithm is a byte in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
UAI$C_AD_II
|
Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. It was used in
VAX VMS releases prior to Version 2.0.
|
|
UAI$C_PURDY
|
Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded
user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used
during VAX VMS Version 2.0 field test.
|
|
UAI$C_PURDY_V
|
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a
variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This
algorithm was used in VMS releases prior to Version 5.4.
|
|
UAI$C_PURDY_S
|
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a
variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This is
the current algorithm that the operating system uses for all new
password changes.
|
UAI$_ENCRYPT2
Returns one of the following values identifying the encryption
algorithm for the secondary password:
- UAI$C_AD_II
- UAI$C_PURDY
- UAI$C_PURDY_V
- UAI$C_PURDY_S
Because the encryption algorithm is a byte in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 byte.
UAI$_ENQLM
Returns the lock queue limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_EXPIRATION
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the expiration date and
time of the account.
Because the absolute time value is a quadword in length, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_FILLM
Returns the open file limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_FLAGS
Returns, as a longword bit vector, the various login flags set for the
user.
Each flag is represented by a bit. The $UAIDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names for these flags:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
UAI$V_AUDIT
|
All actions are audited.
|
|
UAI$V_AUTOLOGIN
|
User can only log in to terminals defined by the Automatic Login
facility (ALF).
|
|
UAI$V_CAPTIVE
|
User is restricted to captive account.
|
|
UAI$V_DEFCLI
|
User is restricted to default command interpreter.
|
|
UAI$V_DISACNT
|
User account is disabled. Same as /FLAG = DISUSER qualifier in
AUTHORIZE.
|
|
UAI$V_DISCTLY
|
User cannot use Ctrl/Y.
|
|
UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE
|
User will not be forced to change expired passwords at login.
|
|
UAI$V_DISIMAGE
|
User cannot issue the RUN or MCR commands or use the foreign command
mechanism in DCL.
|
|
UAI$V_DISMAIL
|
Announcement of new mail is suppressed.
|
|
UAI$V_DISPWDDIC
|
Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against the system
dictionary is disabled.
|
|
UAI$V_DISPWDHIS
|
Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against previously used
passwords is disabled.
|
|
UAI$V_DISRECONNECT
|
User cannot reconnect to existing processes.
|
|
UAI$V_DISREPORT
|
User will not receive last login messages.
|
|
UAI$V_DISWELCOME
|
User will not receive the login welcome message.
|
|
UAI$V_EXTAUTH
|
User is considered to be externally authenticated by their external
user ID and password, and not by the SYSUAF user ID and password. The
SYSUAF record is still used for checking login restrictions and quotas
and for creating the user's OpenVMS process profile.
|
|
UAI$V_GENPWD
|
User is required to use generated passwords.
|
|
UAI$V_LOCKPWD
|
SET PASSWORD command is disabled.
|
|
UAI$V_MIGRATEPWD
|
User's SYSUAF password has been set using AUTHORIZE or SYS$SETUAI and
is likely to be inconsistent with the user's external user password. If
password migration is enabled, the system will attempt to update the
external authentication service the next time the user attempts a login.
|
|
UAI$V_NOMAIL
|
Mail delivery to user is disabled.
|
|
UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED
|
Primary password is expired.
|
|
UAI$V_PWD2_EXPIRED
|
Secondary password is expired.
|
|
UAI$V_RESTRICTED
|
User is limited to operating under a restricted account. (Refer to the
HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security for a description of restricted and captive accounts.)
|
UAI$_JTQUOTA
Returns the initial byte quota with which the jobwide logical name
table is to be created.
Because this quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_LASTLOGIN_I
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last
interactive login.
UAI$_LASTLOGIN_N
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last
noninteractive login.
UAI$_LGICMD
Returns, as an OpenVMS RMS file specification, the name of the default
login command file.
Because a file specification can include up to 63 characters in
addition to a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item
descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which local
interactive access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set
represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23
as 11 p.m. to midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is
allowed. For each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_LOCAL_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch
access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a
1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is allowed. For
each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_LOGFAILS
Returns the count of login failures.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXACCTJOBS
Returns the maximum number of batch, interactive, and detached
processes that can be active at one time for all users of the same
account. The value 0 represents an unlimited number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXDETACH
Returns the detached process limit. A value of 0 represents an
unlimited number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_MAXJOBS
Returns the active process limit. A value of 0 represents an unlimited
number.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which network
access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour
period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is allowed. For
each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_NETWORK_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which network
access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a
1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to
midnight. For each hour the bit is set to 0, access is allowed. For
each hour the bit is set to 1, access is denied.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_OWNER
Returns, as a character string, the name of the owner of the account.
Because the owner name can include up to 31 characters in addition to a
size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should
specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_PBYTLM
Returns the paged buffer I/O byte count limit.
Because the paged buffer I/O byte count limit is a longword decimal
number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4
(bytes).
UAI$_PGFLQUOTA
Returns the paging file quota in pages (on VAX systems) or in blocks
(on Alpha systems).
Because the paging file quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_PRCCNT
Returns the subprocess creation limit.
Because the subprocess creation limit is a longword decimal number, the
buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_PRI
Returns the default base priority in the range 0 through 31.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_PRIMEDAYS
Returns, as a byte bit vector, the primary and secondary days of the
week.
Each bit represents a day of the week, with the bit clear representing
a primary day and the bit set representing a secondary day. The $UAIDEF
macro defines the following symbolic names for these bits:
UAI$V_MONDAY
UAI$V_TUESDAY
UAI$V_WEDNESDAY
UAI$V_THURSDAY
UAI$V_FRIDAY
UAI$V_SATURDAY
UAI$V_SUNDAY
UAI$_PRIV
Returns, as a quadword value, the names of the privileges the user
holds.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_PWD
Returns, as a quadword value, the hashed primary password of the user.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_PWD_DATE
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last
password change.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
A value of --1 indicates that the password is marked as preexpired.
UAI$_PWD_LENGTH
Returns the minimum password length.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME
Returns, as a quadword delta time value, the password lifetime.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
A quadword of 0 means that none of the password mechanisms will take
effect.
UAI$_PWD2
Returns, as a quadword value, the hashed secondary password of the user.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_PWD2_DATE
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the last date the secondary
password was changed.
Because this value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in
the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
A value of --1 indicates that the password could be marked as
preexpired.
UAI$_QUEPRI
Returns the maximum job queue priority.
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which remote
interactive access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set
represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23
as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_REMOTE_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which remote
interactive access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set
represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23
as 11 p.m. to midnight.
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_SALT
Returns the random password salt.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_SHRFILLM
Returns the shared file limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_TQCNT
Returns the timer queue entry limit.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_UIC
Returns, as a longword, the user identification code (UIC). For the
format of the UIC, see the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
UAI$_USER_DATA
Returns up to 255 bytes of information from the user data area of the
system user authorization file (SYSUAF).
You can read information written to the user data area from previous
versions of the operating system as long as the information written
adheres to the guidelines described in the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
UAI$_WSEXTENT
Returns the working set extent, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets
(on Alpha systems), for the user of the specified queue or job.
Because the working set extent is a longword decimal number, the buffer
length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_WSQUOTA
Returns the working set quota, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets
(on Alpha systems), for the specified user.
Because this quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Description
The Get User Authorization Information service returns authorization
information about a specified user.
The contxt value returned by $GETUAI should never be
used as a value to the $SETUAI system service.
You examine for a valid login by checking the bits of UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED
and UAI$V_DISUSER, and by doing a comparison of the UAI$_PWD_DATE item
code against the UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME item code.
The UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED bit is only set by the system when the bit
UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE is set in the user's SYSUAF record and the
comparison between the UAI$_PWD_DATE and UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME indicates a
password is past its valid life.
During a normal login when the UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE bit is not
set, the system compares VAI$_PWD_DATE against UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME and,
if expired, forces the user to change the password. With this
configuration, the UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED bit is not set.
During a normal login when the VAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_EXPIRED is set, the
system compares UAI$_PWD_DATE against UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME and, if
expired, sets the UAI$_PWD_EXPIRED bit and notifies the user to change
the now-expired password. In this case, the user is not forced to
change the password.
Required Access or Privileges
Use the following list to determine the privileges required to use the
$GETUAI service:
- BYPASS or SYSPRV---Allows access to any record in the user
authorization file (UAF).
- GRPPRV---Allows access to any record in the UAF whose UIC group
matches that of the requester.
- No privilege---Allows access to any UAF record whose UIC matches
that of the requester.
You need read access to the UAF to look up
any information other than your own.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SETUAI
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the
return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written
by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The function code is invalid; the item list contains an invalid item
code; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the reserved
parameter has a nonzero value.
|
|
SS$_NOGRPPRV
|
The user does not have the privileges required to examine the
authorization information for other members of the UIC group.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSPRV
|
The user does not have the privileges required to examine the
authorization information associated with the user or for users outside
of the user's UIC group.
|
|
RMS$_RSZ
|
The UAF record is smaller than required; the caller's SYSUAF is
probably corrupt.
|
This service can also return OpenVMS RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For example, an inquiry about a
nonexistent account returns RMS$_RNF, record not found status. For a
description of RMS status codes that are returned by this service,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$GETUTC
Returns the current time in 128-bit UTC format.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETUTC utcadr
C Prototype
int sys$getutc (unsigned int *utcadr [4]);
Arguments
utcadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
coordinated universal time |
| type: |
utc_date_time |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 128-bit time value to be returned.
Description
The Get UTC Time service returns the current system time in 128-bit UTC
format. System time is updated every 10 milliseconds.
