 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, modifies the software IEEE floating-point control
register and, optionally, returns the previous register value.
The service provides the mechanism to set the specified bits in the
IEEE floating-point control register, to clear the specified bits in
the register, and to swap the values of the register.
Format
SYS$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL [clrmsk] ,[setmsk] ,[prvmsk]
C Prototype
int sys$ieee_set_fp_control (struct _ieee *clrmsk, struct _ieee
*setmsk, struct _ieee *prvmsk);
Arguments
clrmsk
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a quadword bit mask to be cleared in the IEEE floating-point
control register.
The $IEEEDEF macro defines symbols for the floating-point control
register. Table SYS-46 shows the symbols, their corresponding masks,
and their meaning:
Table SYS-46 Format of the IEEE Floating-Point Control Register (Alpha Only)
| Symbol |
Mask |
Meaning |
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INV
|
2
|
Invalid operation
|
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_DZE
|
4
|
Divide by 0
|
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_OVF
|
8
|
Overflow
|
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_UNF
|
10
|
Underflow
|
|
IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INE
|
20
|
Inexact
|
|
IEEE$M_MAP_UMZ
|
4000
|
Underflows are mapped to 0.0
|
|
IEEE$M_INHERIT
|
8000
|
Inherit FP state on thread create
|
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_INV
|
20000
|
Invalid operation
|
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_DZE
|
40000
|
Divide by 0
|
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_OVF
|
80000
|
Overflow
|
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_UNF
|
100000
|
Underflow
|
|
IEEE$M_STATUS_INE
|
200000
|
Inexact
|
setmsk
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a quadword bit mask to be set in the IEEE floating-point
control register.
Table SYS-46 shows the format of the IEEE floating-point control
register.
prvmsk
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a quadword to receive the previous value of the IEEE
floating-point control register.
Description
The Set IEEE Floating-Point Control Register service updates the IEEE
floating-point control register, maintained by the operating system,
with the values supplied by the calling program.
The following steps are used to update the register:
- If the prvmsk argument is specified,
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL first reads the previous value of the IEEE
floating-point control register.
- If the clrmsk argument is specified,
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then clears the specified bit masks in the
clrmsk argument.
- If the setmsk argument is specified,
$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then sets the specified bit masks in the
setmsk argument.
A program can swap the IEEE floating-point control register (that is,
save the old value and specify a new value) by specifying the following:
- The clrmsk argument with the address of a quadword
of all 1s
- The setmsk argument with the address of a quadword
that holds the new register value
- The prvmsk argument with the address of a quadword
to save the old register value
Required Access or Privilege
None
Required Quota
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The specified argument cannot be read or cannot be written.
|
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, initializes system process alignment fault reporting.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT match_table ,buffer_size ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$init_sys_align_fault_report (void *match_table, int
buffer_size, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
match_table
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
Describes the system fault match table. The
match_table argument is the 32-bit or 64-bit virtual
address of an array of longwords describing the system fault match
table. The first longword is the number of match entries; the remaining
longwords are the match entries.
The match table is used to restrict the number of alignment faults
reported. Each entry in the table is a bit mask divided into three
groups: mode bits, program counter (PC) space bits, and virtual address
(VA) space bits.
The following table lists the symbols that can be used to define these
bits:
| Bit Type |
Symbols |
|
|
Mode bits
|
AME$M_KERNEL_MODE
|
Kernel mode
|
|
|
AME$M_EXEC_MODE
|
Executive mode
|
|
|
AME$M_SUPER_MODE
|
Supervisor mode
|
|
|
AME$M_USER_MODE
|
User mode
|
|
Program counter bits
|
AME$M_USER_PC
|
PC in User space
|
|
|
AME$M_SYSTEM_PC
|
PC in System space
|
|
Virtual address bits
|
AME$M_SYSTEM_VA
|
VA in System space
|
|
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P0
|
VA in User P0 space
|
|
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P1
|
VA in User P1 space
|
|
|
AME$M_USER_VA_P2
|
VA in User P2 space
|
The following diagram illustrates the data structure of the match table:
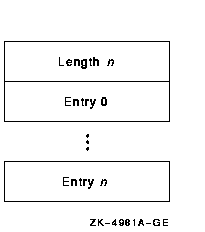
When an alignment fault occurs, a fault bit mask is created with one
bit set in each group. The alignment fault handler then compares this
fault bit mask against each entry in the match table. If the fault bit
mask is a subset of an entry in the match table, the fault is reported.
buffer_size
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The number of bytes to allocate, from nonpaged pool, to save the
alignment fault data. The buffer you allocate must be sufficient to
accommodate one data item of the size specified in the
flags argument.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag bit mask specifying options for the $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA
operation.
If the flags argument is 0, data items of size
AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH will be returned. If the flags
argument is AFR$M_USER_INFO, the user name and image name are added to
each data item and they are returned in a buffer of length
AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH. If the user name and image name are not
available, an empty string is returned in the data item.
Description
The Initialize System Alignment Fault Reporting service initializes
system alignment fault reporting.
System alignment faults must be written to a buffer. The following
diagram illustrates the format in which system alignment fault data is
saved in the buffer:
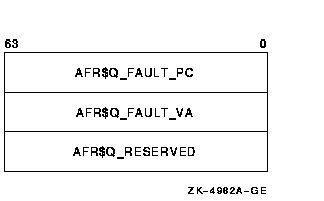
Only one user on a system can initialize system alignment fault
reporting at any time. Subsequent calls will return SS$_AFR_ENABLED.
System alignment fault reporting is disabled when the program that
called the service completes.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT,
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The match table is not read accessible.
|
|
SS$_AFR_ENABLED
|
The service was already called.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
buffer_size argument is less than the minimum size
required. If the
flags argument is 0, AFR$K_VMS_LENGTH + 32 is
required. If the
flags argument is 1, AFR$K_EXTENDED_LENGTH + 32 is
required.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have CMKRNL privilege.
|
$INIT_VOL
Formats a disk or magnetic tape volume and writes a label on the
volume. At the end of initialization, the disk is empty except for the
system files containing the structure information. All former contents
of the volume are lost.
Format
SYS$INIT_VOL devnam, volnam [,itmlst]
C Prototype
int sys$init_vol (void *devnam, void *volnam, void *itmlst);
Arguments
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the device on which the volume is physically mounted. The
descriptor must point to the device name, a character string of 1 to 64
characters. The device name can be a physical device name or a logical
name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical name.
The device does not have to be currently allocated; however, allocating
the device before initializing it is recommended.
volnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Identification to be encoded on the volume. The descriptor must point
to the volume name, a character string of 1 to 12 characters. For a
disk volume name, you can specify a maximum of 12 ANSI characters; for
a magnetic tape volume name, you can specify a maximum of 6 ANSI
"a" characters.
Any valid ANSI "a" characters can be used; these include
numbers, uppercase letters, and any one of the following
nonalphanumeric characters:
! " % ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = >
HP strongly recommends that a disk volume name consist of only
alphanumeric characters, dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and hyphens
(-).
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying options that can be used when initializing the
volume. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each of which describes one option. The list of
item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer that supplies the
information $INIT_VOL needs to process the specific item code. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item descriptor.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing an option for the initialize operation. These codes
are defined by the $INITDEF macro. There are three types of item codes:
|
|
|
|
Boolean item code
|
Boolean item codes specify a true or false value. The form INIT$_
code specifies a true value and the form INIT$_NO_
code specifies a false value. For Boolean item codes, the
buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be
0.
|
|
Symbolic value item code
|
Symbolic value item codes specify one of a specified range of possible
choices. The buffer length and buffer address fields of the item
descriptor must be 0.
|
|
Input value item code
|
Input value item codes specify a value to be used by $INIT_VOL. The
buffer length and buffer address fields of the item descriptor must be
nonzero.
|
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that supplies
information to $INIT_VOL.
|
|
Return length address
|
This field is not used.
|
Item Codes
INIT$_ACCESSED
An input item code that specifies the number of directories allowed in
system space on the volume.
You must specify an integer between 0 and 255 in the input buffer. The
default value is 3.
The INIT$_ACCESSED item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure
Level 1 disks.
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN
An input item code that enables $INIT_VOL to mark bad blocks on the
volume; no data is written to those faulty areas. INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN
specifies faulty areas on the volume by logical block number and block
count.
The buffer from which $INIT_VOL reads the option information contains
an array of quadwords containing information in the following format:
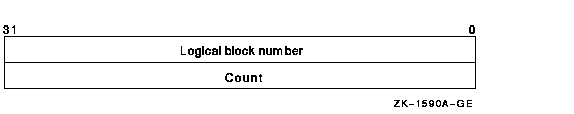
The following table describes the information to be specified for
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN:
| Field |
Symbol Name |
Description |
|
Logical block number
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_LBN
|
Specifies the logical block number of the first block to be marked as
allocated.
|
|
Count
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_COUNT
|
Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated. This range begins with
the first block, as specified in INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_LBN.
|
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 5 and 3, INIT_VOL
starts at logical block number 5 and allocates 3 blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length
field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except
disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block
data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter
EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for
the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code is
necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the
volume's bad block data. For more information, refer to the
OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual (available on the Documentation CD-ROM).
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC
An input item code that specifies faulty areas on the volume by sector,
track, cylinder, and block count. $INIT_VOL marks the bad blocks as
allocated; no data is written to them.
The input buffer must contain an array of octawords containing
information in the following format:
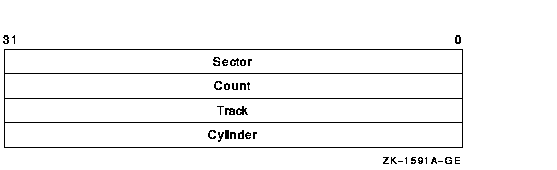
The following table describes the information to be specified for
INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC:
| Field |
Symbol Name |
Description |
|
Sector
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_SECTOR
|
Specifies the sector number of the first block to be marked as
allocated.
|
|
Count
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_COUNT
|
Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated.
|
|
Track
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_TRACK
|
Specifies the track number of the first block to be marked as allocated.
|
|
Cylinder
|
INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_CYLINDER
|
Specifies the cylinder number of the first block to be marked as
allocated.
|
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 12, 3, 1, and 2,
INIT_VOL starts at sector 12, track 1, cylinder 2, and allocates 3
blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length
field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except
disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block
data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter
EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for
the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code is
necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the
volume's bad block data. For more information, refer to the
OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual.
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE
An input item code that specifies the minimum allocation unit in
blocks. The input buffer must contain a longword value. The maximum
size that can be specified for a volume is one-hundredth the size of
the volume; the minimum size is calculated with the following formula:
volume size in blocks/(255 * 4096)
The INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk
Structure Level 2 disks (for Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks,
the cluster size is 1). For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks,
the cluster size default depends on the disk capacity.
- Disks that are 50,000 blocks or larger have a default cluster size
of 3.
- Disks smaller than 50,000 blocks have a default value of 1.
INIT$_COMPACTION
INIT$_NO_COMPACTION---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data compaction should be
performed when writing the volume.
The INIT$_COMPACTION item code applies only to TA90 drives.
INIT$_DENSITY
A symbolic item code that specifies the density value for magnetic
tapes and diskettes.
For magnetic tape volumes, the INIT$_DENSITY item code specifies the
density.
The DENSITY item code is dependent on the type of tape device. If a
tape device is seen as capable of using the MT3 density codes the
buffer for MNT$_DENSITY item code must contain a longword with one of
the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET (MT3$K_TK50,
MT3$K_3480, M53$K_DSDLT, MT3$K_AIT2 and so on). Refer to the
MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
If the device does not support MT3 densities, the buffer specifies the
density in bytes per inch (bpi) at which the magnetic tape is written.
The following are possible symbolic values for tapes:
- INIT$K_DENSITY_800_BPI
- INIT$K_DENSITY_1600_BPI
- INIT$K_DENSITY_6250_BPI
The specified density value must be supported by the drive. If you do
not specify a density item code for a blank magnetic tape, the system
uses a default density of the highest value allowed by the tape drive.
If the drive allows 6250, 1600, and 800 bpi operation, the default
density is 6250. If the drive allows only 1600 and 800 bpi operation,
the default density is 1600. If you do not specify a density item code
for a magnetic tape that has been previously written, the system uses
the previously set volume density.
For diskettes, the INIT$_DENSITY item code specifies how the diskette
is to be formatted. Possible symbolic values for diskettes are as
follows:
- INIT$K_DENSITY_SINGLE_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_DOUBLE_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_DD_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_HD_DISK
For disk volumes that are to be initialized on RX02, RX23, or RX33
diskette drives, the following values specify how the disk is to be
formatted:
- INIT$K_DENSITY_SINGLE_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_DOUBLE_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_DD_DISK
- INIT$K_DENSITY_HD_DISK
Diskettes are initialized as follows:
- RX23 diskettes---DD or HD density
- RX33 diskettes---double density only
- RX02 dual-density diskette drives---single or double density
If you do not specify a density item code for a disk, the system leaves
the volume at the density at which it was last formatted. RX02 disks
purchased from HP are formatted in single density.
Note
Disks formatted in double density cannot be read or written by the
console block storage device (an RX01 drive) of a VAX-11/780 processor
until they have been reformatted in single density.
|
INIT$_DIRECTORIES
An input item code that specifies the number of entries to preallocate
for user directories. The input buffer must contain a longword value in
the range of 16 to 16000. The default value is 16.
The INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_ERASE
INIT$_NO_ERASE---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether deleted data should be
physically destroyed by performing the data security erase (DSE)
operation on the volume before initializing it. The INIT$_ERASE item
code applies to the following devices:
- ODS--2 disk volumes
- ANSI magnetic tape volumes on magnetic tape devices that support
the hardware erase function, for example, TU78 and MSCP magnetic tapes
For disk devices, this item code sets the ERASE volume attribute,
causing each file on the volume to be erased when it is deleted.
INIT$_EXTENSION
An input item code that specifies, by the number of blocks, the default
extension size for all files on the volume. The extension default is
used when a file increases to a size greater than its initial default
allocation during an update. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2
disks, the buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to
65535. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks, the input buffer
must contain a longword value in the range of 0 to 255. The default
value is 5 for both Structure Level 1 and Structure Level 2 disks.
The default extension set by this item code is used only if the
following conditions are in effect:
- No default extension for the file has been set.
- No default extension for the process has been set using the SET RMS
command.
INIT$_FPROT
An input item code that specifies the default protection applied to all
files on the volume. The input buffer must contain a longword
protection mask that contains four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or
denies read, write, create, and delete access to a category of users.
Cleared bits grant access; set bits deny access.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask on
systems:

The INIT$_FPROT item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure
Level 1 disks and is ignored if it is used on an OpenVMS system.
OpenVMS systems use the default file extension set by the DCL command
SET PROTECTION/DEFAULT.
INIT$_HEADERS
An input item code that specifies the number of file headers to be
allocated for the index file. The input buffer must contain a longword
value within the range of 16 to the value set by the INIT$_MAXFILES
item code. The default value is 16.
The INIT$_HEADERS item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_HIGHWATER---Default
INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER
A Boolean item code that sets the file highwater mark (FHM) volume
attribute, which guarantees that users cannot read data that they have
not written.
INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER disables FHM for a volume.
The INIT$_HIGHWATER and INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER item codes apply only to
Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks.
INIT$_HOMEBLOCKS
Specifies where the volume's homeblock and spare copy of the homeblock
are placed on disk. This item code applies only to Files-11 ODS--2
volumes, and can have the following values:
- INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_GEOMETRY
Causes the homeblocks to be placed
at separate locations on disk, to protect against failure of a disk
block. Placement depends on the reported geometry of the disk.
- INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_FIXED
Causes the homeblocks to be placed at
separate fixed locations on the disk; this is the default. Placement is
independent of the reported geometry of the disk. This caters for disks
that report different geometries according to the type of controller to
which they are attached.
- INIT$K_HOMEBLOCKS_CONTIGUOUS
Causes the homeblocks to be placed
contiguously at the start of the disk. This allows container file
systems to maximize the amount of contiguous space on the disk, when
used with the INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING item code.
INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's
directory structure at the beginning of the volume. By default, the
index is placed in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code in conjunction
with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item
codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK
An input item code that specifies the location of the index file for
the volume's directory structure by logical block number. The input
buffer must contain a longword value specifying the logical block
number of the first block of the index file. By default, the index is
placed in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with
INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END results
in an error. From DCL, if you specify INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK with
INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END, then
INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
The INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_END
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's
directory structure at the end of the volume. The default is to place
the index in the middle of the volume.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with
INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes
from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE
A symbolic item code that places the index file for the volume's
directory structure in the middle of the volume. This is the default
location for the index.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with
INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes
from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_INTERCHANGE
An input item code that specifies that the magnetic tape ANSI VOL1
volume label is to be used for interchange in a heterogeneous vendor
environment. On OpenVMS, this item code overrides creation of the ANSI
VOL2 volume label, which contains security attributes specific to
OpenVMS systems.
For more information about the INIT$_INTERCHANGE item code and about
magnetic tape labeling and tape interchange, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 1: Essentials.
INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS
An input item code that specifies the character to be written in the
volume accessibility field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI
magnetic tape. Any valid ANSI "a" characters can be used;
these include numbers, uppercase letters, and any one of the following
nonalphanumeric characters:
! " % ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = >
By default, the operating system provides a routine SYS$MTACCESS that
checks this field in the following manner:
- If the magnetic tape was created on a version of the operating
system that conforms to Version 3 of ANSI, this item code is used to
override any character except an ASCII space.
- If the magnetic tape conforms to an ANSI standard that is later
than Version 3, this item code is used to override any character except
an ASCII 1 character.
INIT$_LABEL_VOLO
An input item code that specifies the text that is written in the owner
identifier field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI magnetic
tape. The owner identifier field can contain up to 14 valid ANSI
"a" characters.
INIT$_MAXFILES
An input item code that restricts the maximum number of files that the
volume can contain. The input buffer must contain a longword value
between 0 and a value determined by the following calculation:
volume size in blocks/cluster factor + 1
Once initialized, the maximum number of files can be increased only by
reinitializing the volume.
