 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT
Performs initial setup for process preemption avoidance.
Format
SYS$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT enable
C Prototype
int sys$setup_avoid_preempt (int enable);
Arguments
enable
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Enables or disables preemption avoidance. If the
enable argument is set to 1, preemption avoidance is
enabled; if 0, preemption avoidance is disabled.
Description
The Setup for Process Preemption Avoidance service is a kernel-mode
initialization routine that locks the necessary internal data
structures in memory so scheduling routines can access them above
pageable IPL. A process or thread can then set or clear the indicator
bit by calling the $AVOID_PREEMPT service.
In addition, if the process or thread has ALTPRI privilege,
$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT sets a bit in the PKTA (a per-kernel-thread data
area) to mark that the process or thread can prevent preemption by
other processes or threads having the same base priority but not those
that have a higher base priority.
Note that without ALTPRI, this service will still function
successfully, but will only enable the $AVOID_PREEMPT service to avoid
preemptions due to quantum end.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$AVOID_PREEMPT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
Also, any values returned by the $LKWSET or $UNLKSET services.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS
Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
Format
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]
C Prototype
int sys$set_default_trans (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct
_iosb *iosb,...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for the option
flag, described in Table SYS-53. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-53 $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS Option Flag
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of
the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same
access mode as that of the caller of the $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
new_tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the new default transaction for the calling
process. If this argument is zero (the default) or if it specifies a
zero TID (an octaword of zeros), the service clears the default
transaction of the calling process.
old_tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
An octaword in which the service returns the identifier (TID) of the
calling process' previous transaction (the one that was set or cleared
by this call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS).
A zero TID is returned if the calling process did not have a default
transaction prior to the call.
Description
The $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS system service:
- Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
If either the new_tid argument passes the null
value or the new_tid argument is omitted or zero, then
the default transaction of the calling process is cleared. Otherwise
the default transaction of the calling process is set to the value
passed in the new_tid argument.
- Returns the identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of
the calling process (the one that was set or cleared by this call to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS), if the old_tid argument is not
zero.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS may fail for various reasons, including a call to
$START_TRANS or $START_BRANCH that changes the default transaction of
the calling process in progress.
Following a successful completion of $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS:
- The calling process does not have a default transaction, if either
the new_tid argument passed the null value or the
new_tid argument was omitted or zero.
- The default transaction of the calling process is that passed in
the new_tid argument, if that argument was specified
and its value was not zero.
- The identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of the
calling process is returned in the old_tid argument,
if that argument was not omitted.
A null value is returned if the
calling process did not previously have a default transaction.
There is also a wait form of the service, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW.
Required Privileges
None.
Required Quotas
ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS,
$START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The options flags were invalid.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
|
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW
Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW always waits for the request to complete before
returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS.
Format
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]
C Prototype
int sys$set_default_transw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags,
struct _iosb *iosb,...);
$SET_DEVICE
Modifies the characteristics of a device or the paths used to access
that device.
For synchronous completion, use the Set Device Characteristics and Wait
($SET_DEVICEW) service. The $SET_DEVICEW service is identical to the
$SET_DEVICE service, except that $SET_DEVICEW returns to the caller
only after the requested action has taken effect.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$SET_DEVICE [efn] [,chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm] [,nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$set_device (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void
*devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, struct_generic_64 *nullarg);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $SET_DEVICE returns the
requested information. The efn argument is a longword
containing this number; however, $SET_DEVICE uses only the low-order
byte.
Upon request initiation, $SET_DEVICE clears the specified event flag
(or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when
$SET_DEVICE returns the requested information, it sets the specified
event flag (or event flag 0).
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which
information is desired. The chan argument is a word
containing this number.
To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the
chan or devnam parameters, but you
should not specify both. If you specify both arguments, the
chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for
chan.
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor-fixed-length string
descriptor |
The name of the device about which $SET_DEVICE is to modify the
characteristics or path settings. The devnam argument
is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name
string.
The device name string can be either a physical device name or a
logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore
(_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the
string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is
performed until either a physical device name is found or the system
default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the
characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the
chan or devnam argument, but you
should not specify both. If both arguments are specified, the
chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for
chan.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be
returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information.
The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.
Currently, $SET_DEVICE allows only one valid item list
entry.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

See the itmlst argument in the $GETDVI system service
description for information on the meaning of these fields in the item
list.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O
status block. See iosb in the $GETDVI system service
description for more information.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $SET_DEVICE completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of the $SET_DEVICE service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is the longword parameter.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP and should be zero.
Item Codes
SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH
Forces an immediate I/O path switch for the specified device. The
active path will be switched from the current I/O path to the path name
specified in the buffer for this item code. Note that issuing
$SET_DEVICE with SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH will initiate the process of
switching the path. A delay may occur between when the service
completes and when the path switch is complete. A synchronous version
of this service, $SET_DEVICEW, is available that will wait until the
path switch attempt is complete before returning to the caller.
The path name specified in this and the following item codes must be
fully specified. It may be in either uppercase or lowercase, however
the entire name must be specified.
The Return Length field in this and the following item codes should set
to zero.
The SDVDEF macro contains these item codes.
SDV$_MP_DISABLE_PATH
Disables the path specified in the buffer for this item code so that it
will no longer be considered as a switch candidate. Note that this does
not apply to the current path, which cannot be disabled. The reasons
one might want to disable a path include the following:
- You know a specific path is broken or that a failover to that path
will cause some members of the cluster to lose access.
- To prevent automatic switching to a selected path while it is being
serviced.
SDV$_MP_ENABLE_PATH
Re-enables the path name specified in the buffer for this item code as
a switch candidate.
Description
The Set Device service modifies the characteristics of devices or I/O
paths that have been established to those devices. For Multipath, the
service allows the user to switch the current I/O path to a different
available path and to enable and disable paths from being used for I/O.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$ASSIGN, $DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The device name string descriptor, device name string, or
itmlst argument cannot be read; or the buffer or
return length longword cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid item code, or the buffer length field
in an item descriptor specified insufficient space for the return
length information.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
Quota for pool has been exceeded.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number
larger than the number of channels.
|
|
SS$_IVDEVNAM
|
The device name string contains invalid characters, or neither the
devnam nor
chan argument was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOOPER
|
Caller does not have OPER privileges.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHPATH
|
The specified pathname does not exist on the host system.
|
|
SS$_PATHAMBIG
|
The specified pathname is ambiguous for this device.
|
$SET_DEVICEW
Modifies the characteristics of a device or the paths used to access
that device.
The $SET_DEVICEW completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the
caller only after the requested action has taken effect.
Format
SYS$SET_DEVICEW [efn] [,chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm] [,nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$set_devicew (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void
*devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, struct_generic_64 *nullarg);
$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, controls or retrieves the activation state for the
implicit affinity system capability of a specific kernel thread or of
the global process default.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY [pidadr] [,prcnam] [,state] [,cpu_id]
[,prev_mask]
C Prototype
int sys$set_implicit_affinity (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam,
struct _generic_64 *state, int cpu_id, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose implicit affinity
is to be modified or returned. The pidadr argument is
the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.
Process selection is made through a combination of the
pidadr and prcnam arguments. If
neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service
operations are made to the user capability mask of the current kernel
thread of the current calling process. The pidadr
argument takes precedence over the prcnam argument
where both are supplied in the service call.
If the bit constant CAP$M_IMPLICIT_DEFAULT_ONLY is specified in the
state argument, then the implicit affinity state
portion of the default capability mask is modified or returned instead.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Process name of the process whose implicit affinity capability state is
to be modified or returned. The prcnam argument is the
32- or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor pointing to the
process name string. A process can be identified with a 1- to
15-character string. The service operations are made to the user
capability mask of the initial thread of the specified process.
If pidadr and prcnam are both
specified, then pidadr is modified or returned and
prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified,
then the context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is
modified or returned.
state
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
State options that can be selected for the affected thread's implicit
affinity. The state argument is a pointer to a
quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to a requested state for
the implicit affinity feature. Only the bits specified below are used;
the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined in the $CAPDEF macro.
The state argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_DEFAULT_ONLY
|
Indicates the specified operations are to be performed on the global
cell instead of on a specific kernel thread. This bit supersedes any
individual kernel thread specified in
pidadr or
prcnam. Specifying this bit constant applies the
implicit affinity operations to all newly created processes.
|
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_SET
|
Indicates that the implicit affinity capability bit is to be set for
the specified kernel thread. This is mutually exclusive with
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_CLEAR.
|
|
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_CLEAR
|
Indicates that the implicit affinity capability bit is to be cleared
for the specified kernel thread. This is mutually exclusive with
CAP$M_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY_SET.
|
cpu_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Identifier of the CPU requested as the first CPU on which this kernel
thread is to execute. The cpu_id is a longword
containing this number, which is in the supported range of individual
CPUs from 0 to SYI$_MAX_CPUS - 1 .
If no explicit CPU is needed, specifying a value of -1 in this argument
indicates the system is to select the initial association based on
system dynamics and load balancing.
Note that, regardless of what explicit CPU is supplied to this
argument, it will be taken only as a suggestion. This service will
attempt to make the requested association, but it will be superseded by
another CPU if the system dynamics are adversely affected by the
operation.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Previous implicit affinity state mask for the specified kernel thread
before execution of this call to $SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY. The
prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword into which $SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY writes a bit mask specifying
the implicit affinity state.
The current state of the kernel thread's current implicit affinity
feature can be determined by testing the returned mask with the
symbolic bit definitions described for the state
argument. These bit definitions are found in the $CAPDEF macro.
Description
The Modify Process Implicit Affinity system service modifies or returns
the implicit affinity state for the specified kernel thread or from the
system default process creation cell.
Setting a kernel thread's implicit affinity function indicates to the
system that it is to schedule the process in ways that will maximize
the cache and TB performance in the current symmetric multiprocessing
(SMP) configuration. This might tend to bias the process towards
specific CPUs more than the standard scheduling algorithm would
normally have allowed.
Required Access or Privileges
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call
SYS$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY to modify its own implicit affinity
capability bit. To modify another process' capability mask, the caller
must have:
ALTPRI---To modify any process with a matching UIC
ALTPRI and GROUP---To modify any process in the same UIC group
ALTPRI and WORLD---To modify any process
To call SYS$SET_IMPLICIT_AFFINITY simply to retrieve the state of a
specific process or global bit, the caller need only have the following
privileges:
None---To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching
UIC
GROUP---To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
WORLD---To retrieve the state of any process
Related Services
$CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_AFFINITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One or more arguments has an invalid value.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD
|
The specified kernel thread does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or more than 15 characters.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_CPUCAP
|
No CPU can run the specified process with new capabilities.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no
operation was specified.
|
$SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW (Alpha Only)
Sets a simple value associated with a process.
Format
SYS$SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW mbz1 ,mbz2 ,mbz3 ,property ,value
,prev_value
C Prototype
int sys$set_process_propertiesw (unsigned int mbz1, unsigned int mbz2,
unsigned int mbz3, unsigned int property, unsigned __int64 value,
unsigned __int64 *prev_value);
Arguments
mbz1,mbz2,mbz3
Reserved for future use by HP. Must be specified as 0.
property
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A constant that selects which property to set.
Valid values for property are defined by the $PPROPDEF macro as follows:
| Property Code |
Description |
|
PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP
|
The type of case lookup to use. This value is set for the life of the
currently active image. This value reverts to the permanent case
setting on image rundown. In the absence of an explicit case lookup
specification in a user-provided NAML, RMS uses this value to determine
the case setting for the current file operation.
Valid values are PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND and PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE.
Refer to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications for additional information.
|
|
PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_PERM
|
The type of case lookup to use. This value is set for the life of the
process or until the case is set again. This value is copied to the
PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP setting at image rundown. Setting this value
affects only future activated images for this process. To change the
case setting for the current active image, you must modify the
PPROP$C_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP setting.
Valid values are PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND and PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE.
Refer to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications for additional information.
|
|
PPROP$C_HOME_RAD
|
The Resource Affinity Domain (RAD) to which the process is assigned.
Newly mapped memory in the process will come from the home RAD of the
process. Currently mapped memory will not move into the new home RAD
unless $PURGWS is issued.
Valid values are integers between 0 and the maximum RAD on the
system. Valid home RADs must also contain either memory or CPUs.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
|
|
PPROP$C_PARSE_STYLE_TEMP
|
The type of command parsing to use. This value is set only for the life
of the image. The value reverts to the permanent style on image
rundown. Valid values are: PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL and
PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED.
|
|
PPROP$C_PARSE_STYLE_PERM
|
The type of command parsing to use. This value is set for the life of
the process unless the style is set again. Valid values are:
PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL and PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED.
|
value
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A quadword value to which to set the property.
prev_value
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) address of a quadword
value |
| access: |
write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a quadword that will receive the previous value of the
property.
Description
The $SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW system service sets a simple value
associated with a process.
This service is used for changing process properties that have a
maximum of a single quadword. You can only change one property value at
a time per call to this service.
Required Access or Privileges
None.
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$GETJPI
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation.
|
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
Controls the association between a calling process and resource domains.
Format
SYS$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN func ,rsdm_id ,domain_number ,[nullarg]
,[access] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$set_resource_domain (unsigned int func, unsigned int *rsdm_id,
unsigned int domain_number, unsigned int nullarg, unsigned int access,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function code specifying the action that $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN is to
perform. The func argument is a longword containing
this function code. See the Function Codes section for a description of
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN function codes.
rsdm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only to join, read only to leave |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Resource domain identification. The rsdm_id argument
is the address of a longword specifying the association of the calling
process with the resource domain.
The RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function returns a resource domain
identification. The RSDM$_LEAVE function requires the
rsdm_id argument as input to specify which resource
domain association the process is leaving.
The resource domain identification can be used as input to the $ENQ and
$ENQW system services.
domain_number
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Domain number that identifies the resource domain. The
domain_number argument is a longword value containing
the resource domain number.
The domain_number argument is required for the
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function but ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholder reserved to HP. You must specify 0.
access
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Types of access desired when using the lock management services within
the resource domain. The access argument is a longword
bit mask specifying the access types required; these can include read,
write, and lock.
The following table lists the symbols that the $RSDMDEF macro defines,
their descriptions, and the lock management system services that might
require each type of access:
| Symbol |
Access Description |
System Service |
|
RSDM$M_READ
|
Read lock value blocks
|
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
|
|
RSDM$M_WRITE
|
Write lock value blocks
|
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW,
|
|
RSDM$M_LOCK
|
Take locks
|
$ENQ, $ENQW
|
The service grants the desired access, provided your process has the
necessary access rights to the resource domain. If you do not specify
the access argument or if you specify 0,
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN attempts to access the domain in the following
order:
- Read, write, lock
- Read, lock
- Write, lock
- Lock
The access attempt terminates with the first success.
The access argument defaults to 0. It is ignored for
the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode requested for the association to the resource domain. The
most privileged access mode granted is the access mode of the caller.
Locks cannot be taken from access modes less privileged than the access
mode of the association.
The acmode argument is a longword containing the
access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the
access modes:
Symbolic
Name |
Access
Mode |
Privilege
Rank |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
High
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
--
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
--
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
Low
|
The acmode argument is optional for the
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function. If you do not specify the
acmode argument, the access mode is set to the access
mode of the calling process. The acmode argument is
ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
Function Codes
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN
A process has the option of forming multiple associations with one or
more resource domains. Each association can have different access
rights to the resource domain, such as to read lock value blocks or to
write lock value blocks. This request sets up a new association with a
resource domain.
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the desired access against the security
profile of the resource domain. If the desired access is allowed, a new
association to the resource domain is created, and a resource domain
identification for the association is returned.
This function code returns the following condition values:
SS$_NORMAL
SS$_BADPARAM
SS$_EXQUOTA
SS$_INSFMEM
SS$_NOOBJSRV
SS$_NOPRIV
RSDM$_LEAVE
This operation requests that a process end an association with a
resource domain.
A process must leave a resource domain association in the same mode as,
or in a more privileged mode than, the mode in which it joined the
resource domain.
Before a process can end its association with a resource domain, it
must release all locks taken using that association.
This function code returns the following condition values:
SS$_NORMAL
SS$_BADPARAM
SS$_IVMODE
SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
Description
The Set Resource Domain system service enables a process to use the
lock management system services $DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, and
$GETLKIW.
The lock management services enable processes with the appropriate
access rights to take and release locks on resource names and to
perform other functions related to lock management. Applications use
resource names to represent resources to which they want to synchronize
access. A resource domain is a namespace for resource names. A process
must join a resource domain to take and release locks and to read and
write value blocks associated with resources in that resource domain.
When a process requests to join a resource domain, $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
performs an access check. After $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the
desired access to the resource domain, the service creates an
association between the resource domain and the calling process. The
association is represented by a resource domain identification. A
process can request different types of access to the same resource
domain; the type of access is a characteristic of the association with
the resource domain.
Each time a process joins a resource domain, a new association is
created.
Processes use their resource domain identifications when using $ENQ or
$ENQW to request a new lock.
The service can grant the following three types of access to resource
domains:
- The right to read lock value blocks
- The right to write lock value blocks
- The right to take and release locks
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN uses system dynamic memory, which uses BYTLM
quota, for the creation of the resource domain data structures.
Related Services
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
func, the
domain_number, or the
rsdm_id argument was specified incorrectly.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller has insufficient BYTLM quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There is insufficient memory to join the resource domain.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
An attempt was made to leave an association created by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOOBJSRV
|
The audit server process, which maintains the security profile for
resource domains, is not running. The process access rights to the
domain cannot be determined, so access is denied.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Access to the resource domain was denied.
|
|
SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
|
Unable to leave the resource domain because there are locks still
associated with this resource domain.
|
|
SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
|
The resource domain was not found.
|
$SET_RETURN_VALUE (Alpha and I64 only)
On Alpha and I64 systems, sets the return values in the Mechanism Array
Format
SYS$SET_RETURN_VALUE mechanism_arg, return_type, return_value
C Prototype
int sys$set_return_value (void *mechanism_arg, unsigned_int
*return_type, void *return_value);
Arguments
mechanism_arg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mechanism vector address |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The address of the location of the mechanism vector. If the
mechanism_arg argument is 0, the mechanism vector for
the currently active signal is used.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
return_type
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of the location of a longword that contains one of the
function return signature codes.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
return_value
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer |
| type: |
scalar |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of the location that contains a value of the appropriate
type. The referenced value is read as a longword, quadword, or
octaword, depending on the return_type.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
Description
The Set Return Value service allows the caller to specify the values in
the Mechanism Array. It can also be used to set a condition code.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
status
|
Success or failure. The given return value is placed in the appropriate
fields of the specified mechanism vector, according to the return type.
|
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
|
|
SS$_NOSIGNAL
|
No signal is currently active for an exception condition.
|
$SET_SECURITY
Modifies the security characteristics of a protected object.
Format
SYS$SET_SECURITY [clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst]
,[contxt] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$set_security (void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan,
unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int
*acmode);
Arguments
clsnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the object class. The clsnam argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to a string that contains the name of
the object class.
The following is a list of the protected object class names:
CAPABILITY
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
DEVICE
FILE
GLXGRP_GLOBAL_SECTION
GLXSYS_GLOBAL_SECTION
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
ICC_ASSOCIATION
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
QUEUE
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
SECURITY_CLASS
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
VOLUME
objnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going
to be retrieved. The objnam argument is the address of
a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the protected
object.
The format of an object name is class specific. The following table
lists object names and describes their formats:
| Object Class |
Object Name Format |
|
CAPABILITY
|
A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR.
|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common
Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service.
|
|
DEVICE
|
Standard device specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
FILE
|
Standard file specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
ICC_ASSOCIATION
|
ICC security object name
node::association_name. The special node name, ICC$::, refers
to entries in the clusterwide registry. For registry entries, the
Access Access Type does not apply.
|
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT)
system service.
|
|
QUEUE
|
Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller
($SNDJBC) system service.
