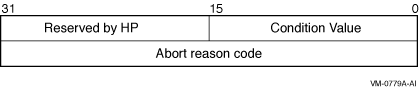|
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$TIMCON
Converts 128-bit Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) format to 64-bit
system format or 64-bit system format to 128-bit UTC format based on
the value of the convert flag.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$TIMCON [smnadr] ,[utcadr] ,cvtflg
C Prototype
int sys$timcon (struct _generic_64 *smnadr, unsigned int *utcadr [4],
unsigned long int cvtflg);
Arguments
smnadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The 64-bit system format value that $TIMCON will use in the conversion.
The smnadr argument will be read from or written to
based on the value of the cvtflg argument. The
smnadr is required when converting UTC time to 64-bit
system format.
utcadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
coordinated universal time |
| type: |
utc_date_time |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
UTC time value that $TIMCON will use in the conversion. The
utcadr argument will be read from or written to based
on the value of the cvtflg argument. The
utcadr argument is required when converting 64-bit
system format to UTC time.
cvtflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
conversion flag |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A longword indicating the direction of the conversion. If the
cvtflg value is 0, UTC time is converted to 64-bit
system value. If the cvtflg value is 1, 64-bit system
format is converted to UTC time.
Description
The Time Converter service converts 64-bit system format time to UTC
format, and vice versa.
When converting a 64-bit system format time to 128-bit UTC format time,
the time zone of the local system is used.
When converting a 128-bit UTC format time to a 64-bit system time, the
time zone differential factor encoded in the 128-bit buffer is used.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_INVTIME
|
The input time cannot be converted because its value is out of the
legal range or is a delta time, or the UTC is of an illegal format.
|
$TRANS_EVENT
Forces a transaction state change for a transaction in which there is
at least one RM participant that has set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag.
Format
SYS$TRANS_EVENT [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,rm_id
,tx_event
C Prototype
int sys$trans_event (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int tid
[4], unsigned int rm_id, unsigned int tx_event);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Reserved to HP. This argument must be zero.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The outcome of the state change is indicated by the contents of the I/O
status block.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
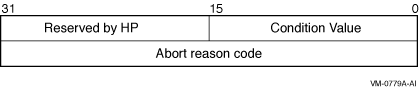
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, if
SS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The astadr argument is
the address of the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed
in the same access mode as that of the caller of the $TRANS_EVENT
service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (TID) of transaction to which the state change is to be
applied.
rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The identifier of the Resource Manager identifier (RMI) with which the
coordinating Resource Manager (RM) participant is associated.
tx_event
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The operation to be performed on the transaction. The permitted values
and the possible successful outcomes are listed in Table SYS-58.
Description
The $TRANS_EVENT system service is used by coordinating RM participants
to change the state of transactions.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $TRANS_EVENT include:
- The caller must have the SYSPRV privilege or be in either executive
or kernel mode.
- The RM participant must have set the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag on the
call to $JOIN_RM. Coordinating resource managers cannot join the
transaction by calling $ACK_EVENT.
- The access mode of the caller must be the same as or more
privileged than that of the transaction within the process.
Table SYS-58 Completion Semantics of the$TRANS_EVENT Service
| Operation |
Completion Semantics |
|
DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE
|
A vote has been received from each RM participant and synchronized
branch.
The status code returned is the combination of the individual
votes. The possible values are:
- SS$_PREPARED. All participants are ready to commit the transaction.
Thus all RM participants voted "yes" and all synchronized branches
called $END_BRANCH. Note that a read-only vote from an RM participant
is counted as a "yes" vote but this response is not returned if all RM
participants voted read-only. Unsynchronized branches are assumed to be
willing to commit. A further operation (commit or abort) is necessary
to complete the transaction.
- SS$_FORGET. All participants are ready to permit the transaction to
be committed but do not require any further notification of transaction
events. Thus no further $TRANS_EVENT calls are required for this
transaction. Possible reasons for this response are:
- All RM participants voted read-only.
- The specified transaction (TID) did not exist.
- The specified transaction was already prepared (Cyclic graph).
- SS$_VETO. The transaction cannot be committed. No further
$TRANS_EVENT calls are required for this transaction. One reason why
the transaction cannot commit, an abort reason code, is placed in the
second longword of the
iosb argument.
|
|
DDTM$K_TX_COMMIT
|
The only status code returned on successful completion is SS$_FORGET.
Sufficient information has been hardened by the DECdtm transaction
manager to commit the transaction.
|
|
DDTM$K_TX_ABORT
|
The only status code returned on successful completion is SS$_FORGET.
Abort processing has been initiated.
|
Required Privileges
SYSPRV is required unless the caller is in executive or kernel mode.
Required Quotas
None.
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,
$START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The request was successfully queued. This value is only returned in R0.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid value for
tx_event parameter.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_FORGET
|
No further $TRANS_EVENT calls are required for this transaction.
- If
tx_event = DDTM$K_TX_ABORT, then abort processing has
been initiated.
- If
tx_event = DDTM$K_TX_COMMIT, then sufficient
information has been hardened to commit the transaction.
- If
tx_event = DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE, then one of the
following has occurred:
- All participants voted read-only.
- The
tid was not known.
- The
rm_id was not known.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_NOLOG
|
The local node did not have a transaction log.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified
rm_id was not a coordinator of the specified
transaction.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSPRV
|
The caller is in user or supervisor mode but did not have SYSPRV set.
|
|
SS$_PREPARED
|
All participants are ready to commit the transaction. A further
operation (commit or abort) is necessary to complete the transaction.
|
|
SS$_TPDISABLED
|
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
|
|
SS$_VETO
|
The
tx_event parameter contains the value
DDTM$K_TX_PREPARE, and DECdtm or a participant was not in a position to
accept an order to commit. One reason why the transaction must abort is
supplied in the abort reason code field of the IOSB. No further call to
$TRANS_EVENT is needed for a transaction when this condition code is
returned.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The access mode of the caller was less privileged than that of a branch
of the transaction in this process.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation:
- Commit operation when transaction is not prepared.