On Alpha systems, the frequency at which system time is updated varies,
depending on the clock frequency of the Alpha processor.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCUTC, $BINUTC, $NUMUTC, $TIMCON
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The argument was not accessible for write in the mode of the caller.
|
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, obtains data from the user image alignment fault
buffer if buffered user alignment fault data reporting has been enabled.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA buffer ,buffer_size ,return_size
C Prototype
int sys$get_align_fault_data (void *buffer, int buffer_size, int
*return_size);
Arguments
buffer
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The user buffer in which the alignment fault data is to be stored. The
buffer is the 32- or 64-bit address of this user
buffer.
buffer_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The size, in bytes, of the buffer specified by the
buffer argument.
return_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The
return_size argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
naturally aligned longword into which the service returns the size of
the buffer. The return_size is set to 0 if there is no
data in the buffer.
Description
The Get Alignment Fault Data service obtains data from the user image
alignment fault buffer if buffered user alignment fault data reporting
has been enabled.
When buffered user alignment fault data reporting is enabled, the
operating system writes each alignment fault into a user-defined
buffer. The user must poll this buffer periodically to read the data.
The user must call the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to enable
buffered user alignment fault data reporting.
For more information about buffered user alignment fault data
reporting, see the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT system service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT,
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The buffer named in the
buffer argument is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
|
Alignment fault reporting has not been enabled.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The buffer size is smaller than the minimum defined by the
AFR$K_USER_LENGTH
symbol.
|
$GET_ARITH_EXCEPTION (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, returns information about the exception context for a
given arithmetic exception.
Format
SYS$GET_ARITH_EXCEPTION sigarg ,mcharg ,buffer
C Prototype
int sys$get_arith_exception (void *sigarg, void *mcharg, void *buffer);
Arguments
sigarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
signal array |
| type: |
vector_longword_signed |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of the signal array for the given arithmetic exception.
mcharg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mech array |
| type: |
vector_quadword_unsigned |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of the mechanism array for the given arithmetic exception.
buffer
| OpenVMS usage: |
vector_quadword |
| type: |
vector_quadword_unsigned |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Four-quadword buffer to receive additional exception context. The
buffer argument is the address of a descriptor that
points to this buffer.
Description
The Get Arithmetic Exception Information service returns, to the buffer
specified by the buffer argument, the following
information for a given arithmetic exception in an array of quadwords:
- First quadword, the PC of the triggering instruction in the trap
shadow
- Second quadword, a copy of the triggering instruction
- Third quadword, the exception summary
- Fourth quadword, the register write mask
Required Access or Privilege
None
Required Quota
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The specified buffer cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The specified buffer length is invalid or out of range.
|
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS
Returns the default transaction of the calling process.
Format
SYS$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS tid
C Prototype
int sys$get_default_trans (unsigned int tid [4]);
Arguments
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the identifier (TID) of the default
transaction of the calling process is returned.
Description
A precondition for the successful completion of $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS is
that the calling process must have a default transaction.
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS may fail for various reasons, including:
- The precondition was not met.
- The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
The postcondition on successful completion of $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS is
described in Table SYS-44:
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS,
$START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The request was successful.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_NOCURTID
|
The calling process did not have a default transaction.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
|
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO (Alpha Only)
Returns "interesting" fields from the specified lock.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS
Galaxy system services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO handle ,name ,timeout ,size ,ipl ,rank ,flags
[,name_length]
C Prototype
int sys$get_galaxy_lock_info (unsigned __int64 lock_handle, char *name,
unsigned int *timeout, unsigned int *size, unsigned int *ipl, unsigned
int *rank, unsigned short int *flags unsigned short int *name_length);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
handle for the galaxy lock |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
input by value |
The 64-bit lock handle that identifies the lock on which to return
information. This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK.
name
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
zero-terminated string |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a buffer. This buffer must be large enough to receive the
name of the lock. Locks names are zero-terminated strings with a
maximum size of 16 bytes.
timeout
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the timeout value of the
lock.
size
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the size of the lock in
bytes.
ipl
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the IPL of the lock.
rank
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is the rank of the lock.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a word. The value returned is the word mask of lock flags.
name_length
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Length of the string returned in the name argument.
Description
This service returns all "interesting" fields from the specified lock.
See the $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK service for detailed information regarding
these values.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access to lock.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE,
$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKID
|
Invalid lock id.
|
|
SS$_IVLOCKTBL
|
Invalid lock table.
|
$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE (Alpha Only)
Returns the minimum and maximum size of an OpenVMS Galaxy lock.
Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS Alpha
Galaxy environment.
For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy system
services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Format
SYS$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE min_size ,max_size
C Prototype
int sys$get_galaxy_lock_size (unsigned int *min_size, unsigned int
*max_size);
Arguments
min_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is minimum legal size of a
galaxy lock structure.
max_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
output by reference |
Pointer to a longword. The value returned is maximum legal size of a
galaxy lock structure.
Description
This service returns the minimum and maximum size of an OpenVMS Galaxy
lock. If a lock is created with the maximum size, the locking services
will record acquire and release information in the lock.
The lock sizes can be used to determine the value of the
section_size parameter to the
$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE service.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access to lock.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE,
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO,
$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
$GET_REGION_INFO (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, gets information about a specified virtual region.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_REGION_INFO function_code ,region_id_64 ,start_va_64 ,nullarg
,buffer_length ,buffer_address_64 ,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$get_region_info (unsigned int function_code, struct _generic_64
*region_id_64, void *start_va_64, void *reserved, unsigned int
buffer_length, void *buffer_address_64, unsigned int *return_length_64);
Arguments
function_code
| OpenVMS usage: |
function code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function code specifying how the information you are requesting should
be looked up. All function codes return region summary information in
the return buffer in the format of the Region Summary Buffer. The
Region Summary Buffer format is shown in the table in the
buffer_address_64 argument.
If less buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary
Buffer, only the amount of information requested is returned. If more
buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary Buffer,
the service will fill in the buffer. The return length will reflect the
amount of useful information written to the buffer, the size of the
Region Summary Buffer.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each function code.
The following function codes are defined:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID
|
Return the region summary information for the region whose ID is
specified in the
region_id_64 argument.
|
|
VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA
|
Return the region summary information for the region that contains the
virtual address specified in the
start_va_64 argument.
|
|
VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA
|
Return the region summary information for the region containing the
starting address. If the starting address is not in a region, return
the region summary information for the next region with a starting
address higher than the specified address.
Note: For the VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA function, OpenVMS
checks for a
start_va_64 argument in the inaccessible address range
in
P2 space. If it finds one, OpenVMS adjusts the address
to account for the discontinuity. For more information about the layout
of the 64-bit virtual address space, refer to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
This function code can be used for wildcard operations. See the
description of the
start_va_64 argument for information on how to program
a wildcard operation on regions.
|
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region about which information is
requested. This argument is read only if the function code
VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID is specified.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
input address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Virtual address associated with region about which information is
requested. This argument is read only if the
function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA or
VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA.
If the function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA,
this argument is a virtual address within the region about which you
are requesting information.
To perform a wildcard search on all regions, specify
VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA as the function code and begin with the
start_va_64 argument specified as -1. For subsequent
calls, specify start_va_64 as the sum of the previous
region's start address and length. Call the $GET_REGION_INFO service in
a loop until the condition SS$_NOMOREREG is returned.
Note
Before performing the lookup function, OpenVMS sign-extends the 64-bit
starting address so that it represents a properly formed virtual
address for the CPU.
|
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
buffer_length
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the buffer into which information is returned.
buffer_address_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
varying_arg |
| type: |
unspecified |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a quadword-aligned buffer into
which to return information if the buffer_length
argument is nonzero.
This argument is ignored if the buffer_length argument
is zero.
Table SYS-45 shows the format of the Region Summary Buffer:
Table SYS-45 Region Summary Buffer Format
| Field name |
Meaning |
Field Size (Bytes) |
Field Offset (Decimal) |
|
VA$L_FLAGS
|
Flags used when region was created
|
4
|
8
|
|
VA$L_REGION_PROTECT
|
Create and owner mode of region
|
4
|
12
|
|
VA$Q_REGION_ID
|
Region identifier
|
8
|
0
|
|
VA$PQ_START_VA
|
Starting (lowest) virtual address of region
|
8
|
16
|
|
VA$Q_REGION_SIZE
|
Total length of region
|
8
|
24
|
|
VA$PQ_FIRST_FREE_VA
|
First free virtual address in region
|
8
|
32
|
|
VA$C_REGSUM_LENGTH
|
Length of Region Summary Buffer
|
constant
|
40
|
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF MACRO in
STARLET.MLB define the REGSUM structure.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned longword into
which the service returns the length of the information in bytes.
Description
The Get Information About a Specified Virtual Region service is a
kernel mode service that can be called from any mode. This service gets
the requested information about the specified region or the next region
in a wildcard search. If the returned value of this service is not a
successful condition value, a value cannot be returned in the
memory locations pointed to by the buffer_address_64
or return_length_64 arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $DELETE_REGION_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
buffer_address_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Unrecognized function code.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified in conjunction with the VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID
function code.
|
|
SS$_NOMOREREG
|
No region at a higher address than specified in the
start_va_64 argument, which was specified in
conjunction with the wildcard function code VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
The value specified in the
start_va_64 argument is not within a region and was
specified in conjunction with the function code VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA.
|
$GET_SECURITY
Retrieves the security characteristics of an object.
Format
SYS$GET_SECURITY [clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst]
,[contxt] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$get_security (void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan,
unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int
*acmode);
Arguments
clsnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the object class. The clsnam argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the
object class.
