 |
Click
for the User's Guide in .PDF format.
This guide contains the following sections:
1 - Getting Started
Installation instructions are included on the web pages at the following
URL:
http://www.hp.com/products/openvms/managementagents/
After you complete the installation, you can start using the Management
Agents to monitor devices on your system.
Follow these numbered steps:
- Enter a URL to view device data from a web browser:
Replace host by the machine name, for example:
https://atst02.zko.dec.com:2381/
|
where "atst02" is the system to be monitored.
The number 2381 following the URL is the port that the Management
Agents use to communicate with the browser. If you do not specify
this number, your browser connects to another web page if the managed
server is running a web server.
- If you are using the default self-signed certificate, your browser
will display a Security Alert message. If you get this alert, click
on the Yes button to proceed. The Login page is the first screen
displayed after the certificate is validated and a secure connection
has been established with the server.
- Before you can view the Device Home Page, you need to provide a valid
user name and password. The login page contains the following information:
| Item of Information |
Description |
| Login Account |
Enter your OpenVMS user name here. User accounts that have
been assigned the WBEM$ADMIN identifier get administrator privileges.
All other accounts are treated as regular user accounts. Users
with administrator privileges can change the default system options,
set thresholds, and so on. |
| Password |
Enter your OpenVMS password 1. Please note that
the secondary password is not validated. |
| 1Please
note that the secondary OpenVMS password is not validated. |
After successful login, the Device Home Page is displayed. The
Device Home Page contains the following information:
| Item of Information |
Description |
| Login Account |
Either "user" or "administrator" is displayed.
If you click on this link, you are prompted to enter a User Name
and Password. Enter your OpenVMS username and password to log
in as a new user. |
Refresh...Options...
Devices...Logout |
Click each choice displayed at the top left to do the following:
| Refresh |
Update the screen with the most recent information. |
| Options |
Configuration Options:
List general options such as Anonymous Access, Local Access
Type, Auto Delete Users, Logging, IP Restricted Logins
and Trust Mode.
Trusted Certificates:
Specify the certificates for management applications on
trusted servers.
Customer Generated Certificates:
Extract a PKCS #10 certificate request and import a PKCS
#7 generated certificate. |
| Devices |
List Systems Insight Manager servers and HTTP Auto-Discovery
devices. |
| Logout |
Log out of the Device Home Page. |
|
| On the left are one or more product icons |
Click the Management Agents for OpenVMS to display
the initial (summary) view of the Management Agents for OpenVMS. |
| Troubleshooting Tips |
At the bottom right, click to display system and browser requirements
as well as troubleshooting questions and answers. |
- When you click the Management Agents for OpenVMS icon, a Summary
page is displayed. On the left are the following choices:
- Configuration
- Mass Storage
- NIC
- Utilization
- Recovery
Note
The fact that a condition icon does not precede an option does
not mean that the option contains no data, but rather, that
the data displayed is static rather than dynamic in nature. |
At any time, you can click the question mark next to a page heading
to display more information and instructions for using the Management
Agents for OpenVMS software. The help available for the Summary page
includes browser requirements and a description of security measures.
In general, the pages accessible from the Summary page contain the
following information:
Enabling Sets allows the user to set information like File system Threshold,
CPU and memory utilization threshold on the Management agents.
Traps allow the Management Agents for OpenVMS to signal when a computer
you are monitoring exceeds a threshold that you have set. Beginning with
Version 2.2 of the Management Agents for OpenVMS, you can enable the
setting and discovery of traps. Currently, the Management Agents for
OpenVMS support traps for disk file space used, environmental parameters,
CPU load, change in Storage device status and Memory utilization.
You can enable traps on any of the following software versions:
- Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Version 5.1 or later
- MultiNet TCP/IP for OpenVMS Version 4.3 or later
- TCPware TCP/IP for OpenVMS Version 5.5 or later
For more information about generating traps when using MultiNet or
TCPware, refer to the MultiNet Installation & Administrator's Guide
and the TCPware Management Guide.
This section contains the following subsections:
Note
TCP/IP Version 5.1 ECO-1 or later must be running as you complete
these steps. |
2.1 - Steps for Enabling SNMP Set and SNMP Traps
When Using HP TCP/IP
If you did not enable traps while installing TCP/IP, you can enable
traps now by following these steps:
- Enter the following command after the DCL prompt:
$ TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP/FLAG=SETS
|
This command allows you to set threshold values. In other words, the
command lets the master agent process SET commands from SNMP clients.
- Enter the following commands after the DCL prompt:
$ TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP/COMMUNITY="elmginkgo" -
_$ /TYPE=(WRITE,TRAP)/ADDRESS=127.0.0.1
$ TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP/COMMUNITY="elmginkgo" -
_$ /TYPE=(WRITE,TRAP)/ADDRESS=ip_address
|
where ip_address is the address where you want the trap message
to be delivered; for example, 16.32.80.97.
- You can send SNMP Version 2 traps by adding a line to the
SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP] TCPIP$VMS_SNMP_CONF.DAT
file for each Version 2 trap destination using the following format
of the trap option:
trap v2c community <ip-address[:port]>
|
where, community specifies the community name, ip_address specifies
the ip-address of host that is listening for traps and port specifies
the port number. The default port number is 162.
- If your system management tool does not understand SNMP Version 2.0
traps, you need to explicitly enable Version 1.0 format SNMP trap packets.
Do this by following these lettered steps:
Note
If you use Systems Insight Manager to manage SNMP events on
your network, you do not need to enable SNMP V1.0 traps as
described below. |
- Set the default to the directory where you want to create the
file:
$ SET DEFAULT SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]
|
- Create the TCPIP$VMS_SNMP_CONF.DAT file, and edit it to include
the following line:
trap v1 elmginkgo <ip-address[:port]>
|
where ip_address is the port where you want the trap notification
to be sent; for example, 16.32.80.97
- Set the owner and protection on this file as follows:
$ SET FILE/OWNER_UIC=[TCPIP$AUX,TCPIP$SNMP] -
_$ /PROT=(W:RE,G:RE,O:RWED,S:RWED) -
_$ TCPIP$VMS_SNMP_CONF.DAT
|
- To verify that your configuration is correct, review the output from
the following command:
$ TCPIP SHOW CONFIGURATION SNMP/FULL
|
The display should be similar to the following:
SNMP Configuration
Flags: Sets
Contact: test
Location not defined
Community Type Address_list
public Read 0.0.0.0
elmginkgo Read Write Trap 16.32.80.97, 127.0.0.1
|
- Enter the following commands to stop and restart SNMP:
| On systems using TCP/IP, enter: |
$ @SYS$MANAGER:TCPIP$SNMP_SHUTDOWN
|
$ @SYS$MANAGER:TCPIP$SNMP_STARTUP
|
- Next, follow the common steps for enabling sets and traps in the Section
2.4.
2.2 - Steps for Enabling Set and SNMP Traps
When Using Multinet
To Enable SNMP sets and Traps on Multinet follow these steps:
- Add the following write community to the file MULTINET:SNMPD.CONF
for Insight Management Agents to set the SNMP data:
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1
READ
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1 WRITE
community elmginkgo <ip address 1> READ
community elmginkgo <ip address 1> WRITE
community elmginkgo <ip address 2> READ
community elmginkgo <ip address 2> WRITE
�
community elmginkgo <ip address n> READ
community elmginkgo <ip address n> WRITE
|
where "IP address 1", "IP address 2", . . ., "IP address n" is
the IP address configured on the OpenVMS system on each of the NIC interface.
If you want to send a Trap to a system, you need to do the following:
Add the following line to Multinet:SNMPD.CONF:
community
elmginkgo <IP address of target system> TRAPS
|
where "IP address of target system" , is the system which
receives the Traps. If the Trap needs to be received on the local
system, then add the following line:
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1 TRAPS
|
Add the following line to SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]TCPIP$VMS_SNMP_CONF.DAT:
|
config trap v1 elmginkgo <IP address of target system>
|
where "IP address of target system", is the system which
receives the Traps. If the traps needs to be received on the local
system, then add the following line:
config
elmginkgo traps 127.0.0.1
|
Add the following line to SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]TCPIP$SNMP_CONF.DAT:
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1 write
|
- Stop the HR_MIB process by executing the following command:
Restart the Multinet SNMP services as described in the Multinet Install
and Admin Guide (Configuring Multinet SNMP Services section).
Start the HR_MIB process by the executing the following command:
|
$ RUN/PROCESS=HR_MIB SYS$SYSTEM:TCPIP$HR_MIB
|
Next, follow the common steps for enabling sets and traps in the Section
2.4.
2.3 - Steps for Enabling Set and SNMP Traps
When Using TCPWare
To Enable SNMP sets and Traps on TCPWare follow these steps:
- Add the following write community to the file TCPWARE:SNMPD.CONF
for Insight Management Agents to set the SNMP data
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1
READ-WRITE
community elmginkgo <ip address 1> READ-WRITE
community elmginkgo <ip address 2> READ-WRITE
�
community elmginkgo <ip address n> READ-WRITE
|
where "IP address 1", "IP address 2", . . ., "IP address n" is
the IP address configured on the OpenVMS system on each of the NIC
interface.