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets.
|
|
SECURITY_CLASS
|
Any class name shown in the Object Class column of this table, or a
class name followed by a period (.) and the template name. Use the DCL
command SHOW SECURITY to display possible template names.
|
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
VOLUME
|
Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted.
|
objhan
| OpenVMS usage: |
object_handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Data structure identifying the object to address. The
objhan argument is an address of a longword containing
the object handle. You can use the objhan argument as
an alternative to the objnam argument; for example, a
channel number clearly specifies the file open on the channel and can
serve as an object handle.
The following table shows the format of the object classes:
| Object Class |
Object Handle Format |
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Event flag number
|
|
DEVICE
|
Channel number
|
|
FILE
|
Channel number
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
Resource domain identifier
|
|
VOLUME
|
Channel number
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
flags |
| type: |
mask_longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Mask specifying processing options. The flags argument
is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the
corresponding option. The flags argument requires the
contxt argument.
The following table describes each flag:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
OSS$M_LOCAL
|
Do not update the master profile for the specified object. This flag
allows you to call $SET_SECURITY several times to modify a local copy
of a profile; once the modifications are satisfactory, you can clear
the OSS$M_LOCAL flag, set the OSS$M_RELCTX flag, and have $SET_SECURITY
update the master profile. The flag applies only to calls made with the
contxt argument.
|
|
OSS$M_RELCTX
|
Release the context structure at the completion of this request.
|
The $OSSDEF macro defines symbolic names for the flag bits. You
construct the flags argument by specifying the
symbolic names of each desired option.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes
is to be modified. The itmlst argument is the address
of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword
of 0.
With the item list, the user modifies the protected object's
characteristics. The user defines which security characteristics to
modify. If this argument is not present, only the
flags argument is processed. Without the
itmlst argument, you can only manipulate the
security profile locks or release contxt resources.
The following data structure depicts the format of a single item
descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the
buffer from which $SET_SECURITY is to read the information. The length
of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item
code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too
small, $SET_SECURITY truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information
that $SET_SECURITY is to modify. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes.
A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer from which
$SET_SECURITY is to read the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
Not used.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Value used to maintain protected object processing context when dealing
with a single protected object across multiple
$GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY calls. Whenever the context value is
nonzero, the class name, object name, or object handle arguments are
disregarded. An input value of 0 indicates that a new context should be
established.
Because an active context block consumes process memory, be sure to
release the context block by setting the RELCTX flag when the profile
processing is complete. $SET_SECURITY sets the context argument to 0
once the context is released.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Access mode to be used in the object protection check. The
acmode argument is the address of a longword
containing the access mode. The acmode argument
defaults to kernel mode; however, the system compares
acmode with the caller's access mode and uses the
least privileged mode. The access modes are defined in the system macro
$PSLDEF library.
HP recommends that this argument be omitted (passed as zero).
Item Codes The following table provides a summary of item codes that
are valid as an item descriptor in the itmlst
argument. The table lists the $SET_SECURITY item codes and gives a
corresponding description. Complete descriptions of each item code are
provided after the table.
| Item Code |
Description |
|
OSS$_ACL_ADD_ENTRY
|
Adds an access control entry (ACE)
|
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE
|
Deletes all unprotected ACEs in an ACL
|
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ALL
|
Deletes the ACL, including protected ACEs
|
|
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ENTRY
|
Deletes an ACE
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
|
Locates an ACE
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
|
Positions the next ACE
|
|
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
|
Locates an ACE of the specified type
|
|
OSS$_ACL_MODIFY_ENTRY
|
Replaces an ACE at the current position
|
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
|
Sets a marker that points to the end of the ACL
|
|
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
|
Sets a marker that points to the beginning of the ACL
|
|
OSS$_OWNER
|
Sets the UIC or general identifier of the object's owner
|
|
OSS$_PROTECTION
|
Sets the protection code of the object
|
OSS$_ACL_ADD_ENTRY
Adds an access control entry (ACE) pointed to by the buffer address so
that it is in front of the current ACE in the access control list
(ACL). See OSS$_ACL_POSITION for more information on explicit access
control list positioning.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE
Deletes all unprotected ACEs in an ACL.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ALL
Deletes an entire ACL, including protected ACEs.
OSS$_ACL_DELETE_ENTRY
Deletes an ACE pointed to by the buffer address or, if the buffer
address is specified as 0, the ACE at the current position.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
Locates an ACE pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations; for
example, for a deletion or modification of the ACE. If the buffer
address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
Advances the current position to the next ACE in the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
Returns an ACE of a particular type if there is one in the buffer
pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE sets the position
within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations. If the buffer address is
0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.
OSS$_ACL_MODIFY_ENTRY
Replaces an ACE at the current position with the ACE pointed to by the
buffer address.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
Sets the ACL position to point to the bottom of the ACL.
OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
Sets the ACL position to point to the top of the ACL.
OSS$_OWNER
Sets the owner UIC of the selected object to the value in the buffer.
The buffer size must be 4 bytes.
OSS$_PROTECTION
Sets the selected object's protection code to the value in the buffer.
The buffer size must be 2 bytes.
Description
The Set Security service modifies the security characteristics of a
protected object. Security characteristics include such information as
the protection code, the owner, and the access control list (ACL).
The security management services, $SET_SECURITY and $GET_SECURITY,
maintain a single master copy of a profile for every protected object
in an OpenVMS Cluster system. They also ensure that only one process at
a time can modify an object's security profile.
When you call $SET_SECURITY, the service performs the following steps:
- It selects the specified protected object.
- It fetches a local copy of the object's security profile, unless
the service is operating on an existing context.
- It modifies the local profile.
- It updates the master copy of the profile if the local flag is
clear and there was no error.
- It deletes the local copy of the profile and returns if RELCTX is
specified or if no context is specified.
There are different ways of identifying which protected object
$SET_SECURITY should process:
- Whenever the contxt argument has a nonzero value,
$SET_SECURITY uses the context to select the object and ignores the
class name, object name, and object handle.
- With some types of objects, such as a file or a device, it is
possible to select an object on the basis of its
objhan and clsnam values.
- When the clsnam and objnam
arguments are provided, $SET_SECURITY uses an object's class name and
object name to select the object.
The context for a security management operation can be established
through either $GET_SECURITY or $SET_SECURITY. Whenever the context is
set by one service, the other service can use it provided the necessary
locks are being held. A caller to $GET_SECURITY needs to set the write
lock flag (OSS$M_WLOCK) to inspect a profile value, maintain the lock
on the object's profile, and then modify some value through a call to
$SET_SECURITY.
There are many situations in which the contxt argument
is essential. By establishing a context for an ACL operation, for
example, a caller can retain an ACL position across calls to
$GET_SECURITY so that a set of ACEs can be read and modified
sequentially. A security context is released by a call to $SET_SECURITY
or $GET_SECURITY that sets the OSS$M_RELCTX flag. Once the context is
deleted, the user-supplied context longword is reset to 0.
Required Access or Privileges
Control access to the object is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The parameter cannot be read and the buffer cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
You specified an invalid object, attribute code, or item size.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
The
clsnam and
objnam arguments are not specified, the
clsnam and
objhan arguments are not specified, or the
contxt argument is not specified.
|
|
SS$_INVBUFLEN
|
The buffer size for one of the item codes was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INVCLSITM
|
The item code that you specified is not supported for the class.
|
|
SS$_INVFILFOROP
|
An invalid file name was specified; the file name contained either a
node or wildcard specification.
|
|
SS$_MMATORB
|
The attempted update cannot be performed. The object profile was
changed by another process.
|
|
SS$_NOCLASS
|
The named object class does not exist.
|
|
SS$_OBJLOCKED
|
The selected object is currently write locked.
|
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT (Alpha Only)
Establishes a request for notification when an OpenVMS system event
occurs.
Format
SYS$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT event ,astadr ,astprm ,acmode ,flags ,handle
C Prototype
int sys$set_system_event (unsigned int event, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int acmode, unsigned
int flags, struct _generic_64 * handle);
Arguments
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event code indicating the type of system event for which an AST is to
be delivered. The event argument is a value indicating
which type of event is of interest.
Each event type has a symbolic name. The $SYSEVTDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
SYSEVT$C_ADD_MEMBER
|
One or more OpenVMS instances have joined the OpenVMS Galaxy sharing
community.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_DEL_MEMBER
|
One or more OpenVMS instances have left the OpenVMS Galaxy sharing
community.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_ADD_ACTIVE_CPU
|
One or more processors have become active within this OpenVMS instance.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_DEL_ ACTIVE_CPU
|
One or more processors have become inactive within this OpenVMS
instance.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_ADD_CONFIG_CPU
|
One or more CPUs have been added to the set of available CPUs for this
OpenVMS instance.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_DEL_CONFIG_CPU
|
One or more processors have been removed from this OpenVMS instance.
|
|
SYSEVT$C_TDF_CHANGE
|
The system's time differential factor has changed.
|
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit or 64-bit reference |
Notification AST routine to receive control after a change in OpenVMS
system configuration occurs.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
quadword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The quadword AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode at which the system event AST is to execute. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode.
Each access mode has a symbolic name. The $PSLDEF macro defines the
following symbols for the four access modes.
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The value of the access mode is maximized with the access mode of the
caller.
flags
Defined in SYSEVTDEF.
|
SYSEVT$M_REPEAT_NOTIFY
|
When this flag is set, event notification is repeated.
|
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
handle |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword for the event
handle.
Description
The Set System Event service establishes a request for notification
when a system event occurs. It may create a new system event
notification object, add an event to a new or existing object, and
enable notification on a new or existing object.
If the handle specified is zero, a new system
notification request object is created, and a handle for the new object
is returned.
If the event specified is non-zero, that event is
added to the set of events which trigger notification on the
notification object.
The service will verify that the input parameters specify a valid
request and enable the object for notification. Notification is
accomplished by AST delivery. After the AST has been delivered,
notification must again be enable on the object before another
notification (AST delivery) can occur if flag is not
set.
Errors are returned in the following cases:
- If quotas are exceeded, an error is returned. It is important to
note that this routine returns an error and will not retry an attempt
to get quota if quota is exhausted on the first attempt.
- See the Condition Values Returned section for types of errors that
can be returned.
- If the astadr argument is omitted, and a new
notification object is being created, SS$_BADPARAM is returned.
- If the event argument is incorrectly specified,
SS$_BADPARAM is returned.
- If the access mode parameter is more privileged than the mode of
the caller, the mode of the caller is used.
- If specified, the handle argument must be
writeable from the mode of the caller. SS$_ACCVIO is returned if this
is not the case.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
ASTLM
Related Services
$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One of more arguments has an invalid value.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process exceeded its quota for outstanding ASTs.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient to complete the service.
|
$SHOW_INTRUSION
Searches for and returns information about records in the intrusion
database matching the caller's specifications.
Format
SYS$SHOW_INTRUSION user_criteria ,intruder ,intruder_len ,breakin_block
,[flags] ,[context]
C Prototype
int sys$show_intrusion (void *user_criteria, void *intruder, unsigned
short int *intruder_len, void *breakin_block, unsigned int flags,
unsigned int *context);
Arguments
user_criteria
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string or item_list_3 |
| type: |
character-coded text string or longword
(unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor or by
reference |
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:
The user_criteria argument is the description of
intruder or suspect. The user_criteria argument is the
address of a character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer
containing the user criteria to match an intrusion record's user
specification in the intrusion database.
The user_criteria argument is a character string of
between 1 and 1058 bytes containing characters to match the user
specification on records in the intrusion database.
A user specification is any combination of the suspect's or intruder's
source node name, source user name, source DECnet for OpenVMS address,
local failed user name, local terminal, or the string UNKNOWN. The user
specification for an intrusion record is based on the input to the
$SCAN_INTRUSION service and the settings of the LGI system parameter.
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Wildcards are allowed for the user_criteria argument.
For more information about using wildcards to scan the intrusion
database, see the Description section.
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE:
The user_criteria argument is now the address of an
32-bit item list. If the item list is used, one item, the
CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL item, must be present in the item list.
The following table lists the valid item descriptions for the
user_criteria argument:
| Item |
Description |
|
CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST
|
Address of an 8192-byte buffer into which the service writes the
associated node information for the returned intrusion record.
|
|
CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST
|
Address of a list of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which
the caller wants to see intrusion information about.
|
|
CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL
|
Address of a buffer, 1-1058 bytes long, containing the intruder or
suspect.
|
If a CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is provided, an intrusion record will only
be returned if it originated on one of the nodes specified. If a
CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is not provided, records from all nodes will be
candidates for display. Multiple CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST items are permitted
in the item list.
If a CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST item is provided, the item is filled with
node-count records on return. The returned intrusion record will have a
breakin block with a valid attempt-count field. The node-count records
will have the name and attempt-count for each node represented.
intruder
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
User specification of the matched intruder or suspect record in the
intrusion database. The intruder argument is the
address of a character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer to
receive the user specification of the matched record in the intrusion
database.
The intruder argument is a 1058-byte string that will
receive the user specification of a record in the intrusion database
that matches the specifications in the user_criteria
and flags arguments.
intruder_len
| OpenVMS usage: |
string length |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of returned string in the intrusion buffer. The
intruder_len argument is the address of a longword to
receive the length of the returned intrusion buffer.
The possible range of the intruder_len argument is 0
to 1058 bytes. If the longword specified by the argument contains a 0
after the call to the service, either the service did not find a record
that matched the user criteria in the intrusion database, or there are
no more matching items in the intrusion database.
breakin_block
| OpenVMS usage: |
record |
| type: |
block of 2 words (unsigned), 1 longword (unsigned), and 1
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Block to receive various information in the intrusion database about a
record matching the user criteria. The breakin_block
argument is the address of a structure with the following format:
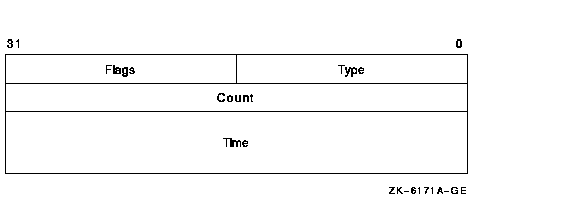
The following table defines the break-in block fields:
| Field |
Description |
|
Type
|
Unsigned word containing the type of the matched record. The possible
values for the type field are TERM_USER, TERMINAL, USERNAME, and
NETWORK. These constants are defined in $CIADEF in STARLET.
|
|
Flags
|
Boolean set to TRUE (1) if the matched record is an intruder. If the
value is set to FALSE (0), the matched record is only a suspect.
|
|
Count
|
Unsigned longword containing the number of login failures or break-in
attempts made by the specified intruder or suspect.
|
|
Time
|
Quadword time format indicating the time when the record will expire.
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Type of records in the intrusion database about which information is to
be returned. The flags argument is a longword bit mask
wherein each bit corresponds to an option.
Each option has a symbolic name. The $CIADEF macro defines the
following valid names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CIA$M_ALL
|
All records will be shown. If the
flags argument is omitted, this value is assumed.
|
|
CIA$M_INTRUDERS
|
Only intruder records matching the criteria specified by the
user_criteria argument will be returned. The value of
the flag field in the break-in block will always be 1.
|
|
CIA$M_ITEMLIST
|
If FALSE, the
user_criteria argument is a character string. If TRUE,
this argument is a 32-bit item list.
|
|
CIA$M_SUSPECTS
|
Only suspect records matching the criteria specified by the
user_criteria argument will be returned. The value of
the flag field in the break-in block will always be 0.
|
Each of these options is mutually exclusive.
context
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Context information to keep between related calls to the
$SHOW_INTRUSION service. The context argument is the
address of a longword that receives a context from the service.
The initial value contained in the unsigned longword pointed to by the
context argument must be 0. The contents of the
unsigned longword must not be changed after the service has set its
value. If the contents of the context argument are
changed between calls to the service, SS$_BADCONTEXT will be returned.
Contexts become invalid after one-half hour of non-use. This means that
if you call the $SHOW_INTRUSION service with a wildcard in the
user_criteria argument and do not call the service to
get the next matching record within one-half hour, the context becomes
invalid. If the context has become invalid, you must restart your
search of the intrusion database from the beginning by resetting the
context to 0.
Description
The Show Intrusion service returns information about records in the
intrusion database that match the criteria you specify.
You can retrieve information about multiple records in the intrusion
database by specifying wildcards for the user_criteria
argument. For example, specifying an asterisk (*) for the
user_criteria argument and CIA$M_ALL_RECORDS for the
flags argument will return information about all
records in the database. Specifying TTA4* for the
user_criteria argument and CIA$M_SUSPECTS_ONLY for the
flags argument will return information about all
suspects who have had failures on terminal TTA4.
If you specify a wildcard string for the user_criteria
argument, you must also include a context argument.
Because the service can only return information about one intrusion
record at a time, you must call the service repeatedly to retrieve
information about more than one record. The service will return
SS$_NOMOREITEMS when information about all of the matching records has
been returned. No intrusion information is returned from the call that
returns SS$_NOMOREITEMS.
Required Access or Privileges
SECURITY privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DELETE_INTRUSION, $SCAN_INTRUSION
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
user_criteria or
context argument cannot be read, or the
intruder,
intruder_len,
breakin_block, or
context argument cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFLEN
|
The length of one of the specified arguments is out of range.
|
|
SS$_BADCONTEXT
|
The
context argument did not contain a 0 on the first call
to the service. The
context argument's value changed between consecutive
calls to the service.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
An invalid value was specified in the
flags argument, or mutually exclusive options were
specified in the
flags argument.
|
|
SS$_NOMOREITEMS
|
All items matching the specified criteria have been returned.
|
|
SS$_NOSECURITY
|
The caller does not have SECURITY privilege.
|
|
|
|
|
This service can also return any of the following messages passed from
the security server:
|
|
SECSRV$_NOSUCHINTRUDER
|
No records matching the specified criteria were found in the intrusion
database.
|
|
SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE
|
The security server is not currently active. Try the request again
later.
|
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64
Returns the address of a 64-bit signal array. A 32-bit signal array and
a mechanism array are passed to a condition handler when it is called.
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit signal array, which
might be required for programs that use 64-bit address space.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 mcharg, sigarg_64
C Prototype
int sys$signal_array_64 (unsigned __int64 mcharg, unsigned __int64
sigarg_64);
Arguments
mcharg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mechanism array |
| type: |
vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The mechanism array. The mcharg argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of this array, which was passed to the condition
handler. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 uses this structure to determine the 64-bit
signal array address.
sigarg_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
64-bit signal array |
| type: |
vector quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference |
The 32- or 64-bit address of the 64-bit signal array is returned in
this argument.
Description
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit version of the
signal array for condition handlers that need it. It is normally needed
only by applications that use 64-bit address space and want to handle
errors involving addresses in that region.
For example, if an access violation occurs on a 64-bit address, the
32-bit signal array passed to the handler will contain only the low 32
bits of the effective address, because each entry is a longword. The
64-bit signal array, which can be obtained using this service, contains
quadword entries, so the 64-bit address can be fully expressed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$PUTMSG, which accepts either a 32-bit or 64-bit signal array as an
argument.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed succesfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
sigarg_64 argument cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
mcharg argument is not a mechanism array in the
expected format.
|
$SNDERR
Writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding
it with the date and time.
Format
SYS$SNDERR msgbuf
C Prototype
int sys$snderr (void *msgbuf);
Argument
msgbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Message to be written to the error log file. The
msgbuf argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the message text.
Description
The Send Message to Error Logger service writes a user-specified
message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and
time. The $SNDERR service requires system dynamic memory.
Required Access or Privileges
To send a message to the error log file, the calling process must have
BUGCHK privilege.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the required BUGCHK privilege.
|
$SNDJBC
Creates, stops, and manages queues and the batch and print jobs in
those queues. The $SNDJBC service completes asynchronously; to
synchronize the completion of most operations, use the Send to Job
Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service.