- Any operation while another call is in progress.
|
$TRANS_EVENTW
Forces a transaction state change for a transaction in which there is
at least one RM participant that has specified the DDTM$M_COORDINATOR
flag.
$TRANS_EVENTW always waits for the request to complete before returning
to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $TRANS_EVENT.
Format
SYS$TRANS_EVENTW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,rm_id
,tx_event
C Prototype
int sys$trans_eventw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct
_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, )
$TRNLNM
Returns information about a logical name.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$TRNLNM [attr] ,tabnam ,lognam ,[acmode] ,[itmlst]
C Prototype
int sys$trnlnm (unsigned int *attr, void *tabnam, void *lognam,
unsigned char *acmode, void *itmlst);
Arguments
attr
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Attributes controlling the search for the logical name. The
attr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword bit mask
specifying these attributes.
Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic
name. The $LNMDEF macro defines these symbolic names. To specify an
attribute, use its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit. All
undefined bits in the longword have the value 0.
If you do not specify this argument or specify it as the value 0 (no
bits set), the following attributes are not used:
| Attribute |
Description |
|
LNM$M_CASE_BLIND
|
If set, $TRNLNM does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase
letters in the logical name to be translated.
|
|
LNM$M_INTERLOCKED
|
If set, $TRNLNM does not translate the current logical name until any
clusterwide logical name modifications in progress are completed. This
attribute is not set by default. If your application requires
translation using the most recent definition of a clusterwide logical
name, use this attribute to ensure that the translation is stalled
until all pending modifications have been made.
|
tabnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the logical name table or the name of a searchlist logical name
that translates the name of one or more tables in which to search for
the specified logical name. The tabnam argument is the
32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a descriptor pointing to this name. This argument is
required.
The name must be entered in uppercase letters. (This requirement
differs from the $CRELNT system service, which automatically changes
tabnam to uppercase.)
If the table name is not the name of a logical name table, it is
assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively until either
the name of a logical name table is found or the number of translations
allowed by the system have been performed. If the table name translates
to a list of logical name tables, the tables are searched in the
specified order.
lognam
| OpenVMS usage: |
logical_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Logical name about which information is to be returned. The
lognam argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a descriptor
pointing to the logical name string. This argument is required.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Access mode to be used in the translation. The acmode
argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit
address (on Alpha systems) of a byte specifying the access mode. The
$PSLDEF macro defines symbolic names for the four access modes.
When you specify the acmode argument, $TRNLNM ignores
all names (both logical names and table names) at access modes less
privileged than the specified access mode. The specified access mode is
not checked against that of the caller.
If you do not specify acmode, $TRNLNM performs the
translation without regard to access mode; however, the translation
process proceeds from the outermost to the innermost access modes.
Thus, if two logical names with the same name but at different access
modes exist in the same table, $TRNLNM translates the name with the
outermost access mode.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for
64-bit |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Item list describing the information that $TRNLNM is to return. The
itmlst argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a list of item
descriptors, each of which specifies or controls an item of information
to be returned. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a
longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a
quadword of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same
format---either 32-bit or 64-bit.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item
descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by the
buffer address field.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the
information currently in the buffer, to be returned in the buffer, or
to be returned by the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the 32-bit address of the buffer that specifies
or receives the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the 32-bit address of a word specifying the
actual length (in bytes) of the information returned by $TRNLNM in the
buffer pointed to by the buffer address field.
|
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
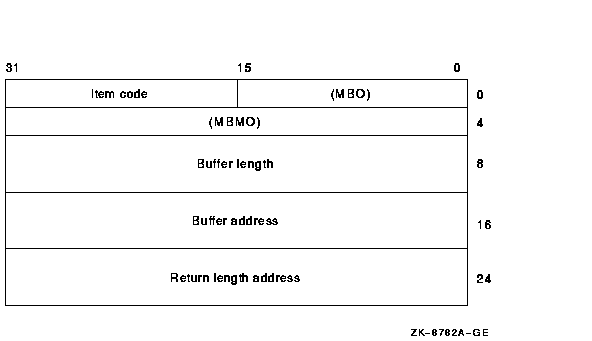
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
MBO
|
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the
information currently in the buffer, to be returned in the buffer, or
to be returned by the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field.
|
|
MBMO
|
The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of the buffer that specifies
or receives the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A quadword containing the 64-bit address of a word specifying the
actual length (in bytes) of the information returned by $TRNLNM in the
buffer pointed to by the buffer address field.
|
Item Codes
LNM$_ACMODE
Returns the access mode that was associated with the logical name at
the time of its creation. The buffer address field in the item
descriptor is the address of a byte in which $TRNLNM writes the access
mode.
LNM$_ATTRIBUTES
Returns the attributes of the logical name and the equivalence name
associated with the current LNM$_INDEX value.
The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword
bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an attribute. The $TRNLNM
service sets the corresponding bit for each attribute possessed by
either the logical name or the equivalence name.