The following is a list of protected object class names:
CAPABILITY
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
DEVICE
FILE
GLXSYS_GLOBAL_SECTION
GLXGRP_GLOBAL_SECTION
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
ICC_ASSOCIATION
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
QUEUE
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
SECURITY_CLASS
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
VOLUME
objnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going
to be retrieved. The objnam argument is the address of
a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the protected
object.
The format of an object name is class specific. The following table
lists object names and describes their formats:
| Object Class |
Object Name Format |
|
CAPABILITY
|
A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR.
|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common
Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service.
|
|
DEVICE
|
Standard device specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
FILE
|
Standard file specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
ICC_ASSOCIATION
|
ICC security object name
node::association_name. The special node name, ICC$::, refers
to entries in the clusterwide registry. For registry entries, the
Access Access Type does not apply.
|
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT)
system service.
|
|
QUEUE
|
Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller
($SNDJBC) system service.
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets.
|
|
SECURITY_CLASS
|
Any class name shown in column 1, or a class name followed by a period
(.) and the template name. Use the DCL command SHOW SECURITY to display
possible template names.
|
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
VOLUME
|
Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted.
|
objhan
| OpenVMS usage: |
object_handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Data structure identifying the object whose associated characteristics
are going to be retrieved. The objhan argument is an
address of a longword containing the object handle. You can use the
objhan argument as an alternative to the
objnam argument; for example, channel number clearly
specifies the file open on the channel and can serve as an object
handle.
The following table shows the format of the object classes:
| Object Class |
Object Handle Format |
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Event flag number
|
|
DEVICE
|
Channel number
|
|
FILE
|
Channel number
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
Resource domain identifier
|
|
VOLUME
|
Channel number
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
flags |
| type: |
mask_longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Mask specifying processing options. The flags argument
is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the
processing option. The flags argument requires the
contxt argument.
The following table describes each flag:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
OSS$M_RELCTX
|
Release the context structure at the completion of this request.
|
|
OSS$M_WLOCK
|
Maintain a write lock on the security profile at the completion of this
request. $GET_SECURITY ignores the flag if the context has already been
established.
|
These symbolic names are defined in the $OSSDEF macro. You construct
the flags argument by specifying the symbolic names of
each flag.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes
is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address
of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword
of 0.
With the item list, the user retrieves the protected object's
characteristics. The user defines which security characteristics to
retrieve. If this argument is not present, only the
flags argument is processed. Without the
itmlst argument, you can only manipulate the
security profile lock or release contxt resources.
The following diagram depicts a single item descriptor:

The following table describes the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the
buffer in which $GET_SECURITY is to write the information. The length
of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item
code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too
small, $GET_SECURITY truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information
that $GET_SECURITY is to return. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes.
A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer in which $GET_SECURITY
is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word in which $GET_SECURITY
writes the length (in bytes) of the information it actually returns.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Value used to maintain the processing context when dealing with a
single protected object across multiple $GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY
calls. Whenever the context value is nonzero, the class name, object
name, or object handle arguments are disregarded. An input value of 0
indicates that a new context should be established.
Because an active context block consumes process memory, be sure to
release the context block by setting the RELCTX flag when the profile
processing is complete. $GET_SECURITY sets the context argument to 0
once the context is released.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Access mode to be used in the object protection check. The
acmode argument is the address of a longword
containing the access mode. The acmode argument
defaults to kernel mode; however, the system compares
acmode with the caller's access mode and uses the
least privileged mode. The access modes are defined in the system macro
$PSLDEF library. HP recommends that this argument be omitted (passed as
zero).
Item Codes The following table provides a summary of item codes that
are valid in an item descriptor in the itmlst
argument. Complete descriptions of each item code are provided after
the table.
| Item Identifier |
Description |
|
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES
|
Returns access bitname translation table for the class.
|
|
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH
|
Returns the size (in bytes) of the access bitname translation table.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
|
Locates an access control entry (ACE).
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
|
Positions to the next ACE.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
|
Locates an ACE of specified type.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE
|
Locates an ACE that either grants or denies access.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_LENGTH
|
Returns the length of the access control list (ACL).
|
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
|
Sets a marker that points to the end of the ACL.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
|
Sets a marker that points to the beginning of the ACL.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_READ
|
Reads the entire ACL.
|
|
OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY
|
Reads an ACE.
|
|
OSS$_CLASS_NAME
|
Returns the full object class name.
|
|
OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE
|
Returns the name of the first template profile of a Security_Class
object.
|
|
OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT
|
Returns the name of the next Security_Class object.
|
|
OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE
|
Returns the name of the next template profile of a Security_Class
object.
|
|
OSS$_OBJECT_NAME
|
Returns the name of the object. The FILE class does not return an
object name.
|
|
OSS$_OWNER
|
Returns the UIC or general identifier of the object's owner.
|
|
OSS$_PROTECTION
|
Returns the protection code of the object.
|
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES
Returns the access name translation table in the buffer pointed to by
the buffer address field of the item descriptor.
The access name translation table is a 32-quadword vector followed by a
variable section containing the access names. Each bit in the vector
represents a single access type. The contents of the quadword is a
string descriptor that corresponds to the ASCII bitname string.
Undefined access types have zero-length names. The return length, if
present, returns the length of the table.
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH
Returns the length of the access name translation table.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
Locates an ACE pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations; for
example, for a deletion or modification of the ACE. If the buffer
address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
Advances the current position to the next ACE in the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
Returns an ACE of a particular type if there is one in the buffer
pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE sets the position
within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations. If the buffer address is
0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE
Returns the ACE in the object's ACL that grants or denies the user
access to that object. OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE returns the ACE found in the
buffer pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_LENGTH
Returns the size (in bytes) of the object's ACL. The buffer address
field points to a longword that receives the size.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
Sets the ACL position to point to the bottom of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
Sets the ACL position to point to the top of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_READ
Returns the portion of the object's ACL to the buffer pointed to by the
buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY
Reads the ACE pointed to by the buffer address.
OSS$_CLASS_NAME
Returns the full object class name.
OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE
Returns the name of the first template profile for the object named in
the objnam argument. This item code is valid only for
security class objects. If the clsnam is not
Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT
Returns the name of the next object. A return length of 0 indicates the
end of the list. This item code is valid only for security class
objects. If the clsnam is not Security_Class,
SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE
Returns the name of the next template. This item code allows you to
step through a list of an object's templates. A return length of 0
indicates the end of the list. This item code is valid only for
security class objects. If the clsnam is not
Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.
OSS_OBJECT_NAME
Returns the name of the object.
OSS$_OWNER
Returns the owner of the object.
OSS$_PROTECTION
Returns the protection code of the object.
Description
The Get Security service returns information about security
characteristics of a selected object. Security characteristics include
such information as the protection code, the owner, and the access
control list (ACL). The security management services, $GET_SECURITY and
$SET_SECURITY, maintain a single master copy of a profile for every
security object in an OpenVMS Cluster environment. They also ensure
that only one process at a time can modify an object's security profile.
There are different ways of identifying which protected object
$GET_SECURITY should process:
- Whenever the contxt argument has a nonzero value,
$GET_SECURITY uses the context to select the object and ignores the
class name, object name, and object handle.
- With some types of objects, such as a file or a device, it is
possible to select an object on the basis of its
objhan and clsnam values.
- If neither a nonzero contxt argument nor an
objhan argument is provided, $GET_SECURITY uses an
object's class name (clsnam) and object name
(objnam) to select the object.
When you call $GET_SECURITY, the service selects the specified
protected object and fetches a local copy of the object's security
profile.
The context for a security management operation can be established
through either $GET_SECURITY or $SET_SECURITY. Whenever the context is
set by one service, the other service can use it, provided the
necessary locks are being held. If you intend to modify the profile,
you must set the write lock flag (OSS$M_WLOCK) when you establish the
context.
There are many situations in which the contxt argument
is essential. By establishing a context for an ACL operation, for
example, a caller can retain an ACL position across calls to
$GET_SECURITY so that a set of ACEs can be read and modified
sequentially. A security context is released by a call to $SET_SECURITY
or $GET_SECURITY that sets the OSS$M_RELCTX flag. Once the context is
released, the user-supplied context longword is set to 0.
Required Access or Privileges
Read or control access to the object is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The parameter cannot be read and the buffer cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
You specified an invalid object, attribute code, or item size.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
The
clsnam and
objnam arguments are not specified, the
clsnam and
objhan arguments are not specified, or the
contxt argument is not specified.
|
|
SS$_INVCLSITM
|
The item code that you specified is not supported for the class.
|
|
SS$_NOCLASS
|
The named security class does not exist.
|
|
SS$_OBJLOCKED
|
The selected object is currently write locked.
|
$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, obtains data from the system alignment fault buffer
if buffered system alignment fault data reporting has been enabled.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA buffer ,buffer_size ,return_size
C Prototype
int sys$get_sys_align_fault_data (void *buffer, int buffer_size, int
*return_size);
Arguments
buffer
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The user buffer in which the alignment fault data is to be stored. The
buffer argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address
of this buffer.
buffer_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The size, in bytes, of the buffer specified by the
buffer argument.
return_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The
return_size argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned longword into which the service returns
the amount of data, in bytes, stored in the buffer. The
return_size argument is set to 0 if there is no data
in the buffer.
Description
The Get System Alignment Fault Data service obtains data from the
system alignment fault buffer if buffered system alignment fault data
reporting has been enabled.
When buffered system alignment fault data reporting is enabled, the
operating system writes each alignment fault into a system-allocated
buffer. The user must poll this buffer periodically to read the data.