If you want to send a Trap to a system, you need to do the following:
Add the following line to TCPWARE:SNMPD.CONF:
|
community elmginkgo <IP
address of target system> TRAPS
|
where IP address of target system"", is the system which
receives the Traps. If the Trap needs to be received on the local
system, then add the following line:
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1 TRAPS
|
Add the following line toSYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]TCPIP$VMS_SNMP_CONF.DAT
:
|
config trap v1 elmginkgo <IP address of target system>
|
where "IP address of target system", is the system which
receives the Traps. If the traps needs to be received on the local
system, then add the following line:
|
config elmginkgo traps 127.0.0.1
|
Add the following line to SSYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]TCPIP$SNMP_CONF.DAT:
|
community elmginkgo 127.0.0.1 write
|
- Stop the HR_MIB process by executing the following command:
Restart the TCPWare SNMP services as described in the TCPWare Installation
and Configuration Guide (Configure SNMP Services section).
Start the HR_MIB process by the executing the following command:
|
$ RUN/PROCESS=HR_MIB SYS$SYSTEM:TCPIP$HR_MIB
|
Next, follow the common steps for enabling sets and traps in the Section
2.4.
2.4 - Common Steps for Enabling Sets and Traps
Regardless of your TCP/IP product (TCP/IP, MultiNet or TCPware), complete
the following steps:
- Edit the file SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM.WEBAGENT]WEBAGENT.INI. In
the last line of the file, remove no from the word noelmginkgo,
so that the line reads as follows:
IDS_SNMP_WRITE_COMMUNITY=elmginkgo
|
Note
The user should have SYSTEM privileges to edit the WEBAGENT.INI
file. |
- If you are running the Management Agents for OpenVMS, enter the following
command to stop the application:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$SHUTDOWN.COM
|
- Start the Management Agents for OpenVMS application by entering the
following command:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$STARTUP.COM
|
- From a web browser, connect to the system as described in Section
1, Getting Started, and then do the following to set thresholds:
- Click User.
- To set a trap, log in using an OpenVMS account, that has WBEM$ADMIN
identifiers granted to it and OK.
- Click the Management Agents for OpenVMS icon.
- Click File System Space Used, CPU Utilization or Memory
Utilization.
- Click Help for instructions in how to set thresholds
for traps.
You can view a trap in any one of the following ways:
- If you are using Systems Insight Manager, at the top of the window
under Uncleared Events, click the event displayed
in red.
- If you are not using Systems Insight Manager and would like to view
the traps on the OpenVMS system with HP TCPIP stack, run the following
program:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:TCPIP$SNMP_TRAPRCV.EXE
|
- To view a system from the Systems Insight Manager, follow these steps:
- In the Systems Insight Manager window, select Options => Discovery
=> Automatic Discovery and add the IP address of the system
into the IP address Inclusion range.
- Click Save to save the Changes, or Save
and Run to make the change immediately.
2.5 - Steps for using different write Community
Name
The default write community name is elmginkgo. If for some
reason, you want to use a different community name, follow the instructions
listed below.
- Shutdown the Insight Management Agents:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$SHUTDOWN.COM
|
- Edit the last line of the file SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM.WEBAGENT]WEBAGENT.INI,
replacing new_name with the new name you choose:
IDS_SNMP_WRITE_COMMMUNITY=new_name
|
- If you are using HP TCPIP:
- To remove the "elmginkgo" community use the following
command:
$
TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP /NOCOMMUNITY="elmginkgo"
|
- Follow the "Steps for Enabling Set and SNMP Traps When Using
HP TCP/IP"and "Common Steps for Enabling Sets and Traps" sections
of the user guide, by replacing the name "elmginkgo" to
the new name you choose.
- Refer to the "HP TCPIP Services for OpenVMS Management Manual" for
further instructions, on SNMP configuration and "HP TCP/IP
Services for OpenVMS Management Command Reference Manual" for
Instruction on using "TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP" command.
- If you are using Multinet:
- Follow the "Steps for Enabling Set and SNMP Traps When Using
Multinet" and "Common Steps for Enabling Sets and Traps" sections
of the user guide, by replacing the name "elmginkgo" to
the new name you choose.
-
If you are using TCPWare:
Follow the "Steps for Enabling Set and SNMP Traps When Using Multinet" and "Common
Steps for Enabling Sets and Traps" sections of the user guide,
by replacing the name "elmginkgo" to the new name you choose.
- Start the Insight Management Agents:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$STARTUP.COM
|
- If you are using System Insight Manager, to monitor the OpenVMS system,
you also need to specify the new write community in System Insight
manager, On System Insight Manager, Select All systems and Select the
OpenVMS system. Use the Tools & Links Tab -> System Protocol
Settings and change the "SNMP settings" write community,
to the new write community name.
3 - Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
This section contains the following subsections:
3.1 - Introduction to the Secure HTTP Server for OpenVMS
The Management Agents for OpenVMS allows you to view subsystem and status
information from a Web browser, either locally or remotely. Version 3.4
of the Management Agents for OpenVMS uses security features for the HTTP
Server, including OpenVMS account login using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL),
certificates, and Operating System authentication.
To view data locally, use one of the following URLs:
or
To view data remotely, use this URL:
For host, substitute the name of the machine or the IP address.
Note
Notice that the URL is followed by ":2381". This is the
secure port or socket number that the HP Management Agents for
OpenVMS use to communicate with the browser. If this number is
not specified, your browser might attempt to connect to another
Web page if the managed server is running a Web Server. |
3.1.1 - HP HTTP Server First-Time Initialization
During first-time initialization, the HTTP Server creates a private
key and a corresponding self- signed X.509 Certificate.
Note
This initialization occurs only the first time the HTTP Server
initializes or after an administrator deletes the private key and
corresponding certificate. |
This certificate is a base64 encoded PEM file named CERT.PEM. The certificate
is stored on the file system in the following location:
$ SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM]CERT.PEM
|
The subdirectory SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM] also contains the private
key. To protect the key, only administrators can access this subdirectory.
If, for any reason, you feel that the private key has been compromised
and you want to generate a new private key and certificate, an administrator
can delete the file SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM]CERT.PEM and then restart
the server. This causes the HTTP server to generate a new certificate
and private key.
3.1.2 - Logging in to Servers
The Login page allows you to access any of the available Web-enabled
services. You can access the desired Web-enabled services by following
the steps in either section 3.1.2.1, Internet Explorer Version 5.0 or
later or section 3.1.2.2, Netscape Version 4.73 or later and Mozilla
Version 0.96 or later.
3.1.2.1 - Internet Explorer Version 5.02 or later
- After you enter the URL https://devicename:2381, Internet Explorer
displays the Security Alert dialog box shown in Figure 1 every time
you connect to it. If you enter port 2301, the port used in previous
versions of the Management Agents, you are directed automatically to
port 2381.
Note
The Security Alert dialog box is displayed as shown in Figure
1. You are required to accept certificates to log in.
If you want to implement your own Public Key Infrastructure
(PKI) or install your own generated certificates in each
managed device, you can install a Certificate Authority Root
Certificate in each browser to be used for management. If
you do this, the Security Alert dialog box shown in Figure
1 is not displayed. You can refer to your browser's online
help for more information about installing the Certificate
Authority Root Certificate. |
Figure 1 - Security Alert Dialog Box
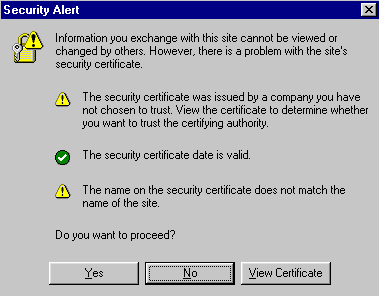
- Click the Yes button. The HP WBEM Login page will
be displayed as shown in the Figure 2.
Figure 2 - HP WBEM Login Dialog Box
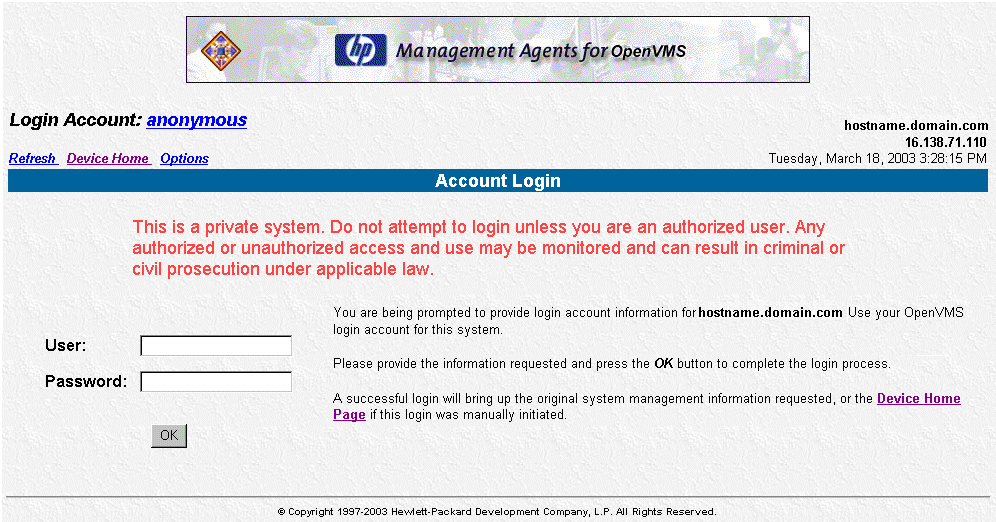
- Enter the OpenVMS user name in the User field.