The $LNMDEF macro defines the following symbolic names for these
attributes:
| Attribute |
Description |
|
LNM$M_CONCEALED
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name at the current index
value for the logical name is a concealed logical name, as interpreted
by OpenVMS RMS.
|
|
LNM$M_CONFINE
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is not copied from a process
to any of its spawned subprocesses. The DCL command SPAWN creates
subprocesses.
|
|
LNM$M_CRELOG
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name was created using the
$CRELOG system service.
|
|
LNM$M_EXISTS
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, an equivalence name with the specified index
does exist.
|
|
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the name of the logical name cannot be given
to another logical name defined in the same table at an outer access
mode.
|
|
LNM$M_TABLE
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is the name of a logical
name table.
|
|
LNM$M_CLUSTERWIDE
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is in a clusterwide table.
|
|
LNM$M_TERMINAL
|
If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name for the logical name
cannot be subjected to further (recursive) logical name translation.
|
LNM$_CHAIN
Processes another item list immediately following the current item
list. The LNM$_CHAIN item code must be the last one in the current item
list. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to the
next item list.
You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
LNM$_INDEX
Searches for an equivalence name that has the specified index value.
The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword
containing a user-specified integer in the range 0 to 127.
If you do not specify this item code, the implied value of LNM$_INDEX
is 0 and $TRNLNM returns information about the equivalence name at
index 0.
Because a logical name can have more than one equivalence name and each
equivalence name is identified by an index value, you should specify
the LNM$_INDEX item code first in the item list, before specifying
LNM$_STRING, LNM$_LENGTH, or LNM$_ATTRIBUTES. These item codes return
information about the equivalence name identified by the current index
value, LNM$_INDEX.
LNM$_LENGTH
Returns the length of the equivalence name string corresponding to the
current LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field in the item
descriptor is the address of the longword in which $TRNLNM writes this
length.
If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value,
$TRNLNM returns the value 0 to the longword pointed to by the return
length field of the item descriptor.
LNM$_MAX_INDEX
Each equivalence name for the logical name has an index associated with
it. When you specify LNM$_MAX_INDEX, $TRNLNM returns a value equal to
the largest equivalence name index. The buffer address field in the
item descriptor is the address of a longword in which $TRNLNM writes
this value. If the logical name exists but has no equivalence name
(and, therefore, no index value), $TRNLNM returns a value of --1.
LNM$_STRING
Returns the equivalence name string corresponding to the current
LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field of the item descriptor
points to a buffer containing this string. The return length address
field of the item descriptor contains an address of a word that
contains the length of this string in bytes. The maximum length of the
equivalence name string is 255 characters.
If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value,
$TRNLNM returns the value 0 in the return length address field of the
item descriptor.
LNM$_TABLE
Returns the name of the table containing the logical name being
translated. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to
the buffer in which $TRNLNM returns this name. The return length
address field of the item descriptor specifies the address of a word in
which $TRNLNM writes the size of the table name. The maximum length of
the table name is 31 characters.
Description
The Translate Logical Name service returns information about a logical
name. You need read access to a shareable logical name table to
translate a logical name located in that shareable logical name table.
For conventions regarding logical names for process-permanent files,
refer to the chapter "Logical Name Services" in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
Read access is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRELNM, $CRELNT, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELLNM, $DELTVA,
$DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK,
$SETSWM, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. An equivalence name for the logical
name has been found.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the location or locations specified by one or
more arguments.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table
name or logical name was not specified. Or, an item list containing
both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The service completed successfully. The buffer length field in an item
descriptor specified an insufficient value, so the buffer was not large
enough to hold the requested data.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The
tabnam argument or
lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not
in the required range of 1 through 255 characters.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGTAB
|
The
tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table.
|
|
SS$_NOLOGNAM
|
The logical name was not found in the specified logical name table or
tables.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller lacks the necessary privilege to access the specified name.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
Logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth
(10 translations).
|
$TRUNCATE
The Truncate service shortens a sequential file.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$TSTCLUEVT
Simulates the occurrence of a cluster configuration event to test the
functionality of the notification AST.
Format
SYS$TSTCLUEVT [handle] ,[acmode] ,[event]
C Prototype
int sys$tstcluevt (unsigned int *handle, unsigned int acmode, unsigned
int event);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification of the asynchronous system trap (AST) to be tested. The
handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is
returned when the $SETCLUEVT service is called.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode for which a configuration event AST is to be triggered. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
Each access mode has a symbolic name. The $PSLDEF macro defines the
following symbols for the four access modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event code indicating the type of configuration for which an AST is to
be triggered.
Each event type has a symbolic name. The $CLUEVTDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CLUEVT$C_ADD
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system.
|
|
CLUEVT$C_REMOVE
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster
system.
|
Description
The Test Cluster Event service simulates the occurrence of a cluster
configuration event to test the functionality of the notification ASTs.
The service allows an application to test itself and must be issued
from within the same process as the application being tested.
$TSTCLUEVT does not affect other processes in the cluster.
The service will allow one specific AST to be fired via the
handle argument, or all ASTs for a specific
configuration event via the event argument. Specifying
both the event and the handle
arguments will return an error.
If the handle argument is specified, the value of the
acmode argument must not be greater than the access
mode of the caller and must match the mode specified when the
$SETCLUEVT service was called.
If the event argument is specified, those ASTs that
match the value specified in the acmode argument, or
that match the caller's mode, will be triggered.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CLRCLUEVT, $SETCLUEVT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
There is an unsatisfactory combination of event and handle parameters,
or the event was specified incorrectly.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
No request was found that matches the description supplied.
|
$ULKPAG
Unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages
in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked
and deleted at image exit.
Format
SYS$ULKPAG inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$ulkpag (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages to be unlocked. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used;
the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored. If the starting and
ending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is unlocked.
If more than one page is being unlocked and you need to determine
specifically which pages had been previously unlocked, you should
unlock the pages one at a time, that is, one page per call to $ULKPAG.
