 |
HP OpenVMS Availability Manager User's Guide
4.2.4 LAN Virtual Circuit Summary Data
You can display interconnect-specific LAN virtual circuit summary data
by clicking the handle at the beginning of a "LAN Virtual Circuit
Summary" row to a vertical position. The screen expands to display
the interconnect-specific VC summary data shown in Figure 4-6.
Figure 4-6 LAN Virtual Circuit Summary Data
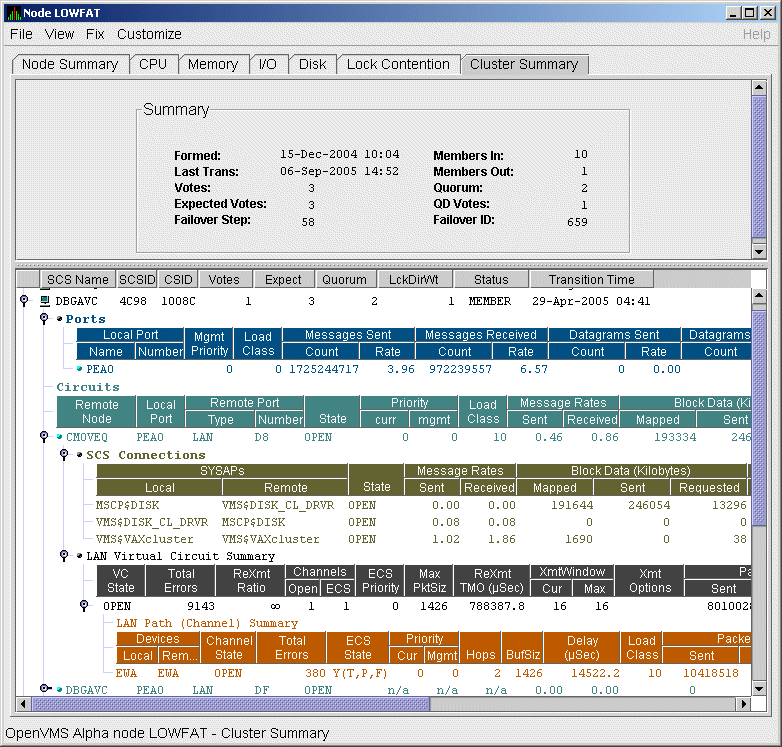
Much of the data in this display corresponds to the information
displayed by the SCACP command SHOW VC. The SHOW CLUSTER command does
not provide a corresponding display. Which data items are displayed
depends on the type of interconnect the virtual circuit is using.
Currently, this feature is available only for LAN virtual circuits. VC
Summary displays for other cluster interconnects such as CI might be
available in the future. When other interconnects are supported, the
interconnect type will be displayed at the beginning of the line---for
example, CI Virtual Circuit Summary---and the associated heading will
have interconnect-specific data items.
Note that LAN Virtual Circuit counters are initialized when PEDRIVER
detects the existence of a PEDRIVER on a remote system. All of a LAN
VC's counters are cumulative from that time.
Some of the data described in Table 4-6 is not displayed in
Figure 4-6 because the screen display is wider than shown. You can
scroll to the right on your terminal screen to display the remaining
fields described in the table.
Table 4-6 describes the LAN Virtual Circuit Summary data items
shown in Figure 4-6.
Table 4-6 LAN Virtual Circuit Summary Data
| Data |
Description |
|
VC State
|
Current internal state of the virtual circuit:
- OPEN---Virtual Circuit is open and usable.
- PATH---At least one open channel has been established, but the
Virtual Circuit has not yet transitioned to OPEN.