The accounts of the system you are logging into map to the system's
OpenVMS accounts. See Section
3.5, Configuring Users and Groups, for more information.
- Enter the OpenVMS password1 in the Password field.
- Click the OK button. The HP WBEM Device Home page
will be displayed.
3.1.2.2 - Netscape Version 4.73 or later and Mozilla Version 0.96
or later
- After you enter the URL https://devicename:2381, Netscape or Mozilla
displays the New Site Certificate dialog box shown in Figure 3 the
first time you connect to it. If you enterport 2301, the port used
in previous versions of the Management Agents, you are directed automatically
to port 2381.
The steps in this section apply in general to Netscape and most
implementations of the Mozilla browser. However, there may be minor
differences depending on the specific version of browser you use.
Note
The New Site Certificate dialog box is displayed as shown in
Figure 3. You are required to accept certificates in order
to log in.
If you want to implement your own Public Key Infrastructure
(PKI) or install your own generated certificates on each
managed device, you can install a Certificate Authority Root
Certificate in each browser to be used for management. If
you do this, the New Site Certificate dialog box shown in
Figure 3 is never displayed. Refer to your browser's online
help for more information about installing the Certificate
Authority Root Certificate. |
Figure 3 - New Site Certificate Dialog Box
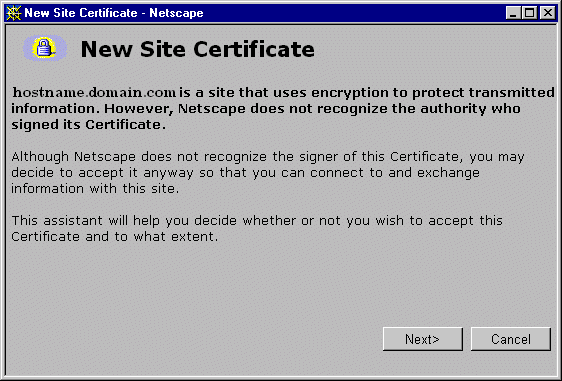
- Click the Next button and follow the on-screen instructions
to accept the New Site Certificate.
If you choose Accept this certificate forever (until it expires),
this dialog box is not displayed the next time you open Netscape
and attempt to view this page. You will be directed to Login page
instead.
After you accept the new site certificate, the Login Page is displayed.
Figure 4 - HP WBEM Login Dialog Box

- Enter the OpenVMS user name in the User field.
The accounts of the system you are logging into map to the system's
OpenVMS accounts. See Section
3.5, Configuring Users and Groups, for more information.
- Enter the OpenVMS password1 in the Password field.
- Click the OK button. The HP WBEM Device Home page will be
displayed.
3.2 - Device Home Page
The Device Home Page is the first page displayed when you access the
device at port 2381 after you login. This page displays available Web-enabled
services.
Anonymous access to information is available without logging in if the
administrator turns that option on in the Device Options web page. To
go to the Device Options web page, select the Options link.
To log in as a different user, select the Login Account link (which
will be only "user", "administrator" or "anonymous").
The login screen is displayed. See Section
3.4, Security, for more information about user accounts.
Figure 5 - Device Home Page
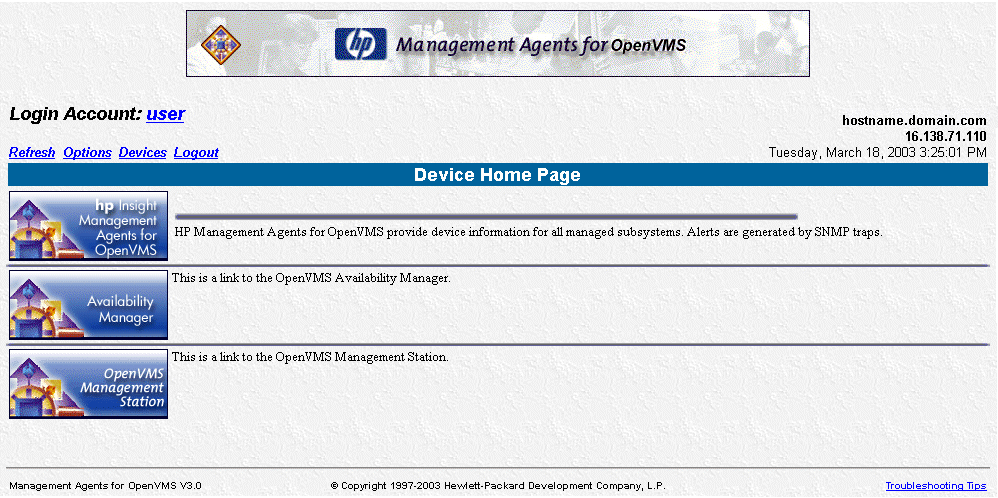
The following options are available on the Device Home Page:
Note
Other web-enabled options may appear. |
- HP Insight Management Agents for OpenVMS
Select this link to view Subsystem and Status Information about
a device that is running the Management Agents for OpenVMS.
- OpenVMS DCL Show Commands
Select this link to view the DCL SHOW page, which provides information
about the current status of the system, as well as the users, memory,
cluster, CPUs, devices and Virtual I/O cached memory on the system.
- Availability Manager
Select this link to view more information about the Availability
Manager.
- OpenVMS Management Station
Select this link to view more information about the OpenVMS Management
Station.
- Login Account
Select the corresponding link ("user", "administrator" or "anonymous")
to change the Login account.
- Refresh
Select this link to reload the device information displayed on the
Device Home Page.
- Options
Select this link to set attributes for the Management Agents for
OpenVMS access and the HTTP server.
- Devices
Select this link to display the Device list.
- Logout
Select this link to log out of the Device Home Page.
- Troubleshooting Tips
Select this link to view Troubleshooting Tips.
3.3 - Configuring the Device Home Page
Options Page
The Options page allows you to change various Management Agents for
OpenVMS settings. The Options page is accessed from the Device Home Page
by clicking the Options hyperlink. The available options are divided
into three groups under Page Sections, as shown in Figure 6:
- Configuration Options
- Trusted Certificates
- Customer Generated Certificates
Note
If you have administrator privileges, you can click the Save
Configuration or Default Configuration buttons. If
you have user privileges, then you will have Read Only Access. |
Figure 6 - Page Sections

Configuration Options
The Configuration Options section allows you to select the appropriate
settings:
- Anonymous Access
Anonymous Access is disabled by default. Enabling Anonymous Access
allows a user to access the Management Agents for OpenVMS without logging
in.
To enable Anonymous Access:
- Select the Anonymous Access checkbox on the Configuration Options
page.
- Click the Save Configuration button in the Configuration
Options section to save your settings. The Configuration Options
page will be refreshed.
- Local Access
Set up the HTTP Server to automatically configure local IP addresses
as part of the selected group. This means that any user with access
to the local console is granted full access if Administrator is selected,
or is granted limited access to unsecured pages if Anonymous is selected,
without being challenged for a username and password.
- Auto Delete Users
Select the checkbox to automatically delete user directories that
have not been accessed for a given time frame. This allows you to retain
information about active users, and delete old information about inactive
users.
To set the Auto Delete Users option:
- Select the Auto Delete Users checkbox.
- In the field provided, specify the number of days you want to keep
information before deleting the cached data for an unused login.
Note
The cached data referred to in Step this st ep is not needed
and will regenerate automatically if it is ever needed in
the future. |
- Click the Save Configuration button in the Configuration
Options section to save your settings. You can click the Default
Configuration button to return all options to their original
settings.
- Logging
Logging allows you to specify the types of log entries you want to
record, and whether you want to write to the log at all.
To set the Logging options:
- Select the Logging checkbox to record information in the log file.
- Select the types of logs to be recorded.
- Click the Save Configuration button in the Configuration
Options section to save your settings.
- IP Restricted Logins
The HTTP Server can restrict login access based on the IP address
of the machine from which the login is attempted. These restrictions
apply only to direct login attempts and not to logins attempted as
part of a trusted Systems Insight Manager server's Single Login or
Secure Task Execution features.