The condition value returned by $ULKPAG indicates whether the page was
previously unlocked.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference---array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages actually
unlocked by $ULKPAG. The retadr argument is the
address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and
ending process virtual addresses.
If an error occurs while multiple pages are being unlocked,
retadr specifies those pages that were successfully
unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were successfully
unlocked, both longwords in the retadr array contain
the value --1.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal
to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously
locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked
pages are automatically unlocked and deleted at image exit.
On Alpha systems, if you are attempting to unlock executable code, you
should issue multiple $ULKPAG calls: one to unlock the code pages and
others to unlock the linkage section references to these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
To call the $ULKPAG service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
For more information, refer to the chapter on memory management in the
OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously locked.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input array cannot be read by the caller; the output array cannot
be written by the caller; or a page in the specified range is
inaccessible or does not exist.
|
$ULKPAG_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory
by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ULKPAG_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64
,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$ulkpag_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be unlocked. The specified
virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be unlocked. The specified
length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it
includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal
to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the unlocked virtual address
range. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range unlocked. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously
locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were unlocked, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1, and a
value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by
the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
To call the $ULKPAG_64 service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$LCKPAG_64, $ULKPAG
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller, or an attempt was made to unlock pages by a caller whose access
mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
$ULWSET
Unlocks pages that were previously locked in the working set by the
Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET) service.
Format
SYS$ULWSET inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$ulwset (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference---array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages to be unlocked. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.
Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used;
the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored. If the starting and
ending virtual address are the same, a single page is unlocked.
If more than one page is being unlocked and you need to determine
specifically which pages had been previously unlocked, you should
unlock the pages one at a time, that is, one page per call to $ULWSET.
The condition value returned by $ULWSET indicates whether the page was
previously unlocked.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference---array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages that were
actually unlocked by $CRMPSC. The retadr argument is
the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting
and ending process virtual addresses.
If an error occurs while multiple pages are being unlocked,
retadr specifies those pages that were successfully
unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were successfully
unlocked, both longwords in the retadr array contain
the value --1.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal
to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Working Set service unlocks pages that were
previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set
($LKWSET) service. Unlocked pages become candidates for replacement
within the working set of the process.
On Alpha systems, if you are attempting to unlock executable code, you
should issue multiple $ULKWSET calls: one to unlock the code pages and
others to unlock the linkage section references to these pages.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG,
$LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
inadr argument cannot be read by the caller; the
retadr argument cannot be written by the caller; or a
page in the specified range is inaccessible or does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
|
$ULWSET_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, unlocks a virtual address range that was previously
locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set ($LKWSET_64)
service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$ULWSET_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64
,return_length_64
C Prototype
int sys$ulwset_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be unlocked from the
working set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a
CPU-specific page boundary.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be unlocked from the working
set. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page
boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested
range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal
to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the unlocked virtual address
range. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range unlocked. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
Description
The Unlock Pages from Working Set service unlocks pages that were
previously locked in the working set by the Lock Pages in Working Set
($LKWSET_64) service. Unlocked pages become candidates for replacement
within the working set of the process.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value
cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
return_va_64 and return_length_64
arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned
address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully
unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were unlocked, the
return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1, and a
value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by
the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $ULWSET
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages
was previously unlocked.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were
previously locked in the working set.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64 or
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller, or an attempt was made to unlock pages by a caller whose access
mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within process private address
space.
|
$UNWIND
Unwinds the procedure call stack.
Format
SYS$UNWIND [depadr] ,[newpc]
C Prototype
int sys$unwind (unsigned int *depadr, void *newpc);
Arguments
depadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Depth to which the procedure call stack is to be unwound. The
depadr argument is the address of a longword value.
The value 0 specifies the call frame of the procedure that was
executing when the condition occurred (that is, no call frames are
unwound); the value 1 specifies the caller of that frame; the value 2
specifies the caller of the caller of that frame, and so on.
If depadr specifies the value 0, no unwind occurs and
$UNWIND returns a successful condition value in R0.
If you do not specify depadr, $UNWIND unwinds the
stack to the call frame of the procedure that called the procedure that
established the condition handler that is calling the $UNWIND service.
This is the default and the normal method of unwinding the procedure
call stack.
newpc
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
New value for the program counter (PC); this value replaces the current
value of the PC in the call frame of the procedure that receives
control when the unwinding operation is complete. The
newpc argument is a longword value containing the
address at which execution is to resume.
Execution resumes at this address when the unwinding operation is
complete.
If you do not specify newpc, execution resumes at the
location specified by the PC in the call frame of the procedure that
receives control when the unwinding operation is complete.
Description
The Unwind Call Stack service unwinds the procedure call stack; that
is, it removes a specified number of call frames from the stack.
Optionally, it can return control to a new program counter (PC)
unwinding the stack. The $UNWIND service is intended to be called from
within a condition-handling routine.
The actual unwind is not performed immediately. Rather, the return
addresses in the call stack are modified so that, when the condition
handler returns, the unwind procedure is called from each frame being
unwound.