- CLOSED---The Virtual Circuit has been closed or has become unusable.
|
|
Total Errors
|
Number of times the virtual circuit has been closed or has had other
errors.
|
|
ReXmt Ratio
|
Ratio of total numbers of transmitted to retransmitted packets during
the most recent data collection interval.
|
|
Channels:
|
|
|
|
Open
|
Number of currently open channels available to the virtual circuit.
|
|
|
ECS
|
Number of equivalent channel set (ECS) channels currently in use by the
LAN virtual circuit.
|
|
ECS Priority
|
Priority a channel must have in order to be included in the Equivalent
channel set (ECS). It is the highest priority any open and tight
channel has.
|
|
MaxPktSiz
|
Maximum data buffer size in use by this LAN virtual circuit.
|
|
ReXmt TMO (µsec)
|
Retransmission timeout, in microseconds. The length of time the virtual
circuit is currently using to wait for an acknowledgment of the receipt
of a packet before retransmitting that packet.
|
|
XmtWindow:
|
|
|
|
Cur
|
Current value of the transmit window (or pipe quota). Maximum number of
packets that are sent before stopping to await an acknowledgment. After
a timeout, the transmit window is reset to 1 to decrease congestion; it
is allowed to increase as acknowledgments are received.
|
|
|
Max
|
Maximum transmit window size currently allowed for the virtual circuit.
|
|
Xmt Options
|
Transmit options enabled:
CKSM---packet checksumming
CMPR---compression
|
|
Packets:
|
|
|
|
Sent
|
Number of packets sent over this virtual circuit.
|
|
|
Received
|
Number of packets received over this virtual circuit.
|
|
Most recent:
|
|
|
|
Time Opened
|
Most recent time the virtual circuit was opened.
|
|
|
Time Closed
|
Most recent time the virtual circuit was closed.
|
4.2.5 LAN Path (Channel) Summary Data
A LAN path or channel is a logical communication path
between two LAN devices. Channels between nodes are determined by a
local device, a remote device, and the connecting network. For example,
two nodes, each having two devices, might establish four channels
between the nodes. The packets that a particular LAN virtual circuit
carries can be sent over any open channel connecting the two nodes.
The difference between channels and virtual circuits is that channels
provide datagram service. Virtual circuits, layered on
channels, provide error-free paths between nodes. Multiple channels can
exist between nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system, but only one
LAN-based virtual circuit can exist between any two nodes at a time.
LAN channel counters are initialized when PEDRIVER
detects the existence of a LAN device on a remote system. All of a LAN
channel counters are cumulative from that time. For more information
about channels and virtual circuits, see the HP OpenVMS Cluster Systems manual.
Displaying Data
You can display LAN channel summary data by clicking the handle at the
beginning of a "LAN Virtual Circuit Summary Data" row
(Figure 4-6), or by right-clicking a data item and choosing the
Channel Summary item from the shortcut menu. The screen expands to
display the LAN channel summary data shown in Figure 4-6. If there
is no handle at the beginning of a "LAN Virtual Circuit
Summary" data row, then managed object data collection is not
enabled for this SCS node.
The data items displayed depend on the type of virtual circuit.
Currently, this feature is available only for LAN virtual circuits.
Some of the data described in Table 4-7 is not displayed in
Figure 4-6 because the screen display is wider than shown. You can
scroll to the right on your terminal screen to display the remaining
fields described in the table.
Table 4-7 LAN Path (Channel) Data
| Data |
Description |
|
Devices:
|
|
|
|
Local
|
Local LAN device associated with the channel.
|
|
|
Remote
|
Remote LAN device associated with the channel.
|
|
Channel State
|
One of the following states:
- OPEN---Channel is usable.
- PATH---Channel handshake has been completed and, if usable, will
transition to OPEN.
- CLOSED---Channel has been shut down or is unusable.
|
|
Total Errors
|
Total of various error counters for this channel (see channel details
for breakdown).
|
|
ECS State
|
Channel ECS membership information:
Losses---one of the following:
- T (tight)---Packet loss history is acceptable.
- L (lossy)---Recent history of packet losses makes channel unusable.
Capacity---one of the following:
- P (peer)---Priority and Buffer size both match the highest
corresponding values of the set of tight channels, entitling the
channel to be an ECS member.
- I (inferior)---Priority or buffer size does not match the
corresponding values of the set of tight channels.
- S (superior)---Priority or buffer size is better than those of the
current corresponding values of the set ECS member channels. This is a
short-lived, transient state because it exists only while the ECS
membership criteria are being re-evaluated.
- U (unevaluated)---Priority or buffer size, or both, have not been
evaluated against the ECS criteria, usually because the channel is
lossy.