Format
SYS$SNDJBC [efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$sndjbc (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int
nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $SNDJBC completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $SNDJBC uses only the low-order byte.
When you queue the request, $SNDJBC clears the specified event flag (or
event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the
operation completes, $SNDJBC sets the specified event flag (or event
flag 0).
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function code specifying the function that $SNDJBC is to perform. The
func argument is a word containing this function code.
The $SJCDEF macro defines the names of each function code.
You can specify only one function code in a single call to $SNDJBC.
Most function codes require or allow for additional information to be
passed in the call. You pass this information by using the
itmlst argument, which specifies a list of one or more
item descriptors. Each item descriptor in turn specifies an item code,
which modifies, restricts, or otherwise affects the action designated
by the function code.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list supplying information to be used in performing the function
specified by the func argument. The
itmlst argument is the address of the item list. The
item list consists of one or more item descriptors, each of which
specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by an item code of
0 or by a longword of 0. The following diagram depicts the structure of
a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length of the buffer; the buffer either supplies
information to be used by $SNDJBC or receives information from $SNDJBC.
The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code
specified, and is given in the description of each item code.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing an item code, which identifies the nature of the
information supplied for use by $SNDJBC or received from $SNDJBC. Each
item code has a symbolic name. The $SJCDEF macro defines these symbol
names.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies or
receives the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word to receive the length (in
bytes) of information returned by $SNDJBC. If you specify this address
as 0, no length is returned.
|
The item codes' symbolic names have the following format:
There are three types of item code:
- Boolean item code. Boolean item codes specify a true or false
value: the form SJC$_code specifies a true value; SJC$_NO_code
specifies a false value. The default value for the Boolean item codes
is false. For all Boolean item codes, the buffer length, buffer
address, and return length fields of the item descriptor must be 0.
- Input value item code. Input value item codes specify an input
value to be used by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer address
fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return length field
must be 0. Specific buffer length requirements are given in the
description of each item code.
- Output value item code. Output value item codes specify a buffer
for information returned by $SNDJBC. The buffer length and buffer
address fields of the item descriptor must be nonzero; the return
length field can be 0 or nonzero. Specific buffer length requirements
are given in the description of each item code.
Several item codes specify a queue name, form name, or characteristic
name. For these item codes, the buffer must specify a string containing
from 1 to 31 characters, exclusive of spaces, tabs, and null
characters, which are ignored. Allowable characters in the string are
uppercase alphabetic characters, lowercase alphabetic characters (which
are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, the dollar sign ($),
and the underscore (_).
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block into which $SNDJBC writes the completion status after
the requested operation has completed. The iosb
argument is the address of the I/O status block.
At request initiation, $SNDJBC sets the value of the quadword I/O
status block to 0. When the requested operation completes, $SNDJBC
writes a condition value in the first longword of the I/O status block.
It writes the value 0 into the second longword; this longword is unused
and reserved for future use.
The condition values returned by $SNDJBC in the I/O status block are
usually condition values from the JBC facility. These condition values
are defined by the $JBCMSGDEF macro. In some cases, the condition value
returned by $SNDJBC can be an error return from a system service or an
OpenVMS RMS service that is used in executing the request. For the
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB request, the condition value returned is the
completion status of the requested job.
The condition values returned from the JBC facility are listed in the
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block section.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $SNDJBC service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$SNDJBC, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $SNDJBC completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If specified, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the
caller of $SNDJBC.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is this longword parameter.
Function Codes This section describes the various function codes that
are applicable to the $SNDJBC system service.
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
Aborts the execution of the current job from an output execution queue
or the job you specified from a batch queue. By default, the job is
deleted. However, for a restartable job, you can requeue it to the same
queue or to another queue.
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
SJC$_QUEUE
You must specify the following input value item code for batch jobs:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
You can specify the following optional input value or Boolean item
codes:
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_REQUEUE
|
---
|
SJC$_ADD_FILE
Adds a file to the open job owned by the requesting process. You use
this operation as part of a sequence of calls to the $SNDJBC service to
create a job with one or more files. The first call in the sequence
specifies the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation to create an open job. Each
subsequent SJC$_ADD_FILE request associates an additional file with the
job. Finally, you make an SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request to complete the batch
or print job specification.
To create a job that contains only one file, you can make a single call
to $SNDJBC that specifies the SJC$_ENTER_FILE function code.
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_DELETE_FILE
|
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
|
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PASSALL
|
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
|
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
Alters the parameters of an existing job that is not currently
executing.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME
|
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
---
|
SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA
|
|
SJC$_CLI
|
SJC$_NO_CLI
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
---
|
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
|
|
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
|
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE
|
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
|
|
SJC$_NOTE
|
SJC$_NO_NOTE
|
|
SJC$_NOTIFY
|
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
|
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8
|
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
|
|
SJC$_PASSALL
|
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RESTART
|
SJC$_NO_RESTART
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies
that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before
modifying the job.
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
Alters the parameters of a queue. The execution of current jobs is
unaffected.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
|
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PROTECTION
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
|
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SWAP
|
SJC$_NO_SWAP
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
Assigns a logical queue to an execution queue. The SJC$_QUEUE item code
specifies the logical queue; the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code
specifies the execution queue.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT
Establishes a checkpoint in a batch job. No operation is performed if
the requesting process is not a batch process.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_CHECKPOINT_DATA
SJC$_CLOSE_DELETE
Deletes the open job owned by the requesting process. No item codes are
allowed.
SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
Completes the specification of the open job owned by the requesting
process and places the job in the queue specified in the
SJC$_CREATE_JOB request that opened the job. If the SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
request completes successfully, the job is no longer an open job; it
becomes a normal batch or print job.
You can specify the following output value item code:
SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
Creates an open job for the requesting process. If the process already
owns an open job, that job is deleted.
An open job is a batch or print job that has not yet been completely
specified. After you make the SJC$_CREATE_JOB request to open the job,
you can make subsequent calls to $SNDJBC using the SJC$_ADD_FILE
function code to specify the files associated with the job. Finally,
you can complete the job specification with an SJC$_CLOSE_JOB request.
If the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation completes successfully, the open job
created is given an entry number; the job is not assigned to the queue
specified in the SJC$_CREATE_JOB operation until the SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
request completes successfully.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME
|
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLI
|
SJC$_NO_CLI
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
|
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE
|
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
|
|
SJC$_NOTE
|
SJC$_NO_NOTE
|
|
SJC$_NOTIFY
|
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
|
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8
|
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RESTART
|
SJC$_NO_RESTART
|
|
SJC$_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_USERNAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
You can specify the following output value item code:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
Creates a queue. If the queue already exists and is not stopped, this
request performs no operation. However, if the queue already exists and
is stopped, the request alters the parameters of the queue based on the
item codes specified in the request; if you specify the
SJC$_CREATE_START item code, the request starts the queue.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON
|
---
|
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_BATCH
|
SJC$_NO_BATCH
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_CREATE_START
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
|
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PRINTER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_PROCESSOR
|
SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR
|
|
SJC$_PROTECTION
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
|
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SERVER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SWAP
|
SJC$_NO_SWAP
|
|
SJC$_TERMINAL
|
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE
Deassigns a logical queue from an execution queue.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
Defines a characteristic name and number and inserts this definition
into the queue file. The characteristic name can be up to 31 characters
in length. Each characteristic name must have a unique number in the
range 0 to 127. If the characteristic name is already defined, the
request alters the definition of the characteristic.
A job cannot execute on an execution queue unless the queue possesses
all the characteristics possessed by the job; the queue can possess
additional characteristics and the job will still execute.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
Defines a form name and number, as well as other physical attributes of
the paper stock used in printers, and inserts this definition into the
system job queue file. If the form name is already defined, this
request alters the definition of the form.
Forms are used only by output execution queues and print jobs. A print
job cannot execute unless the stock name of a form specified for the
queue is the same as the stock name specified for the job. The stock
name of a form, which you specify by using the SJC$_FORM_STOCK item
code, specifies the paper stock used by the printer. Other item codes
specify printing parameters for a job such as the margins, length of
paper, and so on.
Each form must have a unique number. Numbers can range from 0 to 9999.
When a new queue file is created, the system supplies the definition of
a form named DEFAULT with number 0 and default characteristics.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_FORM_NAME
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_FORM_DESCRIPTION
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_LENGTH
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_BOTTOM
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_LEFT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_RIGHT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_TOP
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED
|
SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED
|
|
SJC$_FORM_STOCK
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE
|
SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE
|
|
SJC$_FORM_WIDTH
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_WRAP
|
SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
Deletes the definition of a characteristic name.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
SJC$_DELETE_FORM
Deletes the definition of a form name. There must be no queues or jobs
that reference the form.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_FORM_NAME
SJC$_DELETE_JOB
Deletes a job from the system job queue file. If the job is currently
executing, it is aborted. If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the
$SNDJBC service verifies that the selected job entry exists on the
specified queue before deleting the job.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
You can specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
If you specify the SJC$_QUEUE item code, the $SNDJBC service verifies
that the selected job entry exists on the specified queue before
deleting the job.
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
Deletes a queue and all of the jobs in the queue. The queue must be
stopped, and there must be no other queues or jobs that reference the
queue.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER
Removes all references to the specified queue manager from the shared
master file. It also deletes the queue and journal files associated
with the queue manager. A queue manager must be stopped to be deleted.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
Disables autostart on a node. By default, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
affects the requesting node. To disable autostart on a node other than
the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent, use the
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the affected node.
Disabling autostart on a node forces the appropriate queue manager to
perform these tasks:
- Prevent autostart queues from failing over to the node.
- Mark all of that queue manager's autostart queues on the node as
"stop pending" in preparation for a planned shutdown,
allowing jobs currently executing on the queues to complete.
- Force all autostart queues with failover lists to fail over to the
next available node in the queue manager's failover list on which
autostart is enabled. Each queue fails over when all jobs currently
executing on any of that queue manager's queues on the node have
completed.
You can specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART
Notifies the appropriate queue manager process that a node has
progressed sufficiently in its startup procedure that batch and print
jobs should execute.
By default, SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART affects the requesting node. To
enable autostart on a node other than the node from which the $SNDJBC
request is sent, use the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the
affected node. Once autostart is enabled, the queue manager starts all
autostart-active queues on the appropriate node.
When a node reboots, autostart is disabled until the
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART request is entered.
You can specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
Creates a job containing one file and places the job in the specified
queue. To create a job with more than one file, you must make a
sequence of calls to the $SNDJBC service using the SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_ADD_FILE, and SJC$_CLOSE_JOB function codes.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_AFTER_TIME
|
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLI
|
SJC$_NO_CLI
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_DELETE_FILE
|
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
|
|
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_HOLD
|
SJC$_NO_HOLD
|
|
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
|
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_DELETE
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
|
|
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
|
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
|
|
SJC$_LOWERCASE
|
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
|
|
SJC$_NOTE
|
SJC$_NO_NOTE
|
|
SJC$_NOTIFY
|
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
|
|
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
|
|
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
|
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through 8
|
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
|
|
SJC$_PASSALL
|
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
|
|
SJC$_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RESTART
|
SJC$_NO_RESTART
|
|
SJC$_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_USERNAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
You can specify the following output value item codes:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE
Requeues all jobs in the queue specified by the item code SJC$_QUEUE to
the queue specified by the item code SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE. The
execution of current jobs is unaffected.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_PAUSE_QUEUE
Pauses the execution of current jobs in the specified queue and
prevents the starting of jobs in that queue.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_RESET_QUEUE
Resets the specified queue by (1) terminating and deleting each
executing job that is not restartable, (2) terminating and requeuing
each executing job that is restartable, and (3) stopping the queue.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING
This request performs two functions. If you specify the
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES item code, the request enables recording of the
specified types of accounting records; if you do not specify
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES, the request starts the accounting manager and
opens the system accounting file.
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
SJC$_NEW_VERSION
SJC$_START_QUEUE
Permits the starting of jobs in the specified queue. If the queue was
paused, current jobs are resumed.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
|
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK
|
---
|
|
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES
|
---
|
|
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON
|
---
|
|
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
|
---
|
|
SJC$_BATCH
|
SJC$_NO_BATCH
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
|
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
|
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
|
|
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
|
---
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
|
|
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_BURST
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
|
|
SJC$_JOB_FLAG
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
|
|
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
|
---
|
|
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
|
|
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
|
|
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
|
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
|
|
SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
|
SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
|
|
SJC$_NEXT_JOB
|
---
|
|
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
|
---
|
|
SJC$_PAGINATE
|
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
|
|
SJC$_PROCESSOR
|
SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR
|
|
SJC$_PROTECTION
|
---
|
|
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
|
|
SJC$_RAD
|
SJC$_NO_RAD
|
|
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
|
|
SJC$_RELATIVE_PAGE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
|
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
|
|
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SEARCH_STRING
|
---
|
|
SJC$_SWAP
|
SJC$_NO_SWAP
|
|
SJC$_TERMINAL
|
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL
|
|
SJC$_TOP_OF_FILE
|
---
|
|
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
|
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
|
|
SJC$_WSEXTENT
|
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
|
|
SJC$_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
|
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER
Starts the clusterwide queue manager for the batch and print queuing
system. It also opens the queue database.
The SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request has the following five uses:
- To create a queue database and initially start the queue manager,
issue a SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_NEW_VERSION item
code. See the description of the SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code for more
information. Once the queue manager has been started, it will remain
running unless it is explicitly stopped with an SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
request.
- If an SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER request has been specified, issue a
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request to restart the queue manager.
- In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, issue an
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item
code to modify the list of preferred nodes on which the queue manager
can run. See the description of the SJC_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code
for more information.
- In a cluster, issue an SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request to ensure
that the queue manager process is executing on the most preferred,
available node. If the queue manager is not running on the most
preferred, available node, the queue manager will be moved to that node
without interruption of service. If you are using the default node list
(*), the queue manager will not move. For more information, see the
description of the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code.
- To create additional queue managers, issue an
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER request with the SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER and
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME item codes. Note that the queue manager name
must be different from the name of any queue manager currently defined.
For more information about creating multiple queue managers, refer to
the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
You can specify the following input value or Boolean item codes:
SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER
SJC$_NEW_VERSION
SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES
SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING
This request performs two functions. If you specify the
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES item code, the request disables recording of the
specified types of accounting records. If you do not specify
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES, the request stops the accounting manager and
closes the system accounting file.
You can specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
Stops all queues on a specific node. By default, all queues on the
requesting node are stopped. To stop all queues on a node other than
the node from which the $SNDJBC request is sent, use the
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code to specify the affected node.
Besides stopping all queues on a specific node, this request aborts
each job that is currently executing. Aborted jobs that are restartable
are requeued. Queues for which an autostart list has been specified
fail over to the first available node in the list for which autostart
is enabled.
You can specify the following input value item codes:
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE
Prevents the starting of jobs in the specified queue. The execution of
current jobs is unaffected.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
Shuts down the appropriate queue manager. It disables autostart on all
nodes; stops all queues; aborts each job that is currently executing,
requeuing those jobs that are restartable; and closes the files of the
queue database.
You can specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB
Waits for the completion of a job, then sets the event flag, executes
the completion AST if you specified astadr, and
returns the completion status of the job to the I/O Status Block,
provided you specified the iosb argument.
You must specify one of the following input value item codes:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
SJC$_QUEUE
If SJC$_QUEUE queue is specified, then you must also specify one of the
following:
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
SJC$_JOB_NAME
You can specify the following output value item code:
SJC$_JOB_COMPLETION_STATUS
SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING
Writes an accounting record.
You must specify the following input value item code:
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_MESSAGE
Item Codes
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
Input value item code that specifies the account name of the user on
behalf of whom the request is made. The buffer must specify a string
from 1 to 8 characters. By default, the account name for batch and
print jobs is taken from the requesting process.
You need CMKRNL privilege to use this item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_MESSAGE
Input value item code. It causes the contents of the buffer to be
placed in a "user message" accounting record. The buffer must
specify a string from 1 to 255 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING function code)
SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES
Input value item code. It enables or disables accounting-record types.
When an accounting-record type is enabled, the event designated by that
type will be recorded in the accounting record. The buffer must contain
a longword bit vector wherein each bit set specifies an
accounting-record type. Undefined bits must be 0.
The $SJCDEF macro defines the symbolic names for the accounting-record
types. Following is a list of each accounting-record type and the
system event to which it corresponds:
| Accounting-Record Type |
Corresponding System Event |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_IMAGE
|
Image terminations
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_LOGIN_FAILURE
|
Login failures
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_MESSAGE
|
User messages sent
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_PRINT
|
Print job terminations
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_PROCESS
|
Process terminations
|
The following accounting-record types, when enabled, provide additional
information about image and process termination; specifically, they
describe the type of image or process that has terminated:
| Accounting-Record Type |
Type of Image or Process |
|
SJC$V_ACCT_BATCH
|
Batch process
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_DETACHED
|
Detached process
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_INTERACTIVE
|
Interactive process
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_NETWORK
|
Network process
|
|
SJC$V_ACCT_SUBPROCESS
|
Subprocess
|
(Valid for SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING, SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING function codes)
SJC$_ADD_QUEUE_MANAGER
Boolean item code. It specifies that a new queue manager process should
be defined in the master file. The operating system allows no more than
five queue managers in a cluster.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
SJC$_AFTER_TIME
SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME
The SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code is an input value item code. It specifies
that the job can execute only if the system time is greater than or
equal to the quadword time value contained in the buffer. The buffer
must contain either an absolute time value or a delta time value;
$SNDJBC converts delta time values to absolute time values by adding
the current system time. The time value specified must be in the
future, or it will be set to the current time.
The SJC$_NO_AFTER_TIME item code is a Boolean item code. It cancels the
effect of a SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code previously specified for the job;
the job can execute immediately. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK
Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output execution queues
and only when the SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES item code is also specified. The
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_MASK item code causes the data printed on form alignment
pages to be masked: all alphabetic characters are replaced with the
letter X and all numeric characters with the number 9.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_ALIGNMENT_PAGES
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution
queues. It specifies that the queue be placed in form-alignment state
and that a number of alignment pages be printed. The buffer must
contain a longword value in the range 1 to 20; this value specifies how
many alignment pages are to be printed.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON
Input value item code. For a batch queue, it uses as its value a
comma-separated list of the nodes on which the specified queue can be
located. Each node name must be followed by a double colon (::).
For an output queue, it uses as its value a comma-separated list of the
names of the nodes and devices to which the specified queue's output
can be sent. Each node name must be followed by a double colon, and
each device name can be followed by the optional colon [:].
By specifying this item code, you designate a queue as an autostart
queue. If you specify more than one node name (within an OpenVMS
Cluster environment), the queue can automatically fail over if the node
on which the queue is running is removed from the cluster.
This item code cannot be used with the SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME and
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME item codes.
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_BASE_PRIORITY
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for execution queues. It
specifies the base priority of batch processes initiated from a batch
execution queue or of a symbiont process connected to an output
execution queue. A symbiont process can control several queues;
however, the base priority of the symbiont process is established by
the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a
longword value in the range 0 to 15; this value specifies the base
priority.
By default, the base priority is the value of the system parameter
DEFPRI.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_BATCH
SJC$_NO_BATCH
The SJC$_BATCH item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the
queue is a batch execution queue or a generic batch queue, and thus can
process only batch jobs.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes
are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the
default is SJC$_PRINTER.
The SJC$_NO_BATCH item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the queue is not a batch queue but rather an output execution or
generic output queue, and thus can process only print jobs. It is the
default.
For the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code, SJC$_BATCH and SJC$_NO_BATCH
are supported for compatibility with VAX VMS Version 4.n, but might not
be supported in the future.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS
The SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME and SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER item codes
are both input value item codes. Both specify characteristics for jobs
or queues, and they can be used interchangeably. The characteristics
are user defined.
The SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC and SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC function
codes include and delete, respectively, a specified characteristic from
the system job queue file. A job cannot execute on an execution queue
unless the queue possesses all the characteristics possessed by the
job; the queue can possess additional characteristics and the job will
still execute.
The SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME and SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER item codes
can appear as many times as necessary in a single call to $SNDJBC; the
set of characteristics so defined in the call completely replaces the
set of characteristics defined by a prior call. The
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS item code cancels all defined characteristics
for the job or queue. By default, a queue or job has no defined
characteristics.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
For SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER, the buffer must contain a longword
value in the range 0 to 127. This number identifies a characteristic.
SJC$_NO_CHARACTERISTICS is a Boolean item code.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC_CHARACTERISTIC_NAME
item code:
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_CHARACTERISTIC_NUMBER
item code:
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_CHECKPOINT_DATA
Input value item code. It specifies the value of the DCL symbol
BATCH$RESTART for a batch job that is restarted. The buffer must
contain a string no longer than 255 characters; this string is the
value of the symbol BATCH$RESTART.
(Valid for SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT function code)
SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA
Boolean item code. It cancels a previous specification of the
BATCH$RESTART symbol; the SJC$_NO_CHECKPOINT_DATA item code also
cancels a checkpoint in a print job so that the entire job is
reprinted. By default, the BATCH$RESTART symbol is undefined.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code)
SJC$_CLI
SJC$_NO_CLI
The SJC$_CLI item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful
only for batch jobs. It specifies that the command language interpreter
to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where name is a valid
OpenVMS RMS file name. The buffer must specify a name string from 1 to
39 characters.
The SJC$_NO_CLI item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that the
command language interpreter to be executed is the one specified in the
user authorization file. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE
The SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that jobs cannot be entered in the queue. If the queue is closed, you
can specify the SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE item code to permit jobs to be entered
in the queue. By default, the queue is open.
Whether a queue is open or closed is independent of any other queue
states (such as paused, stalled, stopped).
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT
SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT
The SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch execution queues. It specifies the default
CPU time limit in 10-millisecond units. The buffer contains this
longword value. The value 0 specifies unlimited CPU time. You can
specify a value that represents up to 497 days of CPU time.
The SJC$_NO_CPU_DEFAULT item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for batch execution queues. It specifies that no
default CPU time limit is to apply to the job. It is the default.
A CPU time limit for the process is included in each user record in the
system user authorization file (UAF). You can also specify any or all
of the following: a CPU time limit for individual jobs, a default CPU
time limit for all jobs in a given queue, and a maximum CPU time limit
for all jobs in a given queue. Table SYS-54 shows the action taken
when you specify a value for SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT.
Table SYS-54 CPU Time Limit Decision Table
CPU Time Limit
Specified for
Job? |
Default CPU Time
Limit Specified for
Queue? |
Maximum CPU
Time Specified for Queue? |
Action Taken |
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
Use UAF value
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
Use smaller of job's limit and UAF value
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
Use smaller of job's limit and UAF value
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
Yes
|
Use smaller of job's limit and maximum
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Use smaller of job's limit and maximum
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Use smaller of queue's default and maximum
|
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
Use maximum
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
Use smaller of UAF value and queue's default
|
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT
SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT
The SJC$_CPU_LIMIT item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch execution queues and batch jobs. It specifies
the maximum CPU time limit for batch jobs in 10-millisecond units. The
buffer must contain this longword value. The value 0 specifies
unlimited CPU time. You can specify a value that represents up to 497
days of CPU time.
The SJC$_NO_CPU_LIMIT item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for batch execution queues and batch jobs. It specifies
that no maximum CPU time limit is to apply to the job. It is the
default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for
SJC$_CPU_LIMIT, refer to the description of the SJC$_CPU_DEFAULT item
code and to Table SYS-54.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_CREATE_START
Boolean item code. It specifies that a queue be started after it is
created. By default, a queue remains stopped after it is created.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME
SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER
The SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME and SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER item codes are
input value item codes. They specify the default form for a specific
output queue by name and by number, respectively.
When you specify a default form for an output queue, the queue uses the
queue-specific default form, rather than the systemwide default form,
to process any job that does not explicitly specify a form.
For SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NAME, the buffer must specify a form name. The
string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
For SJC$_DEFAULT_FORM_NUMBER, the buffer must specify a longword value.
You should use only one of these item codes to identify a default form
for the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_DELETE_FILE
SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE
The SJC$_DELETE_FILE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a file should be deleted after the job completes. The file that is
deleted is the batch or print file submitted for execution. You cannot
specify this item code with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB function code, which
alters the parameters for an already existing job; you can make a file
deletion request only when a job is first submitted to the queue.
The SJC$_NO_DELETE_FILE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a file should not be deleted after execution of the job. It is the
default. You can specify this item code with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB
function code; this makes it possible to cancel a file deletion request
that was made when the job was first submitted to the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE
Input value item code. When you specify the SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE function
code, SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE specifies the name of the execution queue
to which the logical queue is assigned. When you specify the
SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, or SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE function code,
SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE specifies the name of the queue into which jobs
are placed. By default, jobs remain in the original queue.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE, and
SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME
Input value item code. It specifies the name of the device managed by
the output execution queue. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to
255 characters. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, the
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME item code is used to specify the name of the node on
which the device is located.
This item code cannot be used with the SJC$_AUTOSTART_ON item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE
SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE
The SJC$_DOUBLE_SPACE item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the
symbiont should print the file with double spacing.
The SJC$_NO_DOUBLE_SPACE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the symbiont should print the file with single spacing. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER
Input value item code. It specifies the entry number of the job on
which to perform the function. The buffer must contain this entry
number.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_DELETE_JOB,
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function codes)
SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
Output value item code. The buffer must specify a longword into which
$SNDJBC will write the entry number of a created job.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_FILE_BURST
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE
SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST
The SJC$_FILE_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output execution queues. It specifies that burst and flag
pages are to be printed preceding a file. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_BURST for a job, it specifies the default for all files in
the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue, it specifies
the default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a burst
page is to be printed preceding a file. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE for a job, this item code specifies that a burst
page is to be printed preceding only the first copy of the first file
in the job; if you specify SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE for an output execution
queue, the item code specifies this behavior as the default for all
jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no burst
page should be printed. It is the default.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FILE_BURST item code:
SJC$_ADD_FILE
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FILE_BURST_ONE item
code:
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FILE_COPIES
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution
queues. It specifies the number of times a file is printed. By default,
a file is repeated once. The buffer must specify a longword value from
1 to 255; this value is the repeat count.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_FILE_FLAG
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE
SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG
The SJC$_FILE_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output execution queues. It specifies that a flag page is to
be printed preceding a file. If you specify SJC$_FILE_FLAG for a job,
this item code indicates the default for all files in the job; if you
specify it for an output execution queue, SJC$_FILE_FLAG indicates the
default for all jobs executed from that queue.
The SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a flag
page is to be printed preceding a file. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE for a job, this item code specifies that a flag page
is to be printed preceding only the first copy of the first file in the
job; if you specify SJC$_FILE_FLAG_ONE for an output execution queue,
it indicates this behavior as the default for all jobs executed from
that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no flag
page should be printed by default for jobs within the queue.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FILE_FLAG item code:
SJC$_ADD_FILE
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FLAG_ONE item code:
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
Input value item code. It specifies the file to be processed. The
buffer contains a 28-byte value that identifies the file to be
processed. This value specifies (in order) the following three
file-identification fields in the OpenVMS RMS NAM block: the 16-byte
NAM$T_DVI field, the 6-byte NAM$W_FID field, and the 6-byte NAM$W_DID
field. These fields occur consecutively in the NAM block.
If you specify SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION, you must omit the
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_FILE_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. It
is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a
list of text modules should be extracted from the device control
library and copied to the printer before a file is printed. The buffer
must contain a list of text module names, with a comma separating each
name.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no text
modules should be copied before printing a file. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
Input value item code. It identifies the file to be processed. The
buffer must contain the file specification of the file to be processed.
The $SNDJBC service converts the file specification to the
corresponding file identification and proceeds as if the
SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION item code had been specified. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION, you must omit the SJC$_FILE_IDENTIFICATION
item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE
SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER
The SJC$_FILE_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a
trailer page is to be printed following a file. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER for a job, this item code indicates the default for
all files in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue,
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER specifies the default for all jobs executed on that
queue.
The SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a
trailer page is to be printed following a file. If you specify
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE for a job, this item code indicates that a
trailer page is to be printed following only the last copy of the last
file in the job; if you specify it for an output execution queue,
SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE indicates this behavior as the default for all
jobs executed on that queue.
The SJC$_NO_FILE_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that no
trailer page should be printed. It is the default.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FILE_TRAILER item code:
SJC$_ADD_FILE
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FILE_TRAILER_ONE item
code:
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FIRST_PAGE
SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE
The SJC$_FIRST_PAGE item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for jobs queued to output execution queues. It
specifies the page number at which printing should begin. The buffer
must contain a nonzero longword value specifying this page number.
The SJC$_NO_FIRST_PAGE item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for jobs queued to output execution queues. It
specifies that printing should begin with the first page. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_FORM_DESCRIPTION
Input value item code. It provides operator-supplied information
describing the form. By default, the form name is used. The buffer must
specify a string of no more than 255 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_LENGTH
Input value item code. It specifies the physical length of the form in
lines. The buffer must contain a nonzero longword integer value. By
default, the form length is 66 lines.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_BOTTOM
Input value item code. It specifies the bottom margin of the form in
lines. By default, the bottom margin is 6 lines.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_LEFT
Input value item code. It specifies the width of the left margin of the
form in characters. By default, the left margin is 0. The buffer must
specify a longword value.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_RIGHT
Input value item code. It specifies the width of the right margin of
the form in characters. By default, the right margin is 0. The buffer
must specify a longword value.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_MARGIN_TOP
Input value item code. It specifies the top margin of the form in
lines. By default, the top margin is 0.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_NAME
SJC$_FORM_NUMBER
The SJC$_FORM_NAME and SJC$_FORM_NUMBER item codes are input value item
codes. They specify a mounted form for the queue by name and by number,
respectively. For SJC$_FORM_NAME, the buffer must specify a form name.
For SJC$_FORM_NUMBER, the buffer must specify a longword value. You
should use only one of these two item codes to identify a form in queue
and job related function codes.
The SJC$_DEFINE_FORM and SJC$_DELETE_FORM function codes include and
delete, respectively, a specified form name and number from the system
job queue file. The mounted form indicates the stock type of the output
queue. A job cannot execute on an output queue unless the stock type of
the form specified (by name or number) for the job item code is the
same as the stock type of the mounted form specified for the queue. For
more information about how the stock type of a form affects job
processing, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FORM_NAME item code:
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
SJC$_DELETE_FORM
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_FORM_NUMBER item code:
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_FORM_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. The
buffer must specify one or more text module names, with a comma
separating each name. This item code specifies that these modules
should be extracted from the device control library and copied to the
printer before each file that is printed on the form.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no device control modules should be copied. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED
SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED
The SJC$_FORM_SHEET_FEED item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the symbiont should pause at the end of each physical page so that
a new sheet can be inserted.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_SHEET_FEED item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that the output symbiont should not pause at the end of every
physical page. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_STOCK
Input value item code. It specifies a name for the paper stock. The
buffer must contain a string of 1 to 31 characters. By default, the
name of the paper stock is the form name.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE
SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE
The SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the symbiont should truncate lines that extend beyond the right
margin. Specifying SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE cancels SJC$_FORM_WRAP. The
SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is the default.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_TRUNCATE item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that the output symbiont should not truncate lines that
extend beyond the right margin.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_WIDTH
Input value item code. It specifies the physical width of the form in
characters. The buffer must contain a nonzero longword integer. By
default, the form width is 132 characters.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_FORM_WRAP
SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP
The SJC$_FORM_WRAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the symbiont should wrap lines that extend beyond the right margin.
Specifying SJC$_FORM_WRAP cancels SJC$_FORM_TRUNCATE.
The SJC$_NO_FORM_WRAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the output symbiont should not wrap lines. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE
The SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a queue is a generic queue.
The SJC$_NO_GENERIC_QUEUE item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that a queue is not a generic queue. It is the default. By
default, a queue is an execution queue; see the Description section for
a full discussion of the types of queue.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION
The SJC$_GENERIC_SELECTION item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that an execution queue can accept jobs from a generic queue.
It is the default. It is meaningful only for execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that an execution queue cannot accept jobs from a generic
queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET
Input value item code. The buffer must specify a queue name. This queue
name identifies an execution queue that can accept jobs from a generic
queue. This item code is meaningful only for generic queues.
This item code can appear up to 124 times in a single call to $SNDJBC.
The set of queues defined in a single call completely replaces the set
defined by a prior call.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_HOLD
SJC$_NO_HOLD
The SJC$_HOLD item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a job
cannot execute and must enter a holding status.
The SJC$_NO_HOLD item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a
job can execute immediately when used with the SJC$_ALTER_JOB function
code. It makes the following types of job eligible for execution: (1) a
job that is holding because it was specified with the SJC$_HOLD item
code, (2) a job that was refused by the symbiont, and (3) a job that
was retained after execution. It is the default. SJC$_NO_HOLD does not
release a job that is specified with the SJC$_AFTER_TIME item code.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_BURST
SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST
The SJC$_JOB_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
burst and flag pages are to be printed preceding each job. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_BURST item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a burst page is not to be printed preceding each job. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_COMPLETION_STATUS
Output item code. Use this item code to receive the completion status
of the job being synchronized.
You can omit the IOSB in the $SNDJBC call and receive the completion
status in this item's value.
(Valid for the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code)
SJC$_JOB_COPIES
Input value item code. It specifies the number of times that the entire
print job is to be repeated. The buffer must contain this nonzero
longword integer value. By default, the print job is repeated once.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_JOB_DEFAULT_RETAIN
Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be held in the
queue as specified by the queue's retention policy.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the
/RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_JOB_ERROR_RETAIN
Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be retained in
the queue if the job completes unsuccessfully. However, the job might
be held in the queue even if it completes successfully if the queue is
set to retain all jobs because the QUI$V_QUEUE_RETAIN_ALL bit is set in
the QUI$_QUEUE_FLAGS item code.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the
/RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SCJ$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_JOB_FLAG
SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG
The SJC$_JOB_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a
flag page is to be printed preceding each job. It is meaningful only
for output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_FLAG item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a flag page is not to be printed preceding each job. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_LIMIT
Input value item code. It specifies the maximum number of jobs that can
execute simultaneously on a queue. The buffer must contain a longword
value in the range 1 to 255. It is meaningful only for batch execution
queues. By default, the job limit is 1.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_NAME
Input value item code. It specifies the name of a job. The buffer must
specify a string from 1 to 39 characters.
For function codes SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, and
SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_JOB_NAME specifies the identifying name of the
job. By default, the name used is the name of the first file in the job.
For function code SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB, SJC$_JOB_NAME specifies the
name of the job on which to operate. The job name is implicitly
qualified by the user name.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE,
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function codes)
SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES
SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES
The SJC$_JOB_RESET_MODULES item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must specify
the names of one or more text modules, with a comma separating each
name. This item code specifies that these modules are to be extracted
from the device control library and copied to the printer before each
print job.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_RESET_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no text modules should be copied to the printer. It is
the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN
Boolean item code. It specifies that you want the job to be retained in
the queue after it has executed, regardless of the job's completion
status.
For more information about user-specified job retention, see the
/RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_JOB_RETAIN_TIME
Input value item code. It specifies a quadword time value representing
the length of time you want the job to be retained in the queue.
If a delta time is provided, the delta begins when the job completes;
however, depending on the queue's job retention policy, the job might
be retained indefinitely.
For more information about user-specified job retention, refer to the
/RETAIN qualifier for the PRINT or SUBMIT command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a print
job can execute only if its total size in blocks is less than or equal
to the specified value. The buffer specifies this nonzero longword
value.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MAXIMUM item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that a print job can execute immediately regardless of its
size. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a print
job can execute only if its total size in blocks is greater than or
equal to the specified value. The buffer specifies this nonzero
longword value.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_MINIMUM item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that a print job can execute immediately regardless of its
size. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING
The SJC$_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that print jobs entered in an output queue should be
scheduled according to size, with the smallest job of a given priority
processed first. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_SIZE_SCHEDULING item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that print jobs of a given priority should not be scheduled
according to print size.
Changing the value of this item code for a queue while print jobs are
pending on any queue produces unpredictable results.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_JOB_STATUS_OUTPUT
Output value item code. When specified, $SNDJBC returns, as a character
string, a textual message describing the status of a submitted job.
Because the message can include up to 255 characters, the buffer length
field of the item descriptor should specify 255 (bytes).
(Valid for SJC$_CLOSE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_JOB_TRAILER
SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER
The SJC$_JOB_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output execution queues. It specifies that a trailer page is
to be printed following each job.
The SJC$_NO_JOB_TRAILER item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that a
trailer page is not to be printed following each job. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_LAST_PAGE
SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE
The SJC$_LAST_PAGE item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for jobs submitted to output execution queues. It
specifies the page number at which printing should end. The buffer
specifies this nonzero longword value.
The SJC$_NO_LAST_PAGE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that printing should end after the last page. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION
The SJC$_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION item code is an input value item code.
It is meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that
the device control library for the queue is SYS$LIBRARY:name.TLB, where
name is a valid RMS file name. The buffer must specify the
OpenVMS RMS file name.
The SJC$_NO_LIBRARY_SPECIFICATION item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that the device control library is SYS$LIBRARY:SYSDEVCTL.TLB.
It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_LOG_DELETE
SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE
The SJC$_LOG_DELETE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the log file produced for a batch job is to be deleted. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_DELETE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the log file produced for a batch job is not to be deleted.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for batch jobs. It
specifies the queue into which the log file produced for the batch job
is entered for printing. The buffer must specify the name of the queue.
By default, the log file is entered in queue SYS$PRINT.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the number of
translations allowed by the system has been performed. The maximum
length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces, tabs,
and null characters are ignored.
If your system uses multiple queue managers to run batch queues on a
separate queue manager from output queues, certain checks that would
otherwise be performed for the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE item code of the $SNDJBC
system service are not performed.
When batch and print queues are managed by the same queue manager, the
queue manager checks to ensure that the queue specified with the
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE is an output queue and that the user has access to the
output queue. These checks are not made if the batch queue specified by
the $SNDJBC service and the output queue specified by the
SJC$_LOG_QUEUE item code are managed by different queue managers. If
you explicitly specify an output queue for the log file when submitting
a batch job, be sure the queue you specify with the SJC$_LOG_QUEUE is
an output queue and not a batch queue. Also, be sure that you have
access to the printer queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
The SJC$_LOG_SPECIFICATION item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs. It specifies the file specification of
the log file produced for a batch job. The buffer must contain this
OpenVMS RMS file specification. Omitted fields in the file
specification are supplied from the default file specification
SYS$LOGIN:name.LOG, where name is the job name. By default a
log file is produced using this default file specification to generate
the log file name.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no log file should be produced for the batch job.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_LOG_SPOOL
SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL
The SJC$_LOG_SPOOL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the log file produced for a batch job is to be printed. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_LOG_SPOOL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the log file for a batch job is not to be printed.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_LOWERCASE
SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE
The SJC$_LOWERCASE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
a job can execute only on a device that has the LOWERCASE
device-dependent characteristic. It is meaningful only for jobs
submitted to output execution queues.
The SJC$_NO_LOWERCASE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that a job can execute whether or not the output device has the
LOWERCASE device-dependent characteristic. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_NEW_VERSION
Boolean item code. When used with the SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function
code, it specifies that a new (empty) version of the queue database is
to be created, whether or not the database files already exist.
This item code is required when initially creating and starting the
queuing system, but it should be used with caution thereafter.
Caution
If you specify this item code and a queue database already exists, the
new master and queue files of the queue database supersede existing
version of those files; however, the journal files of the queue
database are deleted. Thus, jobs and other information are lost.