During the actual unwinding of the call stack, $UNWIND examines each
frame in the call stack to see if a condition handler has been
declared. If a handler has been declared, $UNWIND calls the handler
with the condition value SS$_UNWIND (indicating that the call stack is
being unwound) in the condition name argument of the signal array. When
you call a condition handler with this condition value, that handler
can perform any procedure-specific cleanup operations that might be
required. After the condition handler returns, the call frame is
removed from the stack.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DCLCMH, $SETEXV
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The call stack is not accessible to the caller. This condition is
detected when the call stack is scanned to modify the return address.
|
|
SS$_INSFRAME
|
There are insufficient call frames to unwind to the specified depth.
|
|
SS$_NOSIGNAL
|
No signal is currently active for an exception condition.
|
|
SS$_UNWINDING
|
An unwind operation is already in progress.
|
The Update service allows you to modify the contents of an existing
record in a file residing on a disk device.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$UPDSEC
Writes all modified pages in an active private or global section back
into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued,
based on the number of pages that have been modified.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[updflg] ,[efn] ,[iosb] ,[astadr]
,[astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$updsec (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode, char updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
inadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference---array reference or descriptor |
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages that are to be
written to the section file if they have been modified. The
inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array
containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual
addresses. Addresses are adjusted up or down to CPU-specific pages.
Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used;
the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
$UPDSEC scans pages starting at the address contained in the first
longword specified by inadr and ending at the address
contained in the second longword. Within this range, $UPDSEC locates
read/write pages that have been modified and writes them (contiguously,
if possible) to the section file on disk. Unmodified pages are also
written to disk if they share the same cluster with modified pages.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, a single
page is written to the section file if the page has been modified.
The address specified by the second longword might be smaller than the
address specified by the first longword.
retadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address_range |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference---array reference or descriptor |
Addresses of the first and last pages that were actually queued for
writing, in the first $QIO request, back to the section file on disk.
The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword
array containing, in order, the addresses of the first and last pages.
Addresses always are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific
boundaries.
If $UPDSEC returns an error condition value in R0, each longword
specified by retadr contains the value --1. In this
case, an event flag is not set, no asynchonous system trap (AST) is
delivered, and the I/O status block is not written to.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the service is performed. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols for the four access modes.
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
A page cannot be written to disk unless the access mode used by $UPDSEC
is equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of the
page to be written.
updflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Update specifier for read/write global sections. The
updflg argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the
default) specifies that all read/write pages in the global section are
to be written to the section file on disk, whether or not they have
been modified. The value 1 specifies that the caller is the only or the
last process having the global section mapped for write access and that
only modified pages should be written to the section file on disk.
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event flag to be set when the section file on disk is actually updated.
The efn argument is a longword specifying the number
of the event flag; however, $UPDSEC uses only the low-order byte.
If you do not specify efn, event flag 0 is used.
When you invoke $UPDSEC, the specified event flag or event flag 0 is
cleared; when the update operation is complete, the event flag is set.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status of the updating
operation. The iosb argument is the address of the
quadword I/O status block.
When you invoke $UPDSEC, the I/O status block is cleared. After the
update operation is complete, that is, when all I/O to the disk is
complete, the I/O status block is written as follows:
- The first word contains the condition value returned by $QIO,
indicating the final completion status.
- The first bit in the second word is set only if an error occurred
during the I/O operation and the error was a hardware write error. The
remaining bits of the second word are zeros.
- The second longword contains the virtual address of the first page
that was not written.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using $SYNCH to synchronize completion of the service,
the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to $UPDSEC. The condition value returned in R0 gives you
information about the success or failure of the service call itself;
the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$UPDSEC, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference---procedure reference or
descriptor |
AST routine to be executed when the section file has been updated. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
access mode from which the section file update was requested.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine. The
astprm argument is this longword parameter.
Description
The Update Section File on Disk service writes all modified pages in an
active private or global section back into the section file on disk.
One or more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that
have been modified.
Proper use of this service requires the caller to synchronize
completion of the update request. You do this by first checking the
condition value returned in R0 by $UPDSEC. If SS$_NOTMODIFIED is
returned, the caller can continue. If SS$_NORMAL is returned, the
caller should wait for the I/O to complete and then check the first
word of the I/O status block for the final completion status. You can
use the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service to determine whether the I/O
operation has actually completed.
On VAX systems, for a global section located in memory shared by
multiple processors, only processes running on the processor that
created the section can specify that global section in a call to
$UPDSEC. Processes on another processor that attempt to update the
section file receive an error condition.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$UPDSEC uses the calling process's direct I/O limit (DIRIO) quota in
queuing the I/O request and uses the calling process's AST limit
(ASTLM) quota if the astadr argument is specified.
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG,
$LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET,
$UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. One or more I/O requests were
queued.
|
|
SS$_NOTMODIFIED
|
The service completed successfully. No pages in the input address range
were section pages that had been modified. No I/O requests were queued.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The input address array cannot be read by the caller, or the output
address array cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
You specified an invalid flag.
|
|
+SS$_NOTCREATOR
|
The section is in memory shared by multiple processors and was created
by a process on another processor.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
A page in the specified range is in the system address space.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified range is owned by an access mode more
privileged than the access mode of the caller.
|
|
SS$_UNASCEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
+VAX specific
$UPDSECW
Writes all modified pages in an active private or global section back
into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued,
based on the number of pages that have been modified.
The $UPDSECW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller after writing all updated pages.
For asynchronous completion, use the Update Section File on Disk
($UPDSEC) service; $UPDSEC returns to the caller after queuing the
update request, without waiting for the pages to be updated.
In all other respects, $UPDSECW is identical to $UPDSEC. For all other
information about the $UPDSECW service, refer to the description of
$UPDSEC.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$UPDSECW inadr [,retadr] [,acmode] [,updflg] [,efn] [,iosb]
[,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$updsecw (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,
unsigned int acmode, char updflg, unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb,
void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$UPDSEC_64 (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, writes all pages (or only those pages modified by the
current process) in an active private or global disk file section back
into the section file on disk. One or more I/O requests are queued to
perform the write operation.