Speed---one of the following:
- F (fast)---Channel delay is among the best for tight and peer
channels.
- S (slow)---Channel delay makes channel too slow to be usable
because it would limit the virtual circuit's average delay.
Note: If a channel is lossy, its capacity and speed
are not always kept current. Therefore, displayed values might be those
that the channel had at the time it become lossy.
|
|
Priority:
|
|
|
|
Cur
|
Current priority used to evaluate the channel for ECS membership. This
is the sum of management priority values assigned to the LAN device.
|
|
|
Mgmt
|
Dynamic management-assigned priority.
|
|
Hops
|
Number of switches or bridges in this channel's network path to the
remote LAN device.
|
|
BufSiz
|
Current maximum amount of SCS data that can be contained in a packet
sent over the channel. It is the smallest of the following values:
- Local LAN device buffer sizes
- Remote LAN device buffer sizes
- Local NISCS_MAX_PKTSZ system (SYSGEN) parameter values
- Remote NISCS_MAX_PKTSZ system (SYSGEN) parameter values
- Largest packet size determined by the NISCA Channel Packet Size
probing algorithm that the intervening network can deliver
|
|
Delay (µsec)
|
Running average of measured round-trip time, in microseconds, for
packets sent over the channel.
|
|
Load Class
|
Load class initialized from local and remote LAN device bit rates.
|
|
Packets:
|
|
|
|
Sent
|
Number of packets sent on this channel, including control packets.
|
|
|
Received
|
Number of packets received by this channel.
|
|
Most recent:
|
|
|
|
Time Opened
|
Last time this channel had a verified usable path to a remote system.
|
|
|
Time Closed
|
Time that this channel was last closed.
|
4.3 Detailed Data Accessed Through the Cluster Members Pane
The following sections describe data that appears on lines that you can
open in the Cluster Members pane (Figure 4-2).
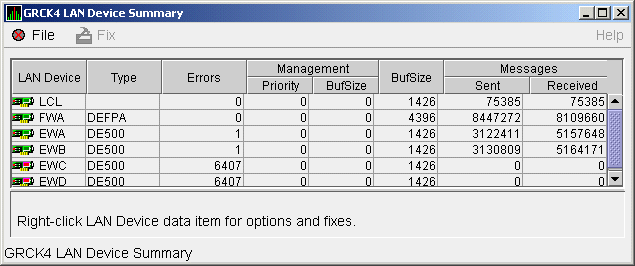
You can display LAN device summary data by first right-clicking a node
name on the Cluster Members pane. On Version 7.3 or later nodes on
which managed objects are enabled, the Availability Manager displays a
menu with the following choices:
- SCA Summary
- LAN Device Summary...
Click LAN Device Summary... to display the Device Summary Data page
(Figure 4-7).
Figure 4-7 LAN Device Summary Data
You can right-click any data item on the page to display a menu with
LAN Device Fixes... on it. These fixes are explained
in Chapter 6.
Table 4-8 describes the LAN device summary data displayed in
Figure 4-7. This data is also displayed with SCACP command SHOW
LAN_DEVICE.
Table 4-8 LAN Device Summary Data
| Data |
Description |
|
LAN Device
|
Name of the LAN device used for cluster communications between local
and remote nodes.
The icon preceding each LAN device can be one of the following
colors:
- Black---not enabled ("Not in use by SCA")
- Yellow---"Run" not set
- Red---"Run" and anything other than Online, Local, or
Restart
- Green---"Run" and a combination of Online, Local, and
Restart only
A tooltip indicates the possible states a device can be in. This can
be a combination of the following: Run, Online, Local, Hello _Busy,
Build_Hello, Init, Wait_Mgmt, Wait_Evnt, Broken, XChain_Disabled,
Delete_pend, Restart, or Restart_Delay. Alternatively, a tooltip might
display "Not in use by SCA."
|
|
Type
|
Type of LAN device used for the cluster.
|
|
Errors
|
Number of errors reported by the device since cluster communications
began using it.
|
|
Management:
|
|
|
|
Priority
|
Current management-assigned priority of the device.