The user must call the $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to enable
buffered system alignment fault data reporting. For more information,
see the $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT,
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The buffer named in the
buffer argument is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
|
Alignment fault reporting has not been enabled.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The buffer size is smaller than the minimum defined by the
AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH or the AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH symbol.
|
$GET_USER_CAPABILITY (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, reserves a user capability, indicating to other
processes that the resource is in use.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GET_USER_CAPABILITY cap_num [,select_num] [,select_mask]
[,prev_mask] [,flags]
C Prototype
int sys$get_user_capability (*cap_num, int *select_num, struct
_generic_64 *select_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct
_generic_64 *flags);
Arguments
cap_num
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Capability number to be reserved by the calling kernel thread. This
number can range from 1 to 16 for an explicit request, or the symbolic
constant CAP$K_GET_FREE_CAP can be specified to get the next available
user capability. The cap_num argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of the longword containing the user capability number or
symbolic constant.
select_num
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The number of the user capability selected by the service call. The
select_num argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
longword into which the system writes the user capability number. For
an explicit numeric request, the value returned in this longword will
match that specified in cap_num; otherwise, this cell
contains the next available user capability.
select_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
A quadword bit mask with a single bit position set, reflecting the user
capability selected by the service. The select_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword into which the
system writes the selected user capability bit mask. This bit mask is
the most efficient method for indicating the reserved user capability
with the $CPU_CAPABILITIES and $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES services.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The previous user capability reservation mask before execution of this
service call. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of a quadword into which the service writes a quadword
bit mask specifying the previously reserved user capabilities taken
from the global cell SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability reservation. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines.
The flags argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
At this time, all bits are reserved to HP and must be 0.
Description
The Reserve a User Capability service provides a way for discrete
processes to communicate and synchronize their use of a user capability
in the system. This service uses the global cell
SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS to indicate that a particular user capability
has been reserved. $GET_USER_CAPABILITY can also return the current
reservation state of all user capabilities in the system.
Reservation of a user capability can be made for an explicit number or
for the next available number. The selected user capability is returned
to the caller through a numeric value in select_num or
by a quadword bit mask in select_mask.
This service does not directly enforce unique use of the individual
user capabilities; it simply provides a common informational and
control resource for processes using the other capability scheduling
services. Code threads that do not use this service to verify whether a
user capability is available are still at risk if differing usages
conflict.
Required Privileges
The caller must have both ALTPRI and WORLD privileges to call
$GET_USER_CAPABILITY to reserve a user capability. No privileges are
required if $GET_USER_CAPABILITY is called only to retrieve the current
user capability reservation mask.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY, $CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified, or no
operation was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for the attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCH_OBJECT
|
No more user capabilities are available.
|
|
SS$_OBJECT_EXISTS
|
A specifically requested user capability has already been reserved.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments were presented to the system service.
|
$GOTO_UNWIND (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, unwinds the call stack.
Format
SYS$GOTO_UNWIND target_invo ,target_pc ,[new_r0] ,[new_r1]
C Prototype
int sys$goto_unwind (void *target_invo, void *(*(target_pc)), unsigned
__int64 *new_r0, unsigned __int64 *new_r1);
Arguments
target_invo
| OpenVMS usage: |
invo_handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains a handle for the target
invocation.
If you do not specify the target_invo argument, or if
the handle value is 0, an exit unwind is initiated.
target_pc
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains the address at which execution
should continue in the target invocation.
If the target_pc argument is omitted or the value is
0, a system-defined target PC is assumed and execution resumes at the
location specified at the return address for the call frame of the
target procedure invocation.
new_r0
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved
R0 location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of this
location are then loaded into the processor R0 register at the time
that execution continues in the target invocation.
If the new_r0 argument is omitted, the contents of the
processor R0 register at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND are used.
new_r1
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved R1
location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of the location
are then loaded into the processor R1 register at the time that
execution continues in the target invocation.
If the new_r1 argument is omitted, the contents of the
processor R1 register at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND are used.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service provides the function for a procedure to
unwind the call stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The specified
target_invo,
target_pc,
new_r0, or
new_r1 argument is not accessible.
|
$GOTO_UNWIND_64 (Alpha and I64 only)
On Alpha and I64 systems, unwinds the call stack.
Format
SYS$GOTO_UNWIND target_invo, target_pc, [NewRetVal], [NewRetVal2]
C Prototype
int sys$goto_unwind_64 (void *target_invo_64, void *(*(target_pc_64)),
unsigned_int64 *new_retval, unsigned_int64 *newretval2);
Arguments
target_invo
| OpenVMS usage: |
invo_handle |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains a handle for the target
invocation.
If you do not specify the target_invo argument, or if
the handle value is 0, the effect of the call is undefined.
target_pc
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains the address at which execution
should continue in the target invocation.
If the target_pc argument is omitted or the value is
0, execution resumes at the location specified at the return address
for the call frame of the target procedure invocation.
If the target_invo argument is omitted or the value is
0, the target_pc argument is ignored. In this case, a
system-defined target PC is assumed.
NewRetVal
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved
RetVal location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of this
location are then loaded into RetVal at the time that execution
continues in the target invocation.
If the NewRetVal argument is omitted, the contents of
RetVal at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND_64 are used.
This argument is called New_R0 in SYS$GOTO_UNWIND for
compatibility with Alpha.
NewRet2
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a location that contains the value to place in the saved
RetVal2 location of the mechanism argument vector. The contents of the
location are then loaded into RetVal2 at the time that execution
continues in the target invocation.
If the NewRet2 argument is omitted, the contents of
RetVal2 at the time of the call to $GOTO_UNWIND_64 are used.
This argument is called New_R1 in SYS$GOTO_UNWIND for
compatibility with Alpha.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service provides the function for a procedure to
unwind the call stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$UNWIND
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An invalid address was given.
|
$GRANTID
Adds the specified identifier record to the rights list of the process
or the system.
Format
SYS$GRANTID [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[id] ,[name] ,[prvatr]
C Prototype
int sys$grantid (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64
*id, void *name, unsigned int *prvatr, unsigned int segment);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) number of the process affected when
$GRANTID completes execution. The pidadr argument is
the address of a longword containing the PID of the process to be
affected. You use --1 to indicate the system rights list. When
pidadr is passed, it is also returned; therefore, you
must pass it as a variable rather than a constant. If you specify
neither pidadr nor prcnam, your own
process is used.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name on which $GRANTID operates. The prcnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor containing the
process name. The maximum length of the name is 15 characters. Because
the UIC group number is interpreted as part of the process name, you
must use pidadr to specify the rights list of a
process in a different group. If you specify neither
pidadr nor prcnam, your own process
is used.
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_holder |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identifier and attributes to be granted when $GRANTID completes
execution. The id argument is the address of a
quadword containing the binary identifier code to be granted in the
first longword and the attributes in the second longword.
Use the id argument to modify the attributes of the
identifier.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights database using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
You must specify either id or name.
Because the id argument is returned as well as passed
if you specify name, you must pass it as a variable
rather than a constant in this case.
name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the identifier granted when $GRANTID completes execution. The
name argument is the address of a descriptor pointing
to the name of the identifier. The identifier is granted as it is
created. You must specify either id or
name.
prvatr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Previous attributes of the identifier. The prvatr
argument is the address of a longword used to store the attributes of
the identifier if it was previously present in the rights list. If you
added rather than modified the identifier, prvatr is
ignored.
Description
The Grant Identifier to Process service adds the specified identifier
to the rights list of the process or the system. If the identifier is
already in the rights list, its attributes are modified to those
specified. This service is meant to be used by a privileged subsystem
to alter the access rights profile of a user, based on installation
policy. It is not meant to be used by the general system user.
The result of passing the pidadr or the
prcnam argument, or both, to SYS$GRANTID is summarized
in the following table:
| prcnam |
pidadr |
Result |
|
Omitted
|
Omitted
|
Current process ID is used; process ID is not returned.
|
|
Omitted
|
0
|
Current process ID is used; process ID is returned.
|
|
Omitted
|
Specified
|
Specified process ID is used.
|
|
Specified
|
Omitted
|
Specified process name is used; process ID is not returned.
|
|
Specified
|
0
|
Specified process name is used; process ID is returned.
|
|
Specified
|
Specified
|
Specified process ID is used and process name is ignored.
|
The result of passing the name or the
id argument, or both, to SYS$GRANTID is summarized in
the following table:
| name |
id |
Result |
|
Omitted
|
Omitted
|
Illegal. The INSFARG condition value is returned.
|
|
Omitted
|
Specified
|
Specified identifier value is used.
|
|
Specified
|
Omitted
|
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is not returned.
|
|
Specified
|
0
|
Specified identifier name is used; identifier value is returned.
|
|
Specified
|
Specified
|
Specified identifier value is used and identifier name is ignored.
|
Note that a value of 0 in either of the preceding tables indicates that
the contents of the address specified by the argument is the value 0.
The word omitted indicates that the argument was not supplied.
Required Access or Privileges
You need CMKRNL privilege to invoke this service. In addition, you need
GROUP privilege to modify the rights list of a process in the same
group as the calling process (unless the process has the same UIC as
the calling process). You need WORLD privilege to modify the rights
list of a process outside the caller's group. You need SYSNAM privilege
to modify the system rights list.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB,
$ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL,
$FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER,
$MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully; the rights list did not contain the
specified identifier.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully; the rights list already held the
specified identifier.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
pidadr argument cannot be read or written;
prcnam cannot be read;
id cannot be read or written; the
name cannot be read; or
prvatr cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
You did not specify either the
id or the
name argument.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier name is invalid; the identifier name is longer
than 31 characters, contains an illegal character, or does not contain
at least one nonnumeric character.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
You specified an invalid process name.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
You specified a nonexistent process.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have CMKRNL privilege or is not running in
executive or kernel mode, or the caller lacks GROUP, WORLD, or SYSNAM
privilege as required.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database.