The default maximum number of files is calculated as follows:
volume size in blocks/(cluster factor + 1) * 2
The INIT$_MAXFILES item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_OVR_ACCESS
INIT$_NO_OVR_ACCESS---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether to override any character in
the accessibility field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI
magnetic tape. For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
To specify INIT$_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume or
have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_EXP
INIT$_NO_OVR_EXP---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether the caller writes to a
magnetic tape that has not yet reached its expiration date. This item
code applies only to the magnetic tapes that were created before VAX
VMS Version 4.0 and that use the D% format in the volume owner
identifier field.
To specify INIT$_OVR_EXP, the caller must either own the volume or have
VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_VOLO
INIT$_NO_OVR_VOLO---Default
A Boolean item code that allows the caller to override processing of
the owner identifier field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI
magnetic tape.
To specify INIT$_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either own the volume or
have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OWNER
An input item code that specifies the UIC that will own the volume. The
input buffer must contain a longword value, which is the UIC. The
default is the UIC of the caller.
For magnetic tapes, no UIC is written unless protection on the magnetic
tape is specified. If the INIT$_VPROT item code is specified but the
INIT$_OWNER item code is not specified, the UIC of the caller is
assigned ownership of the volume.
INIT$_READCHECK
INIT$_NO_READCHECK---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be
performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information
about data checking, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_READCHECK item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_SIZE
An input item code that specifies the number of blocks allocated for a
RAM disk with a device type of DT$_RAM_DISK. The input buffer must
contain a longword value.
INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1
INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_2---Default
Symbolic item codes that specify whether the volume should be formatted
in Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 or Structure Level 2. Structure
Level 1 is incompatible with the following item codes:
- INIT$_READCHECK
- INIT$_WRITECHECK
- INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE
The default protection for a Structure Level 1 disk is full access to
system, owner, and group users, and read access to all other users.
The INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1 item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_USER_NAME
An input item code that specifies the user name that is associated with
the volume. The input buffer must contain a character string from 1 to
12 alphanumeric characters, which is the user name. The default is the
user name of the caller.
INIT$_VERIFIED
INIT$_NO_VERIFIED
A Boolean item code that indicates whether the disk contains bad block
data. INIT$_NO_VERIFIED indicates that any bad block data on the disk
should be ignored. For disks with 4096 blocks or more, the default is
INIT$_VERIFIED.
INIT$_NO_VERIFIED is the default for the following:
- Disks with fewer than 4096 blocks
- DIGITAL Storage Architecture (DSA) devices
- Disks that are not last-track devices
The INIT$_VERIFIED item codes apply only to disks.
INIT$_VPROT
An input item code that specifies the protection assigned to the
volume. The input buffer must contain a longword protection mask that
contains four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies read, write,
create, and delete access to a category of users. Cleared bits grant
access; set bits deny access.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask:

The default is the default protection of the caller.
For magnetic tape, the protection code is written to a specific volume
label. The system applies only read and write access restrictions;
execute and delete access are ignored. Moreover, the system and the
owner are always given read and write access to magnetic tapes,
regardless of the protection mask specified.
When you specify a protection mask for a disk volume, access type E
(execute) indicates create access.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 volumes, an initial security
profile is created from the VOLUME.DEFAULT profile, with the owner and
protection as currently defined for INITIALIZE.
You can use the $SET_SECURITY service to modify the security profile
after the volume is initialized and mounted.
The caller needs read, write, or control access to the device.
INIT$_WINDOW
The INIT$_WINDOW item code specifies the number of mapping pointers to
be allocated for file windows. The input buffer must contain a longword
value in the range 7 to 80. The default is 7.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to
access the data in the file.
The INIT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_WRITECHECK
INIT$_NO_WRITECHECK---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be
performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information
about data checking, refer to the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_WRITECHECK item code applies only to disks.
Description
The Initialize Volume system service formats a disk or magnetic tape
volume and writes a label on the volume. At the end of initialization,
the disk is empty except for the system files containing the structure
information. All former contents of the volume are lost.
A blank magnetic tape can sometimes cause unrecoverable errors when it
is read. $INIT_VOL attempts to read the volume unless the following
three conditions are in effect:
- INIT$_OVR_ACCESS Boolean item code is specified.
- INIT$_OVR_EXP Boolean item code is specified.
- Caller has VOLPRO privilege.
If the caller has VOLPRO
privilege, $INIT_VOL initializes a disk without reading the ownership
information; otherwise, the ownership of the volume is checked.
A blank disk or a diskette with an incorrect format can sometimes cause
a fatal drive error. Such a diskette can be initialized successfully by
specifying the INIT$_DENSITY item code to format the diskette.
Required Access or Privileges
To initialize a particular volume, the caller must either have volume
protection (VOLPRO) privilege or the volume must be one of the
following:
- Blank disk or magnetic tape; that is, a volume that has never been
written
- Disk that is owned by the caller's UIC or by the UIC [0,0]
- Magnetic tape that allows write access to the caller's UIC or that
was not protected when it was initialized
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SET_SECURITY,
$SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be
accessed.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code or an
illegal item code was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSSRQ
|
A concurrent call to SYS$INIT_VOL is already active for the process.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have sufficient privilege to initialize the volume.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
|
|
|
|
The $INIT_VOL service can also return the following condition values,
which are specific to the Initialize Volume utility:
|
|
INIT$_ALLOCFAIL
|
Index file allocation failure.
|
|
INIT$_BADACCESSED
|
Value for INIT$_ACCESSED item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADBLOCKS
|
Invalid syntax in bad block list.
|
|
INIT$_BADCLUSTER
|
Value for INIT$_CLUSTER_SIZE item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADDENS
|
Invalid value for INIT$_DENSITY item code.
|
|
INIT$_BADDIRECTORIES
|
Value for INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADEXTENSION
|
Value for INIT$_EXTENSION item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADHEADERS
|
Value for INIT$_HEADER item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADMAXFILES
|
Value for INIT$_MAXFILES item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADOWNID
|
Invalid value for owner ID.
|
|
INIT$_BADRANGE
|
Bad block address not on volume.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOL1
|
Bad VOL1 ANSI label.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOLACC
|
Invalid value for INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS item code.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOLLBL
|
Invalid value for ANSI tape volume label.
|
|
INIT$_BADWINDOWS
|
Value for INIT$_WINDOWS item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BLKZERO
|
Block 0 is bad---volume not bootable.
|
|
INIT$_CLUSTER
|
Unsuitable cluster factor.
|
|
INIT$_CONFQUAL
|
Conflicting options were specified.
|
|
INIT$_DIAGPACK
|
Disk is a diagnostic pack.
|
|
INIT$_ERASEFAIL
|
Volume not completely erased.
|
|
INIT$_FACTBAD
|
Cannot read factory bad block data.
|
|
INIT$_ILLOPT
|
Item codes not appropriate for the device were specified.
|
|
INIT$_INDEX
|
Invalid index file position.
|
|
INIT$_LARGECNT
|
Disk too large to be supported.
|
|
INIT$_MAXBAD
|
Bad block table overflow.
|
|
INIT$_MTLBLLONG
|
Magnetic tape label specified is longer than 6 characters.
|
|
INIT$_MTLBLNONA
|
Magnetic tape label specified contains non-ANSI "a"
characters.
|
|
INIT$_NOBADDATA
|
Bad block data not found on volume.
|
|
INIT$_NONLOCAL
|
Device is not a local device.
|
|
INIT$_NOTRAN
|
Logical name cannot be translated.
|
|
INIT$_NOTSTRUC1
|
Options not available with Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1.
|
|
INIT$_UNKDEV
|
Unknown device type.
|
$IO_CLEANUP (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, returns all resources allocated by $IO_SETUP.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_CLEANUP fandle
C Prototype
int sys$io_cleanup (unsigned __int64 fandl);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle, passed by value, returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
Description
The Clean Up Fast I/O system service returns various internal resources
allocated by the $IO_SETUP system service. Buffer objects passed to
$IO_SETUP cannot be deleted until every $IO_SETUP call has had a
corresponding $IO_CLEANUP call.
Image rundown executes any required $IO_CLEANUP operations on behalf of
the process.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_PERFORM(W), $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADFANDLE
|
Argument was not a valid
fandle.
|
|
SS$_BUSY
|
The fandle cannot be cleaned up because an I/O is in progress. Reissue
the call to $IO_CLEANUP after the I/O has finished.
|
$IO_FASTPATH (Alpha Only)
Provides the ability to control the set of Fast Path devices and their
assignment to CPUs enabled for Fast Path use.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATH efn ,cpu_mask ,function_code
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpath (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, unsigned int
function_code);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the IO_FASTPATH(W) operation
completes. The efn argument is a longword containing
the number of the event flag.
cpu_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The cpu_mask argument specifies a set of CPUs to be
operated upon.
function_code
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The function_code specifies the operation to be
performed. Note that there is currently only one function code:
FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS - Distribute Fast Path ports across CPUs.
Description
The $IO_FASTPATH system service performs operations on the set of Fast
Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use. The $IO_FASTPATHW
system service completes synchronously. That is, it returns after the
operation is complete.
The FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS function code specifies that the system service
is to distribute the set of system assignable Fast Path ports across
the intersection of a caller-supplied set of candidate CPUs
(cpu_mask) and the current set of usable CPUs. Usable
CPUs are the intersection of the set of CPUs both enabled for Fast Path
use by IO$_PREFERRED_CPUS and whose current state is RUN.
The service does this by:
- Eliminating all CPUs not in the set of usable CPUs from the set of
candidate CPUs.
- Restoring any user assigned ports that are not currently on the
user's preferred CPU to the user's preferred CPU, if that CPU is in the
set of usable CPUs.
- Spreading the system assignable Fast Path ports, and any Fast Path
ports whose user preferred CPU is unavailable, evenly across the set of
usable candidate CPUs.
If the primary CPU is in the set of usable
candidate CPUs, the distribution will be biased against the primary CPU
in that a port will only be assigned to the primary after ports have
been assigned to each of the other usable candidate CPUs.
Required Access or Privileges
PHYS_IO
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$GETDVI, $QIO
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Unsupported value for cpu_mask.
|
|
SS$_ILLIOFUNC
|
Illegal function code.
|
$IO_FASTPATHW (Alpha Only)
Performs operations on the set of Fast Path devices and CPUs enabled
for Fast Path use.
The $IO_FASTPATHW system service is functionally equivalent to the
$IO_FASTPATH service except that it completes synchronously. That is,
it returns after the operation is complete.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATHW efn ,cpu_mask ,function_code
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpathw (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, unsigned
int function_code);
$IO_PERFORM (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, starts the Fast I/O operation. The $IO_PERFORM
service completes asynchronously. For synchronous completion, use the
Perform Fast I/O and Wait ($IO_PERFORMW) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORM fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdata
C Prototype
int sys$io_perform (unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan,
struct _iosa *iosadr, void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned
__int64 devdata);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Software I/O channel number.
iosadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Address of the I/O Status Area (IOSA). This value cannot be 0; that is,
an IOSA is required. The iosadr must be aligned to a
quadword boundary.
bufadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The process buffer address. Must be aligned on a 512-byte boundary.
buflen
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
64-bit integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The byte count for the I/O. The buflen argument must
be a multiple of 512 bytes. Drivers have further limitations on the
maximum size of an I/O request.
devdata
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
pointer or integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A hardware integer passed unchanged to the driver. For disk devices,
this is the media address for the transfer; that is, the virtual block
number (VBN) for virtual I/O functions or the logical block number
(LBN) for logical I/O functions. This argument is ignored for tape
devices.
For drivers with complex parameters, devdata would be
the address of a descriptor or buffer specific to the device and
function and would be documented with the driver.
Description
The Perform Fast I/O system service initiates an I/O operation on the
channel number specified by the chan argument. The
bytes specified by the buflen argument are transferred
between the location (devdata) on the device driver
and the user's buffer starting at the process buffer address
(bufadr). The byte count is read or written according
to the function code previously specified in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with the fandle argument.
Upon completion, the I/O status is written to the IOSA starting at the
location specified by iosadr, and an AST is delivered
to the astadr address supplied in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with fandle. The IOSA address is passed to
the AST as the AST parameter.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_SETUP, $IO_PERFORMW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFADR
|
The data buffer does not reside within the bounds of the data buffer
object for the fandle.
|
|
SS$_BADIOSADR
|
The IOSA does not reside within the bounds of the IOSA buffer object
for this fandle.
|
|
SS$_FANDLEBUSY
|
The operation using this fandle is already in progress.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_UNALIGNED
|
The buffer specified by
bufadr or
iosadr is not properly aligned.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The request is invalid because the
fandle was created from a more privileged access mode,
or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
The HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these device-specific condition values for each
device.
$IO_PERFORMW (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, starts a Fast I/O operation. The $IO_PERFORMW service
completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller after
performing the Fast I/O operation.
In all other respects, $IO_PERFORMW is identical to $IO_PERFORM. For
all other information about the IO_PERFORMW service, refer to the
description of $IO_PERFORM in this manual.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORMW fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdata
C Prototype
int sys$io_performw (unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan,
struct _iosa *iosadr, void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned
__int64 devdata);
$IO_SETUP (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allocates resources for Fast I/O.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_SETUP func ,bufobj ,iosobj ,astadr ,flags ,return_fandle
C Prototype
int sys$io_setup (unsigned int func, struct _generic_64 *bufobj, struct
_generic_64 *iosobj, void (*astadr)(struct _iosa *), unsigned int
flags, unsigned __int64 *return_fandle);
Arguments
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
I/O function code. Must be one of the following:
- IO$_READVBLK
- IO$_WRITEVBLK
- IO$_READLBLK
- IO$_WRITELBLK
Various function modifiers are supported, depending on the device and
driver. Disk drivers support IO$M_NOVCACHE and IO$M_DATACHECK. Some
tape devices support IO$M_REVERSE. Illegal modifiers are detected by
the $IO_PERFORM(W) service.
bufobj
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer object |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Handle describing the buffer object that contains the user's buffer.
This identifier cannot be 0.
iosobj
| OpenVMS usage: |
object handle |
| type: |
vector longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Buffer object handle describing the buffer object that contains the I/O
Status Area (IOSA). This might or might not be the same identifier as
the bufobj argument. This identifier cannot be 0.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Completion AST routine address (0, if none). There is no AST
parameter argument. When the AST routine is called, the AST
parameter will be the address of the IOSA for the operation.
Applications can store data in the IOSA at offset IOSA$IH_CONTEXT.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask. The flags argument is a bit vector in which
each bit corresponds to a flag. Flags are defined in the module IOSADEF.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$IO_SETUP service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
FIO$M_EXPEDITE
|
This is a
high priority I/O; that is, it is to be given preferential
treatment by the I/O subsystem. Use of this bit requires ALTPRI or
PHY_IO privilege.
|
|
FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT
|
The AST procedure does not use, or call any procedure that uses, any
floating-point registers. This is a performance option. If set, AST
delivery will neither save nor restore floating-point registers.
Caution: Use of floating-point registers when FIO$M_AST_NOFLOAT has
been specified can cause unpredictable, difficult to detect, error
conditions.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0.
return_fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Address of an aligned quadword to receive the fandle for this I/O
operation.
Description
The Set Up Fast I/O system service allocates and initializes a number
of internal objects based on the parameters supplied. Because these
objects are then ready for use when a subsequent $IO_PERFORM or
$IO_PERFORMW is issued, the I/O operation will require less CPU time
and fewer multiprocessor steps.
Required Privileges
If you use the flags argument FIO$M_EXPEDITE, a
process must have ALTPRI or PHY_IO privilege.
Required Quota
Byte count
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_PERFORM(W)
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The fandle does not have 8 bytes of writability, or the two buffer
objects do not have 8 bytes of readability each.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid flags options specified.
|
|
SS$_EXBUFOBJLM
|
Buffer object cannot be created because it would bring the total number
of buffer object pages above the systemwide limit MAXBOBMEM.
|
|
SS$_ILLBUFOBJ
|
The buffer object is not valid.
|
|
SS$_ILLIOFUNC
|
The function code is not valid.
|
|
SS$_ILLMODIFIER
|
The I/O function modifier is not permitted.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There is no pool available from which to create a fandle vector, or the
fandle vector is already full and an attempted expansion failed.
|
|
SS$_INSFSPTS
|
Insufficient system page table entries.
|
|
SS$_IVSTSFLG
|
The specified status flag is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOBUFOBJID
|
The process attempted to create a buffer object from user mode but was
not holding required rights identifier VMS$BUFFER_OBJECT_USER.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Valid flag options were specified but from user mode.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTWRITE
|
A page within the address range is not writable.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
Page owner violation. The pages could not be put into the buffer object
because the access mode associated with the call to $IO_SETUP was less
privileged than the access mode associated with the pages. See
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 for additional information.
|
|
SS$_UNALIGNED
|
The I/O Status Area (IOSA) or data buffer is not aligned on a quadword
boundary.
|
$JOIN_RM
Adds a new Resource Manager (RM) participant to a transaction.
Format
SYS$JOIN_RM [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id [,[tid]
,[part_name] ,[rm_context] ,[timout] ,[bid]]
C Prototype
int sys$join_rm (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
rm_id,...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags described in Table SYS-47. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-47 $JOIN_RM Option Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_COORDINATOR
|
Set this flag to specify that the new RM participant is to be a
coordinator of the transaction on this node.
|
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
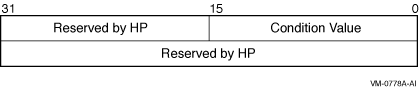
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if
SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The astadr argument is
the address of the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed
in the same access mode as that of the caller of the $JOIN_RM service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The identifier of the RMI with which the new RM participant is
associated. This identifies:
- Types of event that are to be reported to the new RM participant.
- Event handler to which these event reports are to be delivered, and
the access mode in which its ASTs are to be fired.
- Minimum access mode that the new RM participant must be in to
acknowledge one of these event reports by calling $ACK_EVENT.
- Whether or not the DECdtm transaction manager may log information
about the new RM participant.
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the transaction to which the new RM participant
is to be added.
If this argument is omitted (the default) or its value is zero,
$JOIN_RM adds an RM participant to the default transaction of the
calling process.
part_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the new RM participant.