|
|
|
BufSize
|
Current management-assigned maximum buffer size of the device
|
|
BufSize
|
Smaller of interconnect specific buffer size of the device and its
current management-assigned buffer size.
|
|
Messages:
|
|
|
|
Sent
|
Number of LAN packets sent by the device.
|
|
|
Received
|
Number of packets received from remote LAN device.
|
4.3.2 LAN Device Detail Data
To display LAN device detail data, right-click a LAN Path (Channel)
Summary data item on the LAN Virtual Circuit Summary data page
(Figure 4-6). The Availability Manager then displays the shortcut
menu shown in Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8 LAN Path (Channel) Details Menu
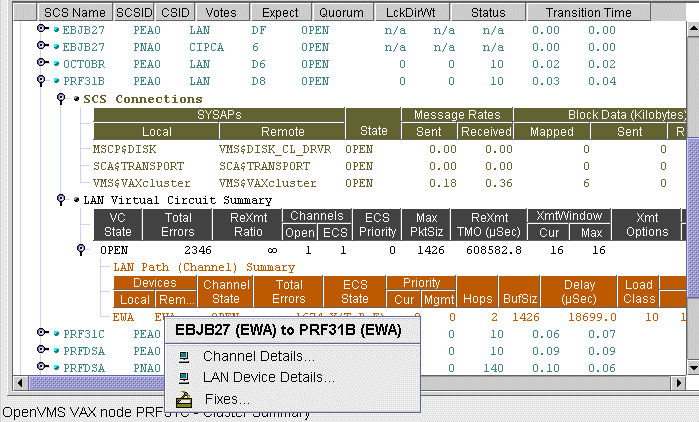
To display device details, select the LAN Device Details... item on the
menu. After a brief delay, a LAN Device Overview Data page
(Figure 4-9) is displayed.
A series of tabs at the top of the LAN Device Overview Data page
indicate additional LAN device pages that you can display. Much of the
LAN device detail data corresponds to data displayed by the SCACP
command SHOW LAN_DEVICE.
The LAN Device Overview Data page (Figure 4-9 displays LAN device
summary data.
Figure 4-9 LAN Device Overview Data
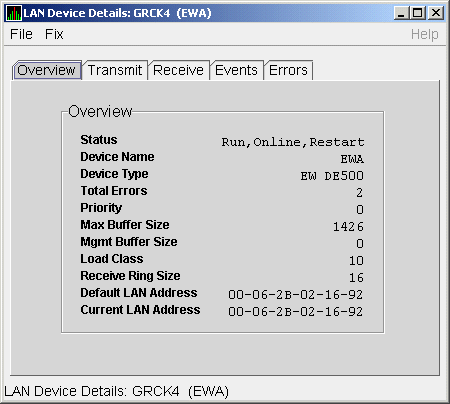
Table 4-9 describes the data displayed in Figure 4-9.
Table 4-9 LAN Device Overview Data
| Data |
Description |
|
Status
|
Device status: Run, Online, Local, Hello _Busy, Build_Hello, Init,
Wait_Mgmt, Wait_Evnt, Broken, XChain_Disabled, Delete_pend, Restart, or
Restart_Delay. Alternatively, "Not in use by SCA" can be
displayed.
|
|
Device Name
|
Name of the LAN device.
|
|
Device Type
|
OpenVMS device type value.
|
|
Total Errors
|
Total number of errors listed on the Errors page.
|
|
Priority
|
Dynamic management-assigned priority.
|
|
Max Buffer Size
|
Maximum data buffer size for this LAN device.
|
|
Mgmt Buffer Size
|
Dynamic management-assigned maximum block data field size.
|
|
Load Class
|
Load class. The rate in MBs currently being reported by the LAN device.
|
|
Receive Ring Size
|
Number of packets the LAN device can buffer before it discards incoming
packets.
|
|
Default LAN Address
|
LAN device's hardware LAN address.
|
|
Current LAN Address
|
Current LAN address being used by this LAN device.
|
4.3.2.2 LAN Device Transmit Data
The LAN Device Transmit Data page (Figure 4-10) displays LAN device
transmit data.