Note that the binary identifier, if given, is not validated against the
rights database.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSNAM
|
The operation requires SYSNAM privilege.
|
|
SS$_RIGHTSFULL
|
The rights list of the process or system is full.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have read access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$HASH_PASSWORD
Applies the hash algorithm you select to an ASCII password string and
returns a quadword hash value that represents the encrypted password.
Format
SYS$HASH_PASSWORD pwd ,alg ,[salt] ,usrnam ,hash
C Prototype
int sys$hash_password (void *pwd, unsigned char alg, unsigned short int
salt, void *usrnam, struct _generic_64 *hash);
Arguments
pwd
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
ASCII password string to be encrypted. The pwd
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
the ASCII password. The password string can contain between 1 and 32
characters and use the uppercase characters A through Z, the numbers 0
through 9, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_).
The caller must validate the password string before calling
$HASH_PASSWORD to ensure that only permitted characters are included.
alg
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_unsigned |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Algorithm used to hash the ASCII password string. The
alg argument is an unsigned byte specifying the hash
algorithm.
The operating system recognizes the following algorithms:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
UAI$K_AD_II
|
Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. This algorithm
was used in releases prior to VAX VMS Version 2.0.
|
|
UAI$C_PURDY
|
Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded
user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used
during VAX VMS Version 2.0 field test.
|
|
UAI$C_PURDY_V
|
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a
variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This
algorithm was used in releases prior to VMS Version 5.4.
|
|
UAI$K_PURDY_S
|
Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a
variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This
algorithm is used to hash all new passwords in VMS Version 5.4 and
later.
|
|
UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM
1
|
Represents the latest encryption algorithm that the operating system
uses to encrypt new passwords. Currently, it equates to UAI$C_PURDY_S.
HP recommends that you use this symbol in source modules because it
always equates with the most recent algorithm.
|
1 The value of this symbol might be changed in future
releases if an additional algorithm is introduced.
Values ranging from 128 to 255 are reserved for customer use; the
constant UAI$K_CUST_ALGORITHM defines the start of this range.
You can use the UAI$_ENCRYPT and UAI$_ENCRYPT2 item codes with the
$GETUAI system service to retrieve the primary and secondary password
hash algorithms for a user.
salt
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Value used to increase the effectiveness of the hash. The
salt argument is an unsigned word containing 16 bits
of data that is used by the hash algorithms when encrypting a password
for the associated user name. The $GETUAI item code UAI$_SALT is used
to retrieve the SALT value for a given user. If you do not specify a
SALT value, $HASH_PASSWORD uses the value of 0.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the user associated with the password. The
usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a character text string containing the user name. The
current password encryption algorithm (UAI$C_PURDY_S) folds the user
name into the ASCII password string to ensure that different users with
the same password produce different hash values. This argument must be
supplied for all calls to $HASH_PASSWORD but is ignored when using the
CRC algorithm (UAI$C_AD_II).
hash
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Output hash value representing the encrypted password. The
hash argument is the address of an unsigned quadword
to which $HASH_PASSWORD writes the output of the hash. If you use the
UAI$C_AD_II algorithm, the second longword of the hash is always set to
0.
Description
The Hash Password service applies the hash algorithm you select to an
ASCII password string and returns a quadword hash value that represents
the encrypted password.
Other OpenVMS password services allow spaces, tabs, and other blank
characters from the user, but they remove those spaces before passing
the string to $HASH_PASSWORD. Before calling $HASH_PASSWORD, all white
space must be removed from the password string to ensure proper
comparison with passwords created by other services.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GETUAI, $SETUAI.
Use $GETUAI to get the values for the salt and
alg arguments. Use $SETUAI to store the resulting hash
using the item codes UAI$_PWD and UAI$_PWD2.
For more information, see the appendix on implementing site-specific
security policies in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input or output buffer descriptors cannot be read or written to by
the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified hash algorithm is unknown or invalid.
|
$HIBER
Allows a process to make itself inactive but to remain known to the
system so that it can be interrupted; for example, to receive ASTs.
Format
SYS$HIBER
C Prototype
int sys$hiber (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Hibernate service allows a process to make itself inactive but to
remain known to the system so that it can be interrupted; for example,
to receive ASTs. A hibernate request is a wait-for-wake-event request.
When you call the Wake Process from Hibernation ($WAKE) service or when
the time specified with the Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service occurs,
the process continues execution at the instruction following the
Hibernate call.
In VAX MACRO, you can call the Hibernate service only by using the
$name_S macro.
A hibernating process can be swapped out of the balance set if it is
not locked into the balance set.
An AST can interrupt the wait state caused by $HIBER if the access mode
at which the AST is to execute is equal to or more privileged than the
access mode from which the hibernate request was issued and the process
is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When the AST service routine completes execution, the system reexecutes
the $HIBER service on behalf of the process. If a wakeup request has
been issued for the process during the execution of the AST service
routine (either by itself or another process), the process resumes
execution. If a wakeup request has not been issued, it continues to
hibernate.
If one or more wakeup requests are issued for the process while it is
not hibernating, the next hibernate call returns immediately; that is,
the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup requests
is maintained.
Although this service has no arguments, a Fortran function reference
must use parentheses to indicate a null argument list, as in the
following example:
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW,
$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,
$WAKE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
$ICC_ACCEPT
Responds to an incoming connection request. This call is used to
complete an ICC connection from the server side.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_ACCEPT conn_handle ,[accept_buf] ,[accept_len] ,[user_context]
,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_accept (unsigned int conn_handle, char * accept_buf,
unsigned int accept_len, unsigned int user_context, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the requested connection.
accept_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of accept data that is sent to the source
of the connection at the completion of the connection process.
accept_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The actual number of bytes in accept_buf to be sent.
user_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) (VAX), quadword (Alpha) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A user-specified value that is subsequently returned on any disconnect
or data events on this connection.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
ICC$M_SYNCH_MODE can be specified to indicate that the data
transmission and reception routines $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_RECEIVE, and
$ICC_REPLY are allowed to return the status SS$_SYNCH in the case of
synchronous completion, and that the AST will not be called.
Description
This service is used by a server to respond to an incoming connection
request. The $ICC_ACCEPT service may only be called after receiving a
connection request AST.
At the completion of the service, the connection is open and data can
be exchanged. Once opened, there is no logical distinction between a
connection opened by a client with the Connect service or a server with
the Accept service.
A server can reject a Connection request by calling the $ICC_REJECT
service.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
$ICC_ACCEPT changes the process BYTLM quota for the length of the
accept_buf parameter, as well as a fixed value for
each potential Receive buffer on the connection. The number of
potential Receive buffers is specified by the MAXFLOWBUFCNT parameter
in the $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
Related Services
$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_CLEARED
|
Remote association closed the link before it was accepted.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
Exceeded BYTCNT/BYTLM.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to accept a connection from a more privileged access mode
than the requested association.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Connection not found or Invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The connection is valid, but the physical link has started to
disconnect.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC
Closes the application's association with ICC.
Format
SYS$ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC assoc_handle
C Prototype
int sys$icc_close_assoc (unsigned int assoc_handle);
Arguments
assoc_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
association_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the association to be closed.
Description
This service closes the application's association with ICC. If multiple
associations are open, only the specified association is closed. When
an association is closed, any active connections on that association
are disconnected. If not explicitly closed by the application,
associations opened in user mode will be closed at image exit;
associations opened in inner modes will be closed at process
termination.
All operations on an association must occur in the access mode at which
the association was opened.
When an association is closed, the entry (if any) in the simple
clusterwide association registry is removed.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
The
assoc_handle was not supplied.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Invalid association handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to close an association from a more privileged access mode
than the requested association.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
$ICC_CONNECT
Establishes a connection to a remote application over an open
association.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECT ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,assoc_handle ,conn_handle
,remote_assoc ,[remote_node] ,[user_context] ,[conn_buf]
,[conn_buf_len] ,[return_buf] ,[return_buf_len] ,[retlen_addr] ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_connect (struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle,
unsigned int *conn_handle, void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node,
unsigned int user_context, char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len,
char *return_buf, unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int
*retlen_addr, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:

Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_BUFFEROVF, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_IVBUFLEN,
SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON, SS$_NOLOGNAM, SS$_NOSUCHOBJ,
SS$_NOSUCHNODE, SS$_PATHLOST, SS$_REJECT, SS$_SSFAIL, SS$_UNREACHABLE,
SS$_WRONGSTATE
The second longword is undefined unless the completion code is
SS$_REJECT. In this case, the application-defined rejection reason code
is supplied by the server when $ICC_REJECT is called.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha), longword (unsigned)
(VAX) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
assoc_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
association_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the association on which the connection is to be opened.
The constant ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE, if used, indicates that the
default association is to be used (and opened if necessary).
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of a longword into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the
connection handle of the created connection on a successful call.
remote_assoc
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor (VAX) |
An ASCII character string (31 characters maximum) specifying the name
of the target application to connect to. Association names are case
sensitive.
remote_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor (VAX) |
The name of the node where the target association resides. A null or
blank string can be used to indicate the local node. If omitted (by
passing zero by value), the simple clusterwide association registry is
to be used. Each node name is a one-to-six character SCS node name. A
comma-delimited list of nodes may be specified, indicating that one is
to be chosen at random.
user_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) (VAX), quadword (Alpha) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A user-specified value to be subsequently returned on any disconnect or
data events on this connection.
conn_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of connection data to be sent to the
target of the connection during the connection process.
conn_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes in conn_buf to be sent.
return_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes in length to receive any incoming
connection accept or reject data returned.
return_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length of the supplied return_buf.
retlen_addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of a longword into which $ICC_CONNECT writes the
actual length (in bytes) of any user accept or reject data returned in
the buffer return_buf.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
ICC$M_SYNCH_MODE can be specified to indicate that the data
transmission and reception routines $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_RECEIVE, and
$ICC_REPLY are allowed to return the status SS$_SYNCH in the case of
synchronous completion, indicating that the AST will not be called.