IP addresses can be explicitly excluded or explicitly included for
each type of user. If an IP address is explicitly excluded, it will
be excluded even if it is also explicitly included. If any IP addresses
are in the inclusion list, then only those IP addresses will be allowed
login access. If no IP addresses are in the inclusion list, then login
access will be allowed from any IP addresses not in the exclusion list.
IP address ranges list with the lower end of the range followed by
a hyphen followed by the upper end of the range. All ranges are inclusive
in that the upper and lower bounds are considered part of the range.
IP address ranges and single addresses are separated by semi-colons.
Enter IP address ranges in the following format: 122.23.44.1-122.23.44.255;172.84.100.35;127.0.0.0-127.0.0.255
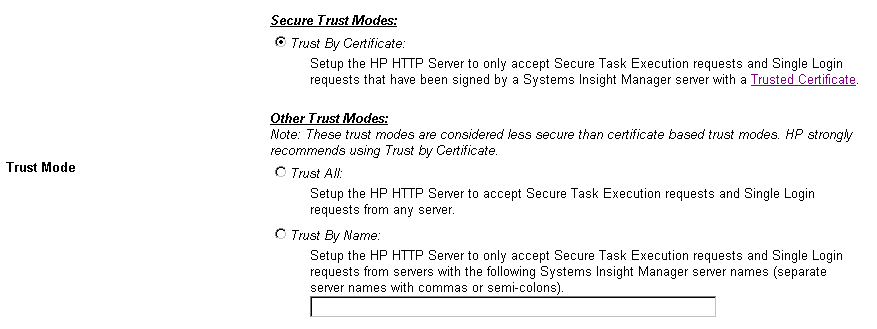
- Trust Mode
The Trust Mode option allows you to select the security required by
your system. Some situations require a higher level of security than
others, so you are given the options shown in Figure 7.
The following Trust Mode options are available:
- Trust All
- Trust By Name
- Trust By Certificate
Figure 7 - Trust Mode
Note
You can click the Default Configuration button
located in the Configuration Options section to return all options
to their original settings. |
- Trust By Name
The Trust By Name mode sets up the HTTP Server to accept only
certain requests from servers with the Systems Insight Manager
names designated in the Trust By Name field. The Trust By Name
option is easy to configure, and prevents non-malicious access.
You might want to use Trust By Name if you have a secure network
but your network has two groups of administrators in two separate
divisions. Trust By Name would prevent one group from changing
settings on the wrong system. This option does not verify anything
other than the Systems Insight Manager server name submitted. To
use the Trust by Name option:
- Select the Trust By Name option.
- Enter the name of the server you want to allow access. If you
want to trust more than one Systems Insight Manager servers,
you can separate the server names with a semi-colon.
Note
Although Trust By Name mode is a slightly stronger method
of security than the Trust All mode, it still leaves
your system vulnerable to security attacks. |
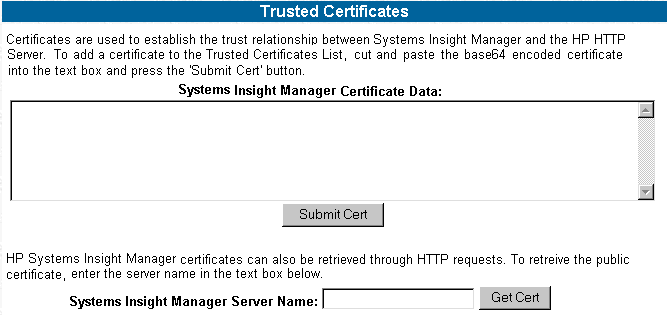
- Trust By Certificate
The Trust by Certificate mode will sets up the HTTP Server to only
accept only certain requests from Systems Insight Manager servers
with Trusted Certificate as shown in Figure 8. This mode will requires
the submitted server to provide authentication by means of certificates.
This mode is the strongest method of security, because it requires
certificate data before allowing access.
Figure 8 - Trusted Certificates
To use the Trust by Certificate option:
- In the Systems Insight Manager Server Name field, enter the name
of the server from which you want to receive a certificate.
- Click the Get Cert button. The certificate data is displayed.
- Click the Options hyperlink. The bottom of the
page should display the Systems Insight Manger servers you currently
trust. You can click the View Certificate hyperlink associated
with the Systems Insight Manager server to view certificate information
related to that server.
Note
If Systems Insight Manager is reinstalled or has regenerated a
certificate, you must remove the trusted servers and start again
with Step 1. |
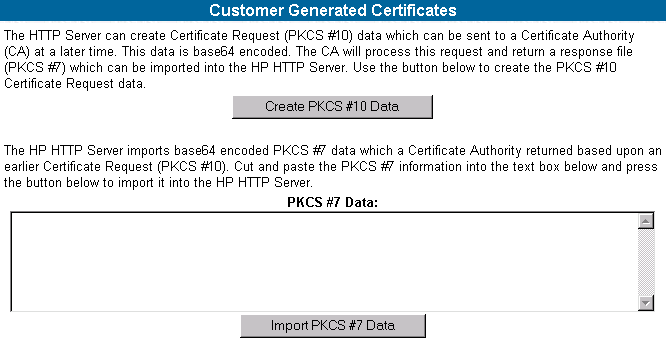
Customer Generated Certificates
The Customer Generated Certificates option allows you to use certificates
that are not generated by HP. If you select this option, the self-signed
certificate that was originally generated by the HTTP Server is replaced
with one that was issued by a Certificate Authority. The first step of
the process is to have the HTTP Server create a Certificate Request (PKCS
#10). This request utilizes the original private key that was associated
with the self-signed certificate and generates the appropriate data for
certificate request.
Note
The private key never leaves the server during this process. |
After the PKCS #10 data has been created, you need to send that data
off to a Certificate Authority. After the Certificate Authority has returned
PKCS #7 data, you need to import this into the HTTP Server. After the
PKCS #7 data has been successfully imported, the original certificate
file certificate SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM]CERT.PEM is overwritten with
the device's from that PKCS #7 envelope. The same private key is used
for the new imported certificate as well as for the previous self-signed
certificate.
Figure 9 - Customer Generated Certificates
To use the Customer Generated Certificates option:
- Click the Create PKCS #10 Data button. A screen
is displayed indicating that the PKCS #10 Certificate Request data
has been successfully generated.
- Copy the certificate data by copying the data.
- Send PKCS #10 certificate request data to a Certificate Authority
and ask to have the certificate request reply data sent in PKCS #7
format. Request that the reply data be in base64 encoded format. If
your organization has its own PKI/Certificate Server send the PKCS
#10 data to the Certificate Authority manager and request the PKCS
#7 reply data.
Note
The selected certificate signer generally charges a fee. |
3.4 - Security
The Management Agents for OpenVMS allows SNMP SET's for some system
parameters. This capability requires you to configure OpenVMS user accounts
to map to the Management Agents administrator and user accounts. See Section
3.5, Configuring Users and Groups, for more information.
There are two types of data: Default (read only) and Sets (read/write).
The WEBAGENT.INI file located in the SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.WEB.IM.WEBAGENT]
directory specifies the level of user who has access to data.
The "read=" and "write=" entries in the WEBAGENT.INI
file set the user accounts required for access, where: 0 = No access,
1 = Anonymous, 2 = User, 3 = Operator, and 4 = Administrator. Changing
these entries changes the security of the Web-enabled services.
3.5 - Configuring Users and Groups
You can configure access to the Management Agents for OpenVMS by using
the SYSUAF utility to grant identifiers to users for Insight Manager
groups.
You must grant the identifiers WBEM$ADMIN , which map directly to the
HTTP server's Administrator and Operator accounts. Every user who has
access to the system, including the SYSTEM account, automatically has
user access to the Management Agents running on that system. Anonymous
access is disabled by default.
Note
Do not use a semicolon (;) in the username field. |
To configure access for specific users and groups:
- Log in as SYSTEM on the OpenVMS system.
- Grant the WBEM$ADMIN identifier to users who will have administrator
privileges. In this example, the SYSTEM account is granted administrator
privileges:
UAF> GRANT/IDENTIFIER WBEM$ADMIN SYSTEM
|
- All other users have the user privilege, even if it has not been
explicitly granted
Note
On a cluster, you need to perform this step only once for OpenVMS
user accounts that are visible across the cluster. The privileges
are automatically available to all nodes on the cluster. |
4 - Troubleshooting Tips
This section contains the following categories of troubleshooting tips:
4.1 - System Requirements for Running the Software
The system requirements for the Management Agents for OpenVMS are the
following:
- HP Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) : Version 1.2 or updates to this version
on OpenVMS
V7.3-2, V8.2 and V8.2-1 and Version 1.3 or updates to this version
on OpenVMS V8.3.
Note
For more information about HP Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), refer
to the HP SSL Installation Guide and Release Notes. |
- Compaq or HP TCP/IP : Version 5.1 or later for OpenVMS Alpha
and Version 5.5 or later for OpenVMS I64.
- A supported web browser
Process Software's MultiNet TCP/IP Version 4.3 for OpenVMS or later
and TCPware TCP/IP Version 5.5 for OpenVMS or later are also supported.