Used by recoverable resource managers to specify the RM participant to
use in a subsequent call to $GETDTI or $SETDTI during recovery.
This argument has no effect if the RMI is volatile. If this argument is
omitted (the default) or its value is zero, the name of the new RM
participant is the same as that of the RMI with which it is associated.
The string passed in this argument can be no longer than 32 characters.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
rm_context
| OpenVMS usage: |
userarg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The context associated with the new RM participant. This is passed in
the event reports subsequently delivered to the new RM participant.
If this argument is omitted (the default) or is zero, the context
associated with the new RM participant is the same as that of the RMI
with which it is associated.
timout
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Reserved to HP.
bid
| OpenVMS usage: |
branch_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier of an authorized branch (BID) that may be added to the
transaction by a subsequent call to $START_BRANCH on the same node as
that of the RMI. This argument is ignored if the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR
flag is clear in the flags argument. The call to
$START_BRANCH should specify the node of the RMI for the
tm_name argument.
Description
The $JOIN_RM system service:
- Adds a new RM participant to the specified transaction. The new RM
participant is associated with the RMI whose identifier is passed in
the rm_id argument.
- Introduces a new transaction to DECdtm if the new RM participant is
a coordinator and the specified transaction is unknown to DECdtm.
- Authorizes a new branch of the transaction if the new RM
participant is a coordinator.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $JOIN_RM are:
- Unless the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, the calling process must
contain at least one branch of the specified transaction.
- The calling process must contain the specified RMI.
- The caller must not be in a less privileged mode than the access
mode of the specified RMI.
- If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, either the calling process
must have the SYSPRV privilege, or the caller must be in executive or
kernel mode.
- If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, the specified RMI must not
be volatile. That is, the DDTM$M_VOLATILE flag must not have been set
on the call to the $DECLARE_RM that created it.
- The access mode of the specified RMI must not be less privileged
than that of the specified transaction in this process.
$JOIN_RM can fail for various reasons, including:
- Preconditions were not met.
- The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was set, but no bid
argument was supplied.
When $JOIN_RM completes successfully, a new RM participant running in
the calling process is added to the transaction. This RM participant is
associated with the specified RMI.
The DECdtm transaction manager will report to the new RM participant
the types of event specified in the call to $DECLARE_RM that created
the RMI with which it is associated. Note however that events of type
prepare, one-phase commit, and commit are never reported to RM
participants that set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag on the call to
$JOIN_RM.
If the call to $DECLARE_RM requested prepare and one-phase commit
events, and the $JOIN_RM call does not set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag,
the new RM participant is entitled to a vote on the outcome of the
transaction.
If the $JOIN_RM call sets the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag, then the new RM
participant is expected to initiate commit or abort processing by a
call to $TRANS_EVENT. No events of type prepare, one-phase commit, or
commit are delivered to the RM participant.
Events of type abort are reported to the RM participant.
The new RM participant is removed from the transaction when the first
of the following conditions is met:
- On successful completion of a call to $ACK_EVENT that acknowledges
an event report delivered to that RM participant, if the event and its
acknowledgment were one of those listed in the following table:
| Event |
Acknowledgment (report_reply) |
|
Abort
|
SS$_FORGET
|
|
Commit
|
SS$_FORGET or SS$_REMEMBER
|
|
Prepare
|
SS$_FORGET
|
|
One-phase commit
|
SS$_NORMAL or SS$_VETO
|
- On completion of a successful call to $TRANS_EVENT that specifies a
commit or abort event, if the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set.
- When a commit or abort event occurs, and no associated event report
is delivered to the RM participant.
- On successful completion of a call to $FORGET_RM that deletes the
RMI with which it is associated.
- When the current process terminates (normally or abnormally).
- When the current image terminates (normally or abnormally).
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set:
- A new branch is authorized for the transaction and its identifier
is returned in the octaword that the bid argument
points to. $JOIN_RM uses the $CREATE_UID system service to generate the
BID. No other call to $ADD_BRANCH, $JOIN_RM, or $CREATE_UID on any
other node ever returns the same BID value.
- The transaction cannot commit until the new branch has been started
by a matching call to $START_BRANCH. (See the description of
$START_BRANCH for the definition of a matching call to $START_BRANCH.)
- If the transaction is not already known to this process, then the
transaction is introduced to this process with an access mode equal to
the access mode of the caller. (See the description of $START_TRANS for
a definition of the access mode of a transaction.)
There is also a wait form of the service, $JOIN_RMW.
Required Privileges
If the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag is set, then either the calling process
must have the SYSPRV privilege or the caller must be in executive or
kernel mode.
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS,
$START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The options flags were invalid, the specified
tid was invalid, or DTM$M_COORDINATOR set but no
bid supplied.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_INVBUFLEN
|
The string passed in the
part_name argument was too long.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSPRIV
|
The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was set and the caller was in user or
supervisor mode but the calling process did not have the SYSPRV
privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOCURTID
|
An attempt was made to add a new participant to the default transaction
(the
tid argument was zero or omitted) but the calling
process did not have a default transaction.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTID
|
The DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag was clear and the calling process did not
contain any branches in the transaction.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHRM
|
The calling process did not contain the specified RMI.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The caller was in a less privileged access mode than that of the RMI.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation
because either:
- An abort event had occurred for the transaction.
- A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction was in progress and it
is too late to add a new RM participant to the transaction.
|
$JOIN_RMW
Adds a new Resource Manager (RM) participant to a transaction.
$JOIN_RMW always waits for the request to complete before returning to
the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $JOIN_RM.
Format
SYS$JOIN_RMW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id [,[tid]
,[part_name] ,[rm_context] ,[timout] ,[bid] ]
C Prototype
int sys$join_rmw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
rm_id,...);
$LCKPAG
Locks a page or range of pages in memory. The specified virtual pages
are forced into the working set and then locked in memory. A locked
page is not swapped out of memory if the working set of the process is
swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page replacement and in
this sense are locked in the working set as well.
Format
SYS$LCKPAG inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$lckpag (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be
locked. The inadr argument is the address of a
2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process
virtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual
address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
On VAX systems, if the starting and ending virtual addresses are the
same, a single page is locked.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages that $LCKPAG
actually locked. The retadr argument is the address of
a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending
process virtual addresses.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages to be locked. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
For the $LCKPAG service to complete successfully, the resultant access
mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already
associated with the pages to be locked.
Description
The Lock Pages in Memory service locks a page or range of pages in
memory. The specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and
then locked in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if
the working set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not
candidates for page replacement and in this sense are locked in the
working set as well.
If more than one page is being locked and you need to determine
specifically which pages were previously locked, the pages should be
locked one at a time.
If an error occurs while the $LCKPAG service is locking pages, the
return array, if requested, indicates the pages that were successfully
locked before the error occurred. If no pages are locked, both
longwords in the return address array contain the value --1.
On Alpha systems, if you are attempting to lock executable code, you
should issue multiple $LCKPAG calls: one to lock the code pages and
others to lock the linkage section references into these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have PSWAPM privilege to lock pages into
memory.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
You can unlock pages locked in memory with the Unlock Pages from Memory
($ULKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked at image
exit.
For more information, refer to the chapter on memory management in the
OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously locked.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input array cannot be read; the output array cannot be written; the
page in the specified range is inaccessible or nonexistent; or an
attempt to lock pages was made by a caller whose access mode is less
privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
|
SS$_LCKPAGFUL
|
The system-defined maximum limit on the number of pages that can be
locked in memory has been reached.
|
|
SS$_LDWSETFUL
|
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not
enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to lock pages in memory.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with
the call to $LCKPAG was less privileged than the access mode associated
with the pages that were to be locked.
|
$LCKPAG_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, locks a range of pages in memory. The specified
virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked in
memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working set
of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for page
replacement and, in this sense, are locked in the working set as well.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$LCKPAG_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64
,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$lckpag_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be locked. The specified
virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be locked. The specified length
will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes
all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode associated with the pages to be locked. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
For the $LCKPAG_64 service to complete successfully, the resultant
access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode
already associated with the pages to be locked.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages locked in memory. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range
locked in bytes.
Description
The Lock Pages in Memory service locks a range of pages in memory. The
specified virtual pages are forced into the working set and then locked
in memory. A locked page is not swapped out of memory if the working
set of the process is swapped out. These pages are not candidates for
page replacement and, in this sense, are locked in the working set as
well.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the
returned address and returned length indicate the pages that were
successfully locked before the error occurred. If no pages were locked,
the return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1,
and a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed
to by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
A process must have PSWAPM privilege to call the $LCKPAG_64 service.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$LCKPAG, $ULKPAG, $ULKPAG_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller, or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose access
mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
|
SS$_LCKPAGFUL
|
The system-defined maximum limit on the number of pages that can be
locked in memory has been reached.
|
|
SS$_LKWSETFUL
|
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not
enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
|
|
SS$_NOPSWAPM
|
The process does not have the privilege to lock pages in memory.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with
the call to $LCKPAG_64 was less privileged than the access mode
associated with the pages that were to be locked.
|
$LKWSET
Locks a range of pages in the working set; if the pages are not already
in the working set, it brings them in and locks them. A page locked in
the working set does not become a candidate for replacement.
Format
SYS$LKWSET inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$lkwset (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be
locked in the working set. The inadr argument is the
address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and
ending process virtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion
of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits
are ignored.
On VAX systems, if the starting and ending virtual addresses are the
same, a single page is locked.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the range of pages
actually locked by $LCKWSET. The retadr argument is
the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting
and ending process virtual addresses.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages to be locked. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
For the $LKWSET service to complete successfully, the resultant access
mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode already
associated with the pages to be locked.
Description
The Lock Pages in Working Set service locks a range of pages in the
working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, it brings
them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not
become a candidate for replacement.
If more than one page is being locked and you need to determine
specifically which pages were previously locked, the pages should be
locked one at a time.
If an error occurs while the $LKWSET service is locking pages, the
return array, if requested, indicates the pages that were successfully
locked before the error occurred. If no pages are locked, both
longwords in the return address array contain the value --1.
Global pages with write access cannot be locked into the working set.
On Alpha systems, if you are attempting to lock executable code, you
should issue multiple $LKWSET calls: one to lock the code pages and
others to lock the linkage section references into these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
You can unlock pages locked in the working set with the Unlock Page
from Working Set ($ULWSET) service.
For more information, refer to the chapter on memory management in the
OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input address array cannot be read; the output address array cannot
be written; a page in the specified range is inaccessible or
nonexistent; or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose
access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the
pages.
|
|
SS$_LKWSETFUL
|
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not
enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
A page in the specified range is in the system address space, or a
global page with write access was specified.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with
the call to $LKWSET was less privileged than the access mode associated
with the pages that were to be locked.
|
$LKWSET_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, locks a range of virtual addresses in the working
set; if the pages are not already in the working set, the service
brings them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does
not become a candidate for replacement.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$LKWSET_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64
,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$lkwset_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be locked in the working
set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a
CPU-specific page boundary.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be locked in the working set.
The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary
so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode associated with the pages to be locked. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
For the $LKWSET_64 service to complete successfully, the resultant
access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode
already associated with the pages to be locked.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages locked in the working
set. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range locked in the working set. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Lock Pages in Working Set service locks a range of pages in the
working set; if the pages are not already in the working set, it brings
them in and locks them. A page locked in the working set does not
become a candidate for replacement.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the
returned address and returned length indicate the pages that were
successfully locked before the error occurred. If no pages were locked,
the return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1,
and a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed
to by the return_length_64 argument.
Global pages with write access cannot be locked into the working set.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$LKWSET, $ULWSET, $ULWSET_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller, or an attempt was made to lock pages by a caller whose access
mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
|
SS$_LKWSETFUL
|
The locked working set is full. If any more pages are locked, not
enough dynamic pages will be available to continue execution.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
No privilege; global pages with write access cannot be locked into the
working set.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
The pages could not be locked because the access mode associated with
the call to $LKWSET_64 was less privileged than the access mode
associated with the pages that were to be locked.
|
$MGBLSC
Establishes a correspondence between pages (maps) in the virtual
address space of the process and physical pages occupied by a global
section.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[flags] ,gsdnam ,[ident] ,[relpag]
C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, struct _secid
*ident, unsigned int relpag);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses into which the section is to be
mapped. The inadr argument is the address of a
2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process
virtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual
address is used to specify which pages are to be mapped; the low-order
byte-within-page bits are ignored for this purpose.
The interpretation of the inadr argument depends on
the setting of SEC$M_EXPREG in the flags argument and
on whether you are using an Alpha or a VAX system. The two system types
are discussed separately in this section.
Alpha System Usage
On Alpha systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the
inadr argument specifies the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space
are not allowed. The addresses must be aligned on CPU-specific pages;
no rounding to CPU-specific pages occurs. The lower address of the
inadr argument must be on a CPU-specific page boundary
and the higher address of the inadr argument must be 1
less than a CPU-specific boundary, thus forming a range, from lowest to
highest, of address bytes. You can use the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code in
the $GETSYI system service to set the inadr argument
to the proper values. You do this to avoid programming errors that
might arise because of incorrect programming assumptions about page
sizes.
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,
indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available
space in a particular region, the inadr argument is
used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or
the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must
be executed with extreme care. Since the user stack is mapped in P1, it
is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently read
or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.
|
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr
longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword is used to determine the
region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,
P1 is chosen. On Alpha systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword must be 0. To ensure
compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,
HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadr
longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
VAX System Usage
On VAX systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the
inadr argument specifies the starting and ending
virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space
are not allowed. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the
same, a single page is mapped.
Note
If the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is not set, HP recommends that the
inadr argument always specify the entire virtual
address range, from starting byte address to ending byte address. This
ensures compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems.
|
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,
indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available
space in a particular region, the inadr argument is
used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or
the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must
be executed with extreme care. Since the user stack is mapped in P1, it
is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently read
or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.
|
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr
longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of
the first inadr longword is used to determine the
region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,
P1 is chosen. On VAX systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of the
first inadr longword is ignored. To ensure
compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,
HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadr
longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses into which the section
was actually mapped by $MGBLSC. The retadr argument is
the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting
and ending process virtual addresses.
On Alpha systems, the retadr argument returns the
starting and ending addresses of the usable range of
addresses. This might differ from the total amount mapped. The
retadr argument is required when the
relpag argument is specified. If the section being
mapped does not completely fill the last page used to map the section,
the retadr argument indicates the highest address that
actually maps the section. If the relpag argument is
used to specify an offset into the section, the retadr
argument reflects the offset.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages mapped into the process
virtual address space. The acmode argument is a
longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols
for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The
flags argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit
when set specifies the corresponding option.
The $SECDEF macro defines symbolic names for the flag bits. You
construct the flags argument by specifying the
symbolic names of each desired option in a logical OR operation.
The following table describes each flag option:
| Flag Option |
Description |
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Map the section with read/write access. By default, the section is
mapped with read-only access. If SEC$M_WRT is specified and the section
is not copy-on-reference, write access is required.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Map a system global section. By default, the section is a group global
section.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Map the section into the first available virtual address range. By
default, the section is mapped into the range specified by the
inadr argument.
See the
inadr argument description for a complete explanation
of how to set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag.
|
gsdnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gsdnam argument is the
address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the group
UIC as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global
sections are unique to UIC groups. Further, all global section names
are implicitly qualified by their identification fields.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section
and, for processes mapping to an existing global section, the criteria
for matching the identification. The ident argument is
the address of a quadword structure containing three fields.
The first longword specifies, in the low-order two bits, the matching
criteria. Their valid values, the symbolic names by which they can be
specified, and their meanings are as follows:
| Value/Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0 SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1 SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2 SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
The version number is in the second longword and contains two fields: a
minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major
identification in the high-order 8 bits.
If you do not specify ident or specify it as the value
0 (the default), the version number and match control fields default to
the value 0.
relpag
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Relative page number within the section of the first page to be mapped.
The relpag argument is a longword containing this
number.
On Alpha systems, the relpag argument is interpreted
as an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for a
file-backed section or CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section.
On Alpha and VAX systems, if you do not specify relpag
or specify it as the value 0 (the default), the global section is
mapped beginning with the first virtual block in a file-backed section
or the first CPU-specific page in a PFN-mapped section.
Description
The Map Global Section service establishes a correspondence between
pages (maps) in the virtual address space of the process and physical
pages occupied by a global section. The protection mask specified at
the time the global section is created determines the type of access
(for example, read/write or read only) that a particular process has to
the section.
When $MGBLSC maps a global section, it adds pages to the virtual
address space of the process. The section is mapped from a low address
to a high address, whether the section is mapped in the program or
control region.
If an error occurs during the mapping of a global section, the return
address array, if specified, indicates the pages that were successfully
mapped when the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, both longwords
of the return address array contain the value --1.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access is required. If the SEC$M_WRT flag is specified, write
access is required.
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space when the
$MGBLSC service maps a section.
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must also have
sufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
This system service causes the working set of the calling process to be
adjusted to the size specified by the working set quota (WSQUOTA). If
the working set size of the process is less than quota, the working set
size is increased; if the working set size of the process is greater
than quota, the working set size is decreased.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG,
$LKWSET, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
For more information, refer to the chapter on memory management in the
OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input address array, the global section name or name descriptor, or
the section identification field cannot be read by the caller; or the
return address array cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ENDOFFILE
|
The starting virtual block number specified is beyond the logical
end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference
pages.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The working set limit of the process is not large enough to accommodate
the increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_INVARG
|
Invalid argument specified to service. Common sources are the incorrect
specification of
relpag or the values in the
inadr array.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
You set a reserved flag.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created
prohibits the type of access requested by the caller; or a page in the
input address range is in the system address space.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page-table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHSEC
|
The specified global section does not exist.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
Logical name translation of the
gsdnam string exceeded the allowed depth.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The virtual address space of the process is full; no space is available
in the page tables for the pages created to contain the mapped global
section.
|
$MGBLSC_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, establishes a correspondence between pages in the
virtual address space of the process and the pages occupied by a global
disk file, page file, or demand-zero section and can map to a
demand-zero section with shared page tables.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64
,length_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
[,start_va_64]
C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc_64 (void *gsdnam_64, struct _secid *ident_64, struct
_generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned
__int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void
*(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32-bit or
64-bit string descriptor pointing to this name string.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two
bits.
