 |
HP COBOL
DBMS Database Programming Manual
GET
Function
The GET statement moves the contents of the current database record of
the run unit to your user work area.
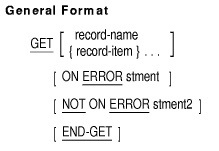
record-name
names a subschema record type.
record-item
is a group or elementary data item in a subschema record type.
Record-item may be qualified.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an on error condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not on error condition.
Syntax Rules
- Each record-item must reference a data item in the same
subschema record type.
- If record-item is a group item, its subordinate group and
elementary items cannot be referenced in the same GET statement.
General Rules
- The GET statement references the current record of the run unit.
- If you use the record-name option, or if you do not
specify either the record-item or the record-name
option, the DBCS makes a copy of the entire current record of the run
unit available to the program in the user work area.
- If you use the record-item option, only those items in the
current record of the run unit are made available to the program in the
user work area.
- Any change made to the user work area does not affect the record in
the database. You must execute a MODIFY and a COMMIT statement to make
permanent changes to the database.
- Use record-name to check that the record type of the
current record is identical to the record type specified by
record-name.
- The GET statement has no effect on currency indicators.
- If a database exception condition occurs during the execution of a
GET statement, the DBCS places a database exception condition code in
the special register DB-CONDITION (see Technical Note). This code
identifies the condition.
Technical Note
GET statement execution can result in these DB-CONDITION database
exception condition codes:
|
DBM$_CRUN_NULL
|
The currency indicator for the run unit is null.
|
|
DBM$_CRUN_POS
|
The currency indicator for the run unit points to a vacated position in
the database.
|
|
DBM$_WRONGRTYP
|
The record type for record-name is not identical to the current record
type, or a record-item is not a group or elementary item in the current
record.
|
|
DBM$_CONVERR
|
A data conversion error occurred in the GET operation.
|
|
DBM$_ILLNCHAR
|
An invalid character was found in a numeric field.
|
|
DBM$_NONDIGIT
|
A nonnumeric character was found in a numeric field.
|
|
DBM$_OVERFLOW
|
A data overflow error occurred in the GET operation.
|
|
DBM$_TRUNCATION
|
A data truncation error occurred in the GET operation.
|
|
DBM$_UNDERFLOW
|
A data underflow error occurred in the GET operation.
|
Additional References
- Section 2.2, on reserved words (database special registers)
- HP COBOL Reference Manual, Chapter 6, section on scope of statements
- Section 4.8.1, on database On Error condition
- USE statement
Examples
- This example gets the current record of the run unit:
- This example gets a PART record only if it is the current record of
the run unit:
- This example gets these items only if they are part of the current
record of the run unit:
KEEP
Function
The KEEP statement inserts a database key value from a currency
indicator or keeplist into a keeplist.

database-key-id
represents a database key identifier. References are made to a keeplist
entry or a currency indicator according to the rules for Database Key
Identifiers.
destination-keeplist
names a keeplist in the Subschema Section to receive the database key
value.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an on error condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not on error condition.
General Rules
- If database-key-id references a database key value in
either a currency indicator or a keeplist, the DBCS:
- Inserts that value as the last entry in
destination-keeplist
- Sets a lock on the associated record to prevent concurrent run
units from accessing it
- If the program does not specify database-key-id, the DBCS
inserts the database key value of the current record of the run unit as
the last entry of destination-keeplist.
- The KEEP statement has no effect on currency indicators.
- If a database exception condition occurs during the execution of a
KEEP statement, the DBCS places a database exception condition code in
the special register DB-CONDITION (see Technical Note). This code
identifies the condition.
Technical Note
KEEP statement execution can result in the database exception
conditions associated with the evaluation of the database key
identifier.
Additional References
- Section 2.2, on reserved words (database special registers)
- Keeplist Description entry
- HP COBOL Reference Manual, Chapter 6, section on scope of statements
- Section 4.4, on database key identifiers
- Section 4.8.1, on database On Error condition
- USE statement
Examples
- Currency indicator access
- To insert the database key value of the current record of the run
unit into KEEPLIST-A:
KEEP CURRENT USING KEEPLIST-A.
|
- To insert the database key value of the current record of the
CLASS_PART set into KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP CURRENT WITHIN CLASS_PART USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
- To insert the database key value of the current record of the BUY
realm into KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP CURRENT WITHIN BUY USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
- To insert the database key value of PART record into KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP CURRENT WITHIN PART USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
- Keeplist access
- To insert the first keeplist entry from KEEPLIST-A as the last
entry in KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP FIRST WITHIN KEEPLIST-A USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
- To insert the last keeplist entry in KEEPLIST-A as the last entry
in KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP LAST WITHIN KEEPLIST-A USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
- To insert the fourth keeplist entry relative to the current
position in KEEPLIST-A as the last entry in KEEPLIST-B:
KEEP OFFSET 4 WITHIN KEEPLIST-A USING KEEPLIST-B.
|
MODIFY
Function
The MODIFY statement changes the contents of specified data items in a
database record.
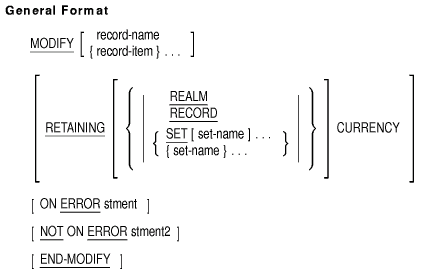
record-name
names a subschema record type.
record-item
is a group or elementary data item in a subschema record type.
Record-item can be qualified.
set-name
names a subschema set type.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an on error condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not on error condition.
Syntax Rules
- Each record-item must reference a data item in the same
subschema record type.
- If record-item is a group item, its subordinate group and
elementary data items cannot be referenced as a record-item in
the same MODIFY statement.
- Use record-name to check that the current record of the
run unit is a record type identical to the record-name record
type.
General Rules
- Changes are made to a database record by:
- Locating the target record (FIND and GET, or FETCH)
- Moving the new data to the data-name references in the user work
area
- Executing the MODIFY statement
- The DBCS changes the contents of the entire database record:
- If you specify record-name
- If you specify neither record-name nor record-item
- Using record-item limits the changes to the database
record to only those items you specify.
- If you modify any data item that is the sort key for that record's
position in a sorted set, the DBCS automatically repositions the record
in that set in accordance with the set-ordering criteria of the set
type.
If the value of the sort key is identical to another record
of this type, and if duplicates are not allowed for this sorted set,
the DBCS does not perform the MODIFY operation, and a database
exception condition occurs.
- Currency indicator update rules for record insertion and removal
are as follows:
- If the MODIFY statement removes a record from the current set, the
currency indicator for that set points to the position in the set
vacated by the record. (At this position the record is no longer
accessible.)
- If the MODIFY statement reinserts a record in a set in another
location, the set currency indicator changes to point to the record in
this new location.
- If you do not include the RETAINING clause (see Section 4.9.1, RETAINING Clause), the
currency indicator for the set is modified to the current record of the
run unit.
- The current record of the run unit must be in a realm in ready
update mode and all records required by the DBCS to execute the MODIFY
statement must be in realms in one of the appropriate READY modes.
- The contents of the user work area (UWA) do not change after the
successful or unsuccessful execution of a MODIFY statement.
- If the execution of a MODIFY statement results in an exception
condition, the record is not changed.
- If a database exception condition occurs during the execution of a
MODIFY statement, the DBCS places a database exception condition code
in the special register DB-CONDITION (see Technical Notes). This code
identifies the condition.
|