The $UPDSEC_64 service completes asynchronously. For synchronous
completion, use the Update Global Section File on Disk and Wait
($UPDSEC_64W) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,updflg ,efn ,iosa_64
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,astadr_64 [,astprm_64]]
C Prototype
int sys$updsec_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int updflg, unsigned int efn, struct
_iosa *iosa_64, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64,...);
Arguments
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting virtual address of the pages to be written to the section
file. The specified virtual address is rounded down to a CPU-specific
page boundary.
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual address range to be written to the section file.
The length specified is rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so
that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode on behalf of which the service is performed. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
A page cannot be written to disk unless the access mode used by
$UPDSEC_64 is equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the
owner of the page to be written.
updflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The update specifier for read/write global sections. The
updflg argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the
default) specifies that all read/write pages in the global section are
to be written to the section file on disk, whether or not they have
been modified. The value UPDFLG$M_WRT_MODIFIED specifies that the
caller is the only process actually writing the global section and that
only those pages that were actually modified by the caller are to be
written to the section file on disk.
Definitions for this flag can be found in the file SECDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB for C and in $SECDEF in STARLET.MLB for macro.
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read_only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The event flag to be set when the section file on disk is actually
updated. The efn argument is a longword specifying the
number of the event flag; however, this service only uses the low-order
byte. If you do not specify the efn, event flag 0 is
used.
When you invoke $UPDSEC_64, the specified event flag or event flag 0 is
cleared. When the update operation is complete, the event flag is set.
iosa_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_area |
| type: |
IOSA structure |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The I/O status area to receive the final completion status of the
updating operation. The iosa_64 argument is the 32- or
64-bit virtual address of the I/O status area. The I/O status area
structure is 32 bytes in length.
The I/O status area structure definition can be found in $IOSADEF in
STARLET.MLB for macro and in the file IOSADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB
for C.
When you call SYS$UPDSEC_64, the I/O status area is cleared. After the
update operation is complete (that is, when all I/O to the disk is
complete), the I/O status block is written as follows:
- isoa$l_status (offset 0)
The first word contains the condition
value return by SYS$QIO, indicating the final completion status.
The first bit in the second word is set only if an error occurred
during the I/O operation and the error was a hardware write error. The
remaining bits of the second word are zeros.
- iosa$l_resd (offset 4)
This field is reserved for future use
by HP. The value in this field is unpredictable.
- iosa$q_count_q (offset 8)
This field is reserved for future
use by HP. The value in this field is unpredictable.
- iosa$ph_upsec_nowrt_va (offset 16)
This field contains the
virtual address of the first byte in the first disk block that was not
written. In the case of an I/O error, this virtual address indicates
the disk block for which the error occurred.
- iosa$q_resq (offset 24)
This field is reserved for future use
by HP. The value in this field is unpredictable.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The process virtual address of the first page that was actually queued
for writing (in the first I/O request) back to the section file on the
disk. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the virtual address.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the first I/O request to write modified pages back to the
section file on disk. The return_length_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into
which the service returns the length of the virtual address range, in
bytes, written by the first I/O request.
astadr_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The asynchronous system trap (AST) routine to be executed when the
section file has been updated. The astadr_64 argument
is the 32- or 64-bit address of this routine. If you specify the
astadr_64 argument, the AST routine executes at the
access mode from which the section file update was requested.
astprm_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine. The
astprm_64 argument is a quadword argument that is
passed to the AST routine.
Description
The Update Global Section File on Disk service writes all pages in an
active private or global section back into the section file on disk. If
the updflg argument indicates that only modified pages
are to be written back to the disk file, only those global pages
modified by the current process are queued to be written back into the
section file on disk.
Proper use of this service requires the caller to synchronize
completion of the update request. To do this, first check the condition
value returned. If SS$_NOTMODIFIED is returned, the caller can
continue. If SS$_NORMAL is returned, the caller should wait for the I/O
to complete and then check the I/O status for final completion status.
If any error is returned by this service, a value cannot be
returned in the memory locations pointed to by the
iosb_64, return_va_64, and
return_length_64 arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
$UPDSEC_64 uses the calling process' direct I/O limit (DIRIO) quota in
queuing the I/O request and uses the calling process' AST limit (ASTLM)
quota if the astadr_64 argument is specified.
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,
$MGBLSC_64, $UPDSEC
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. One or more I/O requests were
queued.
|
|
SS$_NOTMODIFIED
|
The service completed successfully. No pages in the input address range
were section pages that had been modified. No I/O requests were queued.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_va_64,
return_length_64, or
iosb_64 argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
|
|
SS$_EXBYTLM
|
The process has exceeded the byte count quota.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
An illegal event flag number was specified.
|
|
SS$_PAGNOTINREG
|
A page in the specified range is not within the process private address
space.
|
|
SS$_PAGOWNVIO
|
A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_UNASCEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
$UPDSEC_64W (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, writes all modified pages in an active private or
global disk file section back into the section file on disk. Zero or
more I/O requests are queued, based on the number of pages that have
been modified.
The $UPDSEC_64W service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller after writing all updated pages.
In all other respects, $UPDSEC_64W is identical to $UPDSEC_64. For all
other information about the $UPDSEC_64W service, refer to the
description of $UPDSEC_64 in this manual.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$UPDSEC_64W start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,updflg ,efn ,iosa_64
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,astadr_64 [,astprm_64]]
C Prototype
int sys$updsec_64w (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int updflg, unsigned int efn, struct
_iosa *iosa_64, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64
*return_length_64,...);
$VERIFY_PROXY
Verifies that a proxy exists and returns a valid local user for the
caller to use to create a local login.