The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified, and
their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global section. The
file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB
define a symbolic name for each of the three default regions in P0, P1,
and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte offset |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Offset into the global section at which to start mapping into the
process's virtual address space.
If a map to a global disk file section is being requested, the
section_offset_64 argument specifies an even multiple
of disk blocks. If a map to a global page file or demand-zero section
is being requested, the section_offset_64 argument
specifies an even multiple of CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified,
the global section is mapped beginning with the first page of the
section.
If the region_id_64 argument specifies a shared page
table region, section_offset_64 must be an even
multiple of pages mapped by a page table page.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length, in bytes, of the desired mapping of the global disk file
section.
If a map to a global section is being requested, the
length_64 argument must specify an even multiple of
disk blocks. If a map to a global page file or demand-zero section is
being requested, the length_64 argument must specify
an even multiple of CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified, the size
of the disk file is used.
If a shared page-table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, length_64 must
be an even multiple of the number of bytes that can be mapped by a
CPU-specific page-table page or must include the last page within the
memory-resident global section.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. This is also the read access mode and, if the SEC$M_WRT flag
is specified, the write access mode. The acmode
argument is a longword containing the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The
flags argument is a longword bit vector in which each
bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file
define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$MGBLSC_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
If /ALLOCATE was specified when the memory-resident global section
was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, virtually aligned
addresses after the first available space are chosen for the mapping.
It the
region_id_64 argument specifies a shared page-table
region, the first available space is round up to the beginning of the
next CPU-specific page-table page.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP
|
Pages cannot overmap existing address space.
|
|
SEC$M_SHMGS
|
On OpenVMS Galaxy systems, create a shared-memory global section.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
The global section map is a system global section. By default, the
section is a group global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Map the section with read/write access.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future use by HP
and should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is
returned if any undefined bits are set or if an attempt is made to use
the SEC$M_PAGFIL flag, which applies only to the creation of a
page-file backed section.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The process virtual address into which the global disk or page file
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the virtual address.
Upon successful completion of this service, if the
section_offset_64 argument was specified, the virtual
address returned in the return_va_64 argument reflects
the offset into the global section mapped such that the virtual address
returned cannot be aligned on a CPU-specific page boundary. The virtual
address returned will always be on an even virtual disk block boundary.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the usable virtual address range mapped. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range mapped in bytes.
Upon successful completion of this service, the value in the
return_length_64 argument might differ from the total
amount of virtual address space mapped. The value in the
return_va_64 argument plus the value in the
return_length_64 argument indicates the address of the
first byte beyond the end of the mapping of the global disk file
section.
If the value in the section_offset_64 argument plus
the value in the length_64 argument did not specify to
map the entire global section, this byte can be located at an even
virtual disk block boundary within the last page of the mapping.
If the section being mapped does not completely fill the last page used
to represent the global disk file section, this byte can be mapped into
your address space; however, it is not backed up by the disk file.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to which to map the global section. The
specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page-aligned address.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
If the region_id_64 argument specifies a shared
page-table region, start_va_64 must be aligned to a
CPU-specific page-table page boundary.
Description
The Map to Global Section service establishes a correspondence between
pages in the virtual address space of the process and pages occupied by
a global disk file, page file, or memory-resident demand-zero section.
This service adds pages to the virtual address space of the process.
If a global disk file or page file backed section is being mapped,
invalid page table entries are placed in the process page table.
If a memory-resident global section is being mapped, global pages are
not charged against the process's working set quota when the virtual
memory is referenced and the global pages are not charged against the
process's pagefile quota.
If the memory-resident global section was not registered in the
Reserved Memory Registry or /NOALLOCATE was specified when the global
section was registered, invalid page table entries are placed in the
process page table.
If the memory-resident global section was registered in the Reserved
Memory Registry and /ALLOCATE was specified when the memory-resident
global section was registered, valid page table entries are placed in
the process page tables.
If a global disk file or page file backed section is being mapped, and
the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual address within the
specified region is used to start mapping to the global section.
To use the shared page tables associated with a memory-resident global
section, you must first create a shared page table region (with
SYS$CREATE_REGION_64). To map to the memory-resident global section
using the shared page tables you must do the following:
- Specify a shared page table region in the
region_id_64 argument.
- Specify SEC$M_WRT in the flags argument.
- Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG or provide a CPU-specific page-table
page-aligned virtual address in the start_va_64
argument.
- Specify a CPU-specific page-table page-aligned value for the
section_offset_64 argument or zero.
- Specify a value for the map_length_64 argument
that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page-table
page, or include the last page of the section or zero.
See the description of $CREATE_REGION_64 for information about
calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specific page
table page boundary.
A memory-resident global section can be mapped with shared page tables
or private page tables. The following table lists the factors
associated with determining whether the mapping occurs with shared page
tables or private page tables:
| Global Section Created with Shared Page Tables |
Shared Page-Table Region Specified by region_id_64 |
Type of Page Tables Used in Mapping |
|
No
|
No
|
Private
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
Private
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
Private
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Shared
|
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual
address within the specified region is used to map to the global
section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, a memory-resident global section is
being mapped and the region_id_64 argument indicates a
shared page-table region, the first free virtual address within the
specified region is rounded up to a CPU-specific page-table page
boundary and used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the /ALLOCATE qualifier was
specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for the
memory-resident global section, the first free virtual address within
the specified region is rounded up to the same virtual alignment as the
physical alignment of the preallocated pages and used to map to the
global section. Granularity hints are set appropriately for each
process private page-table entry (PTE).
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the virtual address in
the start_va_64 argument is used to map to the global
section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear and a memory-resident global section
is being mapped, the value specified in the
start_va_64 argument can determine if the mapping is
possible and if granularity hints are used in the private page tables.
If a shared page-table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the virtual address specified
by the start_va_64 argument must be on an even
CPU-specific page-table page boundary or an error is returned by this
service. If the region_id_64 argument does not specify
a shared page-table region and the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified
with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for this global section,
granularity hints are used only if the virtual alignment of
start_va_64 is appropriate for the use of granularity
hints (either 8-page, 64-page or 512-page alignment).
Whenever granularity hints are being used within the mapping of a
memory-resident global section, if the length_64
argument is not an exact multiple of the alignment factor, lower
granularity hints factors are used as appropriate at the higher
addressed portion of the global section. If the
section_offset_64 argument is specified, a lower
granularity hint factor can be used throughout the mapping of the
global section to match the physical alignment of the first page mapped.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument contains the value --1.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
If private page tables are used to map to the global section, the
working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased size of the process page tables required by
the increase in virtual address space when the section is mapped.
If private page tables are used to map to a memory-resident global
section, the pagefile quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be
sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables
required by the increase in virtual address space.
If the process is mapping to a global copy-on-reference section, the
pagefile quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space.
Related Services
$CREATE_GDZRO, $CREATE_GFILE, $CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64,
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,
$DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC,
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64, $PURGE_WS, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64,
$UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 argument or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA
|
The process's page file quota is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it is not a global disk-file, page-file, or demand-zero
section.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the
increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The specified access mode is greater than PSL$_USER or the caller's
mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the
region. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the acmode argument does not
match the access mode of the shared PTEs.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
An invalid region ID was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk
blocks if a map to a global section was requested (SEC$M_PAGFIL is
clear in the flags argument).
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages and a map to a global page file section was requested.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page-table region was specified, and a gobal
section was specified that is not a memory-resident demand-zero section.
|
|
SS$_NOSHPTS
|
The region ID of a shared page table region was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHSEC
|
The specified global section does not exist.
|
|
SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page
aligned if a map to a global page-file or demand-zero section is
requested. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the
section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific
page-table page aligned.
|
|
SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG
|
The
section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the
logical end-of-file.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified input address range is not within the specified
region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range already exists and cannot
be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_PROTVIO
|
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created
prohibits the type of access requested by the caller.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped section.
|
|
SS$_SECREFOVF
|
The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached
(2,147,483,647).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the
flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or a page in the specified input address
range is in another region, in system space, or inaccessible; or, the
existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the
region_id_64 argument, the
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page-table
page aligned.
|
|
SS$_NOWRTACC
|
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not
allow write access.
|
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, establishes a correspondence between pages in the
virtual address space of the process and the pages occupied by a global
page frame section.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$MGBLSC_GPFN_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,region_id_64 ,relative_page
,page_count ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
[,start_va_64]
C Prototype
int sys$mgblsc_gpfn_64 (void *gsdnam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int relative_page, unsigned
int page_count, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void
*(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32-bit or
64-bit descriptor pointing to this name string.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two
bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,
and their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the private page frame
section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default
regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.
The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol |
Region |
|
VA$C_P0
|
Program region
|
|
VA$C_P1
|
Control region
|
|
VA$C_P2
|
64-bit program region
|
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be
specified.
relative_page
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Relative CPU-specific page number within the global section to start
mapping.
page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of mapping in CPU-specific pages. If zero is specified, the
global page frame section is mapped to the end of the section.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access-mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be associated with the pages mapped into the process
virtual address space. The acmode argument is a
longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols
for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode
associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The
condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less
privileged than the create mode for the region.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying options for the operation. The
flags argument is a longword bit vector in which each
bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file
define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the
flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on
the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_EXPREG
|
Map the section into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region. If this flag is specified, the
start_va_64 argument is not used.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Pages are permanent. By default, this flag is always present in this
service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Pages form a global page-file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies
SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Map a system global section. By default, the section is a group global
section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Map the section with read/write access. By default, the section is
mapped with read-only access. If SEC$M_WRT is specified, write access
is required.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page frame
section was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the
32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that
contains the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the $MGBLSC_GPFN_64 service returns the length of the virtual
address range in bytes.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global section. The specified
virtual address must be a CPU-specified page-aligned address. If the
flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64
argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. If
SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument is
nonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
Always refer to the return_va_64 and
return_length_64 arguments to determine the range of
virtual addresses mapped.
Description
The Map Global Page Frame Section service establishes a correspondence
between pages in the virtual address space of the process and pages
occupied by a global page frame section. It adds pages to the virtual
address space of the process.
Pages mapped to a global page frame section are not included in or
charged against the process's working set; they are always valid. Do
not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET; this can
result in a machine check if they are in I/O space.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1, and a
value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by
the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
Read access is required. If the SEC$M_WRT flag is specified, write
access is required.
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased length of the process page table required by
the increase in virtual address space.
The page file quota (PAGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to
accommodate the increased number of process page tables required by the
increase in virtual address space. (Note that this service can return
the SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA.)
Related Services
$CREATE_GPFN, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,
$DELTVA_64, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or
the
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH
|
Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found;
however, it is not a global page frame section.
|
|
SS$_ILLRELPAG
|
The specified relative page argument is either larger than the highest
page number within the section or is not a valid 32-bit physical page
frame number.
|
|
SS$_INSFWSL
|
The working set limit of the process is not large enough to accommodate
the increased virtual address space.
|
|
SS$_IVACMODE
|
The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated
with the region.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVREGID
|
Invalid region ID specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHSEC
|
The specified global section does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOWRTACC
|
The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not
allow write access.
|
|
SS$_PROTVIO
|
The file protection mask specified when the global section was created
prohibits the type of access requested by the caller.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the specified region.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted
because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the
caller.
|
|
SS$_REGISFULL
|
The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the
region for the pages created to contain the mapped global section.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated
with a buffer object.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned.
|
$MOD_HOLDER
Modifies the specified holder record of the target identifier in the
rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_HOLDER id ,holder ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib]
C Prototype
int sys$mod_holder (unsigned int id, struct _generic_64 *holder,
unsigned int set_attrib, unsigned int clr_attrib);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary value of target identifier whose holder record is modified when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The id argument is a
longword containing the identifier value.
holder
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_holder |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identifier of holder being modified when $MOD_HOLDER completes
execution. The holder argument is the address of a
quadword containing the UIC identifier of the holder in the first
longword and the value of 0 in the second longword.
set_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The set_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified
and the attributes of the identifier. If you specify the same attribute
in set_attrib and clr_attrib, the
attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the
identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
clr_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The clr_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the
identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
Description
The Modify Holder Record in Rights Database service modifies the
specified holder record in the rights database. Identifier attributes
can be added or removed.
When you specify both the set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first.
Thus, if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the
result is that the bit is set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD,
$FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
holder argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier or holder identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database, or the
specified holder identifier does not exist in the rights database.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOD_IDENT
Modifies the specified identifier record in the rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_IDENT id ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib] ,[new_name] ,[new_value]
C Prototype
int sys$mod_ident (unsigned int id, unsigned int set_attrib, unsigned
int clr_attrib, void *new_name, unsigned int new_value);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary value of identifier whose identifier record is modified when
$MOD_IDENT completes execution. The id argument is a
longword containing the identifier value.
set_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when $MOD_IDENT
completes execution. The set_attrib argument is a
longword containing the attribute mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified
and the attributes of the identifier. If you specify the same attribute
in set_attrib and clr_attrib, the
attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN
|
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier,
unless they own the identifier themselves.
|
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN
|
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated---either from
binary to ASCII or vice versa---but prevents unauthorized users from
translating the identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
clr_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when
$MOD_IDENT completes execution. The clr_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN
|
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier,
unless they own the identifier themselves.
|
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN
|
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated---either from
binary to ASCII or vice versa---but prevents unauthorized users from
translating the identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
new_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
New name to be given to the specified identifier. The
new_name argument is the address of the descriptor
pointing to the identifier name string.
An identifier name consists of 1 to 31 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_), and must contain at
least one nonnumeric character. Any lowercase characters specified are
automatically converted to uppercase.
new_value
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
New value to be assigned to the specified identifier. The
new_value argument is a longword containing the binary
value of the specified identifier. When the identifier value is
changed, $MOD_IDENT also changes the value of the identifier in all of
the holder records in which the specified identifier appears.
Description
The Modify Identifier in Rights Database service modifies the specified
identifier record in the rights database. Identifier attributes can be
added or removed. The identifier name or value can be changed. When you
specify both the set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first.
Thus, if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the
result is that the bit is set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD,
$FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER,
$REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
|
|
SS$_DUPIDENT
|
The specified identifier value already exists.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
The specified identifier name already exists in the rights database.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOUNT
Mounts a tape, disk volume, or volume set and specifies options for the
mount operation.
Format
SYS$MOUNT itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$mount (void *itmlst);
Argument
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying options for the mount operation. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item
descriptors, each of which specifies an option and provides the
information needed to perform the operation.
The item list must include at least one device item descriptor and is
terminated by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer that supplies the
information $MOUNT needs to process the specified item code. The
required length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length is too small, $MOUNT truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code that specifies an
option for the MOUNT operation. The $MNTDEF macro defines these codes.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that supplies
information to $MOUNT.
|
|
Return length address
|
This field is not used.
|
Item Codes
MNT$_ACCESSED
Specifies the number of directories that will be in use, concurrently,
on the volume. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the
range 0 to 255. This value overrides the number of directories
specified when the volume was initialized. To specify MNT$_ACCESSED,
the caller must have OPER privilege. The MNT$_ACCESSED item code
applies only to disks.
MNT$_BLOCKSIZE
Specifies the default block size for tape volumes. The buffer must
contain a longword integer value in the range 20 to 65,532 bytes for
OpenVMS RMS operations or 10 to 65,534 bytes for operations that do not
use RMS. The MNT$_BLOCKSIZE item code applies only to tapes.
If you do not specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE, the default block size is 2048
bytes for Files-11 tape volumes and 512 bytes for foreign and unlabeled
tapes.
You must specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE when mounting (1) tapes that do not
have ANSI HDR2 labels, (2) tapes to which data will be written from
compatibility mode, and (3) tapes that are to contain records whose
size is larger than the default value.
MNT$_COMMENT
Specifies text to be associated with an operator request. The buffer
must contain a character string of no more than 78 characters. This
text will be printed on the operator's console if an operator request
is issued for the device being mounted.
MNT$_DENSITY
Specifies the density at which data is to be written to a foreign or
unlabeled tape. The DENSITY item code suppled is dependent on the type
of tape device. If a tape device is capable of using the MT3 density
codes, the buffer for the MNT$DENSITY item code must contain a longword
with one of the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET
(MT3$K_TK50, MT3$K_3480, MT3$K_SDLT, MT3$K_AIT2, and so on). Refer to
the MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
If the device does not support MT3 densities, the buffer must contain a
longword value that specifies one of the following legal densities: 800
bpi, 1600 bpi, or 6250 bpi.
The specified density will be used only if (1) the tape is foreign or
unlabeled and (2) the first operation is a write.
MNT$_DEVNAM
Specifies the name of the device to be mounted. The buffer must contain
a character string of from 1 to 64 characters, which is the device
name. The device name can be a physical device name or a logical name;
if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical device name.
The MNT$_DEVNAM item code must appear at least once in an item list,
and it can appear more than once. It appears more than once when a
volume set is being mounted, because, in this case, one device is being
mounted for each volume in the volume set.
MNT$_EXTENSION
Specifies the number of blocks by which files will be extended. The
buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 65,535. The
MNT$_EXTENSION item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_EXTENT
Specifies the size of the extent cache in units of extent pointers. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To
specify MNT$_EXTENT, you need OPER privilege. The value 0 (the default)
disables caching. The MNT$_EXTENT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FILEID
Specifies the size of the file-ID cache in units of file numbers. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To
specify MNT$_FILEID, you need OPER privilege. The value 1 disables
caching. The MNT$_FILEID item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FLAGS
Specifies a 2-longword bit vector wherein each bit specifies an option
for the mount operation. The buffer must contain a quadword, which is
the bit vector.
The $MNTDEF macro defines symbolic names for each option (bit) in the
bit vector. You construct the bit vector by specifying the symbolic
names for the desired options in a logical OR operation. In the first
longword you logically OR the MNT$M_ mask bits, and in the second
longword you logically OR the MNT2$M_ mask bits. The following table
describes the symbolic names for each option. The MNT2$M_ options are
at the end of the table.
| Option |
Description |
|
MNT$M_CLUSTER
|
The volume is to be mounted for clusterwide access; that is, every
OpenVMS Cluster node can access the volume. $MOUNT mounts the volume
first on the caller's node and then on every other node in the existing
cluster.