4.2 - Browser Requirements
The browser you use with the Management Agents for OpenVMS must have
the following features supported and enabled:
- HTML tables
- HTML frames
- JavaScript
- Accept all cookies
- Full Java Development Kit 1.1 (JDK 1.1) or later support
- Dynamic HTML
4.3 - Browser Recommendations
Recommendations of browsers to use with the Management Agents are the
following:
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.02 or later
- Netscape Navigator 4.73 or later
- HP Secure Web Browser for OpenVMS Alpha 0.96 or later (Mozilla)
Note
If you are using HP Secure Web Browser, you must install the
Java plugins SDK Version 1.3.1-2 or later for OpenVMS Alpha
and 1.4.2-3 or later for OpenVMS I64.
For more information about HP Secure Web Browser, refer
to the following URL:
http://www.mozilla.org/releases
|
|
Additional browsers, or the browsers mentioned if used with different
operating systems, might or might not work correctly, depending upon
their specific implementations of the required browser technologies.
2 Internet Explorer
6.0 or later is recommended for better results.
4.4 - Known Browser Issues
The following are some known issues in using a browser with the Management
Agents for OpenVMS:
- If you use a proxy server to access the Internet and you are unable
to access a machine that has web-enabled agents installed with a URL
such as https://127.0.0.1:2381/ or https://125.12.18.36:2381/,
try adding the address to the No Proxy list in the browser.
- Internet Explorer does not print background colors and images by
default.
- When switching from a web agent browser window to another application,
you might see the colors in the browser window change or flash. This
is not specific to the web agent window but might happen when you look
at other pages with a browser under the same conditions.
- Frame sizes are optimized for "medium" fonts. If you switch
your browser to use larger or smaller fonts, you must use the mouse
to manually adjust the frame layout.
- A JavaScript error can occur when you resize the browser window in
Netscape Navigator.
- A JavaScript error can occur when you try to print certain pages
in Netscape Navigator.
- If you use HP Secure Web Browser (Mozilla) or Netscape Version 6.2
and later and attempt to log in as a different user, the login screen
re- appears with the new user name listed instead of the Device Home
Page. If this happens, click the "Device Home Page" link
displayed on the page to manually switch to the device page.
- With Internet Explorer 5.5 and update version SP1;Q288993; Q290108;
Q299618, manually refreshing the utilization pages may cause the WBEM$SERVER
process to hang. Upgrading to Internet Explorer 5.5 SP2 solves this
problem.
4.5 - Viewing Cluster Agents
To view OpenVMS clusters from Systems Insight Manager, you need to perform
the following sets of steps:
On an OpenVMS Cluster
- Ensure that the Management Agents for OpenVMS are running by executing
the following DCL command:
Verify that the process WBEM$SVRCLU is listed.
On Systems Insight Manager
- Add the IP address of the OpenVMS Cluster to the address range for
Auto detection.
- Select Menu => Options => Security => Users and Authorizations
tab and add a New Authorization Entry to the users, for the cluster
system.
- Each user will obtain access to the cluster, which can be monitored
using the Cluster Monitor (Tools => System Information
=> Cluster Monitor).
Refer to online help on the Systems Insight Manager pages for details.
4.6 - Troubleshooting Questions and Answers
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions.
| Q: |
I
cannot delete the operator.log and create a new operator log when
Insight Management Agents for OpenVMS is running |
| A: |
Shutdown the Insight Management Agents
for OpenVMS before deleting/ recreating the operator log file. The
Insight Management Agents for OpenVMS can be started, after the new
operator log is created. For example:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$SHUTDOWN
$ ! Delete/recreate the new operator.log
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$STARTUP |
| |
|
| Q: |
I can access the Device Home Page, but
I can't access the URL pointed to by the "Management Agents
for OpenVMS" logo. |
| A: |
Check the "Language Preference Window" in
your Internet Explorer setup (Tools => Internet Options => Language).
The Management Agents for OpenVMS expects your first language selection
to be "English." |
| |
|
| Q: |
Why does the "Version" display
indicate Version 5.5? |
| A: |
Version 5.5 is the MIB level that the HP
SNMP subagents support. The version of the Management Agents for
OpenVMS kit you are using is not the same as the version of the MIB
that is supported. You can find the version of your kit at the bottom
of the Device Home Page, next to the copyright notice. |
| |
|
| Q: |
One of my subagents (MIBs) is not running. |
| A: |
Define a foreign command and use TRACE
to give an indication of failure. For example:
$ STORAGE :== $SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM.AGENTS]CPQSTORAGE_MIB.EXE
$ STORAGE -TRACE
If this does not help you debug the subagent, mail the output
of these commands to HP Technical Support. (The address is provided
at the end of this section.)
Note, however, that the WBEM$SVRCLU subagent runs only on clustered
systems. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I can access the Device Home Page, but
no links to agents are on the page. Why? |
| A: |
This occurs if JavaScript is not supported
or enabled. If you are using a recommended browser, ensure that JavaScript
is enabled. |
|
|
| Q: |
When I try to log in, I get a Java error,
and I am not prompted for account and password. Why? |
| A: |
This occurs if the browser does not fully
support JDK 1.1 or later Java applets or if Java support has been
disabled. Ensure that Java support is enabled in the browser. If
it is not, upgrade to a browser that fully supports JDK 1.1 or later
Java applets. |
| |
|
| Q: |
Is there an easier way to access the local
device with my browser without having to find out its IP address? |
| A: |
Yes. You can access the local device at https://host:2381;
for example, https://127.0.0.1:2381. Also, if you have a
proxy server configured in your browser, you might need to add the
host (for example, 127.0.0.1) to the list of addresses that
should NOT be proxied. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I can successfully access some web-enabled
devices, but I cannot access others. Why? |
| A: |
If your browser has a proxy server configured,
you must enter the address of the web-enabled device in the list
of addresses that should NOT be proxied. |
| |
|
| Q: |
When I access a device, I am prompted many
times to accept cookies. Why? |
| A: |
Browser cookies are required to keep track
of user state and security. Enable cookies in the browser, and disable
prompting for acceptance of cookies. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I entered a valid account and password
to change my access level. It was accepted, but the web page still
indicates that I have only Anonymous access. Why? |
| A: |
This can occur if browser cookies are disabled.
Enable cookies in the browser. They are required for security. |
| |
|
| Q: |
Leaving my browser undisturbed for a while
prompted for login. I entered a valid account and password, but still
the login was rejected. Why? |
| A: |
This can occur if browser cookies are disabled.
Enable cookies in the browser. They are required for security. This
will allow you to log in to your system. |
| |
|
| Q: |
The Management Agents appear to hang on
the Summary page or sometimes on the Device Home Page; at other times,
I keep getting a login prompt even after I enter login information. |
| A: |
You must have a public read community
defined. Here is how to do that:
First determine your SNMP settings:
TCPIP> SHOW CONFIGURATION SNMP
You should see a display similar to the following:
SNMP Configuration
Flags:
Contact: test
Location not defined
Community Type
public Read
If you do not see a Community "public" with type Read,
set one up by entering the following:
$ TCPIP SET CONFIGURATION SNMP/COMMUNITY="public"/TYPE=READ
|
| |
|
| Q: |
Sometimes I cannot get the agents to run;
at other times, I get a login prompt even after I enter login information. |
| A: |
If you have the Version 1.0 product installed
and you entered a POLYCENTER Software Installation (PCSI) PRODUCT
REMOVE command, PCSI does not remove all the files that the V1.0
product created. You must delete the files and reinstall the V3.3
kit as follows:
- Stop any running agents from the account in which they were
started. For versions prior to Version 2.0, enter the following
command:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]STOP_WEBAGENTS
For Version 2.1 and later, enter the following command:
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$SHUTDOWN
Use the DCL command $ SHOW SYSTEM to make sure the agents
are stopped.
- Delete everything in the SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM...] directory.
- Reinstall Version 3.3 (refer to the Installation Guide).
|
| |
|
| Q: |
I keep getting Java errors or other display
errors even after I make the suggested fixes. |
| A: |
Follow these steps:
- Clear the cache in your browser. Do this by selecting the Settings
option in Internet Explorer (View or Tools, Internet Options,
Settings, General, and View Files) and deleting any files that
might have been saved.
- Delete the references of cookies from the browser. This is
especially necessary if other changes in your environment were
made and you have not exited from your browser since those changes
were made.
- Verify that you are running a current or supported browser,
or both, that supports dynamic HTML. The Management Agents work
with Microsoft Internet Explorer Version 5.0 or later and with
Netscape Navigator Version 4.73 or later.
|
| |
|
| Q: |
I am getting a PCSI error part-way through
my installation:
The following product will be installed to destination:
COMPAQ AXPVMS V72_MGMTAGENTS V2.0-16 DISK$ALPHASYS-72:[VMS$COMMON.]