Description
This service establishes a connection to a remote application over an
open association. Connections must be opened in the same mode as their
association. If the user provides the default association constant
ICC$C_DFLT_ASSOC_HANDLE as its association handle, the default
association will be used; it will be opened if it is not already open.
Multiple connections are possible over a single association. When
completion is signaled by the AST routine, the application must check
the completion status field of the IOS_ICC to determine if the server
has accepted or rejected the connection request. The number of
connections is subject to process BYTLM quota.
At image exit, as a result of closing any open user mode associations,
all user mode connections are disconnected. Inner mode connections are
the responsibility of the inner mode code, but are disconnected at
process termination when inner mode associations are closed.
Connections are only visible to the mode in which they were opened.
A client opens connections with the $ICC_CONNECT service; a server
opens connections with the $ICC_ACCEPT service.
Required Access or Privileges
SYSNAM, or access via ICC Security Object. Refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual
for more information.
Required Quota
$ICC_CONNECT changes the process BYTLM quota for the length of the
conn_buf parameter, as well as a fixed value for each
potential Receive buffer on the connection. The number of potential
Receive buffers is specified by the MAXFLOWBUFCNT parameter in the
$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
If $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC is not called before $ICC_CONNECT, the default value
of MAXFLOWBUFCNT is used (currently 5).
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECTW, $ICC_DISCONNECT,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
Overflow on inbound accept or reject data.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
Not enough AST quota (asynchronous request) or insufficient
BYTLM/BYTCNT.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments were supplied, or required arguments not supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
|
|
SS$_INSFP1POOL
|
Not enough process P1 space available.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The length of the context data or the accept or reject data buffer is
more than 1000 bytes.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Invalid association handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to open a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the requested association.
|
|
SS$_LINKABORT
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_NOLINKS
|
Too many connections open.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGNAM
|
The underlying layers failed to start properly during system
initialization.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
No privilege to connect to the specified association. Connection access
is granted either through an ICC security object or through the SYSNAM
privilege. If no security object exists and the caller lacks the SYSNAM
privilege, SS$_NOPRIV is returned rather than SS$_NOSUCHOBJ.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
The remote association name and/or node was not found.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The target node is not known.
|
|
SS$_PATHLOST
|
The communications link to the target node was lost.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
Insufficient resources at remote node.
|
|
SS$_REJECT
|
The remote association or node rejected the connection request.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
Target node currently unreachable.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_CONNECTW
Establishes a link between two ICC associations.
The $ICC_CONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns
to the caller after the server has either accepted or rejected the
connection request.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_CONNECT service; $ICC_CONNECT
returns to the caller as soon as the connection request has been sent
to the server, without waiting for a response from the server.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_CONNECTW ios_icc, [astadr], [astprm], assoc_handle,
conn_handle, remote_assoc, [remote_node], [user_context], [conn_buf],
[conn_buf_len], [return_buf], [return_buf_len], [retlen_addr], [flags]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_connectw (struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, unsigned int assoc_handle,
unsigned int *conn_handle, void *remote_assoc, void *remote_node,
unsigned int user_context, char *conn_buf, unsigned int conn_buf_len,
char *return_buf, unsigned int return_buf_len, unsigned int
*retlen_addr, unsigned int flags);
$ICC_DISCONNECT
Terminates the specified connection.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECT conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf]
,[disc_buf_len]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnect (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The ID of the connection to be disconnected.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_LINKDISCON, $ICC_REJECT
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha), longword (unsigned)
(VAX) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
disc_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of disconnect data to be sent to the
partner in the connection when notifying it that disconnection is being
initiated. Delivery of this data is not guaranteed.
disc_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes in disc_buf to be sent.
Description
This service must be called in the mode in which the association was
opened.
This service terminates the specified connection. After this service is
called, no further communication is possible over this connection. All
outstanding data transmission and reception functions are terminated
with an error before completion is signaled by calling the AST (if
supplied).
A connection may be disconnected by either party. Proper programming
procedure for network communications strongly recommends that the party
that last received a message initiate the disconnection. If the party
that last sent a message initiates the disconnection, there is no
guarantee that the message was delivered.
Similarly, although this interface provides the ability to send
disconnect data, only noncritical information should be transmitted
with the disconnect data mechanism, because there is no guarantee that
the data will have been received or acted upon by the other party to
the connection.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM (disc_buf)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal successful completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough nonpaged pool.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The length of the disconnect data buffer is more than 1000 bytes.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to disconnect a connection from a more privileged access mode
than the requested connection.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The remote association closed the connection before it was accepted or
rejected.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
$ICC_DISCONNECTW
Terminates a link between two ICC associations.
The $ICC_DISCONNECTW service completes synchronously; that is, it
returns to the caller after the connection has completely finished the
disconnection request.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_DISCONNECT service;
$ICC_DISCONNECT returns to the caller as soon as the disconnection
request has been sent to the transport layer, without waiting for
notification that the disconnection has completed.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_DISCONNECTW conn_handle ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[disc_buf]
,[disc_buf_len]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_disconnectw (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _iosb, *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char * disc_buf,
unsigned int disc_buf_len);
$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC
Declares an application association with ICC.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC assoc_handle ,[assoc_name] ,[logical_name]
,[logical_table] ,[conn_event_rtn] ,[disc_event_rtn] ,[recv_rtn]
,[maxflowbufcnt] ,[prot]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_open_assoc (unsigned int *assoc_handle, void *assoc_name,
void *logical_name, void *logical_table, void
(*conn_event_rtn)(__unknown_params), void
(*disc_event_rtn)(__unknown_params), void
(*recv_rtn)(__unknown_params), unsigned int maxflowbufcnt, unsigned int
prot);
Arguments
assoc_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
association_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of a longword into which $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC writes the
handle assigned to the opened association.
assoc_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor (VAX) |
An ASCII character string of up to 31 characters in length specifying
the name of the application opening the association. Null (0 length),
and empty or blank association names are not allowed. If this argument
is omitted (that is, a zero is passed in by value), it signifies that
the user wants to open the default association. This argument is case
sensitive.
logical_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor (VAX) |
A logical name in a clusterwide logical name table used to maintain the
simple association registry. The logical name represents the name of
the service provided by the application. Logical names are case
sensitive.
logical_table
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical name table |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit descriptor (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor (VAX) |
The table containing the logical name logical_name.
Logical name tables are converted to uppercase. Unless your application
requires an application-specific logical name table, this argument
should be either the default ICC Registry search list (ICC$REGISTRY),
or the default registry table (ICC$REGISTRY_TABLE).
conn_event_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming connect
events. This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No
mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different mode).
You must have a conn_event_rtn to operate as a server.
disc_event_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming disconnect
events. This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No
mechanism is provided for the routine to be called at a different
mode). The arguments, conn_event_rtn, and
disc_event_rtn, may reference the same routine.
recv_rtn
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_routine |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The address of the AST routine to be called for incoming new data
events.
If the user provides this routine, it indicates that the user will
supply a buffer of the size required (specified in an argument to the
recv_rtn at each call) each time one is requested. If
the user supplies this routine, receive calls should only be issued
after receive events arrive and sufficient buffer space has been
allocated to handle the incoming data.
This routine will be called in the mode of the caller. (No mechanism is
provided for the routine to be called at a different mode).
maxflowbufcnt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The maximum number of pending inbound messages (per connection) that
ICC will allow the user before initiating flow control. A message is
pending if it is being held within ICC but no receive call(s) are
outstanding from the user.
Default = 5 (Pass 0 to get the default)
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This argument is ignored for non-server applications.
The default protection scheme for this association is as follows:
0 - access for everyone (default)
1 - stops WORLD access
2 - stops both WORLD and GROUP access
Advanced access control is provided by ICC Security objects. Refer to
the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual for information on ICC system management and security.
Description
This service declares an application association with ICC. Servers must
make this call to declare or register their name and to indicate their
readiness to receive incoming connections. Although a client is
permitted to call this routine, it is unnecessary for simple
applications. A client application that wishes to be notified of
disconnection events or Receive Data events must call the
$ICC_OPEN_ASSOC service.
A client can open a connection without specifying an open association;
this automatically creates a default association name of
ICC$PID_nnnnnnnn (where nnnnnnnn is a character representation of the
Process ID).
NETMBX privilege is required to open any association.
The association name space is a controlled resource. Refer to the
HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual for information on managing this resource.
An attempt to open an association with a name not authorized as
described in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual will fail with the error SS$_NOPRIV
returned to the caller. In addition to making entries in the system's
local association name space, a call to $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC may also make
an entry in a simple clusterwide registry of active associations.
An association may only be accessed from the mode in which it was
opened. Inner modes are prevented from using the default association.
An application can open any number of associations subject to available
process BYTLM quota. Currently, there is a systemwide limit of 512 open
associations. There is no limit imposed clusterwide.
Description of User-Supplied Routines (ASTs)
When opening an association, the user may optionally supply a
connect/disconnect AST and/or a Data Event AST. These routines will be
used for all connections established over the specified association. In
addition, for any of the asynchronous services (those provided with
both an immediate return and a "W" form), a completion AST may be
supplied by the user. This section describes these ASTs.
1. Connect and Disconnect AST
The user chooses the name of this routine and supplies the procedure
name as an argument to the Open Association service. Seven arguments
will be passed to the user.