Only system or group volumes can be mounted clusterwide. If you do
not specify MNT$M_GROUP or MNT$M_SYSTEM, $MOUNT mounts the volume as a
system volume, provided the caller has SYSNAM privilege. To mount a
group volume clusterwide, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. To
mount a system volume clusterwide, the caller must have SYSNAM
privilege.
MNT$M_CLUSTER has no effect if the system is not a member of a
cluster. MNT$M_CLUSTER applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_FOREIGN
|
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is
not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_FOREIGN, the following
item codes can each appear in the item list only once: the caller must
either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_GROUP
|
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the group
logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to other users
with the same UIC group number as that of the calling process. To
specify MNT$M_GROUP, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. MNT$M_GROUP
applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_INCLUDE
|
Automatically reconstructs a shadow set to the state it was in before
the shadow set was dissolved (due to dismounting or system failure).
Use this option to mount a shadow set or a volume set of shadow sets.
You must specify the exact name of the original virtual unit and the
device name of at least one of the shadow set members. The shadowing
software reads the shadow set membership information from the named
device to determine the membership of the original shadow set. You can
include the MNT$M_INCLUDE option in executable images to have a shadow
set reconstructed. Using MNT$M_INCLUDE prevents your having to manually
reinstate shadow sets after they have been dismounted.
If you do not select this option, $MOUNT does not automatically
reconstruct the former shadow set.
|
|
MNT$M_INIT_CONT
|
Additional volumes in the volume set are to be initialized without
operator intervention. $MOUNT initializes new volumes with the
protections specified for the first magnetic tape of the volume set and
creates unique volume label names for up to 99 volumes in a volume set.
|
|
|
If MNT$M_INIT_CONT is specified, you must allocate multiple magnetic
tape drives to the volume set. If $MOUNT switches to a drive that has
no magnetic tape loaded or has the wrong magnetic tape loaded or if
$MOUNT tries to read a magnetic tape that is not loaded, it notifies
the operator to load the correct magnetic tape. $MOUNT will dismount
and unload volumes as soon as they have been read or written. The
operator can load the next volume in the volume set before the current
reel of the volume set reaches the end of the magnetic tape.
|
|
|
If writing to the volume set, $MOUNT automatically (1) switches to the
next magnetic tape drive, (2) initializes that magnetic tape with the
same volume name and protection as specified in the volume labels of
the first volume in the set, and (3) notifies the operator that the
switch has occurred. If reading the volume set, $MOUNT generates the
label for the next volume in the volume set and reads that volume.
|
|
|
The label name that $MOUNT generates for each additional volume in the
volume set consists of six characters: the first four characters are
the same as the first four characters of the label name of the previous
volume; the fifth and sixth characters represent the number of the
volume in the volume set.
MNT$M_INIT_CONT applies only to magnetic tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_MESSAGE
|
Messages will be sent to the caller's SYS$OUTPUT device.
|
|
MNT$M_MINICOPY_OPTIONAL
|
$MOUNT fails if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk.
|
|
MNT$M_MINICOPY_REQUIRED
|
$MOUNT continues even if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk.
|
|
MNT$M_MULTI_VOL
|
Specifies, for foreign or unlabeled magnetic tapes, that subsequent
volumes can be processed by overriding MOUNT's access checks. You can
use this option when a utility that supports multivolume magnetic tape
sets needs to process subsequent volumes, and these volumes do not
contain labels that MOUNT can interpret. You need VOLPRO privilege to
specify the MNT$M_MULTI_VOL option. MNT$M_MULTI_VOL can only be used
with the MNT$M_FOREIGN option.
HP recommends the use of this qualifier only when it is not
possible to alter the utility to explicitly perform MOUNT and DISMOUNT
operations on each reel in the set.
|
|
MNT$M_NOASSIST
|
$MOUNT does not request operator assistance if errors are encountered
during the mount operation. If not specified, $MOUNT requests operator
assistance to recover from some error conditions.
|
|
MNT$M_NOAUTO
|
Automatic volume labeling (AVL) and automatic volume recognition (AVR)
are to be disabled. If MNT$M_NOAUTO is specified, the operator must
enter commands from the console to process each additional volume in a
volume set. When a volume is finished processing, the operator
specifies the drive on which the next volume is loaded and the label
name of the next volume. You might want to use MNT$M_NOAUTO to disable
AVL and AVR when not reading a volume set sequentially.
You can enable AVL and AVR by specifying MNT$M_INIT_CONT.
MNT$M_NOAUTO applies only to magnetic tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_NOCACHE
|
All caching associated with the volume is turned off. Specifying
MNT$M_NOCACHE is equivalent to (1) specifying MNT$M_WRITETHRU, (2)
specifying a value of 1 for the item descriptor MNT$_FILEID, and (3)
specifying a value of 0 for the item descriptors MNT$M_EXTENT and
MNT$M_QUOTA.
|
|
MNT$M_NOCOPY
|
Disables full copy operations on all physical devices being mounted or
added to a shadow set. This option provides you with the opportunity to
confirm the states of all of the devices or members of a shadow set
before proceeding with any full copy operation. This prevents any
accidental loss of data that could occur if an unintended device is
added to the shadow set.
If you do not select this option, $MOUNT automatically overwrites
the data on shadow set members that are not current. When you select
this option, a $MOUNT operation fails if any of the specified potential
shadow set members require full copy operations.
|
|
MNT$M_NODISKQ
|
Disk quotas are not to be enforced for the volume to be mounted. If not
specified, disk quotas are enforced. To specify MNT$M_NODISKQ, the
caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
MNT$M_NODISKQ applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_NOHDR3
|
ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are not to be written to magnetic tapes as
they are mounted. If not specified, ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are
written to all tapes.
Use MNT$M_NOHDR3 when writing to volumes that will be read by a
system, such as the RT-11 system, which does not process HDR3 and HDR4
labels correctly. MNT$M_NOHDR3 applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_NOLABEL
|
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is
not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the following
item codes can each appear in the item list only once: MNT$_DEVNAM,
MNT$_VOLNAM, and MNT$_LOGNAM. To specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the caller must
either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_NOMNTVER
|
The volume is not marked as a candidate for automatic mount
verification. If not specified, the volume is marked as a candidate for
mount verification.
|
|
MNT$M_NOREBUILD
|
The volume to be mounted should be returned to active use immediately,
without performing a rebuild operation. This flag defers the disk
rebuild operation, so that the volume to be mounted is returned to
active use immediately. A rebuild operation can consume a considerable
amount of time, depending on the number of files on the volume and on
the number of different file owners (if quotas are in use). The volume
can be rebuilt later with the DCL command SET VOLUME/REBUILD to recover
the free space; for more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
If a disk volume is improperly dismounted, for example, during a
system failure, it must be rebuilt to recover any caching limits that
were enabled on the volume at the time of the dismount. By default,
$MOUNT attempts to rebuild.
When mounting a volume set, you must mount all members of the set
to reclaim all available free space.
MNT$M_NOREBUILD applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_NOUNLOAD
|
The volume to be mounted is not to be unloaded when it is dismounted.
Specifying MNT$M_NOUNLOAD causes the volume to remain loaded when it is
dismounted unless the dismount explicitly requests that the volume be
unloaded.
|
|
MNT$M_NOWRITE
|
The volume to be mounted is software write locked. If not specified,
the volume is assumed to have read and write access.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS
|
If the installation allows, this option overrides any character in the
accessibility field of the volume. The necessity of this option is
defined by the installation. That is, each installation has the option
of specifying a routine that the magnetic tape file system will use to
process this field. By default, the operating system provides a routine
that checks this field in the following manner:
- If the magnetic tape was created on a version of the operating
system that conforms to Version 3 of ANSI, then you must use this
option to override any character other than an ASCII space.
- If a protection is specified and that magnetic tape conforms to an
ANSI standard that is higher than Version 3, then you must use this
option to override any character other than an ASCII 1.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume
or have VOLPRO privilege. MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_EXP
|
A tape that has not yet reached its expiration date can be overwritten.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_EXP, the caller must own the volume or have VOLPRO
privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_IDENT
|
You can mount the volume without specifying the volume name (by using
the MNT$_VOLNAM item code). If specified, the following options must
not be specified: MNT$M_CLUSTER, MNT$M_GROUP, MNT$M_SHARE, and
MNT$M_SYSTEM.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_LOCK
|
The software write lock that occurs when a volume has a corrupted
storage bit mask can be overridden.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_SETID
|
Checks on the volume set identification are not to be performed when
subsequent reels in the volume set are mounted. MNT$M_OVR_SETID applies
only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_SHAMEM
|
Allows you to mount former shadow set members outside of the shadow
set. If you do not specify this option, $MOUNT automatically mounts the
volume write-locked to prevent accidental deletion of data. To specify
this option, you must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
When you use this option, the shadow set generation number is
erased from the volume. If you then remount the volume in the former
shadow set, $MOUNT considers it an unrelated volume and marks it for a
full copy operation.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_VOLO
|
The volume label's owner identifier field is not to be processed.
$MOUNT reads volume owner and protection information from the volume
owner field of the volume labels.
The operating system requires that you specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO to
process magnetic tapes when all of the following conditions exist: (1)
the volume was created on an operating system other than OpenVMS; (2)
the volume was initialized with a protection specified; and (3) the
volume conforms to the Version 3 ANSI label standard.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either have VOLPRO
privilege or own the volume. MNT$M_OVR_VOLO applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_READCHECK
|
Read checks are to be performed following all read operations.
|
|
MNT$M_REQUIRE_MEMBERS
|
Controls whether every physical device specified with the /SHADOW
qualifier must be accessible when the MOUNT command is issued in order
for the $MOUNT system service to take effect.
|
|
MNT$M_SHARE
|
Volume is to be mounted shared and is therefore accessible to other
users. MNT$M_SHARE applies only to disks.
If the volume was previously mounted shared by another user and
MNT$M_SHARE is specified in the current call, all other options
specified in the current call are ignored.
If the caller allocated the device and specified MNT$M_SHARE in the
call to $MOUNT, $MOUNT will deallocate the device so that other users
can access the volume.
|
|
MNT$M_SYSTEM
|
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the system
logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to all other
users, provided that UIC-based protection allows access to the volume.
To specify MNT$M_SYSTEM, the caller must have SYSNAM privilege.
MNT$M_SYSTEM applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_TAPE_DATA_WRITE
|
Enables the tape controller's write cache for this device. Enabling the
write cache improves data throughput for write operations. By default,
the tape controller's write cache is disabled for the device.
This option applies only to tape systems that support a write cache.
|
|
MNT$M_VERIFY_LABEL
|
Requires that any member to be added to the shadow set have a volume
label of SCRATCH_DISK. This helps ensure that the wrong disk is not
added to a shadow set. If you plan to use VERIFY_LABEL, you must first
assign the disk to a label. You can do this either by initializing the
disk to be added to the set with the label SCRATCH_DISK, or by
specifying the label for the disk with the SET VOLUME/LABEL command.
|
|
MNT$M_WRITECHECK
|
Write checks are to be performed after all write operations.
|
|
MNT$M_WRITETHRU
|
Disables the deferred write feature for file headers. By default this
feature is enabled, which improves the performance of the applications,
such as PATHWORKS, that use it. The deferred write feature is not
available on Files-11 ODS-1 volumes.
|
|
MNT2$M_CDROM
|
Mounts a volume assuming the media to be ISO 9660 (or High Sierra)
formatted.
|
|
MNT2$M_COMPACTION
|
Enables data compaction for those magnetic tapes that support data
compaction (TA90, TA91, and others).
|
|
MNT2$M_DISKQ
|
Controls whether quotas are to be enforced on the specified disk volume.
|
|
MNT2$_DSI
|
Enables XAR permissions Owner and Group for XARs containing DIGITAL
System Identifiers (DSI). For more information, refer to the
OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
|
|
MNT2$_INCLUDE
|
Automatically reconstructs a former shadow set to the way it was before
the shadow set was dissolved. Applicable only if you have the volume
shadowing option. For more information, refer to HP Volume Shadowing for OpenVMS.
|
|
MNT2$M_NOCOMPACTION
|
Forces the density to no compaction for those magnetic tapes that
support data compaction (TA90, TA91, and others).
|
|
MNT2$_OVR_LIMITED_SEARCH
|
For disk type devices that do not provide for bad-block revectoring, it
is possible that the Files-11 homeblock has been placed numerous I/Os
from the start of the volume. To decrease the failover time when
accessing media which does not contain a valid Files-11 homeblock, a
limited-search algorithm was implemented. This switch overrides the
limited-search algorithm so that the entire volume will be searched for
a valid Files-11 homeblock.
|
|
MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE
|
This bit mask is set to override those SCSI devices that do not support
forced error functionality. By overriding those SCSI devices not
supporting forced error capabilities, MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE enables those
devices to be mounted; otherwise, the shadowing code would report to
$MOUNT that the device does not support forced error, and the device
would not be mounted.
|
|
MNT2$_OVR_SECURITY
|
Enables you to continue mounting a volume if an error is returned
because the volume has an invalid SECURITY.SYS file. You must have the
VOLPRO privilege or own the volume to use this keyword.
|
|
MNT2$M_SUBSYSTEM
|
Enables the processing of protected subsystem identifiers on the
volume. By default, subsystem identifiers are ignored on all but the
system disk. Requires SECURITY privilege.
|
|
MNT2$M_XAR
|
Enables enforcement of the extended record attribute (XAR) access
controls. For more information about XAR, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
|
MNT$_LIMIT
Specifies the maximum amount of free space in the extent cache. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies the amount of
free space in units of tenths of a percent of the disk's total free
space. The MNT$_LIMIT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_LOGNAM
Specifies a logical name for the volume; this logical name is equated
to the device name specified by the first MNT$_DEVNAM item code. The
buffer must contain a character string from 1 to 64 characters, which
is the logical name.
Unless you specify MNT$M_GROUP or MNT$M_SYSTEM, the logical name is
entered in the process logical name table.
MNT$_OWNER
Specifies the UIC to be assigned ownership of the volume. The buffer
must contain a longword octal value, which is the UIC. If the volume is
Files-11 structured, the specified value overrides the ownership
recorded on the volume. You need either VOLPRO privilege or ownership
of the volume to assign a UIC to a Files-11 structured volume.
MNT$_PROCESSOR
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks,
MNT$_PROCESSOR specifies the name of the ancillary control process
(ACP) that is to process the volume. The specified ACP overrides the
default ACP associated with the device.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks, MNT$_PROCESSOR controls
block cache allocation.
To specify MNT$_PROCESSOR, the caller must have OPER privilege.
The buffer must contain a character string specifying either the string
UNIQUE, a device name, or a file specification. Following is a
description of the action taken for each of these cases:
| String |
Description |
|
UNIQUE
|
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks, UNIQUE
specifies that $MOUNT create a new process to execute a copy of the
default ACP image associated with the device specified by the
MNT$_DEVNAM item code.
For Files-11 Structure Level 2 disks, UNIQUE allocates a separate
block cache.
|
|
ddcu
|
For magnetic tapes and Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks,
ddcu specifies that $MOUNT use the ACP process currently being
used by the device
ddcu. The device specified must be in the format
ddcu, for example, DRA3.
For Files-11 Structure Level 1 disks,
ddcu specifies that $MOUNT take the block allocation from the
specified device.
|
|
filespec
|
Specifies that $MOUNT create a new process to execute the ACP image
with the file specification
filespec. Wildcard characters are not allowed in the file
specification. The file must be in the disk and directory specified by
the logical name SYS$SYSTEM. This operation requires CMKRNL privilege.
|
MNT$_QUOTA
Specifies the size of the quota record cache in units of quota records.
The buffer must contain a longword value, which is this size. To
specify MNT$_QUOTA, you need OPER privilege. The value 0 disables
caching. The MNT$_QUOTA item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_RECORDSIZ
Specifies the number of characters in each record and is used with
MNT$_BLOCKSIZE to specify the data formats for foreign volumes. The
buffer must contain a longword value less than or equal to the block
size. The MNT$_RECORDSIZ item code applies only to tapes.
If you do not specify MNT$_RECORDSIZ, the record size is assumed to be
equal to the block size.
MNT$_SHAMEM
Specifies the name of a physical device to be mounted into a shadow
set. The MNT$_SHAMEM descriptor is a 1- to 64-character string
containing the device name. The string can be a physical device name or
a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate to a
physical device name. An item list must contain at least one item
descriptor specifying a member; this item descriptor must appear after
the MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor.
Volume Shadowing for OpenVMS automatically performs a copy or a merge
operation, if necessary, when it mounts the disk into the shadow set.
MNT$_SHANAM
Specifies the name of the virtual unit to be mounted. The buffer is a
1- to 64-character string containing the device name. The virtual unit
name can be a logical name; if it is a logical name, it must translate
to a virtual unit name.
Because every shadow set is represented by a virtual unit, you must
include at least one MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor in the item list that
you pass to $MOUNT to create and mount the shadow set. If you are
mounting a volume set containing more than one shadow set, you must
include one MNT$_SHANAM item descriptor for each virtual unit included
in the volume set.
The relative position of the item descriptors in the item list
determines the membership of the shadow set. That is, it indicates
which members should be bound to a specific virtual unit to form the
shadow set. You must first specify the virtual unit by using the
MNT$_SHANAM item code. Then, you can specify any number of members that
are to be represented by that virtual unit by using one of the
following item codes: MNT$_SHAMEM, MNT$_SHAMEM_COPY, or
MNT$_SHAMEM_MGCOPY. If you specify one shadow set and want to specify a
second, specify a second virtual unit item descriptor. The members you
specify subsequently are bound to the shadow set represented by the
virtual unit specified in the second virtual unit item descriptor.
MNT$_UCS
Specifies a descriptor containing a Universal Character Sequence (UCS)
defined by ISO 2022 and used when mounting an ISO 9660 CD-ROM. For more
information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
MNT$_UNDEFINED_FAT
Specifies the default file attributes to be used for the records on ISO
9660 media for which no record format has been specified.