Figure 4-10 LAN Device Transmit Data
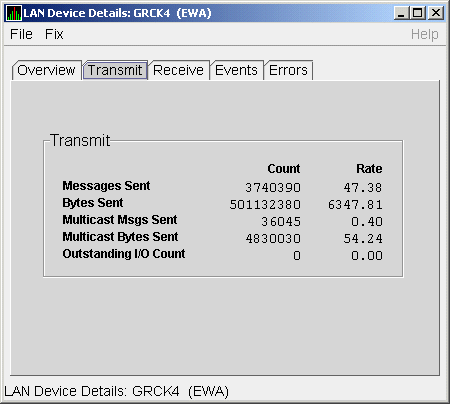
Table 4-10 describes the data displayed in Figure 4-10.
Table 4-10 LAN Device Transmit Data
| Data |
Description |
|
Messages Sent
|
Number of packets sent by this bus, including multicast
"Hello" packets.
|
|
Bytes Sent
|
Number of bytes in packets sent by this LAN device, including multicast
"Hello" packets.
|
|
Multicast Msgs Sent
|
Number of multicast "Hello" packets sent by this LAN device.
|
|
Multicast Bytes Sent
|
Number of multicast bytes in "Hello" packets sent by this LAN
device.
|
|
Outstanding I/O Count
|
Number of transmit requests being processed by LAN driver.
|
4.3.2.3 LAN Device Receive Data
The LAN Device Receive Data page (Figure 4-11) displays LAN device
receive data.
Figure 4-11 LAN Device Receive Data
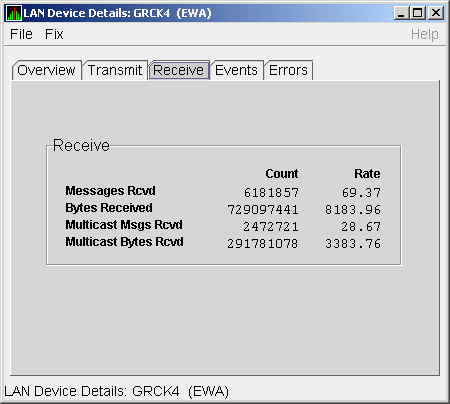
Table 4-11 describes the data displayed in Figure 4-11.
Table 4-11 LAN Device Receive Data
| Data |
Description |
|
Messages Rcvd
|
Number of packets received by this LAN device, including multicast
packets.
|
|
Bytes Received
|
Number of bytes in packets received by this LAN device, including
multicast packets.
|
|
Multicast Msgs Rcvd
|
Number of multicast NISCA packets received by this LAN device.
|
|
Multicast Bytes Rcvd
|
Number of multicast bytes received by this LAN device.
|
4.3.2.4 LAN Device Events Data
The LAN Device Events Data page (Figure 4-12) displays LAN device
events data.
Figure 4-12 LAN Device Events Data
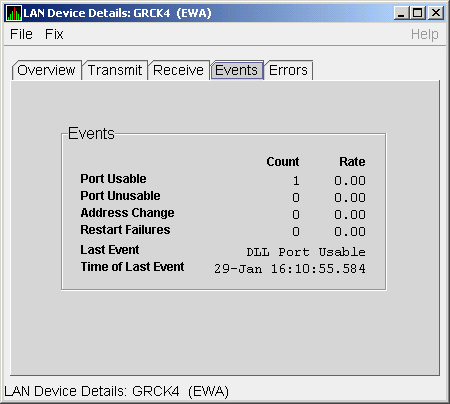
Table 4-12 describes the data displayed in Figure 4-12.
Table 4-12 LAN Device Events Data
| Data |
Description |
|
Port Usable
|
Number of times the LAN device became usable.
|
|
Port Unusable
|
Number of times the LAN device became unusable.
|
|
Address Change
|
Number of times the LAN device's LAN address changed.
|
|
Restart Failures
|
Number of times the LAN device failed to restart.
|
|
Last Event
|
Event type of the last LAN device event (for example, LAN address
change, an error, and so on).
|
|
Time of Last Event
|
Time the last event occurred.
|
|