The first argument notifies the user whether this is an incoming new
connection or a disconnection of an existing connection. The second
identifies the connection. The third and fourth provide access to
incoming connect or disconnect data (if any) sent by the cooperating
application. The fifth argument provides the number of bytes available
for any optional Accept or Reject data (in the case of a connect
request) or the disconnect reason supplied by the cooperating
application (if any).
For connect events, the sixth and seventh arguments are the EPID and
user name of the process requesting the connect, respectively.
The user has the choice of using and declaring a common routine or
separate routines as specified when calling $OPEN_ASSOCIATION.
Format
ConnDiscRtn event_type ,conn_handle ,data_len ,data_bfr ,P5 ,P6 ,P7
|
C Prototype
void ConDiscRtn (unsigned int event_type, unsigned int conn_handle,
unsigned int data_len, char *data_bfr,
unsigned int P5, unsigned int P6, char *P7);
|
Arguments
event_type
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
This field will contain a code describing the type of event. The
possible event codes are defined in ICCDEF:
ICC$C_EV_CONNECT - Connection event
ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT - Disconnection event
|
conn_handle
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The handle of the connection associated with the event.
data_len
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The length (in bytes) of the incoming data. This value specifies the
length of the buffer data_bfr, and will be between 0
and 1000, with zero indicating no data.
data_bfr
Type: character-coded text string
Access: read only
Mechanism: by 32-bit or 64-bit value (Alpha)
by 32-bit value (VAX)
|
The 32-bit address of the P1-space buffer containing the data, or zero
if no data is available. The length of this buffer is specified by the
argument data_len.
Upon return from the AST, the address of the data is no longer valid.
An application wishing to reference the Connection or Disconnection
data after Return must copy the data from the supplied buffer to
storage owned by the application.
P5
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The usage of this argument is dependent on the specified event type
code (event_type).
For connect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_CONNECT), this
argument contains the length (in bytes) of the buffer available for a
reply.
For disconnect events
(event_type=ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT), this argument
contains the user-defined disconnect reason/status from the remote
partner.
P6
Type: longword (unsigned) (VAX), quadword (Alpha)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The usage of this argument is dependent on the specified event type
code (event_type).
For connect events (event_type=ICC$C_EV_CONNECT), this
argument contains the EPID of the process requesting the connection,
passed by value.
For disconnect events
(event_type=ICC$C_EV_DISCONNECT), this argument
contains the user-defined user_context supplied when
the connection was opened. For a client, the
user_context is that supplied to the $ICC_CONNECT
call. For a server, it is the value supplied to $ICC_ACCEPT.
P7
Type: character-coded text string
Access: read only
Mechanism: by reference
|
For connect events: Username, passed by reference (to P1 space buffer)
as a 12-character, space-filled string.
The application must copy this information to local storage before
exiting from the connect routine.
For disconnect events, this argument is zero (0).
2. Data Event Routine
This routine, if supplied by the user when opening the association,
allows the user to be notified of any pending data events over any
connections subsequently opened over that association.
If the user has supplied this routine, the Receive service must only be
called in response to incoming data events signaled by this routine,
and must be called with a buffer large enough to handle the message
size specified.
Use of this routine obligates the user to allocate buffers up to the
size requested by the cooperating application. The only recovery
provided at this time if a sufficiently large buffer cannot be
allocated is to disconnect the connection. Failure to issue a receive
call or disconnect may stall all further communication on this
connection.
Format
DataEventRtn message_size ,conn_handle ,user_context
|
C Prototype
void DataEventRtn (unsigned int message_size, unsigned int conn_handle,
unsigned int user_context);
|
Arguments
message_size
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
This field will contain the number of bytes in the pending data event.
conn_handle
Type: longword (unsigned)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The handle of the connection associated with the event. This value
should be used as the conn_handle argument to
$ICC_RECEIVE.
user_context
Type: longword (unsigned) (VAX), quadword (Alpha)
Access: read only
Mechanism: by value
|
The user-defined user_context supplied when the
connection was opened. For a client, the user context is that supplied
to the $ICC_CONNECT call. For a server, it is the value supplied to
$ICC_ACCEPT.
3. Completion ASTs
Completion ASTs may be supplied to the $ICC_CONNECT[W],
$ICC_DISCONNECT[W], $ICC_TRANSMIT[W], $ICC_RECEIVE[W],
$ICC_TRANSCEIVE[W], and $ICC_REPLY[W] services. In all cases, they are
called at the completion of the requested operation, with the single
argument, the AST parameter supplied when the original service was
called, passed by value.
Completion ASTs are not called if the service returns an error prior to
initiating the operation. $ICC_CONNECT and $ICC_ACCEPT accept the flag
ICC$V_SYNCH_MODE which indicates that the routines $ICC_TRANSMIT[W],
$ICC_RECEIVE[W], and $ICC_REPLY[W] are permitted to return the status
SS$_SYNCH, which will indicate that completion has already occurred and
the AST will not be called.
Required Access or Privileges
Refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual for more information.
Required Quota
BYTCNT, BYTLM
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_RECEIVE, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
Specified association name is already registered (already exists), or
default association is already open.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
One or more process quotas has been exceeded (probably BYTCNT/BYTLM).
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Not enough system resources or process virtual memory available.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempt to open default association from other than user mode.
|
|
SS$_NOLINKS
|
Too many associations open for this process.
|
|
SS$_NONETMBX
|
Request requires NETMBX privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
No privilege for association name access or logical name table access
if using the Registry.
|
|
SS$_SSFAIL
|
Transport association name table is full, systemwide.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments were specified.
Any failures from the system services: $ENQ, $DEQ, $CRELNM,
$TRNLNM.
|
$ICC_RECEIVE
Receives a single message over a connection.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_RECEIVE conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,recv_buf
,recv_buf_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_receive (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *recv_buf,
unsigned int recv_buf_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the fully established connection.
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
four longwords (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:
Completion codes:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKDISCON, SS$_BUFOVL,
SS$_ACCVIO
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha) |
| access: |
longword (unsigned) (VAX) |
| mechanism: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
recv_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of the buffer to receive the incoming data. The length
of this buffer is specified by the argument
recv_buf_len.
recv_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length (in bytes) of the buffer available to hold the incoming
data. This value specifies the length of the buffer
recv_buf.
IOS_ICC Arguments:
recvlen (output)
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc.
$ICC_RECEIVE writes the actual length of the incoming data message
received from the target application (in bytes) into offset
ios_icc$l_rcv_len of the ios_icc.
request_handle (output)
| OpenVMS usage: |
request_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc.
$ICC_RECEIVE writes the Request/Response handle into offset
ios_icc$l_req_handle of the ios_icc.
The request_handle argument is nonzero if the
application is expected to reply to this message.
reply_len (output)
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is returned in the ios_icc. The
$ICC_RECEIVE service writes the maximum length (in bytes) of the
expected Reply message into offset ios_icc$l_reply_len
of the ios_icc, if request_handle is
nonzero.
Description
This service receives a single message over a connection. If a Request
ID is returned at completion, the partner has used a Transceive system
service and requires data to be returned with a Reply service.
For efficiency reasons, the number of parameters on this routine has
been limited to six parameters. Three additional values are returned by
the ios_icc data structure.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVEW,
$ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
Insufficient byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
One or more process quotas has been exceeded.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments supplied.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the mode in which it was opened.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The connection has been disconnected.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value
indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if
specified, will not be called.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_RECEIVEW
The Intra-Cluster Communications Receive and Wait service queues a
receive request to the specified connection.
The $ICC_RECEIVEW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns
to the caller with data.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_RECEIVE service; $ICC_RECEIVE
returns to the caller as soon as the receive request is queued, without
waiting for data on the connection.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_RECEIVEW conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,recv_buf
,recv_buf_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_receivew (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *recv_buf,
unsigned int recv_buf_len);
$ICC_REJECT
Refuses a connection request.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REJECT conn_handle, [reject_buf], [reject_buf_len], [reason]
C Prototype
int sys$icc_reject (unsigned int conn_handle, char * reject_buf,
unsigned int reject_buf_len, unsigned int reason);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the requested connection.
reject_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
A buffer of up to 1000 bytes of reject data to be sent to the source of
the connection at the completion of the rejection process.
reject_buf_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes in reject_buf to be sent.
reason
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
User-specified reject reason code to be supplied to the remote
application.
Default = SS$_REJECT
Description
This service is used by a server to refuse an incoming connection
request. The $ICC_REJECT service may only be called after receiving a
connection request AST. After the completion of the service, the client
is notified that the connection was not opened.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE,
$ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_CLEARED
|
Remote association closed the link before it was rejected.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments supplied.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Connection not found or Invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
The transport layer has initiated disconnect before the Reject could be
sent to the requester.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is already open and cannot be rejected. To close the
connection, call $ICC_DISCONNECT.
|
$ICC_REPLY
Sends a single message over a connection. This service is used in
response to the reception of a Request Handle in a previous
$ICC_RECEIVE system service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REPLY conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,reply_buf
,reply_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_reply (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *reply_buf, unsigned
int reply_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the fully established connection.
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:

Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha), longword (unsigned)
(VAX) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
reply_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of the buffer containing the reply data to be sent.
The length of this buffer is specified by the argument
reply_len.
reply_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length (in bytes) of the reply data to be sent over the connection.
This value specifies the length of the buffer
reply_buf. ICC segments larger buffers internally.
The maximum Reply length is the smaller of the Reply buffer size
supplied in the $ICC_RECEIVE call, or 1MB.