The buffer contains a 32-bit structure that defines a file's record
format, record attributes, and maximum record size.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the Undefined File
Attributes buffer:
The following table defines the buffer fields:
| Buffer Field |
Definition |
|
UNFAT$W_MRS
|
Maximum record size; specifies the maximum record size for all records
in a file: 0 to 32767. Applies only to FIXED or STREAM formats.
|
|
UNFAT$B_RAT
|
Record attributes; specifies the attributes for all records in a file:
NONE, CR, FTN, PRN, NOBKS. Applies only to non-STREAM record formats.
|
|
UNFAT$B_RFM
|
Record format; specifies the format for all records in a file: FIXED,
VARIABLE, STREAM, STREAM_LF, STREAM_CR, LSB_VARIABLE, or MST_VARIABLE.
|
MNT$_VOLNAM
Specifies the name of the volume to be mounted on the device. The
number of characters allowed in a volume name depends on the type of
device, as follows:
| Device Type |
Number of Characters in Label |
|
Magnetic tape
|
0--6
|
|
Files-11 disk
|
1--12
|
|
ISO 9660 disk
|
1--32
|
The operating system requires disk volume labels to be unique in the
first 12 characters within a given domain.
The MNT$_VOLNAM item code can appear more than once in an item list; it
appears more than once when a volume set is being mounted because, in
this case, one volume name is given to each volume in the volume set.
When a disk volume set is being mounted, you must specify MNT$_DEVNAM
and MNT$_VOLNAM once for each volume of the volume set. The $MOUNT
service mounts the volume specified by the first MNT$_VOLNAM item code
on the device specified by the first MNT$_DEVNAM item code in the item
list; it mounts the volume specified by the second MNT$_VOLNAM code on
the device specified by the second MNT$_DEVNAM code, and so on for all
specified volumes and devices. Thus, there must be an equal number of
these two item codes in the item list.
When a tape volume set is being mounted, the number of MNT$_DEVNAM item
codes specified need not be equal to the number of MNT$_VOLNAM item
codes specified, because more than one volume can be mounted on the
same device.
MNT$_VOLSET
Specifies the name of a volume set. The buffer must contain a character
string from 1 to 12 alphanumeric characters, which is the volume set
name.
An ISO 9660 volume set name can be from 1 to 128 characters in length.
Volume set names must be unique in the first 12 characters. In
addition, if the first 12 characters of the volume set name are the
same as the first 12 characters of any volume label, a lock manager
deadlock will occur. To avoid this problem, you must override either
the volume label (by using the MNT$_VOLNAM item code) or the volume set
name (by using the MNT$_VOLSET item code).
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET, volumes specified by the MNT$_VOLNAM item
code are bound into a new volume set or added to an existing volume
set, depending on whether the name specified by MNT$_VOLSET is a new or
already existing name.
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET to add volumes to an existing volume set,
the root volume (RVN1) must either (1) already be mounted or (2) be
specified first (by the MNT$_DEVNAM and MNT$_VOLNAM item codes) in the
item list.
When you specify MNT$_VOLSET to create a new volume set, the first
volume specified (by the MNT$_DEVNAM and MNT$_VOLNAM item codes) in the
item list becomes the root volume.
MNT$_VPROT
Specifies the protection to be assigned to the volume. The buffer must
contain a longword protection mask, which specifies the four types of
access allowed to the four categories of user.
The protection mask consists of four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or
denies read, write, logical, and physical access to a category of
users. Cleared bits grant access; set bits deny access. The following
diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask:
If you do not specify MNT$_VPROT or specify it as the value 0, the
volume receives the protection that it was assigned when it was
initialized. To specify MNT$_VPROT for a Files-11 structured volume,
the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
MNT$_WINDOW
Specifies the number of mapping pointers to be allocated for file
windows. The buffer must contain a longword value in the range 7 to 80.
This value overrides the default value that was applied when the volume
was initialized. The MNT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to
access the data in the file. To specify MNT$_WINDOW, you need OPER
privilege.
Description
The Mount Volume service mounts a tape, disk volume, or volume set and
specifies options for the mount operation.
When a subprocess mounts a private volume without explicitly allocating
the device, the master process of the job becomes the owner of this
device. This provision is necessary because the subprocess can be
deleted and the volume should remain privately mounted for this job.
When a subprocess explicitly allocates a device and then mounts a
private volume on this device, this subprocess retains the device
ownership. In this case, only subprocesses of the device owner, and
processes with SHARE privilege, have access to the device.
The $MOUNT service uses the following system resources to mount volumes
with group or systemwide access allowed:
When $MOUNT mounts a disk volume, the logical name DISK$volume-label is
always created. If you specify a logical name in the mount request that
is different from DISK$volume-label, there will be two logical names
associated with the device.
If the logical name of a volume is in a process-private table, then the
name is not deleted when the volume is dismounted.
Required Access or Privileges
To mount a volume on a device, you must have read or control access to
that device.
To mount a particular volume, the caller must either own or have
privilege to access the specified volume or volumes. The privileges
required depend on the operation and are listed with the item codes
that specify the operation.
The calling process must have TMPMBX or PRMMBX privilege to perform an
operator-assisted mount. SECURITY privilege is required to enable
protected subsystems.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be
accessed.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code; an illegal
item code was specified; or no device was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOGRPNAM
|
The caller does not have GRPNAM privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOHOMEBLK
|
Files-11 home block not found on volume.
|
|
SS$_NOOPER
|
The caller does not have the required OPER privilege.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have sufficient privilege to access a specified
volume.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSNAM
|
The caller does not have SYSNAM privilege.
|
The $MOUNT service can also return a condition value that is specific
to the Mount utility. The symbolic definition macro $MOUNDEF defines
these condition values.
$MTACCESS
Allows installations to provide their own routine to interpret and
output the accessibility field in the VOL1 and HDR1 labels of an ANSI
labeled magnetic tape.
Format
SYS$MTACCESS lblnam ,[uic] ,[std_version] ,[access_char] ,[access_spec]
,type
C Prototype
int sys$mtaccess (unsigned int *lblnam, unsigned int uic, unsigned int
std_version, unsigned int access_char, unsigned int access_spec,
unsigned int type);
Arguments
lblnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
ANSI label to be processed. The lblnam argument is the
address of a longword containing the label. On input, the label passed
is either the VOL1 or HDR1 label read from the magnetic tape; on output
of labels, the value of this field is 0. The type of label passed is
determined by type.
uic
| OpenVMS usage: |
uic |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
UIC of the user performing the operation. The uic
argument is a longword containing the UIC.
std_version
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Decimal equivalent of the ANSI standard version read from the VOL1
label. The std_version argument is a longword
containing the standard version number.
access_char
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Accessibility character specified by the user. The
access_char argument is a byte containing the
accessibility character used for the output of labels.
access_spec
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Value specifying whether the accessibility character passed in
access_char was specified by the user.
The access_spec argument is a byte containing one of
the following values:
| Value |
Meaning |
|
MTA$K_CHARVALID
|
Yes
|
|
MTA$K_NOCHAR
|
No
|
This argument is used only for the output of labels.
type
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Type of accessibility field to process.
The type argument is a byte containing one of the
following values:
| Value |
Meaning |
|
MTA$K_INVOL1
|
Input a VOL1 label
|
|
MTA$K_INHDR1
|
Input a HDR1 label
|
|
MTA$K_OUTVOL1
|
Output a VOL1 label
|
|
MTA$K_OUTHDR1
|
Output a HDR1 label
|
Description
The Magnetic Tape Accessibility service allows installations to provide
their own routine to interpret and output the accessibility field in
the VOL1 and HDR1 labels of ANSI labeled magnetic tapes. The
installation can override the default routine by providing an
MTACCESS.EXE executive loaded image.
The default installation routine first checks the ANSI standard version
of the label. For magnetic tapes with a version number of 3 or less,
the routine outputs either a blank or the character you specified. On
input of these magnetic tapes, the routine checks for a blank and
returns the value SS$_FILACCERR if the field is not blank.
For magnetic tapes with a version number greater than 3, the routine
outputs either the character specified by the
access_char argument or an ASCII 1 if no character was
specified. On input of these magnetic tapes, the routine checks for a
blank. If the field is blank, R0 is set to 0. In that case, you are
given full access and protection is not checked. If the field contains
an ASCII 1, and the VOL1 Implementation Identifier field contains the
system code, R0 is set to SS$_NORMAL. In that case, the protection is
checked.
If the field is not blank and does not contain an ASCII 1, R0 is set to
SS$_FILACCERR, which forces you to override accessibility checking and
allows the magnetic tape file system to check protection.
The following table summarizes the results of label input check:
| Contents of R0 |
Result |
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Check the protection on the magnetic tape.
|
|
0
|
Give the user full access. Protection is not checked.
|
|
SS$_FILACCERR
|
Check for explicit override, then check protection.
|
Note that the default accessibility routine does not output
SS$_NOVOLACC or SS$_NOFILACC. These statuses are included for the
installation's use, and the magnetic tape file system handles these
cases.
The magnetic tape file system calls $MTACCESS to process the
accessibility field in the VOL1 and HDR1 labels. After a call to the
system service, the magnetic tape file system checks that the
installation did not move the magnetic tape. If the magnetic tape was
moved, the magnetic tape file system completes the current operation
with an SS$_TAPEPOSLOST error. Finally, it processes the remainder of
the label according to the status returned by $MTACCESS.
Required Access or Privileges
Because accessibility is an installation-provided routine, the
operating system cannot determine which users have the authority to
override the processing of this field. However, the magnetic tape file
system allows only operator class users to deal with blank magnetic
tapes so that a user must have both OPER and VOLPRO privileges to
initialize or mount blank magnetic tapes.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB,
$ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL,
$FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_FILACCERR
|
The accessibility characteristic in the HDR1 label is not blank and you
cannot access the file without overriding the field.
|
|
SS$_NOFILACC
|
The user has no access to the file.
|
|
SS$_NOVOLACC
|
The user has no access to the volume.
|
$NUMTIM
Converts an absolute or delta time from 64-bit system time format to
binary integer date and time values.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$NUMTIM timbuf ,[timadr]
C Prototype
int sys$numtim (unsigned short int timbuf [7], struct _generic_64
*timadr);
Arguments
timbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
vector_word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Buffer into which $NUMTIM writes the converted date and time. The
timbuf argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a 7-word structure.
The following diagram depicts the fields in this structure:
If the timadr argument specifies a delta time, $NUMTIM
returns the value 0 in the year since 0 and month of year fields. It
returns in the day of month field the number of days specified by the
delta time.
timadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 64-bit time value to be converted. The timadr
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a quadword containing this time. A
positive-time value represents an absolute time, while a negative time
value indicates a delta time.
If you do not specify timadr, $NUMTIM returns the
current system time.
If timadr specifies the value 0, $NUMTIM returns the
base date (November 17, 1858).
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The 64-bit time value cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer
cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_IVTIME
|
The specified delta time is equal to or greater than 10,000 days.
|
$NUMUTC
Converts an absolute 128-bit binary time into its numeric components.
The numeric components are returned in local time.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$NUMUTC timbuf ,[utcadr]
C Prototype
int sys$numutc (unsigned short int timbuf [13], unsigned int *utcadr
[4]);
Arguments
timbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
vector_word_unsigned |
| type: |
word |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Buffer into which $NUMUTC writes the converted date and time. The
timbuf argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a 13-word structure
containing time, inaccuracy of time, and time differential factor. The
time differential factor encoded in the 128-bit buffer is used to
convert the UTC to its numerical components. Negative values in the
inaccuracy field indicate an infinite inaccuracy.
The following diagram depicts the fields in this structure:
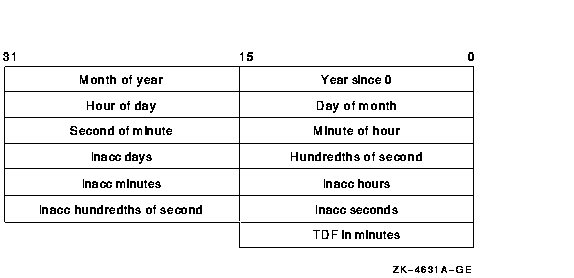
utcadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
coordinated universal time |
| type: |
utc_date_time |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 128-bit UTC time value to be converted.
The utcadr argument is optional; if it is not used,
$NUMUTC will use the current time.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_INVTIME
|
The 128-bit UTC time is not valid.
|
$NXTVOL
The Next Volume service allows you to process the next tape volume in a
multiple volume set. This service applies only to files on magnetic
tape volumes.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$OPEN
The Open service makes an existing file available for processing by
your program. The Open service specifies the type of record access to
be used and determines whether the file can be shared. The Open service
also performs an implicit Display service.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$PARSE
The Parse service analyzes the file specification string and fills in
various NAM block fields.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$PARSE_ACL
Parses the specified text string and converts it to the binary
representation for an access control entry (ACE).
Format
SYS$PARSE_ACL aclstr ,aclent ,[errpos] ,[accnam] ,[nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$parse_acl (void *aclstr, void *aclent, unsigned short int
*errpos, void *accnam, int (*routin)(void));
Arguments
aclstr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Formatted ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes execution. The
aclstr argument is the address of a string descriptor
pointing to the text string to be parsed.
aclent
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Description of the ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes
execution. The aclent argument is the address of a
descriptor pointing to the buffer in which the ACE is written. The
first byte of the buffer contains the length of the ACE; the second
byte contains a value that identifies the type of ACE, which in turn
defines the format of the ACE.
For information about the ACE types and their associated formats, see
$FORMAT_ACL system service documentation.
errpos
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Number of characters from aclstr processed by
$PARSE_ACL. The errpos argument is the address of a
word that receives the number of characters actually processed by the
service. If the service fails, this count points to the failing point
in the string.
accnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_bit_names |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Names of the bits in the access mask when $PARSE_ACL is executing. The
accnam argument is the address of an array of 32
quadword descriptors that define the names of the bits in the access
mask. Each element points to the name of a bit. The first element names
bit 0, the second element names bit 1, and so on.
You can call LIB$GET_ACCNAM to retrieve the access name table for the
class of object whose ACL is to be formatted. If you omit
accnam, the following names are used:
| Bit |
Name |
|
Bit 0
|
READ
|
|
Bit 1
|
WRITE
|
|
Bit 2
|
EXECUTE
|
|
Bit 3
|
DELETE
|
|
Bit 4
|
CONTROL
|
|
Bit 5
|
BIT_5
|
|
Bit 6
|
BIT_6
|
.
.
.
|
|
|
Bit 31
|
BIT_31
|
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
Description
The Parse Access Control List Entry service parses the specified text
string and converts it to the binary representation for an access
control entry (ACE).
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB,
$ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL,
$FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The string or its descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer
descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer cannot be written
by the caller; or the buffer is too small to hold the ACL entry.
|
|
SS$_IVACL
|
The format of the access control list entry is not valid.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
|
$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, disables user process alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
C Prototype
int sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Disable Alignment Fault Reporting service disables user process
alignment fault reporting.
See the description of the $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT service for an
example of a program that can be used to enable and disable user
process alignment fault reporting.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT,
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, initializes user process alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT
C Prototype
int sys$perm_report_align_fault (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Report Alignment Fault service allows the user to permanently
enable user process alignment fault reporting for all subsequent images.
This service reports alignment faults only in exception mode. For more
information about reporting modes, see the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
service.
Image alignment fault reporting takes precedence over process alignment
fault reporting; that is, if both image and process alignment fault
reporting are enabled, faults are reported to the image first.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
Example
|
/**********************************************************************/
/* */
/* SET_ALIGN_REPORT.C */
/* */
/* This program can be used to permanently turn on and off */
/* alignment fault reporting for a process. After creating the */
/* executable, do: */
/* */
/* $ align :== $dir:set_align_report.exe */
/* $ align on */
/* $ run program ! will generate align faults on screen */
/* $ align off */
/* $ run program ! will not generate align faults */
/* */
/**********************************************************************/
#include <stdio>
#include <ctype>
#include <ssdef>
/* alignment fault reporting system services */
extern sys$perm_report_align_fault(),
sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report();
main(argc, argv)
int argc;
char *argv[];
{
int status;
/* check arguments */
if (argc < 2) {
printf ("Insufficient arguments\n");
return (40);
}
/* check if the argument is on or off */
if ((strcmp ("ON", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("on", argv[1]) == 0))
/* on, turn alignment fault reporting on for this process */
status = sys$perm_report_align_fault ();
else if ((strcmp ("OFF", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("off", argv[1]) == 0))
/* off, turn alignment fault reporting off for this process */
status = sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report ();
else
return (SS$_BADPARAM);
/* return status */
return (status);
}
|
This example shows a program that can be used to enable and disable
alignment fault reporting for a process.
$PERSONA_ASSUME (VAX Only)
Modifies the context of the current process to match the context of a
given persona. The $PERSONA_ASSUME service allows an OpenVMS process to
assume the identity of another user or to discard a persona to return
the process to its original state.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_ASSUME persona ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$persona_assume (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is
expected.
If the value of the context passed is 1, then the current persona is
discarded, and the state of the calling process is returned to the
state that existed prior to the first call to $PERSONA_CREATE.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying which Persona services options are to be employed
when the persona is assumed. This argument is ignored when a persona is
being discarded.
The following table describes each flag:
| Flag |
Description |
|
IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY
|
Assume access rights, UIC, authorized privileges, user name, and
security audit flag.
|
|
IMP$M_ASSUME_ACCOUNT
|
Assume OpenVMS account.
|
|
IMP$M_ASSUME_JOB_WIDE
|
Assume the new persona, even in a multiprocess job.
|
Description
When assuming a persona using the IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY option, any
previously enabled image privileges will be disabled. The caller's
process will have only the privileges of the impersonated user enabled.
These privileges are enabled in the Current, Process, and Authorized
privilege masks.
When using IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY, access to the job logical name table
might no longer be possible because the table is protected by the UIC
of the user on whose behalf the current process was created. Also, a
new access to the process' controlling terminal might fail, and the
process might be in a different default resource domain for locking.
Any persona is automatically discarded and deleted upon image exit.
Hence, it is not possible to permanently change the persona of a
process using $PERSONA_ASSUME.