When used with the SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING function code, the
SJC$_NEW_VERSION item code specifies that a new version of the system
accounting file is to be created, whether or not the file already
exists.
|
(Valid for SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING, SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function
codes)
SJC$_NEXT_JOB
Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for paused output execution
queues. It specifies that the current job should be aborted and that
printing should be resumed with the next job.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_NOTE
SJC$_NO_NOTE
The SJC$_NOTE item code is an input value item code. It is meaningful
for batch and output execution queues. It specifies a string to be
printed on the job flag and file flag pages. The buffer must specify
this string.
The SJC$_NO_NOTE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that no
string is to be printed on the job flag and file flag pages. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_NOTIFY
SJC$_NO_NOTIFY
The SJC$_NOTIFY item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a
message is to be broadcast, at the time of job completion, to each
logged-in terminal, of the user who submitted the job.
The SJC$_NO_NOTIFY item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
no message is to be broadcast at the time of job completion. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_NO_RAD (Alpha only)
Boolean input item code. When the SJC$_NO_RAD code is specified in a
request, the RAD value for the queue or job is removed.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_OPEN_QUEUE
Boolean item code. It specifies that jobs can be entered in the queue.
To specify that jobs cannot be entered in the queue, use the
SJC$_CLOSE_QUEUE item code. By default, the queue is open.
Whether a queue is open or closed is independent of any other queue
states (such as paused, stalled, stopped).
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST
SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST
The SJC$_OPERATOR_REQUEST item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. The buffer must contain a
text string. This item code specifies that, when a job begins
execution, the execution queue is to be placed in the paused state and
the specified text string is to be included in a message to the queue
operator requesting service.
The SJC$_NO_OPERATOR_REQUEST item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no message is to be sent to the queue operator. It is
the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
Input value item code. It specifies the owner UIC of a queue. The
buffer must specify the longword UIC. By default, the owner UIC is
[1,4].
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_PAGE_HEADER
SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER
The SJC$_PAGE_HEADER item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output execution queues. It specifies that a page heading is
to be printed on each page of output.
The SJC$_NO_PAGE_HEADER item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that no page heading is to be printed. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES
The SJC$_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES item code is an input value item code. The
buffer must specify one or more text module names, with a comma
separating each name. This item code specifies that these modules are
to be extracted from the device control library and copied to the
printer before each page is printed.
The SJC$_NO_PAGE_SETUP_MODULES item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no device control modules are to be copied. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_DEFINE_FORM function code)
SJC$_PAGINATE
SJC$_NO_PAGINATE
The SJC$_PAGINATE item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output execution queues and jobs submitted to output execution
queues. It specifies that the symbiont should paginate the output by
inserting a form feed whenever output reaches the bottom margin of the
form. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_PAGINATE item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the symbiont should not paginate the output.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through SJC$_PARAMETER_8
SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS
The SJC$_PARAMETER_1 through SJC$_PARAMETER_8 item codes are input
value item codes; the last digit of the item code name is a number from
1 through 8. For each item code specified, the buffer must specify a
string of no more than 255 characters. For batch jobs, the string
becomes the value of the DCL symbol P1 through P8, respectively, within
the outermost command procedure.
For print jobs, the system makes the string available to the symbiont,
though the standard OpenVMS print symbiont does not use this
information. By default, each of the eight parameters specifies a null
string.
For function code SJC$_ALTER_JOB, if any SJC$_PARAMETER item is
specified, the value of each unspecified item is the null string.
The SJC$_NO_PARAMETERS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that none of the SJC$_PARAMETER items are to be passed in the batch or
print job. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_PASSALL
SJC$_NO_PASSALL
The SJC$_PASSALL item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for jobs submitted to output execution queues. It specifies that
the symbiont is to print the file in PASSALL mode.
The SJC$_NO_PASSALL item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the symbiont is not to print the file in PASSALL mode. It is the
default.
(Valid for SJC$_ADD_FILE, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_PRINTER
Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It
specifies that the queue being created is a printer queue. The
SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes are
mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the
default is SJC$_PRINTER.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_PRIORITY
Input value item code. The buffer must specify a longword value in the
range 0 through 255. This value specifies the scheduling priority of
the job in a queue relative to the scheduling priority of other jobs in
the same queue.
By default, the scheduling priority of the job is the value of the
system parameter DEFQUEPRI.
If you specify a value for SJC$_PRIORITY that is greater than the
system parameter MAXQUEPRI and you do not have either ALTPRI or OPER
privilege, the system uses the greater of the following two values:
DEFQUEPRI or MAXQUEPRI. If you have either ALTPRI or OPER privilege,
the system uses any value you specify for SJC$_PRIORITY, even if it is
included in the range between MAXQUEPRI + 1 and 255.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_PROCESSOR
SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR
The SJC$_PROCESSOR item code is an input value item code. The buffer
must specify a valid OpenVMS RMS file name.
When specified for an output execution queue, SJC$_PROCESSOR specifies
that the symbiont image to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where
name is the RMS file name contained in the buffer.
When specified for a generic output queue, SJC$_PROCESSOR specifies
that the generic queue can place jobs only in server queues that are
executing the symbiont image SYS$SYSTEM:name.EXE, where name
is the RMS file name contained in the buffer.
The SJC$_NO_PROCESSOR item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the symbiont image to be executed is SYS$SYSTEM:PRTSMB.EXE. It is
the default.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_PROTECTION
Input value item code. It specifies the protection of a queue.
The buffer must specify a longword in the format shown in the following
diagram:
Bits 0 through 15 specify the protection value: the four types of
access (read, submit, manage, delete) to be granted to the four
categories of user (System, Owner, Group, World). Set bits deny access
and clear bits allow access.
Bits 16 through 31 specify the protection enable mask: they identify
which part of the protection value (bits 0 through 15) is to be applied
to queue protection. If all bits are set in the enable mask, it means
that all of the protection values are to be applied. A value other than
--1 in the protection enable mask means that only those bits set will
affect the corresponding bits in the protection value. When a bit in
the protection enable mask is clear, the corresponding bit in the
existing queue protection value is unchanged.
By default, the queue protection is (S:M,O:D,G:R,W:S).
Note that on VAX systems you can assign ACLs to queues using the
$SET_SECURITY system service.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE
Input value item code. It specifies the queue to which the operation is
directed. The buffer must specify the name of the queue.
The string can contain uppercase or lowercase characters (lowercase are
converted to uppercase), numeric characters, dollar signs ($), and
underscores (_). If the string is a logical name, SYS$SNDJBC translates
it iteratively until the equivalence string is found or the maximum
number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. The
maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters; spaces,
tabs, and null characters are ignored.
(The following function codes are valid for SJC$_QUEUE item code:
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DELETE_JOB
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
SJC$_START_QUEUE
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB)
SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION
The SJC$_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION item code is an input value item code. It
provides operator-supplied information about the queue. The buffer must
specify a string of no more than 255 characters.
The SJC$_NO_QUEUE_DESCRIPTION item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that no description is associated with the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY
Input value item code. SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY specifies the directory
location that contains the system queue and journal files for the queue
manager. The queue file has a file type of QMAN$QUEUES and contains
queue definitions. The journal file has a file type of .QMAN$JOURNAL
and contains job and other information allowing the queue manager to
return to its last known state should a system be stopped unexpectedly.
These files must reside together in the same directory.
The default location of the queue and journal files is
SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE]. The optional use of SJC$_QUEUE_DIRECTORY is for
specifying an alternate location for the queue and journal files. The
specification must include at least the device and directory name;
wildcard characters are not allowed in the directory specification. The
directory specified must be available to all nodes that can run the
queue manager. If the directory specification is a concealed logical
name, it must be defined identically on all nodes in the cluster.
The location of the queue and journal files is stored in the master
file of the queue database. You do not have to respecify the directory
location with subsequent use of SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER.
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NAME
Input value item code. It uniquely identifies the queue manager process
that manages some segment of the queues and jobs in the system. If it
is not present, a default name of SYS$QUEUE_MANAGER is used.
The maximum length of the final character string is 31 characters. As
with queue names, this can be a logical and will be resolved by the
system. Once resolved, the name provided will serve as the file name
for the queue and journal files, the process name, and the user name
for the active process. Only the first 15 and 12 characters of the name
are used for the process and user names, respectively.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER,
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART,
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER, SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE,
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER function codes)
SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES
Input value item code. In an OpenVMS Cluster, SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES
specifies a list of nodes that can run the queue manager. It also gives
the explicit order of failover if the node running the queue manager
exits the cluster. The specified node list is stored in the queue
database.
The default value for the node list is an asterisk (*); it specifies
that all nodes in the cluster are eligible to run the queue manager.
The asterisk can also be specified as an element of the list. For
example, a list can be specified as nodes A, B, C, *. If the node on
which the queue manager is running leaves the cluster, the queue
manager automatically fails over to any available node in the cluster;
that is, if nodes A, B, and C are unavailable, then the queue manager
can run on any other node. When establishing the node list, there is no
validation of the individual nodes. If, for example, a node name is
misspelled, there is no error status returned.
Anytime the SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code is used, the job
controller checks the queue database to see if the node list is other
than the default (*). If the node list is other than the default and
the queue manager is running on a node other than the first available
node of those specified, then the queue manager process is moved from
its current node and restarted on the first available preferred node.
When a current call includes the SJC$_QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code,
the job controller also updates the node list stored in the database.
Despite this transition, queues on the running nodes are not stopped,
and all requests to the queuing system complete as expected.
Note that because the specified node list is saved in the database, it
is used every time the SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code is used,
unless the node list has been changed by a more recent call to $SNDJBC
with the SJC_$QUEUE_MANAGER_NODES item code.
For more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER function code)
SJC$_RAD (Alpha only)
Input value item code used to specify a RAD number on which to create a
batch process. The item accepts a 32-bit integer value as input. The
input is validated to be within the range of 0 to SYI$_RAD_MAX_RADS.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE)
SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING
SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING
The SJC$_RECORD_BLOCKING item code is a Boolean item code. It is
meaningful only for output execution queues. It specifies that the
symbiont can merge the output records it sends to the output device
into a single I/O request. For the standard OpenVMS print symbiont,
record blocking can have a significant performance advantage over
single-record mode. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_RECORD_BLOCKING item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that the symbiont must send each record in a separate I/O
request to the output device.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_RELATIVE_PAGE
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution
queues. The buffer must specify a signed longword integer. This item
code specifies that printing should be resumed after spacing forward
(if the buffer value is positive) or backward (if the buffer value is
negative) the specified number of pages.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_REQUEUE
Boolean item code. It specifies that a job is to be requeued. By
default, the job is deleted.
(Valid for SJC$_ABORT_JOB function code)
SJC$_RESTART
SJC$_NO_RESTART
The SJC$_RESTART item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that a
job can restart after a system failure or can be requeued during
execution. It is the default for print jobs.
The SJC$_NO_RESTART item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
a job cannot restart after a system failure or after a requeue
operation. It is the default for batch jobs.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function
codes)
SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS
SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS
SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS
The SJC$_RETAIN_ALL_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that jobs are to be retained in the queue with a completion status
after they have been executed.
The SJC$_RETAIN_ERROR_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It
specifies that jobs are to be retained only if the job completed
unsuccessfully (the job's completion status has the low bit clear).
The SJC$_NO_RETAIN_JOBS item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that jobs are not to be retained in the queue after they have
completed. It is the default.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME
Input value item code. It specifies the name of the node for which the
command is to execute. The buffer must specify a 1- to 6-character
string that matches the value of the system parameter SCSNODE in effect
on the target node.
When used with the function codes of SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE,
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART, and SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART, this item code
requests a function on a node other than the node from which the
$SNDJBC request is sent.
SJC$_SCSNODE_NAME is meaningful only for execution queues in a cluster
environment. By default, the queue executes on the node from which the
queue is first started. For an output execution queue, you use the
SJC$_DEVICE_NAME item code to specify the name of the device managed by
the queue.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART,
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART, SJC$_START_QUEUE, SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
function codes)
SJC$_SEARCH_STRING
Input value item code. It is meaningful only for output execution
queues. The buffer must specify a string of no more than 63 characters.
This item code specifies that printing is to resume at the page
containing the first occurrence of the specified string. The search for
the string proceeds in the forward direction.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_SERVER
Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It
specifies that the queue being created is a server queue. The term
server indicates that a user-modified or user-written symbiont process
is controlling an output execution queue, or a generic queue has server
execution queues as its targets.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes
are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the
default is SJC$_PRINTER.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_SWAP
SJC$_NO_SWAP
The SJC$_SWAP item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful only
for batch execution queues. It specifies that jobs initiated from a
queue can be swapped. It is the default.
The SJC$_NO_SWAP item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
jobs in this queue cannot be swapped.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE
function codes)
SJC$_TERMINAL
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL
The SJC$_TERMINAL item code is a Boolean item code. It is meaningful
only for output queues. It specifies that the queue being created is a
terminal queue.
The SJC$_BATCH, SJC$_PRINTER, SJC$_SERVER, and SJC$_TERMINAL item codes
are mutually exclusive. If none of these item codes are specified, the
default is SJC$_PRINTER.
The SJC$_NO_TERMINAL item code is a Boolean item code. It designates
the queue type as printer rather than terminal. It is the default.
For the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code, SJC$_TERMINAL and
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL are supported for compatibility with VAX VMS Version
4.n, but might not be supported in the future. For SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE,
SJC$_NO_TERMINAL is supported for compatibility with VAX VMS Version
4.n, and might not be supported in the future.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_TOP_OF_FILE
Boolean item code. It is meaningful only for output queues. It
specifies that printing is to be resumed at the beginning of the file.
(Valid for SJC$_START_QUEUE function code)
SJC$_UIC
Input value item code. This value specifies the 4-byte UIC of the user
on behalf of whom the request is made. By default, the UIC is taken
from the requesting process.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_USERNAME
Input value item code. It specifies the user name of the user on behalf
of whom the request is made. The buffer must specify a string from 1 to
12 characters. By default, the user name is taken from the requesting
process.
You need CMKRNL privilege to use this item code.
(Valid for SJC$_CREATE_JOB, SJC$_ENTER_FILE function codes)
SJC$_WSDEFAULT
SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT
The SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies, in
pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems), the default
working set size for batch jobs or jobs initiated from a batch queue,
or the default working set size of a symbiont process connected to an
output queue. A symbiont process can control several output queues;
however, the default working set size of the symbiont process is
established by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer
must contain a longword integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSDEFAULT item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the system is to determine the working set default. It is the
default.
For batch jobs, the default working set size, working set quota, and
working set extent (maximum size) are included in each user record in
the system user authorization file (UAF). You can specify values for
these items for individual jobs or for all jobs in a given queue, or
for both. Table SYS-55 shows the action taken when you specify a value
for SJC$_WSDEFAULT.
Table SYS-55 Working Set Decision Table
Value Specified
for Job? |
Value Specified
for Queue? |
Action Taken |
|
No
|
No
|
Use UAF value
|
|
No
|
Yes
|
Use value for queue
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Use lower of the two
|
|
Yes
|
No
|
Compare specified value with UAF value; use lower
|
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_WSEXTENT
SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT
The SJC$_WSEXTENT item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies, in
pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems), the working set
extent for batch jobs or jobs initiated from a batch queue, or the
working set extent of a symbiont process connected to an output queue.
A symbiont process can control several output queues; however, the
working set extent of the symbiont process is established by the first
queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a longword
integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSEXTENT item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies
that the system determine the working set extent. It is the default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for
SJC$_WSEXTENT for a batch job or batch queue, refer to the description
of the SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code and to Table SYS-55.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
SJC$_WSQUOTA
SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA
The SJC$_WSQUOTA item code is an input value item code. It is
meaningful only for batch jobs and execution queues. It specifies, in
pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems), the working set
quota for batch jobs or default WSQUOTA for jobs initiated from a batch
queue, or the working set quota of a symbiont process connected to an
output queue. A symbiont process can control several output queues;
however, the working set quota of the symbiont process is established
by the first queue to which it is connected. The buffer must contain a
longword integer value in the range 1 through 65,535.
The SJC$_NO_WSQUOTA item code is a Boolean item code. It specifies that
the system is to determine the working set quota. It is the default.
For information about the action taken when you specify a value for
SJC$_WSQUOTA for a batch job or batch queue, refer to the description
of the SJC$_WSDEFAULT item code and to Table SYS-55.
(Valid for SJC$_ALTER_JOB, SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE, SJC$_CREATE_JOB,
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE, SJC$_ENTER_FILE, SJC$_START_QUEUE function codes)
Description
The Send to Job Controller service creates, stops, and manages queues
and the batch and print jobs in those queues. The $SNDJBC and $GETQUI
(Get Queue Information) services together provide the user interface to
the queue manager and job controller processes. See the description of
the $GETQUI service for a discussion of queues and jobs initiated from
those queues.
$SNDJBC completes asynchronously; that is, it returns to the caller
after queuing the request, without waiting for the operation to
complete.
To synchronize the completion of most operations, you use the Send to
Job Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service. The $SNDJBCW service is
identical to $SNDJBC in every way except that $SNDJBCW returns to the
caller after the operation completes.
Types of Queues
The VMS batch and print queuing system supports several types of
queues, which aid in the processing of batch and print jobs. The
different types of queues can be divided into three major categories
according to the way the system processes the jobs assigned to the
queue. The three types of queues are execution, generic, and logical.
Execution queues schedule jobs for execution; generic and logical
queues transfer jobs to execution queues. Within these major
classifications, queue type is further defined by the kinds of job the
queues can accept for processing. Some types of execution and generic
queues accept batch jobs; other types accept print jobs. Logical queues
are restricted to print jobs.
You create a queue by making a call to $SNDJBC specifying the
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code. Item codes that you optionally specify
in the call determine the type of queue you create. The following list
describes the various types of execution, generic, and logical queues
and indicates which item codes you need to specify to create them:
- Execution queue. An execution queue schedules jobs
for processing. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, jobs are processed
on the node that manages the execution queue. There are two types of
execution queues:
- Batch execution queue. A batch execution queue can
schedule only batch jobs for execution. A batch job executes as a
detached process that sequentially runs one or more command procedures;
you define the list of command procedures as part of the initial job
description. You create a batch execution queue by specifying the
SJC$_BATCH item code in the call to the $SNDJBC service.
- Output execution queue. An output execution queue
schedules print jobs for processing by an independent symbiont process
associated with the queue. The job controller sends the symbiont a list
of files to process; you define this list of files as part of the
initial job description. As the symbiont processes each file, it
produces output for the device, such as a printer or terminal, that it
controls.
The standard print symbiont image provided by the
operating system is designed to print files on hardcopy devices.
User-modified or user-written symbionts also can be designed for this
or any other file processing activity managed by the batch and print
queuing system. The symbiont image that executes jobs from an output
queue is specified by the SJC$_PROCESSOR item code. If you omit this
item code, the standard print symbiont image, PRTSMB, is associated
with the queue.
There are three types of output execution queue:
- Printer execution queue. This type of queue
typically uses the standard print symbiont to direct output to a line
printer. You can specify a user-provided symbiont in the SJC$_PROCESSOR
item code. You create a printer execution queue by specifying the
SJC$_PRINTER item code when you create the output execution queue. A
printer execution queue is the default type of output execution queue.
- Terminal execution queue. This type of queue
typically uses the standard print symbiont to direct output to a
terminal printer. You can specify a user-provided symbiont in the
SJC$_PROCESSOR item code. You create a terminal execution queue by
specifying the SJC$_TERMINAL item code when you create the output
execution queue.
- Server execution queue. This type of queue uses
the user-modified or user-written symbiont you specify in the
SJC$_PROCESSOR item code to process the files that belong to jobs in
the queue. You create a server execution queue by specifying the
SJC$_SERVER item code when you create the output execution queue.