IOS_ICC Argument:
request_handle (input)
| OpenVMS usage: |
request_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
Request/Response handle from the received Transceive request is placed
at offset ios_icc$l_replyto_handle of the
ios_icc.
Description
This service is almost identical to the $ICC_TRANSMIT system service in
that it sends a single message over a connection. The only difference
is that it is used in response to the reception of a Request Handle in
a previous Receive Data system service.
When completion is signaled by calling the AST (if supplied), the data
has been delivered to the communications system, but not necessarily to
the application at the other end of the connection. The user can reuse
the buffer after completion has been signaled.
Alternatively, if the synchronous completion option was requested at
connection time, the service may return the optional success status,
SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, completion has occurred, and no
AST will be delivered.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM (for Reply buffer)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE,
$ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
Insufficient byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments supplied.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the mode in which it was opened.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
An Incoming disconnect event is already in progress.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The
request_handle is invalid.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value
indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if
specified, will not be called.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_REPLYW
The Intra-Cluster Communications Reply and Wait service transmits a
single message over a connection in response to a $ICC_TRANSCEIVE[W]
request.
The $ICC_REPLYW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller when the underlying transport layer has released use of the
reply buffer.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_REPLY service; $ICC_REPLY
returns to the caller as soon as the transmission request has been
queued to the transport layer, without waiting for notification that
the transport layer has released control of the data buffer.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_REPLYW conn_handle, ios_icc, [astadr], [astprm], reply_buf,
reply_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_replyw (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *reply_buf,
unsigned int reply_len);
$ICC_TRANSCEIVE
Sends a single message over a connection and then waits for a reply.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSCEIVE conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf
,send_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_transceive (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the fully established (open) connection.
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
five longwords (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_BUFOVFL, SS$_LINKABORT,
SS$_LINKDISCON
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha), longword (unsigned)
(VAX) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
send_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of the buffer containing the data to be sent. The
length of this buffer is specified by the argument
send_len.
send_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer size |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length (in bytes) of the data to be sent over the connection. This
value specifies the length of the buffer send_buf.
IOS_ICC Arguments:
returned_data_len (output)
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
$ICC_TRANSCEIVE service writes the actual length (in bytes) of the
reply data received into offset ios_icc$l_txrcv_len of
the ios_icc. This value represents how much data in
reply_buf was returned by the target application.
reply_buf (input)
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on
VAX systems) of the buffer available to receive the incoming reply
message is placed in offset ios_icc$a_reply_buffer of
the ios_icc.
reply_buf_len (input)
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_size |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
This parameter is passed through the ios_icc. The
length (in bytes) of the buffer to receive the reply message. This
value specifies the length of the buffer reply_buf.
This value is placed in offset ios_icc$l_txreply_len
of the ios_icc.
Description
This service sends a single message over a connection and then waits
for a reply. When completion is signaled by calling the AST (if
supplied), the data has been delivered to the application at the other
end of the connection and that application has delivered a reply, now
present in the reply buffer. The user can reuse the send and reply
buffers after completion.
For efficiency reasons, the number of parameters on this routine has
been limited to six parameters. Three additional parameters are passed
by the ios_icc data structure.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM (Send and Reply buffers)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE,
$ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW,
$ICC_TRANSMIT, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
Insufficient byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments were supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient process or system memory to complete the request.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the mode in which it was opened.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
An Incoming disconnect event is in progress.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value
indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if
specified, will not be called.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments were specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in wrong state for request.
|
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW
Sends a single message over a connection and waits for a reply.
The $ICC_TRANSCEIVEW service completes synchronously; that is, it
returns to the caller when the data from the reply is available.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_TRANSCEIVE service;
$ICC_TRANSCEIVE returns to the caller when the transmit portion of the
tranceive request has been queued to the transport layer, but without
waiting for notification that the transport layer has released control
of the data buffer or for the reply data from the receiving end of the
connection.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW
conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf ,send_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_transceivew (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc
*ios_icc, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char
*send_buf, unsigned int send_len);
$ICC_TRANSMIT
Sends a single message over a connection.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSMIT conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf
,send_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_transmit (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);
Arguments
conn_handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
connection_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The handle of the fully established (open) connection to send the data
over.
ios_icc
| OpenVMS usage: |
ios_status_block |
| type: |
structure IOS_ICC |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block:
Completion status values:
SS$_NORMAL, SS$_EXQUOTA, SS$_INSFMEM, SS$_LINKABORT, SS$_LINKDISCON
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure_entry_mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit linkage reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The AST routine to be executed when the operation completes.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) (Alpha), longword (unsigned)
(VAX) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 64-bit value (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit value (VAX) |
The parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
send_buf
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte_stream |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 32-bit or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) of the buffer containing the data to be sent. The
length of this buffer is specified by the argument
send_len.
send_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer_length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The length (in bytes) of the data to be sent over the connection. This
value specifies the length of the buffer send_buf. The
maximum transmission size is 1MB.
Description
This service sends a single message over a connection. When completion
is signalled by calling the AST (if supplied), the data has been
delivered to the communications system, but not necessarily to the
system or application at the other end of the connection. After
completion, the user can reuse the buffer.
Alternatively, if the synchronous completion option was requested at
connection time, the service may return the optional success status,
SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, completion has occurred, and no
AST will be delivered.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
BYTLM (send_buf)
Related Services
$ICC_ACCEPT, $ICC_CLOSE_ASSOC, $ICC_CONNECT, $ICC_CONNECTW,
$ICC_DISCONNECT, $ICC_DISCONNECTW, $ICC_OPEN_ASSOC, $ICC_RECEIVE,
$ICC_RECEIVEW, $ICC_REJECT, $ICC_REPLY, $ICC_REPLYW, $ICC_TRANSCEIVE,
$ICC_TRANSCEIVEW, $ICC_TRANSMITW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal completion.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation on parameter.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Bad parameter value specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
Insufficient byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Too few arguments were supplied.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient process or system memory to complete the request.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
Unknown connection specified or invalid connection handle.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
Attempted to use a connection from a more privileged access mode than
the mode in which it was opened.
|
|
SS$_LINKDISCON
|
An Incoming disconnect event is in progress.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
If synchronous mode was requested at connection time, this return value
indicates that completion has already occurred and the AST routine, if
specified, will not be called.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments were specified.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
Connection is in the wrong state for the request.
|
$ICC_TRANSMITW
Sends a single message over a connection.
The $ICC_TRANSMITW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns
to the caller when the underlying transport layer has released use of
the Transmit buffer. This does not mean that the data has been received
by the partner application.
For asynchronous completion, use the $ICC_TRANSMIT service. The
$ICC_TRANSMIT service returns to the caller as soon as the transmission
request has been queued to the transport layer, without waiting for
notification that the transport layer has released control of the data
buffer.
On Alpha, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ICC_TRANSMITW conn_handle ,ios_icc ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,send_buf
,send_len
C Prototype
sys$icc_transmitw (unsigned int conn_handle, struct _ios_icc *ios_icc,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, char *send_buf,
unsigned int send_len);
$IDTOASC
Translates the specified identifier value to its identifier name.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IDTOASC id ,[namlen] ,[nambuf] ,[resid] ,[attrib] ,[contxt]
C Prototype
int sys$idtoasc (unsigned int id, unsigned short int *namlen, void
*nambuf, unsigned int *resid, unsigned int *attrib, unsigned int
*contxt);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary identifier value translated by $IDTOASC. The id
argument is a longword containing the binary value of the identifier.
To determine the identifier names of all identifiers in the rights
database, you specify id as --1 and call $IDTOASC
repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. The
identifiers are returned in alphabetical order.
namlen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Number of characters in the identifier name translated by $IDTOASC. The
namlen argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a word containing
the length of the identifier name written to nambuf.
nambuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Identifier name text string returned when $IDTOASC completes the
translation. The nambuf argument is the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a
descriptor pointing to the buffer in which the identifier name is
written.
resid
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Identifier value of the identifier name returned in
nambuf. The resid argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) of a longword containing the 32-bit code of the identifier.
attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Mask of attributes associated with the identifier returned in
resid. The attrib argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) of a longword containing the attribute mask.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN
|
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated, either from
binary to ASCII or vice versa, but prevents unauthorized users from
translating the identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Context value used when repeatedly calling $IDTOASC. The
contxt argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a longword used
while $IDTOASC searches for all identifiers. The context value must be
initialized to the value 0, and the resulting context of each call to
$IDTOASC must be presented to each subsequent call. After
contxt is passed to $IDTOASC, you must not modify its
value.
Description
The Translate Identifier to Identifier Name service translates the
specified binary identifier value to an identifier name. While the
primary purpose of this service is to translate the specified
identifier to its name, you can also use it to find all identifiers in
the rights database. Owner or read access to the rights database is
required. To determine all the identifiers, call $IDTOASC repeatedly
until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. When SS$_NOSUCHID is
returned, $IDTOASC has returned all the identifiers, cleared the
context value, and deallocated the record stream.
If you complete your calls to $IDTOASC before SS$_NOSUCHID is returned,
use $FINISH_RDB to clear the context value and deallocate the record
stream.
When you use wildcards with this service, the records are returned in
identifier name order.
Required Access or Privileges
None, unless the id argument is NAME_HIDDEN, in which
case you must hold the identifier or have read access to the rights
list.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB,
$ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL,
$FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $MOD_HOLDER,
$MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
namlen,
nambuf,
resid,
attrib, or
contxt argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
The contents of the context longword are not valid.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
SS$_NOIOCHAN
|
No more rights database context streams are available.
|
|
SS$_NORIGHTSDB
|
The rights database does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database, or
the entire rights database has been searched if the ID is --1.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file that you access with
OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated
with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status
codes, refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
|