The arguments are read in caller's mode, so an invalid argument can
cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_DELETE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
IMP$_NOCHJIB
|
The Job Information Block cannot be modified.
|
|
IMP$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
Invalid persona argument.
|
$PERSONA_ASSUME (Alpha Only)
Allows an OpenVMS thread to assume the identity of another persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_ASSUME persona ,[flags], [previous], [acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$persona_assume (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int flags,
unsigned int *previous, unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is
expected.
If the value passed is ISS$C_ID_NATURAL, then the state of the calling
thread is returned to the natural persona.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Ignored.
previous
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle of
the currently active persona being replaced is written.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode to be considered when assuming a persona. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
Only equal or more privileged access modes can use this persona.
Description
This service establishes the specified persona as the active security
profile and returns the persona identification handle of the persona
that was active at the point in which the call to this service was made.
On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent
personae are deleted.
The arguments are validated against the caller's mode, so an invalid
argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Certain required arguments were not specified.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the
caller.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The operation requires IMPERSONATE privilege.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
Invalid persona argument.
|
$PERSONA_CLONE (Alpha Only)
Creates a copy of an existing persona within the context of the current
process. The service returns the assigned persona identification for
the new persona in the persona argument. This persona
can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CLONE persona ,[input]
C Prototype
int sys$persona_clone (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *input);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is
written.
input
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification of the
persona to be cloned. If this argument is 0, null, or absent, the
currently active persona is cloned.
Description
The Clone Persona service creates a copy of an existing persona within
the context of the current process. The service returns the assigned
persona identification for the new persona in the
persona argument. This persona can be assumed using
the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent
personae are deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient memory.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the
caller.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
|
$PERSONA_CREATE (VAX Only)
Creates a persona that can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CREATE persona ,usrnam ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$persona_create (unsigned int *persona, void *usrnam, unsigned
int flags);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is
written.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor - fixed-length descriptor |
Name of the user to be impersonated. The usrnam
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character string
containing the user name. The string can contain a maximum of 12
alphanumeric characters.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying which Persona services options are to be employed
when the persona is created.
The following table describes each flag:
| Flag |
Description |
|
IMP$M_ASSUME_DEFPRIV
|
Create a persona with only default privileges.
|
|
IMP$M_ASSUME_DEFCLASS
|
Create a persona with default classification.
|
Description
On calling the Create Persona service, the required information
concerning the OpenVMS user specified by the usrnam
argument is read from the User Authorization File and Rights database
and is stored in system memory. A handle that identifies the created
persona is returned in the persona argument.
It is not possible to create a persona for a user name that has been
disabled.
No changes are made to the caller's process as a result of calling
$PERSONA_CREATE.
Some of the $PERSONA_CREATE service executes in the caller's access
mode (assumed to be user mode). An improper use of the
usernam argument can cause an access violation to be
signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
All calls to $PERSONA_CREATE require DETACH privilege and access to the
system authorization database.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_DELETE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
persona argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_NODETACH
|
Operation requires DETACH privilege.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient memory.
|
|
IMP$_USERDISABLED
|
User name disabled.
|
Any condition value returned by the $LKWSET, $GETUAI, or, $FIND_HELD
can also be returned.
$PERSONA_CREATE (Alpha Only)
Creates a persona that can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CREATE persona ,[usrnam] ,[flags], [usrpro], [itmlst]
C Prototype
int sys$persona_create (unsigned int *persona, void *usrnam, unsigned
int flags, unsigned int *usrpro, unsigned int *itmlst);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is
written.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length descriptor |
Name of the user to be impersonated. The usrnam
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character string
containing the user name. The string can contain a maximum of 32
alphanumeric characters.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes:
- ISS$V_CREATE_AUTHPRIV - This bit is used to create a persona with
the privilege fields set to the authorized privileges of the specified
user.
- ISS$V_CREATE_DEFPRIV - This bit is used for backward compatibility
with the previous implementation of personae. This bit is accepted but
not processed, as it describes the default behavior of the service.
- ISS$V_NOACCESS - Tells $PERSONA_CREATE not to access the SYSUAF
file. Only valid in exec or kernel mode.
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing an encoded security profile. The
usrpro argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a buffer that contains encoded security profile data. This
profile can be created by calling the SYS$CREATE_USER_PROFILE system
service.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes describing modifications to the security profile. The
itmlst argument is the address of an item_list
defining changes to be made to the specified user profile.
This section lists the ISS$ item codes and definitions.
Item Codes
ISS$_WORKPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the working privileges for the new persona as a
quadword value.
ISS$_MODE
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the access mode of the new persona as a longword
value. The mode cannot be more privileged than that of the caller.
ISS$_FLAGS
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the flags field of the new persona as a longword
bit mask. The following bits are currently defined for this field:
- ISS$V_PERMANENT - Mark this persona as permanent. It will survive
image activations/deactivations.
- ISS$V_SECAUDIT - Always audit this persona's operations.
- ISS$V_DEBIT - Debit and credit the process BYTLM/BYTCNT for this
persona. (This flag is always set for user mode persona.)
ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX
The index indicates into which rights chain the rights are placed.
Values for the index are: ISS$M_ENABLED_PERSONA, ISS$M_ENABLED_SYSTEM,
ISS$M_ENABLED_INSTALLED, ISS$M_ENABLED_SUBSYSTEM, and
ISS$M_ENABLED_TEMPORARY. All subsequent rights item packets use the
index until a new ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX item changes the index. If a rights
index is not specified, the rights item packets will use the PERSONA
chain as the default. Rights item packets include: ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS,
ISS$_RIGHTS, ISS$_ADD_AUTHRIGHTS, and ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS.
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS (Reserved for use by HP.)
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user authorized rights of the new persona as a
list of quadword values. Any existing authorized rights will be
overwritten. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA
rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying
different indexes.
ISS$_RIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user rights of the new persona as a list of
quadword (paired longword) values. Any existing authorized rights will
be overwritten. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA
rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying
different indexes. The format of the list is the same as
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS.
The format of the list is as follows:
ISS$_USERNAME
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the user name of the new persona as a 32-byte
character string.
ISS$_ACCOUNT
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the account of the new persona as a 32-byte
character string.
ISS$_NOAUDIT
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the No Audit field of the new persona as a
longword value.
ISS$_UIC
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the UIC of the new persona as a longword value.
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the authorized privileges for the new persona as a
quadword value.
ISS$_PERMPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the permanent privileges for the new persona as a
quadword value.
ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the image working privileges for the new persona
as a quadword value.
ISS$_ENABLED
$PERSONA_CREATE sets the Rights Enable field of the new persona as a
longword bit mask. These bits correspond to the indices of the
different rights chains. By setting the bit in the ENABLED field, the
corresponding rightslist chain will be enabled, and its rights will be
included in all rights checks. Valid bits are: ISS$V_ENABLED_PERSONA,
ISS$V_ENABLED_SUBSYSTEM, ISS$V_ENABLED_IMAGE, ISS$V_ENABLED_SYSTEM, and
ISS$V_ENABLED_TEMPORARY.
ISS$_ADD_AUTHRIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE adds the rights to the current list of authorized
rights. $PERSONA_CREATE expects the same format as that outlined in
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA
rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying
different indexes.
ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS
$PERSONA_CREATE adds the rights to the current list of rights.
$PERSONA_CREATE expects the same format as that outlined in
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS. By default, the rights will be placed in the PERSONA
rights chain. See ISS$_RIGHTS_INDEX for more information on specifying
different indexes.
Description
When you call this service, you can specify either the
usrnam or usrpro argument, but not
both. The required information specifying the OpenVMS user is read from
either the User Authorization File (UAF) and rights database or the
usrpro buffer and is stored in system memory. Any
modifications specified in the itmlst are then applied
to complete the new persona. A persona identification handle that
refers to the created persona is returned in the persona argument. This
service creates a default VMS extension for the persona.
It is possible to call $PERSONA_CREATE in any mode. To call
$PERSONA_CREATE in kernel mode, the calling sequence is different. Only
the usrpro argument is valid (usrnam
cannot be used because kernel mode access to the SYSUAF file is not
allowed), and it is necessary to set the PSB$M_NOACESS value in the
flags.
No changes are made to the caller's thread as a result of calling
$PERSONA_CREATE.
The arguments are validated against the caller's mode, so an invalid
argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
All calls to $PERSONA_CREATE require IMPERSONATE privilege and read
access to the system authorization database.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
persona argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The operation requires IMPERSONATE privilege.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient memory.
|
|
SS$_USERDISABLED
|
User name disabled.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the
caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Certain required arguments were not specified.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The value of at least one of the arguments is incorrect.
|
|
SS$_BADCHECKSUM
|
The buffer specified by
usrpro is not valid.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The buffer length for data within the
usrpro or
itmlst was invalid.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
At least one argument in the item code is invalid.
|
|
SS$_INVARG
|
An incorrect combination of arguments was specified.
|
|
SS$_INVSECDOMAIN
|
The buffer specified by
usrpro contains data that originated outside the local
security domain.
|
Any condition value returned by the $LKWSET, $GETUAI, or $FIND_HELD
service can also be returned.
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION (Alpha Only)
Creates an extension on the current persona. A persona extension is a
mechanism to attach support for additional security credentials.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION persona ,extensionID ,buffer ,length ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$persona_create_extension (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int
*extensionID, void *buffer, unsigned int *length, unsigned int *flags);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification to which
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION attaches a new persona extension.
Two special values for persona are also permitted: 0,
which means the current persona, and -1, which means the process'
natural persona is used.
extensionID
| OpenVMS usage: |
extension_ID |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extension identification (EID) for
which the registered CREATE routine will be called to create a new
persona extension block.
buffer
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a buffer containing data to be used in creating the persona
extension data structure. The interpretation of the data within this
buffer is the responsibility of the extension create routine. For
example, this data could be a Type-Length-Value (TLV) structure
containing fields in the extension data structure. Specifying this
buffer is optional; a caller who does not want to supply a buffer
should specify an address of zero (0).
length
| OpenVMS usage: |
size |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the size, in bytes, of the
buffer argument. Specifying length is
optional; a caller who does not want to supply a length should specify
an address of zero (0). Specifying a buffer without a length is the
same as not specifying a buffer.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
flags |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Flag mask specifying the options to be employed when the persona
extension is created. Specifying flags is optional; a caller who does
not want to supply flags should specify an address of zero (0).
| Flag |
Description |
|
PXB$V_PRIMARY_EXTENSION
|
This extension is recorded as the persona's primary extension. If a
persona already has a primary extension, the error SS$_UNSUPPORTED is
returned and the extension is not created. The primary extension is
returned when the persona is queried for its "Primary Extension." There
is no other meaning for this value.
|
Description
This service creates an extension by calling the registered Extension
Create routine for the specified extension and by attaching it to the
persona represented by the persona argument.
When a return fails, no persona extension is created.
A VMS extension is already associated with every persona. An attempt to
create a VMS extension using this service returns SS$_DUPLNAM.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege
enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
A buffer or return address specified in the item list cannot be read.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid identifier code.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
The persona already has an extension of this type.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
|
|
SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
|
The caller does not have the privilege to extend its original
identity/persona.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHEXT
|
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
|
|
SS$_UNSUPPORTED
|
An unsupported request was made; check the PRIMARY_EXTENSION flags bit.
|
$PERSONA_DELEGATE (Alpha Only)
Delegates or assigns the currently active persona to another process.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELEGATE serverPID ,persona ,input
C Prototype
int sys$persona_delegate (unsigned int *serverPID, unsigned int
*persona, unsigned int *input);
Arguments
serverPID
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_ID |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extended process identification
(PID) of the server process to which $PERSONA_DELEGATE grants the
current persona.
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the identification that the
$PERSONA_RESERVE service reserved in the server's process for this
client's persona.
input
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification that
describes which persona is delegated to the server. If the
input argument is zero (0) or null, or if the input
value is zero (0), the current persona is delegated. If the input value
is -1, then the natural persona of the process is delegated.
Description
This service delegates or assigns either the specified persona or the
currently active persona to another process. The server process must
have reserved a persona slot for the current process to use by calling
$PERSONA_RESERVE before calling this service.
The delegation of persona is only supported for processes residing on
the same node in the cluster. When a return fails, the persona is not
delegated.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The arguments cannot be read by the service.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The process specified does not exist.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
|
$PERSONA_DELETE
Deletes a persona created using the $PERSONA_CREATE, the
$PERSONA_CLONE, or the $PERSONA_RESERVE service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELETE persona
C Prototype
int sys$persona_delete (unsigned int *persona);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is
expected.
Description
The PERSONA_DELETE service frees the resources used by the persona. No
changes to the caller's process are made as a result of calling
$PERSONA_DELETE.
The persona argument is validated against the caller's
mode, so an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be
signaled.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND,
$PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation.
|
|
SS$_PERSONADELPEND
|
Persona is in use; delete pending on release.
|
|
SS$_NODELPERMANENT
|
Permanent personae cannot be deleted.
|
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION (Alpha Only)
Deletes an extension attached to a persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION persona ,extensionID
C Prototype
int sys$persona_delete_extension (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int
*extensionID);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification for which
$PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION calls the registered Extension Delete
function.
extensionID
| OpenVMS usage: |
extension_ID |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the extension identification (EID) for
which the registered DELETE routine is called in order to delete a
persona extension block from the specified persona.
Description
This service deletes an extension data structure by calling the
registered Extension Delete routine for the specified extension.
When a return fails, the persona extension is not deleted.
The VMS extension associated with each persona cannot be deleted. An
attempt to delete that extension returns SS$_UNSUPPORTED.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege
enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE,
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
|
The caller does not have the privilege to delete pieces of the thread's
original identity/persona.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHEXT
|
The extension specified does not exist in the persona.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied was invalid.
|
|
SS$_UNSUPPORTED
|
The specified extension cannot be deleted.
|
$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP (Alpha Only)
Translates a text name of an extension (for example, VMS or NT) into an
extension identification (EID) that can be used in other
persona-related system services.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP extensionName ,extensionID
C Prototype
int sys$persona_extension_lookup (void *extensionName, unsigned int
*extensionID);
Arguments
extensionName
| OpenVMS usage: |
extension_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length descriptor |
Address of a character string descriptor pointing to the name of the
extension being looked up.
extensionID
| OpenVMS usage: |
extension_ID |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the value of the extension
identification (EID) returned by the service is written.
Description
This service translates a text name of an extension into an extension
identification (EID) that can be used in other persona-related system
services.
There are currently two extension names: VMS and NT.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY,
$PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The string descriptor supplied in the extensionName argument cannot be
read by the service.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid argument was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTEXT
|
The supplied extensionName does not exist on this system.
|
$PERSONA_FIND (Alpha Only)
Enables the caller to find the personae within a process that have
certain attributes or settings.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_FIND persona ,itmlst ,contxt
C Prototype
int sys$persona_find (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst, unsigned int
*contxt);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification that
matches all of the items present in the item list is written.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes specifying which information about the persona is to be
compared. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each describing an item of information or an item
list processing directive. The list of item descriptors is terminated
by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram shows the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table lists the item descriptor fields and their
definitions:
| Field |
Description |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $PERSONA_FIND is to locate the
information. The length of the buffer depends on the item code
specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value
of buffer length is too small, $PERSONA_FIND fails the comparison.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information $PERSONA_FIND is to test, or specifying a directive for
processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes.
Each item code is described in the Description section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which
$PERSONA_FIND locates the information used for the comparison.
|
|
Return length address
|
An unused longword containing the user-supplied address of a word into
which the system service writes the length in bytes of the information
it returned. This longword is unused for PERSONA_FIND.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Context value used when repeatedly calling $PERSONA_FIND. The
contxt argument is the address of a longword used
while $PERSONA_FIND searches for all personae that match the criteria.
The context value must be initialized to zero, and the resulting
context of each call to $PERSONA_FIND must be presented to each
subsequent call. After contxt is passed to
$PERSONA_FIND, you must not modify its value.
Description
This service enables the caller to find the personae within a process
that have certain attributes or settings.
A persona identification is returned only if all the items specified in
the item list match those in the persona and its extensions.
The item list cannot be changed between context-saved calls. Results
are unpredictable if the item list is changed between calls.
Repeated calls to $PERSONA_FIND return subsequent matching personae.
When the service returns SS$_NOMOREPROC, there are no more personae to
examine.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the OpenVMS
persona extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_USERNAME
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_ACCOUNT
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS account name as text string
|
|
ISS$_DOMAIN
|
Q,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename
|
|
ISS$_PRINCIPAL
|
Q,F
|
64
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION
|
Q,F
|
32
|
The text string VMS
|
|
ISS$_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_WORKCLASS
|
Q,M
|
Varying
|
Working classification
|
|
ISS$_RIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Enabled list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_NOAUDIT
|
Q,M
|
4
|
No audit counter---0 means audits disabled
|
|
ISS$_UIC
|
Q,M,F
|
4
|
Current UIC
|
|
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Authorized privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_PERMPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Permanent privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Image working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_ENABLED
|
Q
|
4
|
Mask of enabled rights chains
|
|
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Authorized list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_MINCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Minimum classification
|
|
ISS$_MAXCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Maximum classification
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Required Access or Privileges
The caller may require extension-specific privileges to search on some
data items. The Persona Item Codes section lists the privileges that
are needed.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP,
$PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_IVCONTEXT
|
The context value is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
|
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the
specified personae.
|
|
SS$_NOMOREPROC
|
There are no more personae to check.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHEXT
|
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
|
$PERSONA_MODIFY (Alpha Only)
Sets attribute values for a persona.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_MODIFY persona ,itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$persona_modify (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the persona identification for which
this service is to set information.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes specifying which information in the persona is to be
modified. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each describing an item of information or an item
list processing directive. The list of item descriptors is terminated
by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram shows the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table lists the item descriptor fields and their
definitions:
| Field |
Description |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer from which $PERSONA_MODIFY is to get information.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information $PERSONA_MODIFY is to change, or specifying a directive for
processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes.