When you create an output execution queue, you can initially mark
it as either a printer, terminal, or server execution queue. However,
when the queue is started, the symbiont process associated with the
queue can change the queue type from the type designated at its
creation to a printer, terminal, or server execution queue, as follows:
- When an output execution queue associated with the standard print
symbiont is started, the symbiont determines whether it is controlling
a printer or terminal. It communicates this information to the job
controller. If necessary, the job controller then changes the type
designation of the output execution queue.
- When an output execution queue associated with a user-modified or
user-written symbiont is started, the symbiont has the option of
identifying the queue to the job controller as a server queue. If the
user-written or user-modified symbiont does not notify the job
controller that it wants to change the queue type designation, the
output execution queue retains the queue type designation it received
when it was created.
- Generic queue. A generic queue holds a job until
an appropriate execution queue becomes available to initiate the job;
the job controller then requeues the job to the available execution
queue. In a cluster environment, a generic queue can direct jobs to
execution queues that are located on other nodes in the cluster.
You create a generic queue by specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE
item code in the call to the $SNDJBC service. You designate each
execution queue to which the generic queue can direct jobs by
specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code. Because a generic queue
can direct jobs to more than one execution queue, you can specify the
SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code up to 124 times in a single call to
$SNDJBC to define a complete set of execution queues for any generic
queue. If you do not specify the SJC$_GENERIC_TARGET item code, the
generic queue directs jobs to any execution queue that is the same type
of queue as the generic queue; that is, a generic batch queue will
direct a job to any available batch execution queue, and so on. There
is one exception: a generic queue will not direct work to any execution
queue that was created in a call to $SNDJBC that specified the
SJC$_NO_GENERIC_SELECTION item code.
There are two types of generic
queue:
- Generic batch queue. A generic batch queue can
direct jobs only to batch execution queues. You create a generic batch
queue by specifying both the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE and SJC$_BATCH item
codes in the call to the $SNDJBC service.
- Generic output queue. A generic output queue can
direct jobs to any of the three types of output execution queue:
printer, terminal, or server. Creating a generic output queue that
directs jobs to any combination of the three types of output execution
queue is possible. Typically, however, when you create a generic output
queue, you specify a list of type-specific target queues. This way, the
generic output queue directs jobs to a single type of output execution
queue. Thus, you can control whether the jobs submitted to the generic
output execution queue are output on a line printer or a terminal
printer or are sent to a server symbiont for processing. You create a
generic output queue by specifying the SJC$_GENERIC_QUEUE item code in
the call to the $SNDJBC service.
- Logical queue. A logical queue performs the same
function as a generic output queue, except that a logical queue can
direct jobs to only a single printer, terminal, or server execution
queue. A logical queue is only an output queue that has been assigned
to transfer its jobs to one execution queue.
To change an output
queue into a logical queue, you make a call to the $SNDJBC service
while the output queue is in a stopped state. The call must specify the
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE function code and the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item
code. You use the SJC$_DESTINATION_QUEUE item code to specify the
execution queue to which the logical queue should direct jobs. When the
logical queue is started, it automatically requeues its jobs to the
specified execution queue as that execution queue becomes available.
You can change a logical queue back to its original output queue
definition by specifying the SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE function code in a
subsequent call to the $SNDJBC service.
Queue Protection
This section describes UIC-based protection checking that is performed
by the $SNDJBC service to control access to queues.
As an alternative to this form of protection checking, you can
associate ACLs with queues using the appropriate security services. See
the $GET_SECURITY and $SET_SECURITY system services for more
information.
There are two aspects to UIC-based queue protection:
- When you create a queue, you assign it a UIC by using the
SJC$_OWNER_UIC item code. If you do not specify this item code, the
queue is given the default UIC [1,4].
- You can assign a queue a protection mask by specifying the
SJC$_PROTECTION item code. This protection mask specifies read, submit,
manage, and delete access for the four categories of user: Owner,
Group, World, and System.
In addition, certain queue operations require the caller of $SNDJBC to
have certain privileges. The function codes that require privileges are
listed in the Privileges and Restrictions section.
When a job is submitted to a queue, it is assigned a UIC that is the
same as the UIC of the process submitting the job, unless the SJC$_UIC
item code is specified to supply a different UIC.
For each requested operation, the $SNDJBC service checks the UIC and
privileges of the requesting process against the UIC of the queue,
protection specified for the queue, and the privileges, if any,
required for the operation. This checking is performed in a way similar
to the way that the file system checks access to a file by comparing
the owner UIC and protection of the file with the UIC and privileges of
the requester.
Operations that apply to jobs are checked against read and delete
protection specified for the queue in which the job is entered and the
owner UIC of the job. In general, read access to a job allows you to
determine that the job exists; delete access to a job allows you to
affect the job.
Operations that apply to queues are checked against the submit and
manage protection specified for the queue and the owner UIC of the
queue. In general, submit access to a queue allows you to submit jobs
to the queue; manage access to a queue allows you to act as an operator
for the queue, including the ability to affect jobs in the queue, to
affect accounting, and to alter queues. OPER privilege grants manage
access to all queues.
Privileges and Restrictions
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have both OPER
and SYSNAM privilege:
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE_MANAGER
SJC$_START_QUEUE_MANAGER
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE_MANAGER
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege:
SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE
SJC$_DEFINE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_DEFINE_FORM
SJC$_DELETE_CHARACTERISTIC
SJC$_DELETE_FORM
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING
SJC$_STOP_ACCOUNTING
To specify the following function code, the caller can have OPER
privilege or manage access:
SJC$_DELETE_QUEUE
To specify the following function code, the caller must have OPER
privilege, execute access to the queue containing the specified job, or
read access to the specified job:
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege, manage access to the specified queue, or submit access to
the specified queue:
SJC$_ADD_FILE
SJC$_CLOSE_DELETE
SJC$_CLOSE_JOB
SJC$_CREATE_JOB
SJC$_ENTER_FILE
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege or manage access to the specified queue or queues:
SJC$_ALTER_QUEUE
SJC$_ASSIGN_QUEUE
SJC$_DEASSIGN_QUEUE
SJC$_DISABLE_AUTOSTART
SJC$_ENABLE_AUTOSTART
SJC$_MERGE_QUEUE
SJC$_PAUSE_QUEUE
SJC$_RESET_QUEUE
SJC$_START_QUEUE
SJC$_STOP_ALL_QUEUES_ON_NODE
SJC$_STOP_QUEUE
To specify the following function codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege, manage access to the queue containing the specified job, or
delete access to the specified job:
SJC$_ABORT_JOB
SJC$_ALTER_JOB
SJC$_DELETE_JOB
To specify the following function codes, no privilege is required:
SJC$_BATCH_CHECKPOINT
SJC$_WRITE_ACCOUNTING
To specify a scheduling priority (using the SJC$_PRIORITY item code)
higher than the value of the system parameter MAXQUEPRI, the caller
needs OPER or ALTPRI privilege.
To specify the following item codes, the caller must have OPER
privilege:
SJC$_OWNER_UIC
SJC$_PROTECTION
To specify the following item codes, the caller must have CMKRNL
privilege:
SJC$_ACCOUNT_NAME
SJC$_UIC
SJC$_USERNAME
Required Quota
To specify the astadr argument, the process must have
sufficient ASTLM quota.
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the
return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written
by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The function code is invalid; the item descriptor contains an invalid
buffer length value; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the
reserved parameter has a nonzero value.
|
|
SS$_DEVOFFLINE
|
The job controller process is not running.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
You specified the
astadr argument, and the process has exceeded its
ASTLM quota.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The
efn argument specifies an illegal event flag number.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient space exists for completing the request.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
Queue form or characteristic name is not a valid logical name.
|
|
SS$_MBFULL
|
The job controller mailbox is full.
|
|
SS$_MBTOOSML
|
The mailbox message is too large for the job controller mailbox.
|
|
SS$_SHELVED
|
The job controller attempted to access a shelved file. The service does
not automatically unshelve files.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The
efn argument specifies an unassociated event flag
cluster.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block
|
JBC$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
JBC$_AUTONOTSTART
|
The queue is autostart active, but not started. You have tried to start
an autostart queue when none of its available nodes has autostart
enabled.
|
|
JBC$_BUFTOOSMALL
|
The request could not be completely satisfied due to limited buffer
size. The amount of information retrieved in response to the query
exceeds the amount of data the queue manager can return in response to
a single request.
|
|
JBC$_DELACCESS
|
The file protection of the specified file, which was entered with the
delete option, does not allow delete access to the caller.
|
|
JBC$_DUPCHARNAME
|
The command specified a duplicate characteristic name. Each
characteristic must have a unique name.
|
|
JBC$_DUPCHARNUM
|
The command specified a duplicate characteristic number. Each
characteristic must have a unique number.
|
|
JBC$_DUPFORM
|
The specified form number is invalid because it is already defined;
each form must have a unique form number.
|
|
JBC$_DUPFORMNAME
|
The command specified a duplicate form name. Each form must have a
unique name.
|
|
JBC$_EMPTYJOB
|
The open job cannot be closed because it contains no files.
|
|
JBC$_EXECUTING
|
The parameters of the specified job cannot be modified because the job
is currently executing.
|
|
JBC$_INCDSTQUE
|
The type of the specified destination queue is inconsistent with the
requested operation.
|
|
JBC$_INCFORMPAR
|
The specified length, width, and margin parameters are inconsistent;
the value of the difference between the top and bottom margin
parameters must be less than the form length, and the difference
between the left and right margin parameters must be less than the line
width.
|
|
JBC$_INCOMPLETE
|
The requested queue management operation cannot be executed because a
previously requested queue management operation has not yet completed.
|
|
JBC$_INCQUETYP
|
The type of the specified queue is inconsistent with the requested
operation.
|
|
JBC$_INTERNALERROR
|
An internal error caused loss of process status. A system error
prevented the queue manager from obtaining the completion status of a
process.
|
|
JBC$_INVCHANAM
|
A specified characteristic name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVDSTQUE
|
The destination queue name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVFORNAM
|
The form name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_INVFUNCOD
|
The specified function code is invalid.
|
|
JBC$_INVITMCOD
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVPARLEN
|
The length of a specified string is outside the valid range for that
item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVPARVAL
|
A parameter value specified for an item code is outside the valid range
for that item code.
|
|
JBC$_INVQUENAM
|
The queue name is not syntactically valid.
|
|
JBC$_ITMREMOVED
|
The meaningless items were removed from the request. One or more item
codes not meaningful to this command were specified. The command is
processed and the meaningless items are ignored.
|
|
JBC$_JOBNOTEXEC
|
The specified job is not executing.
|
|
JBC$_JOBQUEDIS
|
The request cannot be executed because the system job queue manager has
not been started.
|
|
JBC$_JOBQUEENA
|
The system job queue manager cannot be started because it is already
running.
|
|
JBC$_MISREQPAR
|
An item code that is required for the specified function code has not
been specified.
|
|
JBC$_NOAUTOSTART
|
The node does not have the autostart feature enabled.
|
|
JBC$_NODSTQUE
|
The specified destination queue does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOOPENJOB
|
The requesting process did not open a job with the SJC$_CREATE_JOB
function.
|
|
JBC$_NOPRIV
|
The queue protection denies access to the queue for the specified
operation.
|
|
JBC$_NOQUESPACE
|
The system job queue file was full and could not be extended.
|
|
JBC$_NORESTART
|
The specified job cannot be requeued because it was not defined as
restartable.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHCHAR
|
The specified characteristic does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHENT
|
There is no job with the specified entry number.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHFORM
|
The specified form does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHJOB
|
The specified job does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHMGR
|
The specified queue manager does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The specified node does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOSUCHQUE
|
The specified queue does not exist.
|
|
JBC$_NOTALLREQUE
|
Not all jobs in the source queue could be requeued to the target queue.
Some of the jobs specified were not suitable for execution on the
specified target queue.
|
|
JBC$_NOTASSIGN
|
The specified queue cannot be deassigned because it is not assigned.
|
|
JBC$_NOTMEANINGFUL
|
The specified item code is no longer meaningful.
|
|
JBC$_NOTSUPPORTED
|
The specified item code or function code is not supported.
|
|
JBC$_PRIOSMALL
|
The scheduling priority has a smaller value than requested. A user
without ALTPRI or OPER privilege specified a value for a job's priority
that exceeded the queue's maximum priority for nonprivileged jobs. The
job is entered in the queue, but its scheduling priority is lower than
the value requested by the user.
|
|
JBC$_QMANNOTSTARTED
|
The queue manager could not be started.
|
|
JBC$_QUEDISABLED
|
The disabled queue cannot be modified, nor can jobs be submitted to it.
|
|
JBC$_QUENOTMOD
|
The modifications were not made because the queue was not stopped.
|
|
JBC$_QUENOTSTOP
|
The specified queue cannot be deleted because it is not in a stopped
state.
|
|
JBC$_REFERENCED
|
The specified queue cannot be deleted because of existing references by
other queues or jobs.
|
|
JBC$_STARTED
|
The specified queue cannot be started because it is already running.
|
|
JBC$_STKNOTCHANGE
|
The stock associated with a form cannot be changed.
|
|
JBC$_TOOMUCHINFO
|
The size of the data in request exceeds system constraints. The amount
of data specified for a record within the queue manager's database is
too large.
|
When you use the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code, the return value
is the exit status of the specified job.
When you start a symbiont queue with the SJC$_START_QUEUE function code
or the SJC$_CREATE_QUEUE function code with the SJC$_CREATE_START item
code, any error encountered by the symbiont process will be returned in
the IOSB.
Examples
| #1 |
$ vfyold = f$verify(1)
$ create sys$scratch:accounting.c
#include <efndef.h>
#include <lib$routines.h>
#include <sjcdef.h>
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stsdef.h>
struct ItemList3
{
short int ItemLength;
short int ItemCode;
void *ItemBuffer;
void *ItemRetLen;
};
#define MAXITMLST 3
main()
{
int i;
struct ItemList3 JbcIL[MAXITMLST];
unsigned short int IOSB[4];
int RetStat, JbcMask, JbcFunc;
/* To start accounting: */
JbcFunc = SJC$_START_ACCOUNTING;
/* Specify image and interactive */
JbcMask = SJC$M_ACCT_IMAGE | SJC$M_ACCT_INTERACTIVE;
i = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemLength = sizeof( JbcMask );
JbcIL[i].ItemCode = SJC$_ACCOUNTING_TYPES;
JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = (void *) &JbcMask;
JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL;
JbcIL[i].ItemLength = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemCode = 0;
JbcIL[i].ItemBuffer = NULL;
JbcIL[i++].ItemRetLen = NULL;
RetStat = sys$sndjbcw(EFN$C_ENF,JbcFunc,0, JbcIL,IOSB,0,0);
if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( RetStat ))
lib$signal( RetStat );
if (!$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS( IOSB[0] ))
lib$signal( IOSB[0] );
return SS$_NORMAL;
}
$ cc/decc/prefix=all sys$scratch:accounting.c/object=sys$scratch:
$ link/executable=sys$scratch:accounting.exe sys$scratch:accounting
$ show accounting
$ prvold = f$setprv("OPER")
$ run sys$scratch:accounting
$ show accounting
$ priv = f$setprv(prvold)
$ vfyold = f$verify(vfyold)
$ exit
|
This C program demonstrates an $SNDJBCW call.
| #2 |
! Declare system service related symbols
INTEGER*4 SYS$SNDJBCW,
2 STATUS
INCLUDE '($SJCDEF)'
! Define item list structure
STRUCTURE /ITMLST/
UNION
MAP
INTEGER*2 BUFLEN, ITMCOD
INTEGER*4 BUFADR, RETADR
END MAP
MAP
INTEGER*4 END_LIST
END MAP
END UNION
END STRUCTURE
! Define I/O status block structure
STRUCTURE /IOSBLK/
INTEGER*4 STS, ZEROED
END STRUCTURE
! Declare $SNDJBCW item list and I/O status block
RECORD /ITMLST/ SUBMIT_LIST(6)
RECORD /IOSBLK/ IOSB
! Declare variables used in $SNDJBCW item list
CHARACTER*9 QUEUE /'SYS$BATCH'/
CHARACTER*23 FILE_SPECIFICATION /'$DISK1:[COMMON]TEST.COM'/
CHARACTER*12 USERNAME /'PROJ3036 '/
INTEGER*4 ENTRY_NUMBER
! Initialize item list for the enter file operation
SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFLEN = 9
SUBMIT_LIST(1).ITMCOD = SJC$_QUEUE
SUBMIT_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(QUEUE)
SUBMIT_LIST(1).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 23
SUBMIT_LIST(2).ITMCOD = SJC$_FILE_SPECIFICATION
SUBMIT_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(FILE_SPECIFICATION)
SUBMIT_LIST(2).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 12
SUBMIT_LIST(3).ITMCOD = SJC$_USERNAME
SUBMIT_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(USERNAME)
SUBMIT_LIST(3).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFLEN = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).ITMCOD = SJC$_NO_LOG_SPECIFICATION
SUBMIT_LIST(4).BUFADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(4).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFLEN = 4
SUBMIT_LIST(5).ITMCOD = SJC$_ENTRY_NUMBER_OUTPUT
SUBMIT_LIST(5).BUFADR = %LOC(ENTRY_NUMBER)
SUBMIT_LIST(5).RETADR = 0
SUBMIT_LIST(6).END_LIST = 0
! Call $SNDJBCW service to submit the batch job
STATUS = SYS$SNDJBCW (,
2 %VAL(SJC$_ENTER_FILE),,
2 SUBMIT_LIST,
2 IOSB,,)
IF (STATUS) STATUS = IOSB.STS
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS))
END
|
This Fortran program demonstrates the use of the $SNDJBCW service to
submit a batch job that is to execute on behalf of another user. No log
file is produced for the batch job. This program saves the job's entry
number. You need CMKRNL privilege to run this program.
$SNDJBCW
The Send to Job Controller and Wait and $GETQUI services together
provide the user interface to the Job Controller (JBC) facility. The
$SNDJBCW service allows you to create, stop, and manage queues and the
jobs in those queues. Queues can be generic, batch, execution, or
output queues. Jobs can be batch or print jobs.
The $SNDJBCW service queues a request to the job controller. For most
operations, $SNDJBCW completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller after the operation completes; however, if the requested
operation is a pause queue, stop queue, or abort job operation,
$SNDJBCW returns to the caller after queuing the request. There is no
way to synchronize completion of these operations. Also, $SNDJBCW does
not wait for a job to complete before it returns to the caller. To
synchronize completion of a job, the caller must specify the
SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB function code.
The $SNDJBCW service is identical to the Send to Job Controller
($SNDJBC) service except that $SNDJBC completes asynchronously; the
$SNDJBC service returns to the caller immediately after queuing the
request, without waiting for the operation to complete.
For additional information about $SNDJBCW, refer to the documentation
of $SNDJBC.
The $SNDJBC and $SNDJBCW services supersede the Send Message to
Symbiont Manager ($SNDSMB) and Send Message to Accounting Manager
($SNDACC) services. You should write new programs using $SNDJBC or
$SNDJBCW, instead of $SNDSMB or $SNDACC. You should convert old
programs using $SNDSMB or $SNDACC to use $SNDJBC or $SNDJBCW, as
convenient.
Format
SYS$SNDJBCW [efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$sndjbcw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned
int nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$SNDOPR
Performs the following functions:
- Sends a user request to operator terminals
- Sends a user cancellation request to operator terminals
- Sends an operator reply to a user terminal
- Enables an operator terminal
- Displays the status of an operator terminal
- Initializes the operator log file
Format
SYS$SNDOPR msgbuf ,[chan]
C Prototype
int sys$sndopr (void *msgbuf, unsigned short int chan);
Arguments
msgbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
User buffer specifying the operation to be performed and the
information needed to perform that operation. The
msgbuf argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the buffer.
The format and contents of the buffer vary with the requested
operation; however, the first byte in any buffer is the request code,
which specifies the operation to be performed. The $OPCMSG macro
defines the symbolic names for these request codes.