Format
SYS$VERIFY_PROXY rem_node ,rem_user ,[proposed_user] ,local_user
,local_user_length ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$verify_proxy (void *rem_node, void *rem_user, void
*proposed_user, void *local_user, unsigned short int *local_user_len,
unsigned int flags);
Arguments
rem_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote node name of the proxy to be verified. The
rem_node argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to the remote node name string.
A remote node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specific
characters, format, or case are required for a remote node name string.
All node names are converted to their DECnet for OpenVMS full name
unless the PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND flag is set with the
flags argument.
Wildcards are not recognized. If you specify a wildcard character in
the rem_node argument, it is ignored and assumed to be
part of the requested node name.
rem_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote user name of the proxy to be verified. The
rem_user argument is the address of a character-string
descriptor pointing to the user name string.
A remote user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and brackets ([ ]). Any
lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
The rem_user argument can be specified in user
identification code (UIC) format ([group, member]).
Brackets are allowed only if the remote user name string specifies a
UIC. Group and member are character-string representations of octal
numbers with no leading zeros.
Wildcards are not allowed for the remote user specification. If
wildcard characters are present in the string specified by the
rem_user argument, the service returns SS$_BADPARAM.
proposed_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user the caller suggests be used for the proxy login. The
proposed_user argument is the address of a
character-string descriptor pointing to the proposed local user name.
The proposed local user consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_). Any lowercase
characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
See the Description section for information about the interaction of
this argument with the return value of the local_user
argument.
local_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user the caller must use for a proxy login. The
local_user argument is the address of a 32-byte
character-string descriptor pointer to receive the local user name the
caller must use for a proxy login for the proxy with the remote node
name specified by the rem_node argument and the remote
user name specified by the rem_user argument.
A local user name is a 32-character blank padded string of alphanumeric
characters, including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_).
local_user_length
| OpenVMS usage: |
output length |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of the returned local user name in the
local_user argument. The
local_user_length argument is the address of an
unsigned word to receive the length, in bytes, of the character string
returned in the local_user argument.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Functional specification for the service and type of user the
local_user argument represents. The
flags argument is a longword bit mask wherein each bit
corresponds to an option.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $PRXDEF macro defines the
following symbolic name:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND
|
The service should not convert the node name specified in the
rem_node argument to its corresponding DECnet for
OpenVMS full name. If this flag is set, it is the caller's
responsibility to ensure that the fully expanded node name is passed
into the service.
|
Description
The Verify Proxy service verifies the existence of a proxy in the proxy
database and returns the local user name the caller must use for any
proxy logins.
The following description shows how the service determines which local
user name the caller must use for proxy logins.
Proxies that match the remote node and remote user specified by the
rem_node and rem_user arguments,
respectively, are searched in the following order if the remote user
name is not a UIC:
- rem_node::rem_user
- *::rem_user
- rem_node::*
- *::*
Proxies that match the remote node and remote user specified by the
rem_node and rem_user arguments,
respectively, are searched for in the following order if the remote
user name is a UIC:
- rem_node::rem_user
- *::rem_user
- rem_node::[group,*]
- rem_node::[*,member]
- rem_node::[*,*]
- *::*
The following table describes how the local user name the caller must
use for any proxy logins is determined if a matching proxy record is
found by the search:
Remote
User |
Proposed
User |
Proxy
Default User |
Proxy Local
User Names |
Returned Local
User Name |
|
rem_user
|
null
|
null
|
n/a
|
error
|
|
rem_user
|
null
|
default user
|
n/a
|
default user
|
|
rem_user
|
null
|
*
|
n/a
|
rem_user
|
|
rem_user
|
prop_user
|
default user
|
n/a
|
prop_user
|
|
rem_user
|
prop_user
|
default user
|
prop_user
|
prop_user
|
|
rem_user
|
prop_user
|
default user
|
local user
|
error
|
|
rem_user
|
prop_user
|
default user
|
*
|
rem_user if it equals prop_user
|
|
rem_user
|
prop_user
|
*
|
local user
|
rem_user if it equals prop_user
|
Required Access or Privileges
You must have SYSPRV privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_PROXY, $DELETE_PROXY, $DISPLAY_PROXY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
rem_node,
rem_user, or
proposed_user argument cannot be read by the service;
or the
local_user or
local_user_length argument cannot be written by the
service.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The length of the
rem_node,
rem_user,
proposed_user, or
local_user argument was out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
rem_user or
proposed_user argument contains an invalid user name.
|
|
SS$_NOREADALL
|
The caller does not have access to the proxy database.
|
|
|
|
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from
the security server, or any OpenVMS RMS error message encountered
during operations on the proxy database:
|
|
SECSRV$_BADLOCALUSERLEN
|
The local user name length is out of range.
|
|
SECSRV$_BADNODENAMELEN
|
The node name length is out of range.
|
|
SECSRV$_BADREMUSERLEN
|
The remote user name length is out of range.
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHPROXY
|
The proxy specified by the
rem_node and
rem_user arguments does not exist in the proxy
database.
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHUSER
|
No valid user was found for the requested proxy.
|
|
SECSRV$_PROXYNOTACTIVE
|
Proxy processing is currently stopped. Try the request again later.
|
|
SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
|
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again
later.
|
$WAIT
The Wait service suspends image execution until an asynchronous record
service completes. Upon completion of the service, RMS returns control
to your program at the point following the Wait service call.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$WAITFR
Tests a specific event flag and returns immediately if the flag is set;
otherwise, the process is placed in a wait state until the event flag
is set.