Portion done: 0%...10%...20%...30%...40%
%PCSI-E-READERR, error reading
$6$DKA300:[SYS0.][SYSUPD]COMPAQ-AXPVMS-V72_MGMTAGENTS-V0200-16-1.PCSI;1
-DDIS-E-TNF, invalid element syntax
%PCSI-E-OPFAILED, operation failed
Terminating is strongly recommended. Do you want to terminate? [YES]
%PCSI-E-CANCEL_WIP, termination resulted in an incomplete modification to the system
%PCSI-E-S_OPCAN, operation cancelled by request
%PCSIUI-E-ABORT, operation terminated due to an unrecoverable error condition
|
| A: |
You probably have a corrupt kit. Please
copy a new kit to your target machine and try again. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I enter everything to start the Management
Agents for OpenVMS, but it does not run. |
| A: |
Make sure that SNMP is running. |
| |
|
| Q: |
Importing certificates created with certain
SSL tools to the Management Agents for OpenVMS results in one of
the following error messages:
- The certificates are not of base64 encoded format
- Unable to add certificate
|
| A: |
Certificates created using most SSL tools
can be used with the Management Agents for OpenVMS. To add a certificate
to the Trusted Certificates list, cut and paste the base64 encoded
certificate into the text box and press the "Submit Cert" button.
Take care to copy and paste the entire contents of the certificate
including the "--Begin Certificate--" and "--End Certificate--" lines
before pressing the "Submit Cert" button. If the certificate
generated by your tool does not contain the "--Begin Certificate--" and "--End
Certificate--" lines, you need to add them yourself. |
| |
|
| Q: |
Upon using Internet Explorer version 5.5
Service Pack 1 or later with Management Agents Version 3.3 or later
kit, Internet Explorer generates an error message occasionally that
indicates that the page could not be displayed. |
| A: |
Please refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base
Article - 305217 titled "Page Cannot Be Displayed Error During
SSL 3.0 Server Session Timeout" to know more on the cause and
refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base Article - 183110 titled "INFO:
WinInet Limits Connections Per Server" for information on workarounds
available for this problem. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I cannot get into agents from Systems Insight
Manager application or directly through a browser. If connect to
the 2301 port I get the security alert, then the redirect and "Page
cannot be displayed" message on the browser? |
| A: |
Check if DSNLink is installed on the system.
DSN_Tunnel process uses port 2381. Edit the dsn_services.dat file
and change the dsn_tunnel port from 2381 to 12381. Rebuild Worldwide
configuration. Restart WBEM. |
| |
|
| Q: |
Inspite of configuring SNMP and Management
agents on a TCPware or Multinet stack correctly, I find Management
agents don't work correctly? |
| A: |
Check for public community entry in SNMP
configuration file on TCPware or Multinet. The public community entry
in the file snmpd.conf should read as follows: The entries in the
file tcpware:snmpd.conf or multinet:snmpd.conf should be as follows
(Assuming IP address of the target system is 192.168.0.18)
! Communities:
! community <community name> <internet address> <READ-ONLY|READ-WRITE|TRAPS>
!
community public 127.0.0.1 READ-ONLY
|
| Q: |
When trying to login to the Management
agents using either Mozilla or Netscape after I hit OK with a valid
username/password, I don't get directed to the Device Home page? |
| A: |
After you click the OK button, click Device
home to get directed to the Device Home Page. |
| |
|
| Q: |
I have a disk configured as a shadow disk.
The Management Agents provide false alarm (TRAP of Disk/Memory/CPU
utilization) with the Management Agents V3.3 or later kit. |
| A: |
This is due to the solution provided in
the Management Agents V3.3, which displays all the disks connected
to the system, irrespective of it being a member of shadow set or
not. To overcome this, perform the following:
- Delete the SYS$SYSTEM:UCX$MGT_THRESHOLDS.DAT and
SYS$SYSTEM:UCX$MGT_THRESHOLDS.BAK files
$ DELETE SYS$SYSTEM:UCX$MGT_THRESHOLDS.DAT;*
$ DELETE SYS$SYSTEM:UCX$MGT_THRESHOLDS.BAK;*
Note
Deleting the files will reset all the thresholds (Disk/CPU/Memory
Utilization). |
-
Re-start the Insight Management Agents.
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$SHUTDOWN
$ @SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]WBEM$STARTUP
- Reset all the threshold values in the Insight Management Agents.
|
| |
|
Note
When you enter a problem report, the development engineers will
need your configuration and the output of some of the following
commands:
$ PRODUCT SHOW HISTORY/FULL
$ SHOW SYSTEM
$ SHOW PROCESS/QUOTA/ID=(the id for the WBEM$SERVER process)
$ SHOW PROCESS/ACCOUNT/ID=(the id for the WBEM$SERVER process)
$ TCPIP SHOW CONFIGURATION SNMP/FULL
$ INSTALL LIST SYS$SHARE:PCSI$SHR.EXE
$ DIR/PROT SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM...]*.TPL
$ DIR/PROT SYS$SPECIFIC:[000000]WBEM.DIR
$ DIR/PROT SYS$SPECIFIC:[WBEM]*.DIR
$ TCPIP SHOW VERSION/ALL
|
|
If you need additional help, use your normal support channels, or send
email to HP Technical Support at the following URL:
1 Secondary account passwords are not supported. Only the
primary password will be used for authentication, even if a secondary
password has been defined for the user account.
2 Internet Explorer 6.0 or later is recommended for better
results.
5 - Appendix
This section lists all the SNMP MIB Variables (Attributes) and Traps
supported by the Management Agents for OpenVMS Version 3.4.
cpqHealth Agent
Attributes
|
| cpqHeMibRev Group |
cpqHeMibRevMajor
cpqHeMibRevMinor
cpqHeMibCondition |
| cpqHeOsCommon |
cpqHeOsCommonPollFreq |
| cpqHePostMsg |
cpqHePostMsgCondition
cpqHePostMsgIndex
cpqHePostMsgCode
cpqHePostMsgDesc |
| cpqHeThermal |
cpqHeThermalCondition
cpqHeThermalDegradedAction
cpqHeThermalTempStatus
cpqHeThermalSystemFanStatus
cpqHeThermalCpuFanStatus
cpqHeThermalFanIndex
cpqHeThermalFanRequired
cpqHeThermalFanPresent
cpqHeThermalFanCpuFan
cpqHeThermalFanStatus |
| cpqHeTemperature |
cpqHeTemperatureChassis
cpqHeTemperatureIndex
cpqHeTemperatureLocale
cpqHeTemperatureCelsius
cpqHeTemperatureThreshold
cpqHeTemperatureCondition |
| cpqHeFltTolPwrSupply |
cpqHeFltTolPwrSupplyCondit |
| cpqHeCriticalErrorTable |
cpqHeCriticalErrorIndex
cpqHeCriticalErrorStatus
cpqHeCriticalErrorType
cpqHeCriticalErrorTime |
| Traps |
cpqHe3ThermalTempDegraded
cpqHe3ThermalTempOK
cpqHe3ThermalSystemFanFailed
cpqHe3ThermalSystemFanOK
cpqHe3FltTolPwrSupplyDegraded |
cpqHost Agent
| Attributes |
| cpqHoCpuUtilEntry |
cpqHoCpuUtilUnitIndex
cpqHoCpuUtilMin
cpqHoCpuUtilFiveMin
cpqHoCpuUtilThirtyMin
cpqHoCpuUtilHour |
| cpqHoFileSysTable |
cpqHoFileSysIndex
cpqHoFileSysDesc
cpqHoFileSysSpaceTotal
cpqHoFileSysSpaceUsed
cpqHoFileSysPercentSpaceUsed |
| cpqHoInfo |
cpqHoName
cpqHoVersion
cpqHoDesc
cpqHoOsType
cpqHoTelnet |
| cpqHoMibRev |
cpqHoMibRevMajor
cpqHoMibRevMinor
cpqHoMibCondition |
| cpqHoOsCommon |
cpqHoOsCommonPollFreq |
| cpqHoSWRunning Table |
cpqHoSWRunningIndex
cpqHoSWRunningName
cpqHoSWRunningDesc |
| cpqHoSwVerTable |
cpqHoSwVerIndex
cpqHoSwVerName
cpqHoSwVerDescription
cpqHoSwVerLocation
cpqHoSwVerVersion |