The following table shows each operation that $SNDOPR performs and the
request code that specifies that operation:
| Request Code |
Corresponding Operation |
|
OPC$_RQ_CANCEL
|
Sends a user cancellation request to specified operator terminals. You
use this request code to notify one or more operators that a previous
request is to be canceled. To specify OPC$_RQ_CANCEL, you must also
specify the
chan argument.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_LOGI
|
Initializes the operator log file.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_REPLY
|
Sends an operator reply to a user who has made a request. Operators use
this request code to report the status of a user request. The format of
the message buffer for this request is the format of the reply found in
the user's mailbox after the call to $SNDOPR completes. All functions
of $SNDOPR that deliver a reply to a mailbox do so in the format
described for this request code.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_RQST
|
Sends a user request to operator terminals. This request code is used
to make an operator request. If you specify a reply to the request (by
using the
chan argument), the operator request is kept active
until the operator responds.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_STATUS
|
Reports the status of an operator terminal. Operators use this request
to display the operator classes for which the specified terminal is
enabled and a list of outstanding requests.
|
|
OPC$_RQ_TERME
|
Enables an operator terminal. You use this request to enable a
specified terminal to receive operator messages.
|
The following diagrams depict the message buffer for each of these
request codes. Each field within a diagram has a symbolic name, which
serves to identify the field; in other words, these names specify
offsets into the message buffer. The list following each diagram shows
each field name and what its contents can or should be. The $OPCDEF
macro defines the field names, as well as any other symbolic name that
can be specified as the contents of a field.
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_RQST
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_RQST.
|
|
OPC$Z_MS_TARGET_CLASSES
|
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which
operator terminal types are to receive the request. The $OPCDEF macro
defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types. You construct
the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names in a logical OR
operation. Following is the symbolic name of each operator terminal
type:
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS
|
Card device operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL
|
Central operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER
|
OpenVMS Cluster operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE
|
Device status information
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS
|
Disk operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK
|
Network operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES
|
Tape operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT
|
Printer operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY
|
Security operator
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1
through
OPC$M_NM_OPER12
|
System-manager-defined operator functions
|
|
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID
|
This longword field contains a user-supplied longword message code.
|
|
OPC$L_MS_TEXT
|
This variable-length field contains an ASCII string specifying text to
be sent to the specified operator terminals. $SNDOPR uses the buffer
size of the device to which the message is being sent.
|
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_CANCEL
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_CANCEL.
|
|
OPC$Z_MS_TARGET_CLASSES
|
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which
operator terminal types are to receive the cancellation request. The
$OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types.
You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names
in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each
operator terminal type:
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS
|
Card device operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL
|
Central operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY
|
Security operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER
|
OpenVMS Cluster operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE
|
Device status information
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS
|
Disk operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK
|
Network operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES
|
Tape operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT
|
Printer operator
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1
through
OPC$M_NM_OPER12
|
System-manager-defined operator functions
|
|
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID
|
This longword field contains a user-supplied longword message code.
|
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_REPLY
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_REPLY.
|
|
Reserved
|
This 1-byte field is reserved for future use.
|
|
OPC$W_MS_STATUS
|
This 2-byte field contains the low-order word of the longword condition
value that $SNDOPR returns in the mailbox specified by the
chan argument. You can find a list of these longword
condition values under Condition Values Returned in the Mailbox. To
test the completion status, you need to extract the low-order word from
the longword condition value and compare it to the contents of the
OPC$W_MS_STATUS field.
|
|
OPC$L_MS_RPLYID
|
This 4-byte field contains a user-supplied message code.
|
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT
|
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the terminal to which the
operator reply is to be sent. To obtain the unit number of the
terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item
code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device
name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail
end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is,
starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic
character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character
constitute the unit number.
After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in
the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the
following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME.
|
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME
|
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying
the device name of the terminal that is to receive the operator reply.
The maximum total length of the string is 14 bytes. See the preceding
field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device
name.
|
|
OPC$L_MS_OTEXT
|
This variable-length field contains an ASCII string specifying
operator-written text to be sent to the user terminal. The length of
the string must be in the range 0 to 255 bytes. This field is optional.
|
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_TERME
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_TERME.
|
|
OPC$Z_MS_ENAB_TERMINALS
|
This 3-byte field contains a user-supplied value. The value 0 indicates
that the specified terminal is to be disabled for the specified
operator classes. Any nonzero value indicates that the specified
terminal is to be enabled for the specified operator classes.
|
|
OPC$B_MS_MASK
|
This 4-byte field contains a 4-byte bit vector that specifies which
operator terminal types are to be enabled or disabled for the specified
terminal. The $OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator
terminal types. You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired
symbolic names in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic
name of each operator terminal type:
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS
|
Card device operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL
|
Central operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY
|
Security operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER
|
OpenVMS Cluster operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE
|
Device status information
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS
|
Disk operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK
|
Network operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES
|
Tape operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT
|
Printer operator
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1
through
OPC$M_NM_OPER12
|
System-manager-defined operator functions
|
|
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT
|
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal to
be enabled or disabled for the specified operator terminal types. To
obtain the unit number of the terminal, you can call $GETDVI,
specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item code. The information returned will
consist of the node name and device name as a padded string. Because
the unit number is found on the tail end of the string, you must parse
the string. One way to do this is, starting from the tail end, to
search for the first alphabetic character; the digits to the right of
this alphabetic character constitute the unit number.
After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in
the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the
following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME.
|
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME
|
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying
the device name of the operator terminal to be enabled or disabled for
the specified operator terminal types. The maximum total length of the
string is 16 bytes. See the preceding field description
(OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name.
|
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_STATUS
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_STATUS.
|
|
Reserved
|
This 3-byte field is reserved for future use.
|
|
Reserved
|
This 4-byte field is reserved for future use.
|
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT
|
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal
whose status is to be requested. To obtain the unit number of the
terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item
code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device
name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail
end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is,
starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic
character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character
constitute the unit number.
After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in
the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the
following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME.
|
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME
|
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying
the device name of the operator terminal whose status is requested. The
maximum total length of the string is 14 bytes. See the preceding field
description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn how to obtain the device name.
|
Message Buffer Format for OPC$_RQ_LOGI
|
OPC$B_MS_TYPE
|
This 1-byte field contains the request code OPC$_RQ_LOGI.
|
|
OPC$Z_MS_TARGET_CLASSES
|
This 3-byte field contains a 24-bit bit vector that specifies which
operator terminal types are to receive the cancellation request. The
$OPCDEF macro defines symbolic names for the operator terminal types.
You construct the bit vector by specifying the desired symbolic names
in a logical OR operation. Following is the symbolic name of each
operator terminal type:
|
OPC$M_NM_CARDS
|
Card device operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CENTRL
|
Central operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_SECURITY
|
Security operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_CLUSTER
|
OpenVMS Cluster operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DEVICE
|
Device status information
|
|
OPC$M_NM_DISKS
|
Disk operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_NTWORK
|
Network operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_TAPES
|
Tape operator
|
|
OPC$M_NM_PRINT
|
Printer operator
|
OPC$M_NM_OPER1
through
OPC$M_NM_OPER12
|
System-manager-defined operator functions
|
|
|
OPC$L_MS_RQSTID
|
This longword field contains a user-supplied value.
The value 0 specifies that the current operator log file is to be
closed and a new log file opened with all classes enabled
(OPC$B_MS_TARGET is ignored).
The value 1 specifies that the current operator log file is to be
closed but no new log file is to be opened.
The value 2 specifies that the classes in OPC$B_MS_TARGET are added
to the current operator log file classes. A log file is opened if
necessary.
The value 3 specifies that the operator classes in OPCB_MS_TARGET
are to be removed from the operator log file classes. If all classes
are removed, the log file is closed.
|
|
OPC$W_MS_OUNIT
|
This 2-byte field contains the unit number of the operator terminal
that is making the initialization request. To obtain the unit number of
the terminal, you can call $GETDVI, specifying the DVI$_FULLDEVNAM item
code. The information returned will consist of the node name and device
name as a padded string. Because the unit number is found on the tail
end of the string, you must parse the string. One way to do this is,
starting from the tail end, to search for the first alphabetic
character; the digits to the right of this alphabetic character
constitute the unit number.
After extracting the unit number, count the remaining characters in
the string. Then, construct a counted ASCII string and use this for the
following field, OPC$T_MS_ONAME.
|
|
OPC$T_MS_ONAME
|
This variable-length field contains a counted ASCII string specifying
the device name of the operator terminal that is making the
initialization request. The maximum total length of the string is 14
bytes. See the preceding field description (OPC$W_MS_OUNIT) to learn
how to obtain the device name.
|
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Channel assigned to the mailbox to which the reply is to be sent. The
chan argument is a longword value containing the
number of the channel. If you do not specify chan or
specify it as the value 0 (the default), no reply is sent.
If a reply from the operator is desired, you must specify the
chan argument.
Description
The $SNDOPR service performs the following functions:
- Sends a user request to operator terminals
- Sends a user cancellation request to operator terminals
- Sends an operator reply to a user terminal
- Enables an operator terminal
- Displays the status of an operator terminal
- Initializes the operator log file
This system service requires system dynamic memory; it cannot be called
from kernel mode.
The general procedure for using this service is as follows:
- Construct the message buffer and place its final length in the
first word of the buffer descriptor.
- Call the $SNDOPR service.
- Check the condition value returned in R0 to make sure the request
was successfully made.
- Issue a read request to the mailbox specified, if any.
- When the read operation completes, check the 2-byte condition value
in the OPC$W_MS_STATUS field to make sure that the operation was
performed successfully.
The format of messages displayed on operator terminals follows:
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss.cc
message specific information
|
The following example shows the message displayed on a terminal as a
result of a request to enable that terminal as an operator terminal:
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 13:44:40.37
Operator _NODE$LTA5: has been enabled, username HOEBLE
|
The following example shows the message displayed on an operator
terminal as a result of a request to display the status of that
operator terminal:
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 12:11:10.48
Operator status for operator _NODE$OPA0:
CENTRAL, PRINTER, TAPES, DISKS, DEVICES, CARDS, CLUSTER, SECURITY,
OPER1, OPER2, OPER3, OPER4, OPER5, OPER6, OPER7, OPER8, OPER9,
OPER10, OPER11, OPER12
|
The following example shows the message displayed on an operator
terminal as a result of a user request:
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 30-DEC-2001 12:57:32.25
Request 1285, from user ROSS on NODE_NAME
Please mount device _NODE$DMA0:
|
Required Access or Privileges
OPER privilege is required for the following functions:
- Enabling a terminal as an operator's terminal
- Replying to or canceling a user's request
- Initializing the operator communication log file
In addition, the operator must have SECURITY privilege to affect
security functions.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR,
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified message has a length of 0 or has more than 986 bytes.
|
|
SS$_DEVNOTMBX
|
The channel specified is not assigned to a mailbox.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The service was called from kernel mode or the system dynamic memory is
insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number. An invalid channel number is
one that is 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_MBFULL
|
The mailbox used to support communication is full. Retry at a later
time.
|
|
OPC$_NOPERATOR
|
The service completed successfully; the Operator Communications Manager
(OPCOM) is not running and the message will not be sent. Note that
OPC$_NOPERATOR is a success status and must be tested for explicitly.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to reply to or cancel a user's
request; the process does not have read/write access to the specified
mailbox; or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
Condition Values Returned in the Mailbox
|
OPC$_BLANKTAPE
|
The service completed successfully; the operator responded with the DCL
command REPLY/BLANK_TAPE=n.
|
|
OPC$_INITAPE
|
The service completed successfully; the operator responded with the DCL
command REPLY/INITIALIZE_TAPE=n.
|
|
OPC$_NOPERATOR
|
The service completed successfully; no operator terminal was enabled to
receive the message.
|
|
OPC$_RQSTCMPLTE
|
The service completed successfully; the operator completed the request.
|
|
OPC$_RQSTPEND
|
The service completed successfully; the operator will perform the
request when possible.
|
|
OPC$_RQSTABORT
|
The operator could not satisfy the request.
|
|
OPC$_RQSTCAN
|
The caller canceled the request.
|
Examples
| #1 |
#include <ssdef.h>
#include <opcdef.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <descrip.h>
#include <starlet.h>
#include <lib$routines.h>
char input_buffer[256]; /* Input buffer, if needed */
/* VMS descriptors: */
$DESCRIPTOR(input_desc, input_buffer);
$DESCRIPTOR(prompt_desc, "Request> ");
struct dsc$descriptor req_desc;
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int status, /* Status of system calls */
length = 0; /* Length of message text */
struct OPC request; /* Request message buffer */
/* Check for too many arguments on command line */
if (argc > 2)
return (SS$_OVRMAXARG);
/* See if request string present on command line... */
if (argc > 1)
{
/* It is. Compute length and copy pointer */
length = strlen(argv[1]);
input_desc.dsc$a_pointer = argv[1];
}
/* If no message present, prompt user for message text */
while (length == 0)
{
status = lib$get_input(&input_desc, &prompt_desc, &length);
if (status != SS$_NORMAL)
return (status);
};
if (length > 128) /* Limit message length */
length = 128; /* to 128 characters */
/* Set up request buffer... */
request.opc$b_ms_type = OPC$_RQ_RQST;
request.opc$b_ms_target = OPC$M_NM_CENTRL;
request.opc$l_ms_rqstid = 0;
memcpy(&request.opc$l_ms_text, input_desc.dsc$a_pointer, length);
/* Set up request buffer descriptor and send message */
req_desc.dsc$w_length = length + 8;
req_desc.dsc$a_pointer = (char *) &request;
return (sys$sndopr(&req_desc, 0));
}
|
This example allows you to build an operator request and send the
request to the operator.
| #2 |
IMPLICIT NONE
! Symbol definitions
INCLUDE '($DVIDEF)'
INCLUDE '($OPCDEF)'
! Structures for SNDOPR
STRUCTURE /MESSAGE/
UNION
MAP
BYTE TYPE,
2 ENABLE(3)
INTEGER*4 MASK
INTEGER*2 OUNIT
CHARACTER*14 ONAME
END MAP
MAP
CHARACTER*24 STRING
END MAP
END UNION
END STRUCTURE
RECORD /MESSAGE/ MSGBUF
! Length of MSGBUF.ONAME
INTEGER*4 ONAME_LEN
! Status and routines
INTEGER*4 STATUS,
2 LIB$GETDVI,
2 SYS$SNDOPR
! Type
MSGBUF.TYPE = OPC$_RQ_TERME
! Enable
MSGBUF.ENABLE(1) = 1
! Operator type
MSGBUF.MASK = OPC$M_NM_OPER1
! Terminal unit number
STATUS = LIB$GETDVI (DVI$_UNIT,
2 ,
2 'SYS$OUTPUT',
2 MSGBUF.OUNIT,,)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS))
! Terminal name
STATUS = LIB$GETDVI (DVI$_FULLDEVNAM,
2 ,
2 'SYS$OUTPUT',,
2 MSGBUF.ONAME,
2 ONAME_LEN)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS))
! Remove unit number from ONAME and set up counted string
ONAME_LEN = ONAME_LEN - 3
MSGBUF.ONAME(2:ONAME_LEN+1) = MSGBUF.ONAME(1:ONAME_LEN)
MSGBUF.ONAME(1:1) = CHAR(ONAME_LEN)
! Call $SNDOPR
STATUS = SYS$SNDOPR (MSGBUF.STRING,)
IF (.NOT. STATUS) CALL LIB$SIGNAL(%VAL(STATUS))
END
|
This HP Fortran for OpenVMS program enables the current terminal to
receive OPER1 operator messages.
$SPACE
The Space service lets you space (skip) a tape file forward or backward
a specified number of blocks.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, initializes user image alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT report_method ,report_buffer ,buffer_length
C Prototype
int sys$start_align_fault_report (int report_method, void
*report_buffer, int buffer_length);
Arguments
report_method
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Method by which image alignment faults are to be reported.
The following table shows valid values for the
report_method argument:
| Value |
Meaning |
|
AFR$C_BUFFERED
|
Alignment fault PCs and fault addresses are saved in a user-supplied
buffer.
|
|
AFR$C_EXCEPTION
|
Alignment faults are elevated to user mode exceptions.
|
report_buffer
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The 32-bit address of the buffer into which to write the fault data.
The report_buffer argument is needed only if the value
of the report_method argument is AFR$C_BUFFERED.
buffer_length
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the buffer specified in the report_buffer
argument.
The buffer must have a minimum size of AFR$K_USER_LENGTH + 32. However,
a larger buffer allows for more information to be collected.
Description
The Start Alignment Fault Reporting service initializes user image
alignment fault reporting.
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service allows the user to gather
alignment fault data for one image. Reporting is enabled for the life
of the image. When the image terminates, the alignment fault reporting
is disabled.
User alignment fault data can be written to a buffer or broadcast as an
informational exception message.
If the AFR$C_BUFFERED value is given in the
report_method buffer, alignment fault PCs and fault
addresses are saved in a user-supplied buffer.
The following diagram illustrates the format in which user alignment
fault data is stored in the buffer:
If the AFR$C_EXCEPTION value is given in the
report_method argument, alignment faults are elevated
to user mode exceptions. These exceptions can be trapped in a handler;
otherwise, an informational exception message might be broadcast and
the program continues to execute.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The buffer specified in the
report_buffer argument is not accessible.
|
|
SS$_AFR_ENABLED
|
The service has already been called for this image.
|
|
SS$_ARG_GTR_32_BITS
|
The report buffer's virtual address lies in 64-bit virtual address
space.
|
|
SS$_ALIGN
|
The buffer specified in the
report_buffer argument is not quadword aligned.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The buffer size is smaller than that defined by the AFR$K_USER_LENGTH +
32 symbol.
|
Example
|
#include <afrdef>
#include <stdio>
#include <ssdef>
#define USER_BUFFER_ITEMS 10
#define GET_BUFFER_SIZE USER_BUFFER_ITEMS*AFR$K_USER_LENGTH
#define SAVE_BUFFER_SIZE 128+64
#define fault_pc afr$l_fault_pc_l
#define fault_va afr$l_fault_va_l
static int usr_buff_len;
static char *usr_buff;
static int rep_method;
void
cause_af()
{
int addr;
int *ptr;
int arr[2];
addr = (int) &arr[0];
ptr = (int *) ++addr;
*ptr = 1; /* cause alignment fault */
}
main()
{
int i;
char get_buffer[GET_BUFFER_SIZE];
struct afrdef *data_item;
int offset;
int status;
int return_size;
rep_method = AFR$C_BUFFERED;
usr_buff_len = SAVE_BUFFER_SIZE;
usr_buff = (char *)malloc (usr_buff_len);
if(( status = sys$start_align_fault_report(rep_method, usr_buff,
usr_buff_len))
!= SS$_NORMAL) return(status);
for (i=0;i<USER_BUFFER_ITEMS;i++)
cause_af();
while (((status = sys$get_align_fault_data (get_buffer,
GET_BUFFER_SIZE,
&return_size)) > 0) &&
(return_size > 0)) {
/* got some data, print it */
offset = 0;
while (offset < return_size) {
data_item = (struct afrdef *)(&get_buffer[offset]);
printf ("Alignment fault at PC = %8.8X, VA = %8.8X\n",
data_item->fault_pc, data_item->fault_va);
offset += AFR$K_USER_LENGTH;
}
}
return (status);
}
|
This example shows how to use the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service to
initialize user image alignment fault reporting on Alpha systems.
$START_BRANCH
Adds a new branch to a transaction.
Format
SYS$START_BRANCH [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid ,tm_name
,bid [,[timout], [acmode], [tx_class]]
C Prototype
int sys$start_branch (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct
_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
tid [4], void *tm_name, unsigned int bid [4],...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags, described in Table SYS-56. All undefined bits must be 0. If
this argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-56 $START_BRANCH Option Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_BRANCH_UNSYNCHED
|
Specifies that the new branch is unsynchronized.
