HP OpenVMS Systems |
|
[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Index] [Contents] DIGITAL SNA Access Server Migration Guide How the Access Server and SNA Server Work TogetherTogether, the Access Server and the SNA Server function as a gateway between a DECnet or TCP/IP network and an IBM host. The combination of the Access Server and the SNA Server, working together, is called the Access Server Gateway. The Access Server Gateway provides connectivity between existing DIGITAL OpenVMS access routines and IBM hosts. This new gateway may replace a DECnet SNA Gateway or be implemented alongside an existing DECnet SNA Gateway.NOTEYou can run the Access Server Gateway on any Intel or DIGITAL Alpha system that is running the Windows NT Server. Each Access Server Gateway that communicates with the IBM host must have the Access Server, the SNA Server, and Windows NT Server installed and running on the same node. An Access Server Gateway may be connected to the IBM host network in a variety of ways:
Figure 1-2 shows
how the SNA Server and the Access Server might work together in a network
configuration. Communication between the IBM host and the OpenVMS system
occurs through the Windows NT Server, which hosts both the DIGITAL SNA
Access Server and the Microsoft SNA Server. This is a generic configuration
that would be used with any of the following connectivity options: SDLC,
802.2, X.25, DFT, Channel, or TwinAx.
Figure 1-2: Network Configuration with SNA Server and Access Server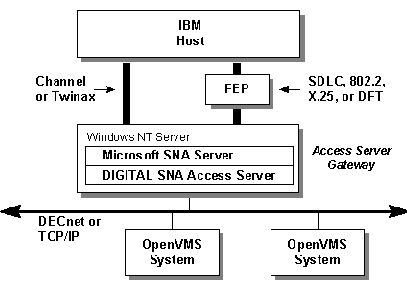 You can replace all or part of your DECnet SNA Gateway
(except LU6.2 functionality) with the gateway capabilities of the Access
Server and SNA Server running on a Windows NT Server. Proper planning and
implementation can significantly minimize the impact of this migration
on the existing system and its users. The rest of this guide steps you
through the stages of your migration.
[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Index] [Contents] DIGITAL SNA Access Server Migration Guide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||