| cpqHoSystemStatus |
cpqHoMibStatusArray |
cpqStore Agent
| Attributes |
| IDE |
| cpqIdeMibRev |
cpqIdeMibRevMajor
cpqIdeMibRevMinor
cpqIdeMibCondition |
| cpqIdeOsCommon |
cpqIdeOsCommonPollFreq |
| SCSI |
| cpqScsiCntlrTable |
cpqScsiCntlrIndex
cpqScsiCntlrBusIndex
cpqScsiCntlrModel
cpqScsiCntlrSlot
cpqScsiCntlrStatus
cpqScsiCntlrCondition
cpqScsiCntlrSerialNum
cpqScsiCntlrBusWidth |
| cpqScsiMibRev |
cpqScsiMibRevMajor
cpqScsiMibRevMinor |
| cpqScsiOsCommon |
cpqScsiOsCommonPollFreq |
| cpqScsiOsCommonModuleTable |
cpqScsiOsCommonModuleIndex
cpqScsiOsCommonModuleName
cpqScsiOsCommonModulePurpose |
| cpqScsiPhyDrvTable |
cpqScsiPhyDrvCntlrIndex
cpqScsiPhyDrvBusIndex
cpqScsiPhyDrvIndex
cpqScsiPhyDrvModel
cpqScsiPhyDrvFWRev
cpqScsiPhyDrvVendor
cpqScsiPhyDrvSize
cpqScsiPhyDrvScsiId
cpqScsiPhyDrvStatus
cpqScsiPhyDrvHighReadSectors
cpqScsiPhyDrvLowReadSectors
cpqScsiPhyDrvHighWriteSectors
cpqScsiPhyDrvLowWriteSectors
cpqScsiPhyDrvHardReadErrs
cpqScsiPhyDrvSeekErrs
cpqScsiPhyDrvUsedReallocs
cpqScsiPhyDrvCondition
cpqScsiPhyDrvSerialNum
cpqScsiPhyDrvLocation
cpqScsiPhyDrvParent
cpqScsiPhyDrvSectorSize
cpqScsiPhyDrvHotPlug
cpqScsiPhyDrvPlacement |
| cpqScsiTargetTable |
cpqScsiTargetCntlrIndex
cpqScsiTargetBusIndex
cpqScsiTargetScsiIdIndex
cpqScsiTargetType
cpqScsiTargetModel
cpqScsiTargetFWRev
cpqScsiTargetVendor
cpqScsiTargetLocation
cpqScsiTargetPhyWidth |
| Fiber Channel |
cpqFcaCntlrBoxIndex
cpqFcaCntlrBoxIoSlot
cpqFcaCntlrModel
cpqFcaCntlrFWRev
cpqFcaCntlrStatus
cpqFcaCntlrCondition
cpqFcaCntlrProductRev
cpqFcaCntlrWorldWideName
cpqFcaCntlrSerialNumber
cpqFcaCntlrCurrentRole
cpqFcaCntlrRedundancyType
cpqFcaCntlrRedundancyError |
cpqFcaPhyDrvBoxIndex
cpqFcaPhyDrvIndex
cpqFcaPhyDrvModel
cpqFcaPhyDrvFWRev
cpqFcaPhyDrvBay
cpqFcaPhyDrvStatus
cpqFcaPhyDrvUsedReallocs
cpqFcaPhyDrvRefHours
cpqFcaPhyDrvHReads
cpqFcaPhyDrvReads
cpqFcaPhyDrvHWrites
cpqFcaPhyDrvWrites
cpqFcaPhyDrvHSeeks
cpqFcaPhyDrvSeeks
cpqFcaPhyDrvHardReadErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvRecvReadErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvHardWriteErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvRecvWriteErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvHSeekErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvSeekErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvSpinupTime
cpqFcaPhyDrvFunctTest1
cpqFcaPhyDrvFunctTest2
cpqFcaPhyDrvFunctTest3
cpqFcaPhyDrvOtherTimeouts
cpqFcaPhyDrvBadRecvReads
cpqFcaPhyDrvBadRecvWrites
cpqFcaPhyDrvFormatErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvNotReadyErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvHasMonInfo
cpqFcaPhyDrvCondition
cpqFcaPhyDrvHotPlugs
cpqFcaPhyDrvMediaErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvHardwareErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvAbortedCmds
cpqFcaPhyDrvSpinUpErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvBadTargetErrs
cpqFcaPhyDrvSize
cpqFcaPhyDrvBusFaults
cpqFcaPhyDrvHotPlug
cpqFcaPhyDrvPlacement
cpqFcaPhyDrvBusNumber
cpqFcaPhyDrvSerialNum
cpqFcaPhyDrvPreFailMonitoring
cpqFcaPhyDrvCurrentWidth
cpqFcaPhyDrvCurrentSpeed |
| Traps |
| cpqScsiphydrvStatuschange |
cpqSysInfo Agent
| Attributes |
| cpqSiAsset |
cpqSiSysSerialNum |
| cpqSiMibRev |
cpqSiMibRevMajor
cpqSiMibRevMajor
cpqSiMibCondition |
| cpqSiOsCommon |
cpqSiOsCommonPollFreq |
| cpqSiSystemBoard |
cpqSiProductId
cpqSiProductName |
cpqStdEqip Agent
| Attributes |
| cpqSeCpuCacheTable |
cpqSeCpuCacheUnitIndex
cpqSeCpuCacheLevelIndex
cpqSeCpuCacheSize
cpqSeCpuCacheSpeed
cpqSeCpuCacheStatus
cpqSeCpuCacheWritePolicy |
| cpqSeCpuTable |
cpqSeCpuUnitIndex
cpqSeCpuSlot
cpqSeCpuName
cpqSeCpuSpeed
cpqSeCpuStatus
cpqSeCpuExtSpeed
cpqSeCpuDesigner
cpqSeCpuThreshPassed |
| cpqSeEisaFunctTable |
cpqSeEisaFunctSlotIndex
cpqSeEisaFunctIndex
cpqSeEisaFunctType
cpqSeEisaFunctCfgRev
cpqSeEisaFunctSels |
| cpqSeFixedDiskTable |
cpqSeFixedDiskIndex
cpqSeFixedDiskType
cpqSeFixedDiskCyls
cpqSeFixedDiskHeads
cpqSeFixedDiskSectors
cpqSeFixedDiskCapacity |
| cpqSeFloppyDiskTable |
cpqSeFloppyDiskIndex
cpqSeFloppyDiskType |
| cpqSeFpuTable |
cpqSeFpuUnitIndex
cpqSeFpuChipIndex
cpqSeFpuSlot
cpqSeFpuName
cpqSeFpuSpeed
cpqSeFpuType |
| cpqSeMemory |
cpqSeTotalMem
cpqSeBaseMem |
| cpqSeMibRev |
cpqSeMibRevMajor
cpqSeMibRevMinor
cpqSeMibCondition |
| cpqSeOsCommon |
cpqSeOsCommonPollFreq |
| cpqSeParallelPort Table |
cpqSeParallelPortIndex
cpqSeParallelPortAddr
cpqSeParallelPortDesc |
| cpqSePciSlot Table |
cpqSePciSlotBusNumberIndex
cpqSePciSlotDeviceNumberIndex
cpqSePciPhySlot
cpqSePciSlotSubSystemID
cpqSePciSlotBoardName |
| cpqSeRom |
cpqSeSysRomVer |
| cpqSeSerialPort Table |
cpqSeSerialPortIndex
cpqSeSerialPortAddr
cpqSeSerialPortDesc |
| cpqSeComplex |
cpqSeComplexUUID
|
cpqThresh Agent
| Attributes |
| cpqMeAlarm |
cpqMeAlarmNextIndex |
| cpqMeMibRev |
cpqMeMibRevMajor
cpqMeMibRevMinor
cpqMeMibCondition
cpqMeAlarmIndex
cpqMeAlarmInterval
cpqMeAlarmVariable
cpqMeAlarmSampleType
cpqMeAlarmValue
cpqMeAlarmStartupAlarm
cpqMeAlarmRisingThreshold
cpqMeAlarmFallingThreshold
cpqMeAlarmPermanence
cpqMeAlarmOwner
cpqMeAlarmStatus |
| Traps |
cpqMeRisingAlarmExtended
cpqMeFallingAlarmExtended |
cpqNIC Agent
| Attributes |
cpqNicMibRevMajor
cpqNicMibRevMinor
cpqNicMibCondition
cpqNicIfLogMapIndex
cpqNicIfLogMapIfNumber
cpqNicIfLogMapDescription
cpqNicIfLogMapGroupType
cpqNicIfLogMapAdapterCount
cpqNicIfLogMapAdapterOKCount
cpqNicIfLogMapPhysicalAdapters
cpqNicIfLogMapMACAddress
cpqNicIfLogMapSwitchoverMode
cpqNicIfLogMapCondition
cpqNicIfLogMapStatus
cpqNicIfLogMapNumSwitchovers
cpqNicIfLogMapOverallCondition
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterPort
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterSlot
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterIoAddr
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterMemAddr
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterEntry.length
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterIndex
cpqNicIfLogMapAdapterCount
cpqNicIfLogMapGroupType
cpqNicIfLogMapDescription
cpqNicIfLogMapStatus
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterIfNumber
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterRole
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterStatus
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterDuplexState
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterDma
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterIrq
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterMACAddress
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterGoodReceives
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterGoodTransmits
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterBadReceives
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterBadTransmits
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterAlignmentErrors
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterCarrierSenseErrors
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterFrameTooLongs
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterMultipleCollisionFrames
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterFCSErrors
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterLateCollisions
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterInternalMacReceiveErrors
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterSingleCollisionFrames
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterExcessiveCollisions
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterDeferredTransmissions
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterInternalMacTransmitErrors
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterCondition
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterState
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterStatsValid
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterInOctets
cpqNicIfPhysAdapterOutOctets
|
svrClu Agent
| Attributes |
svrCluMibMajorRev
svrCluMibMinorRev
svrCluSoftwareVendor
svrCluSoftwareVersion
svrCluSoftwareStatus
svrCluClusterType
svrCluExtensionOID
svrCluThisMember
svrCluClusterName
svrCluMemberIndex
svrCluMemberName
svrCluMemberComment
svrCluMemberStatus
svrCluMemberAddressIndex
svrCluMemberAddressIndex |
| Traps |
svrCluMemberAdded
svrCluMemberDeleted |
cpqIDA Agent
| Attributes |
cpqDaMibRevMajor
cpqDaMibRevMinor
cpqDaMibCondition
cpqDaOsCommonPollFreq
cpqDaCntlrIndex
cpqDaCntlrModel
cpqDaCntlrFWRev
cpqDaCntlrStndIntr
cpqDaCntlrSlot
cpqDaCntlrCondition
cpqDaCntlrProductRev
cpqDaCntlrPartnerSlot
cpqDaCntlrCurrentRole
cpqDaCntlrBoardStatus
cpqDaCntlrPartnerBoardStatus
cpqDaCntlrBoardCondition
cpqDaCntlrPartnerBoardCondition
cpqDaCntlrDriveOwnership
cpqDaCntlrSerialNumber
cpqDaCntlrRedundancyType
cpqDaCntlrRedundancyError
cpqDaCntlrAccessModuleStatus
cpqDaCntlrDaughterBoardType
cpqDaCntlrHwLocation
cpqDaAccelCntlrIndex
cpqDaAccelStatus
cpqDaAccelMemory
cpqDaAccelBadData
cpqDaAccelErrCode
cpqDaAccelBattery
cpqDaAccelReadErrs
cpqDaAccelWriteErrs
cpqDaAccelCondition
cpqDaAccelReadMemory
cpqDaAccelSerialNumber
cpqDaAccelTotalMemory
cpqDaLogDrvCntlrIndex
cpqDaLogDrvIndex
cpqDaLogDrvFaultTol
cpqDaLogDrvStatus
cpqDaLogDrvAutoRel
cpqDaLogDrvRebuildBlks
cpqDaLogDrvHasAccel
cpqDaLogDrvAvailSpares
cpqDaLogDrvPhyDrvIDs
cpqDaLogDrvCondition
cpqDaLogDrvPercentRebuild
cpqDaLogDrvStripeSize
cpqDaLogDrvOsName
cpqDaSpareCntlrIndex
cpqDaSparePhyDrvIndex
cpqDaSpareStatus
cpqDaSpareReplacedDrv
cpqDaSpareRebuildBlks
cpqDaSpareCondition
cpqDaSpareBusNumber
cpqDaSpareBay
cpqDaSpareReplacedDrvBusNumber
cpqDaSpareReplacedDrvBay
cpqDaSparePercentRebuild
cpqDaPhyDrvCntlrIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvModel
cpqDaPhyDrvFWRev
cpqDaPhyDrvBay
cpqDaPhyDrvStatus
cpqDaPhyDrvUsedReallocs
cpqDaPhyDrvRefHours
cpqDaPhyDrvHReads
cpqDaPhyDrvReads
cpqDaPhyDrvHWrites
cpqDaPhyDrvWrites
cpqDaPhyDrvHSeeks
cpqDaPhyDrvSeeks
cpqDaPhyDrvHardReadErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvRecvReadErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvHardWriteErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvRecvWriteErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvHSeekErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvSeekErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvSpinupTime
cpqDaPhyDrvDrqTimeouts
cpqDaPhyDrvOtherTimeouts
cpqDaPhyDrvSpinupRetries
cpqDaPhyDrvBadRecvReads
cpqDaPhyDrvBadRecvWrites
cpqDaPhyDrvFormatErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvPostErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvReallocAborts
cpqDaPhyDrvThreshPassed
cpqDaPhyDrvHasMonInfo
cpqDaPhyDrvCondition
cpqDaPhyDrvHotPlugs
cpqDaPhyDrvMediaErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvHardwareErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvAbortedCmds
cpqDaPhyDrvSpinUpErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvBadTargetErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvSize
cpqDaPhyDrvBusFaults
cpqDaPhyDrvIrqDeglitches
cpqDaPhyDrvHotPlug
cpqDaPhyDrvPlacement
cpqDaPhyDrvBusNumber
cpqDaPhyDrvSerialNum
cpqDaPhyDrvPreFailMonitoring
cpqDaPhyDrvCurrentWidth
cpqDaPhyDrvCurrentSpeed
cpqDaPhyDrvFailureCode
cpqDaPhyDrvBlinkTime
cpqDaPhyDrvErrCntlrIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvErrIDIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvErrIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvErrType
cpqDaPhyDrvScsiOp
cpqDaPhyDrvScsiStatus
cpqDaPhyDrvCamStatus
cpqDaPhyDrvSenseKey
cpqDaPhyDrvQualifier
cpqDaPhyDrvSenseCode
cpqDaPhyDrvBlockValid
cpqDaPhyDrvBlock
cpqDaPhyDrvTime
cpqDaPhyDrvErrDesc
cpqDaPhyDrvThrCntlrIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvThrIndex
cpqDaPhyDrvThrUsedReallocs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrRefHours
cpqDaPhyDrvThrHardReadErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrRecvReadErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrHardWriteErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrRecvWriteErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrSeekErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrSpinupTime
cpqDaPhyDrvThrDrqTimeouts
cpqDaPhyDrvThrOtherTimeouts
cpqDaPhyDrvThrSpinupRetries
cpqDaPhyDrvThrBadRecvReads
cpqDaPhyDrvThrBadRecvWrites
cpqDaPhyDrvThrFormatErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrPostErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrNotReadyErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrReallocAborts
cpqDaPhyDrvThrHotPlugs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrMediaErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrHardwareErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrAbortedCmds
cpqDaPhyDrvThrSpinUpErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrBadTargetErrs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrViUsedReallocs
cpqDaPhyDrvThrViSpinupTime
cpqDaPhyDrvThrIrqDeglitches
cpqDaCntlrPerfCntlrIndex
cpqDaCntlrPerfInstance
cpqDaCntlrPerfSampleInterval
cpqDaCntlrPerfVersion
cpqDaCntlrPerfCpuPercentBusy
cpqDaCntlrPerfCommandCount
cpqDaCntlrPerfAvgLatency
cpqDaLogDrvPerfCntlrIndex
cpqDaLogDrvPerfIndex
cpqDaLogDrvPerfInstance
cpqDaLogDrvPerfSampleInterval
cpqDaLogDrvPerfAvgQueueDepth
cpqDaLogDrvPerfReads
cpqDaLogDrvPerfWrites
cpqDaLogDrvPerfTotalIO
cpqDaLogDrvPerfCacheHits
cpqDaLogDrvPerfCacheMisses
cpqDaLogDrvPerfReadAheadSectors
cpqDaLogDrvPerfSectorsRead
cpqDaLogDrvPerfSectorsWritten |
| Traps |
cpqDa3LogDrvStatusChange
cpqDa4SpareStatusChange
cpqDa5AccelStatusChange
cpqDa5AccelBadDataTrap
cpqDa5AccelBatteryFailed
cpqDa5CntlrStatusChange
cpqDa5PhyDrvStatusChange
cpqDa5PhyDrvThreshPassedTrap |
cpqStsys Agent
| Attributes |
cpqSsMibRevMajor
cpqSsMibRevMinor
cpqSsMibCondition
cpqSsBoxCntlrIndex
cpqSsBoxBusIndex
cpqSsBoxModel
cpqSsBoxFWRev
cpqSsBoxVendor
cpqSsBoxFanStatus
cpqSsBoxCondition
cpqSsBoxTempStatus
cpqSsBoxSidePanelStatus
cpqSsBoxFltTolPwrSupplyStatus
cpqSsBoxBackPlaneVersion
cpqSsBoxTotalBays
cpqSsBoxPlacement
cpqSsBoxDuplexOption
cpqSsBoxBoardRevision
cpqSsBoxSerialNumber |
| Traps |
cpqSs3FanStatusChange
cpqSs3TempFailed
cpqSs3TempDegraded
cpqSs3TempOK
cpqSs3SidePanelInPlace
cpqSs3SidePanelRemoved
cpqSs4PwrSupplyDegraded |
6 - Trademarks
Hewlett-Packard and the HP logo are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Development
Company, L.P. in the U.S. and/or other countries.
MultiNet and TCPware are registered trademarks of Process Software.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their
respective holders.
© Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. All rights
reserved.
» return to the Management Agents
home page
|