Format
SYS$WAITFR efn
C Prototype
int sys$waitfr (unsigned int efn);
Argument
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag for which to wait. The efn
argument is a longword containing this number; however, $WAITFR uses
only the low-order byte.
Description
The Wait for Single Event Flag service tests a specific event flag and
returns immediately if the flag is set. Otherwise, the process is
placed in a wait state until the event flag is set. The wait state
caused by this service can be interrupted by an asynchronous system
trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST executes is equal to
or more privileged than the access mode from which the $WAITFR service
was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service
routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WAITFR
request on behalf of the process. At this point, if the event flag has
been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WFLAND, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
$WAKE
Activates a process that has placed itself in a state of hibernation
with the Hibernate ($HIBER) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$WAKE [pidadr] ,[prcnam]
C Prototype
int sys$wake (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be activated. The
pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
longword that contains the PID. The pidadr argument
can refer to a process running on the local node or a process running
on another node in the cluster.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Process name of the process to be activated. The
prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a 32-
or 64-bit character string descriptor pointing to the process name. A
process running on the local node can be identified with a 1 to 15
character string.
To identify a process on a particular node in a cluster, specify the
full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process
name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
The process name is implicitly qualified by the UIC group number of the
calling process. For this reason, you can use the
prcnam argument only if the process to be activated is
in the same UIC group as the calling process. To activate a process in
another UIC group, you must specify the pidadr
argument.
Description
The Wake Process from Hibernation service activates a process that has
placed itself in a state of hibernation with the Hibernate ($HIBER)
service. If you specify neither the pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, the wake request is issued for the
calling process.
If the longword at address pidadr is the value 0, the
PID of the target process is returned.
If one or more wake requests are issued for a process not currently
hibernating, a subsequent hibernate request completes immediately; that
is, the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup
requests is maintained.
You can also activate a hibernating process with the Schedule Wakeup
($SCHDWK) service.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following privileges to use $WAKE:
- GROUP privilege to wake another process in the same group, unless
the process has the same UIC as the calling process
- WORLD privilege to wake any other process in the system
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW,
$HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM,
$SUSPND
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or you specified an invalid
process identification.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to wake the specified process.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the VSMcluster system.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
$WFLAND
Allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to
wait.
Format
SYS$WFLAND efn ,mask
C Prototype
int sys$wfland (unsigned int efn, unsigned int mask);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of any event flag within the event flag cluster to be used. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $WFLAND uses only the low-order byte. Specifying the number of
an event flag within the cluster serves to identify the event flag
cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters: cluster 0 and cluster 1.
Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains
event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3.
Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains
event flag numbers 96 to 127.
mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event flags for which the process is to wait. The mask
argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, selects the
corresponding event flag for which to wait.
Description
The Wait for Logical AND of Event Flags service allows a process to
specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait. The process is
put in a wait state until all specified event flags are set, at which
time $WFLAND returns to the caller and execution resumes.
The wait state caused by this service can be interrupted by an
asynchronous system trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST
executes is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which
the $WAITFR service was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs
at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service
routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WFLAND
request on behalf of the process. At this point, if all the specified
event flags have been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
$WFLOR
Allows a process to specify a set of event flags for which it wants to
wait.
Format
SYS$WFLOR efn ,mask
C Prototype
int sys$wflor (unsigned int efn, unsigned int mask);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of any event flag within the event flag cluster to be used. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $WFLOR uses only the low-order byte. Specifying the number of
an event flag within the cluster serves to identify the event flag
cluster.
There are two local event flag clusters: cluster 0 and cluster 1.
Cluster 0 contains event flag numbers 0 to 31, and cluster 1 contains
event flag numbers 32 to 63.
There are two common event flag clusters: cluster 2 and cluster 3.
Cluster 2 contains event flag numbers 64 to 95, and cluster 3 contains
event flag numbers 96 to 127.
mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event flags for which the process is to wait. The mask
argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, selects the
corresponding event flag for which to wait.
Description
The Wait for Logical OR of Event Flags service allows a process to
specify a set of event flags for which it wants to wait. The process is
put in a wait state until any one of the specified event flags is set,
at which time $WFLOR returns to the caller and execution resumes.
The wait state caused by this service can be interrupted by an
asynchronous system trap (AST) if (1) the access mode at which the AST
executes is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which
the $WFLOR service was issued and (2) the process is enabled for ASTs
at that access mode.
When a wait state is interrupted by an AST and after the AST service
routine completes execution, the operating system repeats the $WFLOR
request on behalf of the process. At this point, if any of the
specified event flags has been set, the process resumes execution.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DACEFC, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLAND
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
You specified an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
$WRITE
The Write service transfers a user-specified number of bytes (beginning
on a block boundary) to an RMS file of any file organization.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
Appendix A
Obsolete Services
The following table lists the obsolete system services and the current
services that have replaced them.
| Obsolete Service |
Current Service |
|
$BRDCST
|
$BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW
|
|
$CHANGE_ACL
|
$GET_SECURITY, $SET_SECURITY
|
|
$CNTREG
|
$DELTVA
|
|
$CRELOG
|
$CRELNM
|
|
$DELLOG
|
$DELLNM
|
|
$GETCHN
|
$GETDVI, $GETDVIW
|
|
$GETDEV
|
$GETDVI, $GETDVIW
|
|
$INPUT
|
$QIO, $QIOW
|
|
$OUTPUT
|
$QIO, $QIOW
|
|
$SETSFM
|
This service is still supported but its use is strongly discouraged.
|
|
$SETSSF
|
This service is still supported but its use is strongly discouraged.
|
|
$SNDACC
|
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW
|
|
$SNDSMB
|
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW
|
|
$TRNLOG
|
$TRNLNM
|
|