If this flag is clear, the new branch is synchronized.
|
|
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT
|
Set this flag if you do not want the transaction to be the default
transaction of the calling process. If this flag is clear, the
transaction becomes the default transaction of the calling process.
An error is returned if this flag is clear and the calling process
has an current default transaction.
|
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:

astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of
the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same
access mode as that of the caller of the $START_BRANCH service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (TID) of the transaction to which the new branch will be
added.
tm_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the node on which the call was made to $ADD_BRANCH that
authorized the new branch to be added to the transaction. Note that
this cannot be a cluster alias.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
bid
| OpenVMS usage: |
branch_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The identifier (BID) of the new branch that is to be added to the
transaction.
An BID value of zero is invalid.
timout
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Reserved to HP.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The access mode of the new branch in this process. This is the least
privileged mode that a caller must be in to remove this branch from the
transaction by calling $END_BRANCH. Note that it can be removed from
the transaction by calling $ABORT_TRANS from any access mode.
This argument only influences the access mode of the first branch in
this process. Subsequent branches have the same access mode as the
first. The access mode of the new branch is the least privileged of:
- The access mode of the caller.
- The access mode specified by the acmode argument.
Note that if a branch already exists in this process, then neither the
access mode of the caller nor the access mode specified by the
acmode argument may be less privileged than that
branch.
The default value of this argument is the access mode of the caller.
tx_class
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
A string that specifies the transaction class for the transaction on
the local node if the transaction does not already have a transaction
class on the local node. This string is passed in the event reports
delivered to Resource Manager identifiers (RMIs) and Resource Manager
(RM) participants on the local node.
This argument is ignored if the transaction already has a transaction
class on the local node.
This string must be no longer than 31 characters.
Description
The $START_BRANCH system service:
- Adds a new branch running in the calling process to the specified
transaction.
- Adds the local DECdtm transaction manager to the specified
transaction if the local DECdtm transaction manager is not already a
participant in that transaction.
- Sets the default transaction of the calling process to the new
transaction, if the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear and the process
does not have a default transaction.
- Delivers a transaction started event to each RMI in the calling
process that meets both of the following conditions:
- Requested Transaction Started events for the corresponding
transaction type (default or non-default)
- Has an access mode that is the same as or more privileged than that
specified in this call to $START_BRANCH.
The new branch should have been previously authorized. Authorization is
provided either by a matching call to $JOIN_RM with the
DDTM$M_COORDINATOR flag set or by a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH. Two
calls, one to $ADD_BRANCH and one to $START_BRANCH or one to $JOIN_RM
and one to $START_BRANCH, are said to be matching when the following
conditions are true:
- The same TID values are passed to both calls.
- The BID returned by the call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM is the same
as that passed to the call to $START_BRANCH.
- The call to $START_BRANCH is made on the node identified by the
tm_name argument passed to the call to $ADD_BRANCH or
on the node on which the call to $JOIN_RM was made.
- The call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM is made on the node identified
by the tm_name argument passed to the call to
$START_BRANCH.
$START_BRANCH does not check that there has been a matching call to
$ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM unless the tm_name argument
passed to $START_BRANCH specifies the local node.
Note
The atomicity of the transaction is not guaranteed if there is a call
to $START_BRANCH that does not have a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH or
$JOIN_RM.
|
Preconditions for the successful completion of $START_BRANCH are:
- The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
- The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
- There must not have been a successful call to $START_BRANCH on the
local node that passed the specified BID.
- If the tm_name argument specifies the local node,
there must have been a matching call to $ADD_BRANCH or $JOIN_RM on the
local node.
- If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear, the calling process must
not have an unended default transaction.
- If this process already contains a branch of this transaction, then
the access mode of the caller must be the same as or more privileged
than the access mode of that branch.
$START_BRANCH may fail because:
- Preconditions were not met.
- An abort event occurred for the transaction.
- A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction is in progress and it
is too late to add a new branch to the transaction.
- The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process is in progress.
When $START_BRANCH completes successfully:
- A new branch running in the calling process has been added to the
transaction.
- All Transaction Started events reported to RMIs in the calling
process have been acknowledged.
- If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear, the transaction is the
default transaction of the calling process.
A branch may:
- Invoke resource manager operations, explicitly passing the TID.
- Invoke resource manager operations without specifying the TID, if
the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process, and
the resource manager supports default transactions.
- Call $ADD_BRANCH to authorize another branch to be added to the
transaction.
(The way to invoke a resource manager operation is defined by the
interfaces provided by the resource manager; refer to the resource
manager documentation.)
A synchronized branch is removed from the transaction by calling
$END_BRANCH, specifying the appropriate BID and TID. An unsynchronized
branch is removed from the transaction by DECdtm during commit or abort
processing.
The branch is also removed from the transaction (and the transaction
aborted):
- On termination of the current image or process.
- On successful completion of a call to $ABORT_TRANS in the calling
process that passes the appropriate TID and BID.
There is also a wait form of the service, $START_BRANCHW.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS,
$START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_ALRCURTID
|
Either:
- An attempt was made to make the transaction specified by the
tid argument the default transaction (the
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear) when the calling process had an
unended default transaction.
- The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process was in progress.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Either the options flags were invalid or the
tid argument was omitted but the
bid argument was not zero.
|
|
SS$_BRANCHSTARTED
|
There has already been a call to $START_BRANCH on the local node
specifying that TID and BID (returned only if the node specified by the
tm_name argument was the local node).
|
|
SS$_CONNECFAIL
|
The node specified by the
tm_name argument was not the local node, and there was
no communications link between the DECdtm transaction managers on the
local node and the specified node.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_INVBUFLEN
|
The string passed in the
tx_class argument was longer than 31 characters, or
the string passed in the
tm_name argument was longer than 256 characters.
|
|
SS$_NOLOG
|
The local node did not have a transaction log.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHBID
|
Either:
- The specified BID was not returned by any call to $ADD_BRANCH or
$JOIN_RM on the local node (returned only if the node specified by the
tm_name argument was the local node).
- An BID of zero was supplied.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTID
|
The local node did not have any branches in the specified transaction
(returned only if the node specified by the
tm_name argument was the local node).
|
|
SS$_TPDISABLED
|
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
The transaction was in the wrong state for the attempted operation
because either:
- An abort event has occurred for the transaction.
- A call to $END_TRANS to end the transaction is in progress and it
is now too late to add a new branch to the transaction.
|
$START_BRANCHW
Adds a new branch to a transaction.
$START_BRANCHW always waits for the request to complete before
returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to
$START_BRANCH.
Format
SYS$START_BRANCHW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,tid
,tm_name ,bid [,[timout] ,[acmode], [tx_class]]
C Prototype
int sys$start_branchw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct
_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
tid [4], void *tm_name, unsigned int bid [4],...);
$START_TRANS
Starts a new transaction.
Format
SYS$START_TRANS [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[tid]
,[timout] ,[acmode] ,[tx_class]]
C Prototype
int sys$start_trans (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb,...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags, which are described in Table SYS-57. All undefined bits must be
0. If this argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-57 $START_TRANS Option Flags
| Flag |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT
|
Set this flag if you do not want the new transaction to be the default
transaction of the calling process. An error is returned if this flag
is set and the
tid argument is zero or omitted.
If this flag is clear, the new transaction becomes the default
transaction of the calling process. An error is returned if this flag
is clear and the calling process already has a default transaction.
|
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Set this flag to specify that successful synchronous completion is to
be indicated by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the
AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O
status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST routine that is executed when the service completes if SS$_NORMAL
is returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address
of this routine. This routine is executed in the same access mode of
the caller of the $START_TRANS service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
tid
| OpenVMS usage: |
trans_id |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the service returns the identifier
(TID) of the new transaction.
No other call to $START_TRANS on any node ever returns the same TID
value.
The default value of this argument is zero. An error is returned if the
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is set and this argument is either omitted or
zero.
timout
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Timeout for the new transaction. This is the time at which the DECdtm
transaction manager is to abort the transaction if the transaction has
not already committed.
A positive time value specifies an absolute time. The absolute value of
a negative time specifies an offset (delta time) from the current time.
The transaction is aborted at the next timer interval if you specify
either a zero time value or any time in the past. If this argument is
omitted, the new transaction has no timeout.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
An access mode of the new branch of the new transaction.
An access mode is maintained for each transaction per process. All
branches in a transaction in a process have the same access mode.
Subsequent operations do not alter it. The access mode of a branch is
the least privileged mode in which a successful call to $END_TRANS may
be made.
Note that the transaction may be aborted by a call to $ABORT_TRANS from
any access mode.
The access mode of the branch is the least privileged of the following:
- The access mode of the caller
- The access mode specified by the acmode argument
If the acmode argument is omitted, the access mode of
the new branch is the same as that of the caller.
tx_class
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
A string that specifies the transaction class for the new transaction
on the local node. This string is passed in the event reports delivered
to RMIs and RM participants on the local node.
This string must be no longer than 31 characters. If this argument is
omitted or the string is of length zero, the new transaction has no
transaction class on the local node. In this case, the class of the
transaction on the local node can be specified by a subsequent call to
$START_BRANCH on that node.
Description
The $START_TRANS system service starts a new transaction whose commit
or abort processing is to be coordinated by the local DECdtm
transaction manager. The service:
- Adds a branch running in the calling process to the new
transaction. The identifier (BID) of the new branch is 0.
- Sets the default transaction of the calling process to the new
transaction, if the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear and the process
does not have a default transaction.
- Delivers an event of type Transaction Started to each RMI in the
calling process that requested Transaction Started events and has an
access mode that is the same as or more privileged than that specified
in this call to $START_TRANS. See the description of the
acmode argument.
The event delivered to all such RMIs is either a default
transaction-started event or a nondefault transaction-started event,
depending on whether the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear or not.
Preconditions for the successful completion of $START_TRANS are:
- The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
- The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
- If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag is clear, the calling process must
not have an unended default transaction.
$START_TRANS may fail for various reasons including:
- Preconditions were not met.
- The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process is in progress.
When $START_TRANS completes successfully:
- A new transaction has started, with a unique identifier.
- The transaction has a single branch, with a BID of 0.
- All Transaction Started events reported to RMIs in the calling
process have been acknowledged.
- If the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear, the transaction is the
default transaction of the calling process.
A branch may:
- Invoke resource manager operations, explicity passing the TID.
- Invoke resource manager operations without specifying the TID, if
the transaction is the default transaction of the calling process, and
the resource manager supports default transactions.
- Call $ADD_BRANCH to authorize another branch to be added to the
transaction.
(The way to invoke a resource manager operation is defined by the
interfaces provided by the resource manager. Refer to the resource
manager documentation for additional information.)
DECdtm cannot commit the transaction until the process calls $END_TRANS.
The transaction is aborted:
- On termination of the current image or process.
- On successful completion of a call to $ABORT_TRANS in the calling
process, specifying a BID of 0.
There is also a wait form of the service, $START_TRANSW.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quotas
ASTLM, BYTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,
$START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_ALCURTID
|
Either:
- An attempt was made to start a default transaction (the
DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear) when the calling process had an
unended default transaction.
- The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS by the calling process was in progress.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Either the DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was set and the
tid argument was omitted, or the options flags were
invalid.
|
|
SS$_CURTIDCHANGE
|
The DDTM$M_NONDEFAULT flag was clear and a call to change the default
transaction of the calling process was in progress.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The job buffered I/O byte limit quota (BYTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_INVBUFLEN
|
The string passed to the
tx_class argument was longer than 31 characters.
|
|
SS$_NOLOG
|
The local node did not have a transaction log.
|
|
SS$_TPDISABLED
|
The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node.
|
$START_TRANSW
Starts a new transaction.
$START_TRANSW always waits for the request to complete before returning
to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $START_TRANS.
Format
SYS$START_TRANSW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[tid]
,[timout] ,[acmode]]
C Prototype
int sys$start_transw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct
_iosb *iosb,...);
$STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, disables user image alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
C Prototype
int sys$stop_align_fault_report (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Stop Alignment Fault Reporting service disables user image
alignment fault reporting.
The service returns SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED if user image alignment fault
reporting is not enabled; otherwise, it returns success.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
|
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service has not been called.
|
$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT (Alpha Only)
On Alpha systems, disables systemwide alignment fault reporting.
Format
SYS$STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
C Prototype
int sys$stop_sys_align_fault_report (void);
Arguments
None.
Description
The Stop System Alignment Fault Reporting service disables systemwide
alignment fault reporting.
The service returns SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED if systemwide alignment fault
reporting is not enabled; otherwise, it returns success.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL privilege is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA,
$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT,
$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller lacks sufficient privilege.
|
|
SS$_AFR_NOT_ENABLED
|
The $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service has not been called.
|
$SUBSYSTEM
Saves or restores the process image rights for the current protected
subsystem.
Format
SYS$SUBSYSTEM enbflg
C Prototype
int sys$subsystem (unsigned int enbflg);
Argument
enbflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
boolean |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Value specifying whether the protected subsystem identifiers are to be
saved or restored. If the enbflg argument is set to 0,
the active subsystem is saved. If it is set to 1, the subsystem is
restored.
Description
A protected subsystem image is a main image that has in its access
control list a special type of ACE that names a set of identifiers and
their attributes. Whenever the operating system activates a main image
that has protected subsystem identifiers associated with it, these
identifiers are automatically granted to the process for the duration
of the image.
In essence, a protected subsystem provides the same behavior as if the
image had been installed with the identifiers. Subsystem identifiers
are sometimes referred to as image rights, in contrast to process
rights and system rights.
The Subsystem service provides an easy way for a protected subsystem
image to dynamically save and restore its subsystem identifiers. A
protected subsystem might choose to turn off its subsystem identifiers
at certain times to temporarily revoke the user's access to the objects
comprising the protected subsystem. For example, DCL uses the
$SUBSYSTEM service to temporarily remove any image identifiers from the
process during Ctrl/Y interrupt processing.
The image rights are saved in the process control region and
automatically deleted on image rundown ($RMSRUNDWN).
For more information about protected subsystems, refer to the
HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully; protected subsystem had no
identifiers associated with it.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully; protected subsystem had identifiers
associated with it.
|
$SUSPND
Allows a process to suspend itself or another process.
Format
SYS$SUSPND [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$suspnd (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be suspended. The
pidadr argument is the address of the longword PID.
The pidadr argument can refer to a process running on
the local node or a process running on another node in the OpenVMS
Cluster system.
You must specify the pidadr argument to suspend a
process whose UIC group number is different from that of the calling
process.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the process to be suspended. The prcnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
the process name. A process running on the local node can be identified
with a 1- to 15-character string.
To identify a process on a particular node on a cluster, specify the
full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process
name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
A process name is implicitly qualified by its UIC group number. Because
of this, you can use the prcnam argument only to
suspend processes in the same UIC group as the calling process.
To suspend processes in other groups, you must specify the
pidadr argument.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Longword of bit flags specifying options for the suspend operation.
Currently, only bit 0 is used for the flags argument.
When bit 0 is set, the process is suspended at kernel mode and ASTs are
not deliverable to the process.
To request a kernel mode suspend, the caller must be in either kernel
mode or executive mode. The default (bit 0 is clear) is to suspend the
process at supervisor mode, where executive or kernel mode ASTs can be
delivered to the process. If executive or kernel mode ASTs have been
delivered to a process suspended at supervisor mode, that process will
return to its suspended state after the AST routine executes.
Description
The Suspend Process service allows a process to suspend itself or
another process.
A suspended process can receive executive or kernel mode ASTs, unless
it is suspended at kernel mode. If a process is suspended at kernel
mode, the process cannot receive any ASTs or otherwise be executed
until another process resumes or deletes it. If you specify neither the
pidadr nor the prcnam argument, the
caller process is suspended.
If the longword value at address pidadr is 0, the PID
of the target process is returned.
The $SUSPND service requires system dynamic memory.
The $SUSPND service completes successfully if the target process is
already suspended.
Unless it has pages locked in the balance set, a suspended process can
be removed from the balance set to allow other processes to execute.
Note that a kernel mode suspend request can override a supervisor mode
suspend state, but a supervisor suspend request cannot override a
kernel mode suspend state.
The Resume Process ($RESUME) service allows a suspended process to
continue. If one or more resume requests are issued for a process that
is not suspended, a subsequent suspend request completes immediately;
that is, the process is not suspended. No count is maintained of
outstanding resume requests.
Note
When the $SUSPND service is called and the target process is on a
different cluster node than that of the process calling the $SUSPND
service, the kernel mode suspend flag (bit 0) is ignored. As a result,
any suspend is treated as a supervisor-mode suspend.
|
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following privileges to use $SUSPND:
- GROUP privilege to suspend another process in the same group,
unless the process to be suspended has the same UIC as the calling
process
- WORLD privilege to suspend any other process in the system
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW,
$HIBER, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM,
$WAKE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The target process was not created by the caller and the calling
process does not have GROUP or WORLD privilege, or flag bit 0 was set
from outer mode.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the OpenVMS Cluster system.
|
|
SS$_NOSUSPEND
|
The process was previously marked as not suspendable by the
PCB$V_NOSUSPEND flag.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
|
SS$_WAIT_CALLERS_MODE
|
Bit 1 was used in the
flags argument.
|
$SYNCH
Checks the completion status of a system service that completes
asynchronously.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$SYNCH [efn] ,[iosb]
C Prototype
int sys$synch (unsigned int efn, struct _iosb *iosb);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag specified in the call to the system service
whose completion status is to be checked by $SYNCH. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $SYNCH uses only the low-order byte.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block specified in the call to the system service whose
completion status is to be checked by $SYNCH. The iosb
argument is the address of this quadword I/O status block.
Description
The Synchronize service checks the completion status of a system
service that completes asynchronously. The service whose completion
status is to be checked must have been called with the
efn and iosb arguments specified,
because the $SYNCH service uses the event flag and I/O status block of
the service to be checked.
This service performs a true test for the completion of an asynchronous
service, such as $GETJPI. $SYNCH operates in the following way:
- When called, $SYNCH waits (by calling $WAITFR) for the event flag
to be set.
- When the event flag is set, $SYNCH checks to see whether the I/O
status block is nonzero. If it is nonzero, then the asynchronous
service has completed, and $SYNCH returns to the caller.
- If the I/O status block is the value 0, then the asynchronous
service has not yet completed and the event flag was set by the
completion of an event not associated with the completion of $GETJPI.
In this case, $SYNCH clears the event flag (by calling $CLREF) and
waits again (by calling $WAITFR) for the event flag to be set,
repeating this cycle until the I/O status block is nonzero.
The $SYNCH service always sets the specified event flag when it returns
to the caller. This ensures that different program segments can use the
same event flag without conflicting. For example, assume that calls to
$GETJPI and $GETSYI both specify the same event flag and that $SYNCH is
called to check for the completion of $GETJPI. If $GETSYI sets the
event flag, $SYNCH clears the flag and waits for $GETJPI to set it.
When $GETJPI sets the flag, $SYNCH returns to the caller and sets the
event flag. In this way, the flag set by $GETSYI is not lost, and
another call to $SYNCH will show the completion of $GETSYI.
The $SYNCH service is useful when a program calls an asynchronous
service but must perform some other work before testing for the
completion of the asynchronous service. In this case, the program
should call $SYNCH at that point when it must know that the service has
completed and when it is willing to wait for the service to actually
complete.
When a program calls an asynchronous service (for example, $QIO) and
actually waits in line (by calling $WAITFR) for its completion without
performing any other work, you could improve that program by calling
the synchronous form of that service (for example, $QIOW). The
synchronous services such as $QIOW execute code that checks for the
true completion status in the same way that $SYNCH does.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully. The asynchronous service has
completed, and the I/O status block contains the condition value
describing the completion status of the asynchronous service.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The I/O status block cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
An illegal event flag was specified.
|
|
SS$_UNASEFC
|
The process is not associated with the cluster containing the specified
event flag.
|
|