Each item code is described in the Description section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from
which $PERSONA_MODIFY is to get the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
This field is ignored on a call to PERSONA_MODIFY.
|
Description
The Modify Persona Data service sets attribute values for a persona.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the OpenVMS
persona extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_USERNAME
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_ACCOUNT
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS account name as text string
|
|
ISS$_DOMAIN
|
Q,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename
|
|
ISS$_PRINCIPAL
|
Q,F
|
64
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION
|
Q,F
|
32
|
The text string VMS
|
|
ISS$_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_WORKCLASS
|
Q,M
|
Varying
|
Working classification
|
|
ISS$_RIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Enabled list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_NOAUDIT
|
Q,M
|
4
|
No audit counter---0 means audits disabled
|
|
ISS$_UIC
|
Q,M,F
|
4
|
Current UIC
|
|
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Authorized privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_PERMPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Permanent privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Image working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_ENABLED
|
Q
|
4
|
Mask of enabled rights chains
|
|
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Authorized list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_MINCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Minimum classification
|
|
ISS$_MAXCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Maximum classification
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Required Access or Privileges
This service requires that the caller have the IMPERSONATE privilege
enabled or be in exec or kernel mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP,
$PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer cannot be
read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_NOIMPERSONATE
|
The caller does not have the privilege to obtain information about the
specified personae.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHEXT
|
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied was invalid. This service may also return
status codes associated with the various extension routines.
|
$PERSONA_QUERY (Alpha Only)
Retrieves attribute values from a persona (and accompanying extensions).
Format
SYS$PERSONA_QUERY persona ,itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$persona_query (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst);
Arguments
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is
written.
Two special values for persona are also permitted: 0,
which means use the current persona, and -1, which means use the
process' natural persona.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes describing which information about the persona is to be
returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information or
an item list processing directive. The list of item descriptors is
terminated by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram shows the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table lists the item field descriptors and their
definitions:
| Field |
Description |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer into which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information.
The length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the item
code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too
small, $PERSONA_QUERY truncates the data.
If the buffer length is specified as 0, the service does not return
any data in the buffer; instead, the service returns the size of buffer
required to contain the data in the Return Length address. This allows
run-time determination of the size of buffer needed to hold the
requested information.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information $PERSONA_QUERY is to return, or specifying a directive for
processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes.
Each item code is described in the Description section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer into
which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word into which
the service writes the length in bytes of the information it returned.
If the buffer length field is zero (0), then you must specify a return
length address.
|
Description
The Query for Persona Data service returns the requested items in the
buffers supplied.
OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the OpenVMS
persona extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_USERNAME
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_ACCOUNT
|
Q,M,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS account name as text string
|
|
ISS$_DOMAIN
|
Q,F
|
32
|
OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename
|
|
ISS$_PRINCIPAL
|
Q,F
|
64
|
OpenVMS user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION
|
Q,F
|
32
|
The text string VMS
|
|
ISS$_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_WORKCLASS
|
Q,M
|
Varying
|
Working classification
|
|
ISS$_RIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Enabled list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_NOAUDIT
|
Q,M
|
4
|
No audit counter---0 means audits disabled
|
|
ISS$_UIC
|
Q,M,F
|
4
|
Current UIC
|
|
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Authorized privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_PERMPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Permanent privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
|
Q,M
|
8
|
Image working privilege mask
|
|
ISS$_ENABLED
|
Q
|
4
|
Mask of enabled rights chains
|
|
ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Authorized list of rights identifiers
|
|
ISS$_MINCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Minimum classification
|
|
ISS$_MAXCLASS
|
Q
|
Varying
|
Maximum classification
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Common Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the common
persona extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_COMMON_USERNAME
|
Q
|
varying
|
User name as text string
|
|
ISS$_COMMON_ACCOUNT
|
Q
|
varying
|
Account name as text string
|
|
ISS$_COMMON_FLAGS
|
Q
|
4
|
Flags as a longword
|
|
ISS$_DOMAIN
|
Q
|
varying
|
Domain name as text string
|
|
ISS$_COMMON_PRINCIPAL
|
Q
|
varying
|
Principal name as text string
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION
|
Q
|
32
|
Extension name as text string
|
|
ISS$_DOI
|
Q
|
8
|
Domain Of Interpretation quadword
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
General Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the general
persona extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_SWITCH_EXTENSION
|
Q,M
|
4
|
Extension ID to be used for subsequent item code processing
|
|
ISS$_FLAGS
|
Q,M
|
4
|
Various flags (ISS$_FLAG_PERMANENT)
|
|
ISS$_MODE
|
Q
|
4
|
Persona creation mode (user, supervisor, exec, or kernel)
|
|
ISS$_UID
|
Q
|
16
|
UID assigned when persona created
|
|
ISS$_PERSONA_ID
|
Q
|
4
|
Persona ID of this PSB
|
|
ISS$_PRIMARY_EXTENSION
|
Q,M
|
4
|
Extension id of primary authenticator
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION_COUNT
|
Q
|
4
|
Count of extensions attached to persona
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION_ARRAY
|
Q
|
varying
|
Array of longwords containing extension ids of all extensions attached
to persona
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
NT Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the NT persona
extension data:
| Item Code |
Use+ |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
|
ISS$_NT_PRINCIPAL
|
Q,F
|
varying
|
Principal name as text string
|
|
ISS$_NT_TOKEN_USERNAME
|
Q,F
|
varying
|
NT user name as text string
|
|
ISS$_NT_TOKEN_DOMAINNAME
|
Q,F
|
varying
|
NT domain as text string
|
|
ISS$_EXTENSION
|
Q,F
|
varying
|
The text string "NT"
|
|
ISS$_NT_FLAGS
|
Q,M
|
4
|
Various flags
|
|
ISS$_NT_USER_REFCOUNT
|
Q,M
|
4
|
NT-Specific User Field
|
|
ISS$_NT_CREDENTIALS
|
Q,M
|
varying
|
All Token and Security info
|
|
ISS$_NT_NT_OWF_PASSWORD
|
Q,M
|
varying
|
NT Password
|
|
ISS$_NT_LM_OWF_PASSWORD
|
Q,M
|
varying
|
LM Password
|
|
ISS$_NT_TOKEN_USERSESSIONKEY
|
Q,F
|
16
|
User's session key
|
|
ISS$_NT_TOKEN_LMSESSIONKEY
|
Q,F
|
8
|
LM session key
|
+Use descriptions are: Query, Modify, and Find.
Required Access or Privileges
No privileges are required to call this service.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP,
$PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer length or
buffer cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_BADITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHEXT
|
The extension requested does not exist on the system.
|
|
SS$_PERSONANONGRATA
|
The persona ID supplied is invalid.
|
$PERSONA_RESERVE (Alpha Only)
Reserves a persona ID in the server's persona table to be filled in by
the $PERSONA_DELEGATE system service.
Format
SYS$PERSONA_RESERVE clientPID ,persona
C Prototype
int sys$persona_reserve (unsigned int *clientPID, unsigned int
*persona);
Arguments
clientPID
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_ID |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword containing the External Process Identification
(EPID) of the client process for which the server is reserving the slot.
persona
| OpenVMS usage: |
persona |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a longword into which the persona identification is written.
This service sets aside the identification for the client's
to-be-delegated persona.
Description
This service reserves a persona identifier slot within the current
process for a specific client process to use in delegating its persona
to this process. A reserved persona slot can be deleted by a call to
the $PERSONA_DELETE service. When a return fails, no persona slot has
been reserved for the client process.
The delegation of persona is only supported for processes residing on
the same node of a cluster.
Required Access or Privileges
IMPERSONATE
Required Quota
BYTLM
Related Services
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE,
$PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION,
$PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP,
$PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid parameter was specified.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
$PROCESS_AFFINITY (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows modification of the CPU affinity set for a
specified kernel thread.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY [pidadr] [,prcnam] [,select_mask] [,modify_mask]
[,prev_mask] [,flags]
C Prototype
int sys$process_affinity (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct
_generic_64 *select_mask, struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct
_generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose affinity mask is
to be modified or returned. The pidadr argument is the
32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and prcnam arguments. If
neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service
operations are made to the user affinity mask of the current kernel
thread of the calling process. The pidadr argument
takes precedence over the prcnam argument in any
circumstances where both are supplied in the service call.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Process name of the process whose affinity mask is to be modified or
returned. The prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit
address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name
string. A process can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string.
The service operations are made to the user affinity mask of the
initial thread of the specified process.
If pidadr and prcnam are both
specified, then pidadr is modified or returned and
prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified,
then the context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is
modified or returned.
select_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying which bits of the specified process' affinity mask are
to be modified. The select_mask argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set,
specifies that the corresponding CPU position in the mask is to be
modified.
The individual CPU bits in select_mask can be
referenced by their symbolic name constants, CAP$M_CPU0 through
CAP$M_CPU31. These constants (zero-relative to match system CPU IDs)
specify the position in the mask quadword that correspond to the bit
name. Multiple CPUs can be selected by ORing together the appropriate
bits.
modify_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying the settings for those explicit affinities selected in
the select_mask argument. The
modify_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the
corresponding CPU is to be added to the specified process affinity set;
when clear, the corresponding CPU is to be removed from the specified
process affinity set.
The bit constants CAP$M_CPU0 through CAP$M_CPU31 can be used to modify
the appropriate bit position in the quadword pointed to by
modify_mask. Multiple CPUs can be added to the
affinity set by ORing together the appropriate bits.
To add a specific CPU to the affinity mask set, that bit position must
be set in both select_mask and
modify_mask. To remove a specific CPU from the
affinity mask set, that bit position must be set in
select_mask and clear in modify_mask.
The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_ADD, when specified in
modify_mask, indicates that all CPUs specified in
select_mask are to be added to the affinity mask set.
The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_REMOVE indicates that all CPUs in
select_mask are to be removed from the affinity mask
set.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous CPU affinity mask for the specified kernel thread before
execution of this call to $PROCESS_AFFINITY. The
prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword into which $PROCESS_AFFINITY writes the previous explicit
affinity bit mask.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for affinity modification. The flags
argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an
option. Only the bits specified below are used; the remainder of the
quadword bits are reserved and must be 0.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines.
The flags argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT
|
Indicates whether to modify the permanent process affinities in
addition to the current image copy. If CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT is set,
then both the permanent and current affinities are modified. If the
flag bit is clear or
flags is unspecified, then just the current image
process affinities are modified.
This bit also determines which of the affinity masks are returned in
prev_mask. If set, the permanent mask, used to
reinitialize the current set at image rundown, is returned. If the bit
is clear or the
flags argument is not specified, the current running
mask is returned.
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
|
Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a nonrunnable state
under some circumstances. No operation of this service will allow a
transition from a runnable to blocked state; however, if the kernel
thread is already at a blocked state, this bit determines whether the
result of the operation must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
is set or
flags is unspecified, the kernel thread will be
checked to ensure it can safely run on one of the CPUs in the active
set; otherwise, any valid state operations on kernel threads already in
a blocked state will be allowed.
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE
|
Indicates whether a check is made to verify that all CPUs in the select
mask that are about to be selected for affinity binding are in the
active set. This does not apply to CPUs that are about to be cleared
from the current affinity set. Unlike CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU where only a
single CPU has to be valid for the condition to pass,
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE requires that all CPUs in the selected set
must pass the criteria.
|
|
CAP$M_PURGE_WS_IF_NEW_RAD
|
Causes the working set of the process to be purged if the choice of
affinity results in a change to the home RAD of the process.
|
Description
The Modify Process Affinity system service, based on the arguments
select_mask and modify_mask, adds or
removes CPUs from the specified kernel thread's affinity mask sets. If
specified, the previous affinity mask is returned in
prev_mask. With the modify_mask
argument, multiple CPUs can be added to or removed from the process
affinity mask set in the same system service call.
Adding a specific CPU to the process affinity mask indicates that the
kernel thread is able to execute only on that CPU or on the others
specified in the mask. Affinity scheduling takes effect as soon as the
affinity mask becomes nonzero, limiting the CPU selection for the
kernel thread to what is specified and available. Thread selection and
execution is still subject to standard capability requirements, but
only the affinity CPU set is considered when looking for an available
site. When the affinity mask is cleared, all CPUs are again considered
available and affinity is deactivated.
Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or
both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask
is specified, then select_mask must be specified as an
argument. If modify_mask is not specified, then no
modifications are made to the affinity mask for the specified kernel
thread. In this case, select_mask is ignored. If
prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is
returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will
transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
bit in the flags argument requires that the final
thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise,
interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread
is already in one.
Required Privileges
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY
to modify its own affinity mask. To modify another process' affinity
mask, the caller must have:
ALTPRI---To modify any process with a matching UIC
ALTPRI and GROUP---To modify any process in the same UIC group
ALTPRI and WORLD---To modify any process
To call SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY simply to retrieve the specific process or
global mask, the caller need only have the following privileges:
None---To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching
UIC
GROUP---To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
WORLD---To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES
$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
|
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_CPUCAP
|
No CPU can run the specified process with new affinities.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no
operation was specified.
|
$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, allows modification of the user capability set for a
specified kernel thread, or for the global user capability process
default.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES [pidadr] [,prcnam] [,select_mask]
[,modify_mask] [,prev_mask] [,flags]
C Prototype
int sys$process_capabilities (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam,
struct _generic_64 *select_mask, struct _generic_64 *modify_mask,
struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose user capability
mask is to be modified or returned. The pidadr
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the
PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and prcnam arguments. If
neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service
operations are made to the user capability mask of the current kernel
thread of the calling process. The pidadr argument
takes precedence over the prcnam argument where both
are supplied in the service call.
If the constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is specified in
flags, then the user portion of the default process
user capability mask is modified or returned instead, regardless of the
values specified in pidadr.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Process name of the process whose user capability mask is to be
modified or returned. The prcnam argument is the 32-
or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor pointing to the
process name string. A process can be identified with a 1- to
15-character string. The service operations are made to the user
capability mask of the initial thread of the specified process.
You can use the prcnam argument only if the process
identified by the descriptor has the same UIC group number as the
calling process. To obtain information about processes in other groups,
the pidadr argument must be used.
If pidadr and prcnam are both
specified, then prcnam is ignored. If neither argument
is specified, then the context of the current kernel thread of the
calling process is modified or returned.
select_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying which bits of the specified process' user capability
mask are to be modified. The select_mask argument is
the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when
set, specifies that the corresponding user capability is to be modified.
The individual user capability bits in select_mask can
be referenced by their symbolic bit constant names, CAP$M_USER1 through
CAP$M_USER16. These constants (not zero-relative) specify the position
in the mask quadword that corresponds to the bit name. Multiple
capabilities can be selected by ORing together the appropriate bits.
Alternatively, the constant CAP$K_ALL_USER, when specified as the
select_mask argument, selects all user capabilities.
modify_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Mask specifying the settings for those capabilities selected in the
select_mask argument. The modify_mask
argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein
a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding user capability is to
be added to the specified kernel thread; when clear, the corresponding
user capability is to be removed.
The symbolic bit constants CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16 can be used
to modify the appropriate bit position in modify_mask.
Multiple capabilities can be modified by ORing together the appropriate
bits.
To add a specific user capability to a kernel thread, that bit position
must be set in both select_mask and
modify_mask. To remove a specific user capability from
a kernel thread, that bit position must be set in
select_mask and clear in modify_mask.
The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_ADD, when specified in
modify_mask, indicates that all capabilities specified
in select_mask are to be added to the appropriate
capability set. The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_REMOVE indicates
that all specified capabilities are to be removed from the set.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous user capability mask for the specified process or thread
before execution of this call to $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES. The
prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword into which $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES writes the previous bit mask.
If CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the flags
argument, then prev_mask will contain the user portion
of the global default capability mask.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability modification. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified below are used; the
remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and must be zero.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined by the $CAPDEF macro.
The flags argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY
|
Indicates that the specified operations are to be performed on the
global context cell instead of on a specific kernel thread. This bit
supersedes any individual kernel thread specified in
pidadr or
prcnam. Specifying this bit constant applies the
service operations to the capabilities for all newly created processes.
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT
|
Indicates whether to modify the permanent user process capabilities in
addition to the current image copy. If CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT is set,
then both the permanent and current user process capabilities are
modified. If this bit is clear or
flags is unspecified, then just the current image
process capabilities are modified.
This bit also determines which of the capability masks are returned
in
prev_mask. If set, the permanent mask, used to
reinitialize the current set at image rundown, is returned. If the bit
is clear or the
flags argument is not specified, the current running
mask is returned.
|
|
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
|
Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a nonrunnable state
under some circumstances. No operation of this service will allow a
transition from runnable to blocked state; however, if the kernel
thread is already at a blocked state, this bit determines whether the
result of the operation must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
is set or
flags is unspecified, the kernel thread will be
checked to ensure it can safely run on one of the CPUs in the active
set; otherwise, any state operations on kernel threads already in a
blocked state will be allowed.
|
|
CAP$M_PURGE_WS_IF_NEW_RAD
|
Causes the working set of the process to be purged if the choice of
capability results in a change to the home RAD of the process.
|
Description
The Modify Process User Capabilities system service, based on the
arguments select_mask and
modify_mask, adds or removes user capabilities for the
specified kernel thread. If specified, the previous capability mask is
returned in prev_mask. With the
modify_mask argument, multiple user capabilities for a
kernel thread can be added or removed in the same system service call.
Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or
both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask
is specified, then select_mask must be specified as an
argument. If modify_mask is not specified, then no
modifications are made to the user capability mask for the specified
kernel thread. In this case, select_mask is ignored.
If prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask
is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will
transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU
bit in the flags argument requires that the final
thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise,
interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread
is already in one.
If the symbolic bit constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the
flags argument, the user capability modifications or
the mask read requests are made only to the global initialization cell
regardless of what process selections values are specified in the
pidadr and prcnam arguments.
Required Access or Privileges
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call
SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES to modify its own user capability mask. To
modify another process' user capability mask, the caller must have:
ALTPRI---To modify any process with a matching UIC
ALTPRI and GROUP---To modify any process in the same UIC group
ALTPRI and WORLD---To modify any process
To call SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES simply to retrieve the specific
process or global mask, the caller need only have the following
privileges:
None---To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching
UIC
GROUP---To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
WORLD---To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
|
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or more than 15 characters.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_CPUCAP
|
No CPU can run the specified process with new capabilities.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no
operation was specified.
|
|
















